
AN IDENTIFICATION METHOD OF RELATED GROUP THREADS
FOR A RECENT BUG THREAD BY PEAK CHARACTERISTICS
OF SIMILARITIES
Yuuki Imanara, Kota Itakura, Masaki Samejima and Masanori Akiyoshi
Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, Osaka University, 2-1, Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka, Japan
Keywords:
Bug tracking system, Related group thread, SVM, Peak characteristics of similarities.
Abstract:
This paper addresses the problem to identify the related group threads that has dependent relationships with
recent bug threads. Because most of recent bug threads have no dependent relationships with group threads,
basic approach based on similarity regards them as having dependent relationships wrongly. In this paper, we
propose an identification method of related group threads by peak characteristics of similarities. The proposed
method removes recent bug threads that have no dependent relationships by Support Vector Machine based on
vectors representing peak characteristics of similarities between the recent bug thread and group threads. The
application result shows that the precision rate is improved by 49% and the recall rate is kept 76% on average
using the proposed method.
1 INTRODUCTION
In open source software development, communities
for developers are organized, and they discuss who
fixes the bug and how to fix it. In order to support their
discussion and manage bug information, bug tracking
systems (Serrano and Ciordia, 2005; Matsushita et al.,
2005) are introduced.
The bug tracking system generally consists of bug
threads posted by developers. Each bug thread has a
title, the progress to fix, developers’ comments, and
the dependent relationship. The dependent relation-
ship indicates the relationship that one bug can not
be fixed unless the other bug is fixed (Souza et al.,
2007). The bug threads that have dependent rela-
tionships each other are organized as “group thread”.
Every time a recent bug is reported, developers find
the group thread which the recent bug thread has
dependent relationships with bug threads in, that is
called “related group thread” to improve their discus-
sion (Black, 2002; Chen et al., 2010). Because there
are dozens of group thread, it is difficult for devel-
opers to find the related group thread (Zimmermann,
2009; Gall et al., 2003). The purpose of this research
is to identify the related group thread for the recent
bug thread automatically.
Since threads that has dependent relationships
each other have common symptom of the bugs, com-
ments on the threads are often similar (Nagwani and
Singh, 2009). So, the similar group thread to the re-
cent bug thread can be regarded as the related group
thread. With this concept, the basic approach is to
derive similarities between the recent bug thread and
each group thread by Cosine Similarity (Sullivan,
2001), and to decide the related group thread as the
group thread that has the highest similarity more than
a threshold. The threshold is derived from similari-
ties among existing bug threads. However, some of
the recent bug threads are similar to the thread group,
but do not have dependent relationship with the exist-
ing bug threads because the recent bug does not have
enough comments and the similarity is not correctly
derived. This causes misidentification of the related
group thread. So, it is necessary to extract charac-
teristics of the misidentified related group thread and
remove the recent bug thread before the identifica-
tion (Imanara et al., 2011).
We propose an identification method of related
group thread by peak characteristics of similarities. In
case that the recent bug thread has dependent relation-
ships with the related group thread, the similarity with
the related group thread is very high but the similarity
with the other group thread is low. We call the char-
acteristics of similarities “peak characteristics”. So,
the peak characteristics of similarities can be on these
similarities with the related group thread. Two kinds
179
Imanara Y., Itakura K., Samejima M. and Akiyoshi M..
AN IDENTIFICATION METHOD OF RELATED GROUP THREADS FOR A RECENT BUG THREAD BY PEAK CHARACTERISTICS OF SIMILARITIES.
DOI: 10.5220/0003506401790184
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Software and Database Technologies (ICSOFT-2011), pages 179-184
ISBN: 978-989-8425-77-5
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
of feature vectors, higher similarities and differential
of similarities, generated from the peak characteris-
tics. And Support Vector Machine (SVM) based on
the feature vectors classify the recent bug thread not
to have dependent relationships.
