
MODEL-BASED STOCHASTIC SIMULATION OF SUPER PEER
PROMOTION IN P2P VOIP USING GRAPH TRANSFORMATION
Ajab Khan and Reiko Heckel
Department of Computer Science, University of Leicester, Leicester, U.K.
Keywords:
Stochastic modelling and simulation, P2P VoIP, P2P VoIP network architecture, Graph transformation.
Abstract:
The concept of super peer has been introduced to improve the performance of popular P2P VoIP applications.
A super peer is the strongest peer in the network that has the capacity to act as a server for a set of VoIP clients.
There is no doubt that by taking benefit of heterogeneity, super peer can do improve the efficiency, without
compromising the decentralised nature of P2P networks. The core issue in the formation of super peer based
overlay network is the selection of super peer among the participant peers. To solve this problem a number of
solutions have been proposed in the literature. Generally, super peer are selected among the best nodes in the
network, for example those with the most abondant resources, such as bandwidth, CPU cycles or memory. The
next issue is when the peer shall be selected for this extended role either as when peer joins the network, or at
any time during the session or promotion to super peer should be subject to requirements. In order to validate
these approaches of super peer selection, simulation would be an ideal choice, but most existing simulation
approaches cannot cope with unbounded dynamic changes of network topology.
We propose an approach to modelling and simulation of P2P systems based on graph transformations, a visual
rule based formalism that has recently been supported by facilities for stochastic modelling and simulation.
We are considering a P2P VoIP applications such as Skype, we model three alternative solutions to the problem
of peer promotion to super peers and evaluate these through simulation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today’s P2P network (Milojicic, 2002) contains sev-
eral new and attractive features, which makes them
quite different from classical P2P networks. Al-
though, network may still contain millions of peers.
As a result of this massive number of peers, they are
subject to high degree of churn (Stutzbach and Re-
jaie, 2006), with a number of peers joining and de-
parting from the system respectively. This massive
size of network and geographically diverse location
of peers pose several challenges for developers and
researchers. As immediate affect its impossible to
use either a central authority or fixed communication
topologies. Instead a dynamically changing overlay
topology is used, where control is kept decentralised.
The respective overlay topology is maintained by co-
operation of virtual links between peers, these virtual
connection are created and removed based on the re-
quirements of particular application.
Peers in P2P networks are always in full control
of their local resources and can therefore, any time
impose new policies regarding use of their shared re-
sources in the network (Ji, 2004). A peer may
even suddenly stop its cooperation by behaving self-
ish (Gupta and Somani, 2004). Due to this lack of
global control and unreliability of the P2P architec-
ture, these systems are prone to dependability prob-
lems. Classical P2P applications were lagging the
enforcement of particular overlay topology. The di-
rect result of this approach was adaptation of inef-
ficient scheme such as flooding. However, now re-
searchers and developers have realised the impor-
tance of building and maintaining appropriate topolo-
gies for development of efficient robust P2P Sys-
tems (Zhao, 2003; Rowstron and Druschel, 2001;
Montresor, 2004; Dabek, 2001; Yang and Garcia-
Molina, 2003).
Along with many file sharing applications (Mon-
tresor, 2004), P2P VoIP is also considering the im-
plementation of structured topologies by distinguish-
ing peer and super peer (Guha et al., 2006). One of
the successful VoIP application developed based on
structure topology is Skype (Skype, 2011; Guha et al.,
2006). The topology is composed of two-level hierar-
chy: Nodes with powerful CPU, more free memory
32
Khan A. and Heckel R..
MODEL-BASED STOCHASTIC SIMULATION OF SUPER PEER PROMOTION IN P2P VOIP USING GRAPH TRANSFORMATION.
DOI: 10.5220/0003526000320042
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Communication Networking and Optical Communication System (DCNET-2011), pages 32-42
ISBN: 978-989-8425-69-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

and greater bandwidth take on server-like responsi-
bilities and provide services to a set of client peers.
This approach allows decentralized overlay network
to run more efficiently by exploiting heterogeneity
and distributing load to machines that can handle the
burden. It has also overcome the flaws of the client
server model, because of multiple separate points of
failures, thus increasing the health of the P2P overlay
network (Guha et al., 2006; Yang and Garcia-Molina,
2003).