2 IDENTIFICATION OF
RELATED GROUP THREADS
FOR A RECENT BUG THREAD
2.1 Problem on Identification of Related
Group Threads
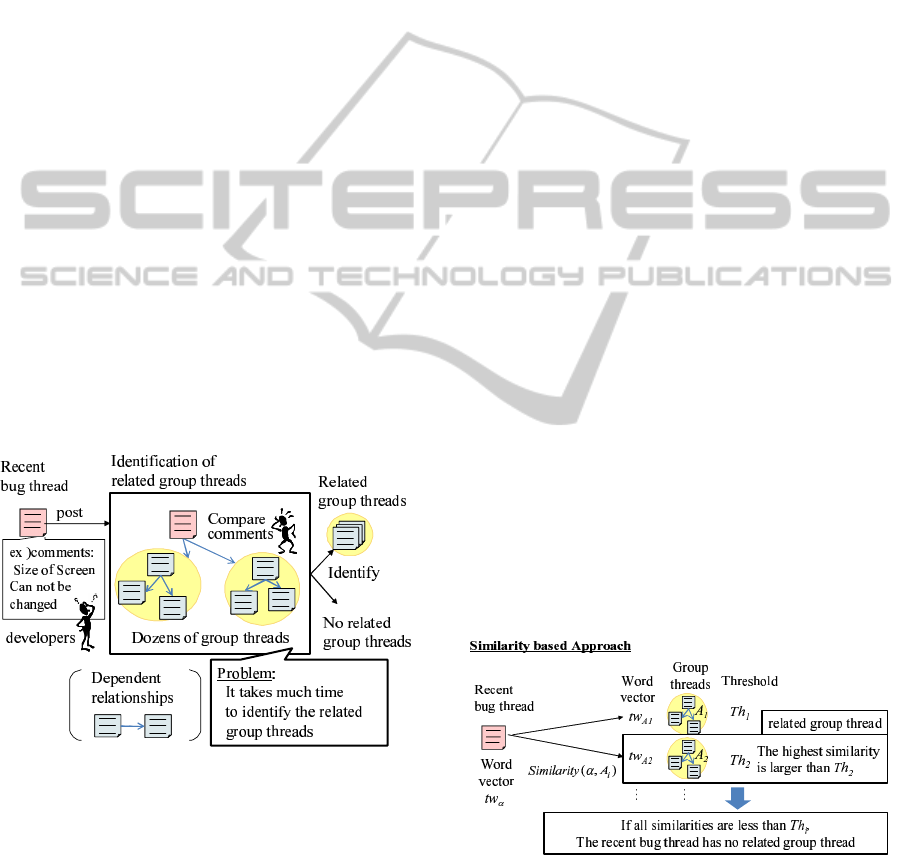
Fig. 1 shows the outline of identification of related
group threads for a recent bug thread. Bug threads in
the bug tracking system have dependent relationships
each other. The dependent relationship between bug
threads indicates that one bug thread can not be fixed
until the other is fixed. In Fig. 1, the dependent rela-
tionship between bug threads α, β is shown as an ar-
row: α → β means that α blocks β or β depends on α,
which is the case that β can not be fixed until α is not
fixed. The bug threads that have dependent relation-
ships each other, called as “dependent bug threads”
organize a group of bug threads. We define the group
of bug threads as “group thread”.
Figure 1: The outline of identification of related group
threads.
When the developer receives the bug report, the
developer posts the recent bug thread to the bug track-
ing system. Developers compare comments on the
recent bug thread to comments on the existing bug
threads in group threads. Finding the group thread
which the recent bug thread has a dependent relation-
ship with a bug thread in, developers address fixing
the bug with referring the group thread called “related
group thread”. However, there are dozens of group
threads in the bug tracking systems and some of ex-
isting bug threads have many comments. Developers
read comments of bug threads in the group threads
and identify whether the related group thread for the
recent bug thread exists or not. However, because the
task is a time-consuming for developers, some depen-
dent relationships are not still identified in the bug
tracking systems. The goal of this research is to iden-
tify the related group thread if the recent bug has a
dependent relationship with the related group thread.