Building and maintaining a super peer based
overlay topology is not simple. Rapid architec-
tural changes in both ordinary and super peers re-
quires robust and efficient protocols, capable of self-
reconfiguring, in spite of both controlled and selfish
events like joining, leaving or crashing nodes. In case
the P2P is used for VoIP traffic, the network needs
to reconfigure fast enough so that Quality of Service
(QoS) is not affected (Khan et al., 2009).
Several questions arise for the design of network
protocols: Which peer should be promoted to super
peer? Can selection of super peer based on the higher
bandwidth is enough? Is promotion at the time of
registering is better from promotion at any time dur-
ing session? How about promotion whenever there
is a need for super peer? The performance of such
a protocol can be measured by answering the ques-
tion: How many peers are connected, how many are
present but yet to be connected, how many super peers
are there, how many clients are happy in the network,
how many VoIP calls have been supported?
Various solutions have been proposed to these
problems, e.g. (Zhao, 2003) suggested the deploy-
ment of super peers directly managed by content ser-
vice providers; (Lo et al., 2005) proposed three dif-
ferent approaches for selection of super peers; (Mon-
tresor, 2004) presented a super peer overlay topology
algorithm and validated his approach using the Psim
simulator; (Oneil et al., 2000; Biondi and Desclaux,
2006; Guha et al., 2006) proposed super peer promo-
tion based on bandwidth, CPU power and time spent
in the network; (Gupta and Somani, 2004) proposes
that an incentive should be given to intermediate
nodes and resource owners; (Heckel, 2005) proposes
to maintain redundant links between peers, (Ren et al.,
2006) propose an autonomous system-aware peer-
relay protocol called ASAP; (Lysne et al., 2005) pro-
poses solutions based on changes in routing strate-
gies; (Yang and Garcia-Molina, 2003) discussed gen-
eral design issues however, their focus is on central-
ized design of such networks.
However, peer dynamics and complexity of P2P
network makes it difficult and expensive to validate
these solutions through testing of real networks. Ge-
ographical distribution of peers, network dynamics
and lack of central control make testing difficult and
costly. The simulation of network reconfiguration as
well as dynamic role assignment is not easy, as ex-
isting simulators do provide very limited support for
networks with dynamic topology (Heckel, 2005; NS2,
2008; Khan et al., 2010).
We propose to model dynamic role assignment
and associated architectural reconfigurations in P2P
VoIP networks by means of graph transformation sys-
tems and use a new approach to the stochastic implan-
tation of such systems to evaluate the performance of
network protocols. We consider the P2P network ar-
chitecture as a graph, in which network nodes are rep-
resented by graph vertices and graph edges represent
network connections. Reconfiguration in such a net-
work can naturally be modelled by graph transforma-
tion, in a visual and rule-based formalism (Khan et al.,
2009; Heckel, 2005; Khan et al., 2010). Stochastic
simulation techniques for validation have been devel-
oped in (Khan et al., 2009).
In this paper we are going to present a case study
based on the popular VoIP application Skype and dis-
cuss four different variations for promotion of peer to
the role of the super peer.
2 CASE STUDY: SKYPE
NETWORK
Skype is P2P VoIP application developed in 2003 by
the owners of KaZaA. Skype claims that it has cur-
rently more than 200 million users. Real statistics
shows that averagely 25 million users always remain
on-line. It currently contributes more than 8% traffic
to VoIP applications over internet.
Skype architecture of its operation is getting pop-
ularity in P2P research community and Telecom op-
erators, and detailed valuable studies can be seen in
the literature (Baset and Schulzrine, 2006; Biondi
and Desclaux, 2006; Idrees and Khan, 2008). But
due to proprietary protocol, sophisticated nature and
anti reverse engineering techniques (Biondi and De-
sclaux, 2006), many interesting question still remains
unanswered. Since, its first release many versions
have been released but the core architecture of the
network still remain the same. Skype network con-
sists of Skype Clients and Super Peers (Baset and
Schulzrine, 2006). The networks nodes are hetero-
geneous in terms of network locality, CPU power,
memory, and most importantly network bandwidth
and type of IP. Skype client with sufficient resources
in terms of bandwidth can promote to the new role of
Super peer, while at the same time, it continues pri-
MODEL-BASED STOCHASTIC SIMULATION OF SUPER PEER PROMOTION IN P2P VOIP USING GRAPH
TRANSFORMATION
33

mary role of the client for the physical user (Baset
and Schulzrine, 2006; Oneil et al., 2000). Super peers
form an overlay network among themselves whereas
each client has to first register with central registra-
tion server and then subsequently select one of the
super peer as their local host or local serving point of
contact (Baset and Schulzrine, 2006). The client will
use super node for searching on-line buddies as well
as for actual traffic routing if client is behind NAT
or firewall. The registration server is the only server
in the Skype network, responsible for storing user in-
formation including passwords, authenticating users
at login, and provide client with super peer address
for local host connection. All relevant information
regarding on-line users, there current status is stored
in distributed fashion, which does improve the scal-
ability and stability, although these information can
sometime be out of date.
The Skype call cost in terms of the bandwidth
is not clear due to the proprietary nature but analy-
sis in (Baset and Schulzrine, 2006) suggests that call
cost is between 56 Kbps to 16 Kbps whereas (Adami
et al., 2009) states that cost in terms of bandwidth is
25 Kbps when call is active. The client and super peer
also sends each other keep alive messages which con-
sume bandwidth as well. The actual cost is not clear
but (Guha et al., 2006) states that 5 Kbps to 8 Kbps
is the cost of keeping connection with super node or
super node to super node overlay. These keep a live
messages enable both the client and super peer to self-
organise, if the client or super peer has left the net-
work. The super peer based on the local awareness
of bandwidth may accept or reject overlay topology
formation or local host request. Both client and su-
per peer can leave the network either by crashing or
by using cooperative exit procedure provided by the
application GUI.
3 A GRAPH BASED MODEL FOR
SKYPE PROTOCOL
We use graph transformations to model the struc-
tural evolution of the Skype network. As one of the
most basic models for entities and relations, graphs
are a representations of structural models. Formally,
a graph consists of a set of vertices V and a set of
edges E such that each edge e ∈ E has source and
target vertex s(e) and t(e) in V, respectively. More
advanced notions allow for nodes and edges to be at-
tributed with textual, boolean or numeric data (Lara,
2007). Graphs occur at two levels: type level and in-
stance level. A type-level graph is comparable to a
class or ER diagram containing the types of nodes
and edges, declarations of attributes, etc. Instance
graphs represent the states of the system, typed over
the type graph. With graphs as states, transforma-
tion rules provide state changing operations (Heckel,
2005; Khan et al., 2009).
The type graph TG in Fig 1 represents a model of
Skype architecture as described in before. It defines
the types of registration server (RS), super peer (SN),
Skype client (SC) and their common super type. The
node LK is used to model the link between SC and SN
while OV represents the connection between existing
SNs, to model the overlay topology. The Call and
RouteCall is used to model two different call types.
The edges type offline is used to show that users is
registered but not currently in the network, online is
used to show when user is successfully authenticated,
overlay-index is used to model the connection be-
tween the SN and RS, route show when call is routed
through the SN, caller is used to show the caller of
the call and callee is used to model the recipient of
the call.
In the model whenever a new SC joins the net-
work it first get registered with RS and subsequently
user get connected with RS through offline edge. A
registered user when joins the network, a client status
SC is assigned and offline edge is replaced by online.
After this stage the current SC has to select one of the
SN as local host. The SN will be responsible for the
client request such as queering network and if SC is
behind NAT or firewall, the actual call packets will be
relayed through SN.
In the model SC is promoted to SN based on three
alternate choices. In Fig 2 we have shown these pro-
motion constraints and other mandatory features of
the protocol as feature tree. In the feature tree we
have shown that SC can promote to the role of the
SN based on three choices. First, as soon as it gets
on-line and bandwidth is more than 1.5 Mbps, we
call this approach as static protocol. Second, SC can
promote any time during session in the network, still
bandwidth will be considered, we call this approach
as dynamic protocol. Third, SC can promote to SN
only whenever there is need for a new SN, we call
this as need based protocol.