2.2 Similarity based Approach
The bugs that have the dependent relationships tend
to have the common characteristics: using the same
module, causing similar troubles (e.g. software
crash), being under the same environment (e.g. Op-
erating System), and so on. So, our approach is
based on similarities between the recent bug thread
and the group threads. The similarity based approach
is shown in Fig. 2.
Because the dependent bug threads include some
common words, the group thread is characterized by
the common words. We call these common words
“topic words”. The topic words consist of the com-
mon words CW
k
between the dependent bug threads
on the kth dependent relationship in a group thread:
Topic Words =
[
k
CW
k
The common words CW
k
are union of words W
α
in the bug thread α and words W
β
in the bug thread
β where the kth dependent relationship exists (W
α
is
a group of words that appear in comments except for
stop words):
CW
k
= W
α
∩W
β
Figure 2: Similarity based approach.
Then the similarity between the recent bug thread
and the group thread on the topic words is decided by
Cosine Similarity (Sullivan, 2001). The value of Co-
sine Similarity is derived from the frequencies tw
α,i
,
tw
A,i
of each topic word i in the recent bug thread α
ICSOFT 2011 - 6th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
180

and the group thread A:
TW
α
= {tw
α,1
,tw
α,2
, · ··tw
α,m
}
TW
A
= {tw
A,1
,tw
A,2
, · ··tw
A,m
}
Similarity(α, A) =
TW
α
· TW
A
kTW
α
kkTW
A
k
where the group thread A is a union of the bug threads
in the group thread.
It is considered that Similarity(α, A) is high if the
recent bug thread α has a dependent relationship with
the group thread A. So, the basic approach is to decide
that the recent bug thread has no related group thread
if the similarity is small. This is judged by a threshold
for similarity on each group thread. After that, the
group thread that has higher similarity than any other
group threads can be regarded as the related group
thread.
However, the recent bug threads that have no re-
lated group threads tend to have relatively high sim-
ilarities with group threads. And, most of the recent
bug threads have no related group threads, which are
from 80% to 90% of the recent bug threads in a bug
tracking system “Bugzilla@Mozilla”
1
. So, these re-
cent bug threads are not identified correctly by just
similarity based approach.
3 IDENTIFICATION METHOD BY
PEAK CHARACTERISTICS OF
SIMILARITIES
3.1 Peak Characteristics of Similarities
As described in Section 2.2, the recent bug threads
that have no related group threads tend to have rel-
atively high similarities with group threads. On the
other hand, the recent bug threads that have related
group thread tend to have very high similarity with
the related group thread but small similarities with the
other group threads. The Fig. 3 shows similarities in
the case of the recent bug threads that have related
group threads and otherwise. On the Fig. 3, the hori-
zontal axis indicates the group threads and the vertical
axis indicates the similarities with them, this results
are generated from bug threads in Bugzilla@Mozilla.
As shown in Fig. 3, we can see a few group
threads that have much higher similarities than any
other group threads and define these characteristics as
“peak characteristics”. Because peak characteristics
are not appeared in the recent bugs that have no re-
lated thread group. Therefore, we propose an identifi-
1
https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/
Figure 3: Peak characteristics of similarities.
cation method by peak characteristics of similarities.
The outline of the proposed method is shown in Fig. 4.
Figure 4: Outline of the proposed method.
When a developer inputs the recent bug thread to
the proposed method, the proposed method derived
similarities with group threads and applies Support
Vector Machine (SVM) based on vectors of these sim-
ilarities to classify the recent bug thread that have no
related group threads. In order to derive the similarity
between the recent bug thread and the group thread,
the frequency of each topic word in the recent bug
thread and in the bug threads in the group thread. The
similarity is derived from the frequencies by the Co-
sine similarity as described in Section 2.2. How to
AN IDENTIFICATION METHOD OF RELATED GROUP THREADS FOR A RECENT BUG THREAD BY PEAK
CHARACTERISTICS OF SIMILARITIES
181

generate vectors for SVM is described in Section 3.2.
Additionally, as well as similarity based approach,
the group thread that has higher similarity than any
other group threads and its own threshold can be re-
garded as the related group thread. Because there are
many bug threads in the group threads, an appropri-
ate threshold for each group thread can be decide by
the bug threads. The automatic setting method of the
thresholds is described in Section 3.3
3.2 Identification Method using
Support Vector Machine (SVM)
The recent bug thread that has no related group
threads has relatively high similarities with group
threads. On the other hand, the recent bug thread that
has the related group thread has very high similari-
ties with the related group thread. We think that this
difference on the peak characteristics of similarities
is useful to classify the recent bug thread that has no
related group threads by SVM.
In order to extract the peak characteristics, the
similarities with group threads are sorted in descend-
ing order as shown Fig. 5. There are differences of
similarities in high order. So, we design the two kinds
of vectors for SVM: one is a vector V
1
of similarities
in the top k and the other is a vector V
2
of differences
between a similarity in the top l and in the top (l + 1):
V
1
= Sort
1
(Similarity(α, A
1
), · ·· Similarity(α, A
n
))
V
2
= Sort
1
(Similarity(α, A
1
), · ·· Similarity(α, A
n
))
−Sort
2
(Similarity(α, A
1
), · ·· Similarity(α, A
n
))
where Sort
r
(·) is a function to change similarities in
the top (r − 1) to 0, and to arrange similarities in de-
scending order.
Using both vectorsV = {V
1
,V
2
}, SVMs in the pro-
posed method judge that the recent bug thread has no
related group thread p by the following function:
y
p
= sign(w
T
p
V − h
p
)
where y
p
indicates a result of the judgment: y
p
=
−1 means that the recent bug thread does not have
dependent relationships and y
p
= 1 means that the
recent bug thread has ones in the group thread p.
sign(u) indicates the identification function on SVM:
sign(u) = −1 on u ≤ 0 and sign(u) = 1 on u > 0. w
p
is a vector of weight parameters and h
p
is a vector
of thresholds in SVM, which are decided by training
with the existing bug threads in thread groups. Be-
cause it can be decided whether existing bug threads
t in the thread group p is in a thread group or not,
the vector of word frequencies a
t, p
and whether the
bug thread t has dependent relationships or does not
Figure 5: Similarities in descending order.
b
t, p
= {−1, 1} can be used for the training. The train-
ing process is formulated as the following optimiza-
tion problem:
minimize ||w
p
||
subject to b
t, p
(a
t, p
w
p
− h
p
) − 1 ≥ 0 (t = 1, 2·· ·)
In order to prevent from removing the recent bug
thread that has related group thread, only if SVMs
based on both vectors V = {V
1
,V
2
} judge that the re-
cent bug thread has no related group thread, the re-
cent bug thread is regarded to have no related group
thread. When either of SVMs judges that the recent
bug thread has related group thread, the related group
thread is judged by thresholds in the next step.
3.3 Automatic Setting of Thresholds
There are many bug threads in the bug tracking sys-
tem. So, the proposed method searches the thresholds
to maximize F −measure in inputting the bug threads
by changing thresholds slightly. The F − measure is
decided by the following formula:
F − measure =
2· precision·recall
precision+ recall
precision =
N
c
N
c
+ N
w
recall =
N
c
N
c
+ N
u
where N
c
is the number of correctly identified
threads, N
w
is the number of wrongly identified thre-
ICSOFT 2011 - 6th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
182

ads and N
u
is the number of not-identified threads.
The detailed process of automatic setting is de-
scribed in the following:
1. For initializing thresholds Th
p
for the group
thread p, values of all thresholds Th
p
are set to 0.
2. All combinations of values of thresholds are gen-
erated with increasing values of thresholds Th
p
by
∆Th
p
for all p.
3. F-measure are decided with the combinations
of thresholds and the threshold that makes F-
measure maximize is used for the proposed
method.