In order to model VoIP calls traffic, we assume
a codec costing 60 Kbps of bandwidth during active
call. The model supports direct calls in P2P architec-
ture as well as relayed calls. We also randomly update
the bandwidth of the nodes in order to model the be-
haviour of the shared bandwidth and background traf-
fic. In the model if SN leaves the network either by
crashing or cooperative exit, the model is capable to
reconfigure the client back to connect to a new SN.
In Figure 2 feature tree shows the mandatory fea-
DCNET 2011 - International Conference on Data Communication Networking
34

Figure 1: Type graph.
Figure 2: Feature tree.
tures such as go on-line, link SC to SN, load balancing
by simply disconnecting, down grade to client (if SN
is having bandwidth less than the minimum 256 kbps),
VoIP call respectively. In the model an SC can exit by
crashing as well as exit through a cooperative proce-
dure. All these features are kept constant whereas the
promotion strategies are changed in order to check the
performance of different SN promotion strategies.
The objective of modelling these three variations
of promotion of SC to SN is to evaluate different
approaches of promotion against each other. This
will also provide information that which approach has
scaled the network to what number of SNs and SCs.
In addition to that the model will provide information
regarding the performance of each approach based
on the number of connected, unconnected and happy
nodes.
4 SC PROMOTION TO SN AS
GRAPH TRANSFORMATION
A graph transformation rule p : L −→ R consists of
a pair of TG-typed instance graphs L, R such that the
intersection L∩R is well defined. The left-hand side L
represents the pre-conditions of the rule whereas the
right-hand side R describes the post-conditions. Their
intersection represents the elements that are required,
but not destroyed, by the transformation (Heckel,
2005). Graph transformation rules also use negative
application conditions (NACs). A NAC assures that
the rule will only be applied if the pattern specified
NAC does not match the graph (Heckel, 2005; Khan
et al., 2009). Graph transformation rule also use at-
tributes. The use of attribute enable the rule impose
constraints on the attribute value, which will make
sure that attribute constraint is evaluated in the pre-
condition and attribute value is updated as postcondi-
tion of the rule.
We are now going to introduce a set of transfor-
mation rules based on a simple client promotion to the
extended role of super peer(SN) scenario. Here, due
to limitation of space we are not introducing the rules
for connecting SC to SN, crashing, controlled exits,
whereas the connection rules are already published in
our previous work (Khan et al., 2010). However, in
the simulation all these rules are provided in order to
give results on the complete model.
Rules in Figure 3: Promote a Newly Joining SC to
Extended Role of SN. In this rule a recently on-line
MODEL-BASED STOCHASTIC SIMULATION OF SUPER PEER PROMOTION IN P2P VOIP USING GRAPH
TRANSFORMATION
35
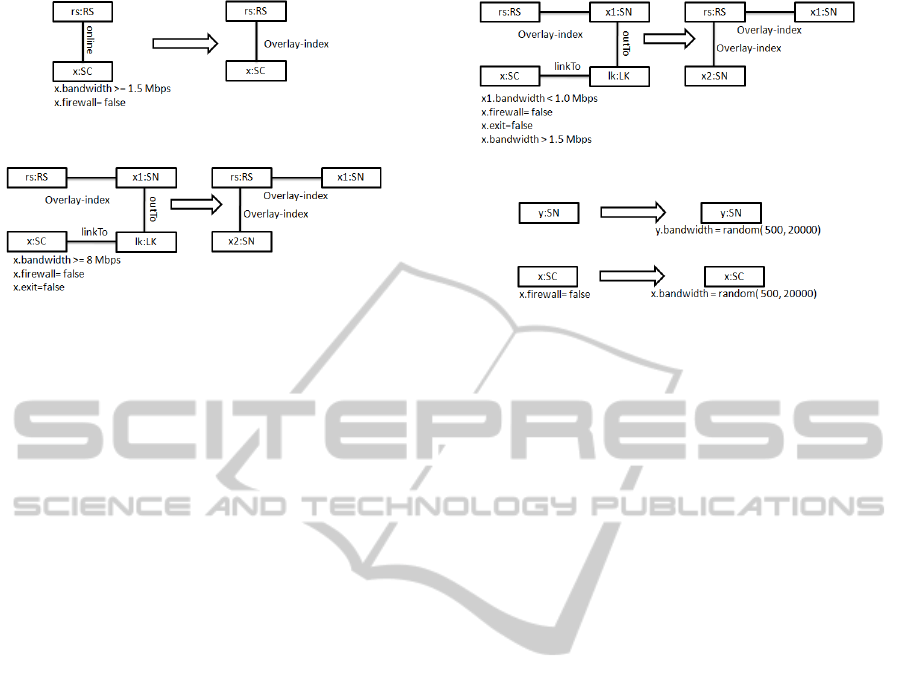
Figure 3: SC promotion to SN at start of joining.