4 EVALUATION EXPERIMENT
4.1 Target of Experiment
We extract the bug threads from “bugzilla@mozilla”
about two kinds of open source software: “firefox”
and “thunderbird”. The number of bug threads on
firefox is 6272, the number of group threads is 37
and 137 bug threads belong to them. The num-
ber of bug threads on thunderbird is 674, the num-
ber of group threads is 62 and 185 bug threads be-
long to them. We compare four methods: similarity
based approach, similarity based approach and SVM
with similarity vector V
1
, similarity based approach
and SVM with similarity vector V
2
and the proposed
method. In this experiment, 50 bug threads belong-
ing to group threads and 50 bug threads isolated from
group threads are randomly extracted and they are
used for training data of SVM and automatic thresh-
old setting.
4.2 Experimental Result
Fig. 6 shows the result of recall and precision de-
scribed in Section 3.3. According to Fig. 6, the
proposed method can improve precision dramatically.
The method using either of SVMs decreases the re-
call rate. But the proposed method uses both SVMs
and identify the bug thread that has no related group
thread only when both SVM judges that the recent
bug thread has no related group thread.
Fig. 7 shows the number of the recent bug threads
that are wrongly identified as having the related group
threads regardless of having no related group threads.
By using SVMs based on peak characteristics of sim-
ilarities, we can decrease the wrong identifications by
90% compared to similarity based approach.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We proposed an identification method of related
group threads by peak characteristics of similarities.
The proposed method removes recent bug threads that
have no dependent relationships by Support Vector
Machine based on vectors representing peak charac-
teristics of similarities between the recent bug thread
and group threads. The application result showed that
the precision rate was improved by 49% and the re-
call rate was kept 76% on average using the proposed
method.
Figure 6: Recall and precision by each method.
Figure 7: The number of wrong identifications by each
method.
REFERENCES
Black, R. (2002). Managing the Testing Process: Practi-
cal Tools and Techniques for Managing Hardware and
Software Testing. John Wiley & Sons.
Chen, I., Li, C., and Yang, C. (2010). Mining co-location re-
lationships among bug reports to localize fault-prone
modules. IEICE Transactions on Information and Sys-
tems, 93(5):1154–1161.
AN IDENTIFICATION METHOD OF RELATED GROUP THREADS FOR A RECENT BUG THREAD BY PEAK
CHARACTERISTICS OF SIMILARITIES
183

Gall, H., Jazayeri, M., and Krajewski, J. (2003). CVS re-
lease history data for detecting logical couplings. In
Proc. of International Workshop on Principles of Soft-
ware Evolution (IWPSE2003), pages 12–23.
Imanara, Y., Itakura, K., Samejima, M., and Akiyoshi, M.
(2011). A detection system of dependent relation-
ships among bug report threads. In Proc. of the 4th
Japan-China Joint Symposium on Information Sys-
tems (JCIS2011), pages 65–68.
Matsushita, M., Sasaki, K., and Inoue, K. (2005). Coxr:
open source development history search system. Proc.
of Supporting Knowledge Collaboration in Software
Development, pages 821–826.
Nagwani, N. K. and Singh, P. (2009). Weight similarity
measurement model based, object oriented approach
for bug databases mining to detect similar and dupli-
cate bugs. In Proc. of the International Conference on
Advances in Computing, Communication and Control
(ICAC3 ’09), pages 202–207.
Serrano, N. and Ciordia, I. (2005). Bugzilla, itracker, and
other bug trackers. IEEE Software, 22(2):11–13.
Souza, C. R. D., Quirk, S., Trainer, E., and Redmiles, D. F.
(2007). Supporting collaborative software develop-
ment through the visualization of socio-technical de-
pendencies. In Proc. of the 2007 international ACM
conference on Supporting group work (GROUP ’07,
pages 147–156.
Sullivan, D. (2001). Document Warehousing and Text Min-
ing: Techniques for Improving Business Operations,
Marketing, and Sales. John Wiley & Sons.
Zimmermann, T. (2009). Changes and bugs mining and
predicting development activities. In Proc. of IEEE
International Conference on Software Maintenance
(ICSM2009), pages 443–446.
ICSOFT 2011 - 6th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
184