Figure 4: SC promotion to SN at any time.
Skype client x will be promoted to its extended role
as super peer SN, only if the client x current band-
width is more than 1.5 Mbps and is connected to the
internet without firewall. After promotion to the new
role, SN client x will still retain the primary role of
the client for the owner user and at the same time will
serve other SCs. Once successfully promoted, client
x informs the server RS about the recent changes to its
role in the network. The static protocol use this rule
to promote SC to SN.
Rules in Figure 4: Promote an SC to Extended
Role of SN at Linked State. In this rule a client
which is already using the network, can be promoted
to the extended role as SN. In this rule a client x,
is having currently sufficient bandwidth and is con-
nected to the internet without firewall. Further x is
not leaving the network as cooperativeexit procedure.
This client x can be promoted to SN. The attribute exit
informs regarding the intended departure of the client
x. Once selected for promotion, client terminates its
dependency connection with the SN and inform the
server RS regarding the new assignment through edge
overlay − index. The dynamic protocol use this rule
along with rule in Fig 3 to promote SC to SN. This
protocol has the capability to promote at the start as
well as during active session of the client.
Rules in Figure 5: Promote an SC to Extended
Role of SN at Linked State if there is Need for SN.
In this rule an SC which is currently linked with one of
the SN. This linked client can be promoted to the ex-
tended role of SN if the current host SN bandwidth is
less than 1 Mbps. This SN can select client x from de-
pendent clients and promote the same to the extended
role of SN. The client x will be selected based on the
bandwidth attribute value which must be greater than
1.5 Mbps. The need based protocol only use this rule
to promote SC to SN.
Rules in Figure 6(a): Assign Random Value to SN
Bandwidth Attribute. In this rule SN bandwidth
Figure 5: Need based promotion at linked state.
(a) Bandwidth usage and release of SN.
(b) Bandwidth usage and release of SC.
Figure 6: Bandwidth use and release in SC and SN.
attribute will be assigned random value between 500
Kbps and 2 Mbps. The core purpose of this rule is
to change the value of the bandwidth to model other
traffic apart from VoIP in the network. Since, P2P are
highly dynamic most action in the network including
roles of peer depend upon the available bandwidth at
certain time in simulation. So due to this a client may
start network participation with SN but may end up
with a role of SC.
Rules in Figure 6(b): Assign Random Value to SC
Bandwidth Attribute. In this rule SC bandwidth
attribute will be assigned random value between 500
Kbps and 2 Mbps if the SC is connected with internet
through public IP. In the same way this model the traf-
fic that client computer is generating apart from VoIP
application. This is one of the reason that dynamic
protocol use both the rules as in Fig 4 and Fig 5 to
promote at both the stages (Start and linked states).
Rules in Figure 7(a): VoIP Call Request Initiated
by SC with Public IP. In this rule an SC with pub-
lic IP connection with the internet can request for es-
tablishment of VoIP call with other on-line network
participant. Before the call request is generated, SCs
existing calls status is checked by using the NAC con-
ditions. The NACs assure that requesting client SC
must not be involved in already directly established
P2P calls as caller or callee. We have used the node
Call to model the direct P2P call.
Rules in Figure 7(b): VoIP Call Request Initiated
by SC Behind Firewall. In this rule an SC behind
port restricted firewall can request for establishment
of VoIP call with other on-line network participant,
The on-line participant can either be SN or SC. The
callee of the call can be either connected through pub-
lic IP or behind firewall. In all cases the VoIP traffic
from this SC will be relayed by the respective host SN
of the requesting SC. The NACs will make sure that
DCNET 2011 - International Conference on Data Communication Networking
36
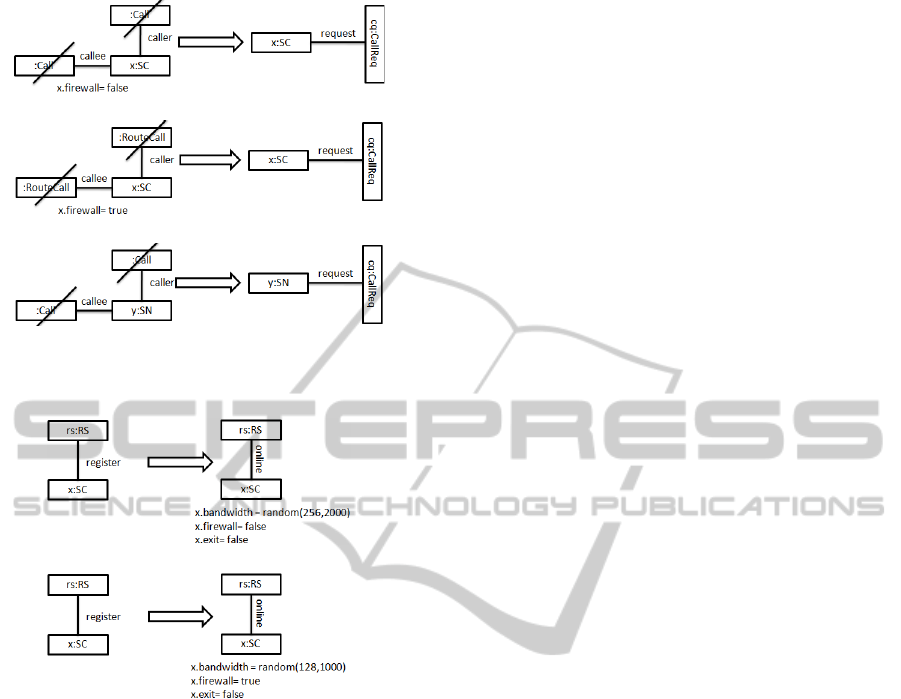
(a) SC with Public VoIP call request.
(b) SC behind firewall VoIP call request.
(c) SN VoIP call request.
Figure 7: VoIP call request initiated by SC and SN.
(a) User with Public IP go on-line.
(b) User behind firewall go on-line.
Figure 8: User go on-line.
requesting SC is not involved in VoIP calls. We have
used the node Routeall to model relayed call through
SN.
Rules in Figure 7(c): VoIP Call Request Initiated
by SN. In this rule an SN initiate request for VoIP
call with other network participant. As stated earlier
SN are clients with extended role as Super peer. An
SN can not only request calls but also relay traffic for
other SCs such as Fig 7(b). The call procedure for SN
is the same as that of in Fig 7(a).
Rules in Figure 8(a): User Go On-line with Public
IP. In this rule a registered user joins the network.
This rules considers that a user is connected to the
internet through public IP. Further, based on static IP
the user is assigned a random bandwidth between 256
Kbps to 2 Mbps. This new user can be considered as
candidate for the extended role of SN if it fulfils the
bandwidth requirement.
Rules in Figure 8(b): User Go On-line Behind a
Firewall. In this rule a registered user joins the net-
work. This rules considers that a user is behind a re-
stricted firewall. Further, the firewall attribute is set
to true and this user is assigned a random bandwidth
between 128 Kbps to 1 Mbps. This user can not par-
ticipate in the election process of SN as it has firewall
enabled, which restrict this user to communicate or
coordinate directly in the network. This user will al-
ways be dependent on one of the SN.
5 STOCHASTIC SIMULATION OF
GRAPH TRANSFORMATION
SYSTEM
Stochastic graph transformation (Heckel, 2005) can
be used to model architectural reconfiguration (Khan
et al., 2009) and non-functional properties such as
performance and reliability. In simple words stochas-
tic graph transformation system (SGTS) is a graph
transformation system(GTS) where each transforma-
tion rule is associated with a positive real number rep-
resenting the rate of the exponentially distributed de-
lay of its application to the model. It is important
to note that graph transformation can not only model
these dynamic networks but it does support a num-
ber of validation and verification techniques such as
model checking based on CSL and stochastic simu-
lation based on translation to Markov chains (Heckel
et al., 2006). Model checking seem the right choice
only when abstract properties has to be verified but
this approach become hard to use when model is
much more complex and dynamic. On the other hand,
Monte-Carlo stochastic simulation is typically based
on the execution of particular processes, which are se-
lected probabilistically by means of a random number
generator (RNG).
Let us consider that a S
G
= hG , F i is a gener-
alised stochastic graph transformation system when-
ever G is a GTS and F : E
G
→ (R → [0, 1]) is a
function which associates with every event in G a
general cumulative probability distribution function.
We assume that F(e)(0) = 0 (null delay condition)
(Khan et al., 2009). Moreover, the probability dis-
tribution is dependent on the event (rulename and
match) rather than just the rule. The concept of the
SGTS is explained (Heckel et al., 2006) in detail. Our
interest in stochastic graph transformation systems is
closely associated with their simulation, where the
stochastic aspect is useful in order to resolve the non-
deterministic character of ordinary GTSs.
We simulate our model using GraSS (for Graph-
based Stochastic Simulation), a tool introduced in
(Torrini et al., 2010) and used for our previous work
MODEL-BASED STOCHASTIC SIMULATION OF SUPER PEER PROMOTION IN P2P VOIP USING GRAPH
TRANSFORMATION
37

(Khan et al., 2010). The tool has been developed
in Java-Eclipse, as plugin of a graph transformation
engine called VIATRA. VIATRA (Bergmann et al.,
2008) relies on a RETE-style implementation of in-
cremental pattern-matching, in which precomputed
matching information is stored and updated as trans-
formation proceeds. The architecture of the tool is
shown in Fig 9. Essentially, the stochastic engine re-
ceives the set of enabled rule matches (i.e.the active
events) from the transformation engine, turns them
into timed events, by assigning to each of them an
expected time value, randomly determined on the ba-
sis of the probability distribution which is associated
with the event type, and sends the events that has been
scheduled first back to the transformation engine for
execution.
In GraSS a GTS is represented as a VIATRA
model, consisting of the model space with the current
graph and the transformation rules. Moreover, GraSS
takes as input an XML file with the definitions of the
distributions associated with transformation rules and
respective rates. In order to collect statistics the rules
with empty post-conditions that are used as probes
as can be seen in the architecture Fig 9. Each probe
rule returns the number of its matches in the current
graph for each state of the transformation system. We
used a number of probe rules for collection of simula-
tion results in this paper for the purpose of reader un-
derstanding we are presenting one probe rule in both
graphical representation in Fig 10 as well as VIATRA
code translation shown below:
gtrule SC_linked_SN()=
{
precondition pattern lhs(SC,SN,LK)=
{
SN(SN);
SC(SC);
LK(LK);
find LK_LinkTo(LK,SC);
find LK_OutTo(LK,SN);
}
action
{
println("SC linked with SN");
}
}
This probe is used to find average number of
SCs that are linked with SNs. Additional parameters
needed for a simulation run are provided to GraSS as
part of the VIATRA model (see (Torrini et al., 2010)).
The textual output of a simulation experimentconsists
of SSJ TallyStore class reports (L’Ecuyer et al., 2002).
In this experiments we are going to compare three
different protocols for SC promotion to SN. We have
used time based simulation, in order to produce com-
parative results. We have taken simulation unite as
24 hour for these experiments. We use exponential
distribution as will as normal distribution. Although
due to limitation of space it is not possible to present
complete set of rules along with respective probabil-
ity distribution and necessary justification. We have
used normal distribution for all those rules for which
implementation boundaries are known. Based on this
we have used normal distribution for rule that termi-
nates VoIP calls by keeping in mind that experiments
in (Guha et al., 2006) confirms that minimum call du-
ration observed was 2 minutes(m) and 50 seconds(s)
and maximum observed duration was 3 hour(h) and
26 m whereas the average as per there experiments
was 12m and 53s. Further, we have used exponential
distribution for rules presented in this paper at Fig 8.
As we are not sure that when a user will go on-line
so the rules that makes user to go on-line have been
assigned exponential distribution. Similarly, the pro-
motion rules use same exponential distribution.
We performed two different experiments in which
we run several simulations of each of the three pro-
tocols based on 24 hour simulation time. In the first
experiment we varied the rate of the rule that make
client on-line by{ 3,4,5,6,7}. In this experiment a sin-
gle rule is used which makes user to go on-line. This
rule also randomly set the firewall to true and false.
The aim is to simulate such behaviour that model does
not have any control on the population behind fire-
wall and with static IPs. Due to limitation of space
this rule is not presented in the paper. In the second
experiment we have fixed the rate of the rule in Fig
8(a) at 5 and we varied the rate of rule in Fig 8(a) by{
3,4,5,6,7}. The aim behind this is to reduce the num-
ber of candidate for SNs and increase the number of
SCs behind firewall. The rates for these rules either in
experiment 1 or 2 are selected based on the assump-
tion that if Skype user gets on-line every 8 hour over
24h period then rate based on this principal would be
3, and so on. The aim behind these varying rates is to
produce same number of average as that of real Skype
network (SkypeStatistics, 2011) in the 24h period in
order to confirm the confidence of the model.
In order to comment on the performance of these
three protocols, we have used several probes rules
such as to find numbers of SCs, SNs, linked SCs, and
number of clients that are happy with existing SN. In
our experiments an SC is happy with current SN if
its current host is having more than 1 Mbps available
bandwidth.
DCNET 2011 - International Conference on Data Communication Networking
38
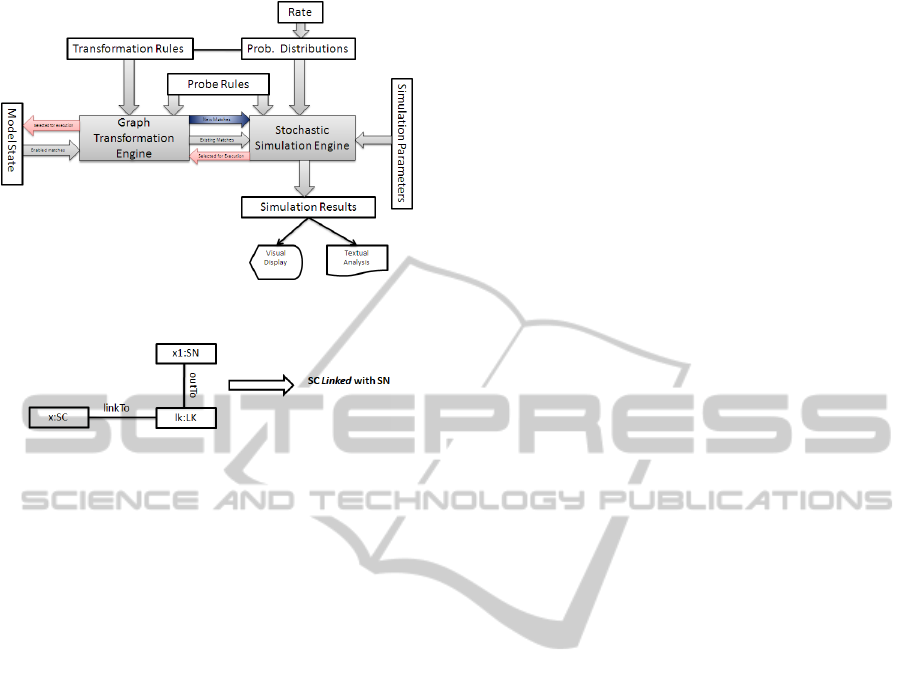
Figure 9: Graph based stochastic simulation (GraSS).
Figure 10: Probe rule SC connected with SN graphical view.
6 SIMULATION RESULTS
In the first experiment we compared three approaches
of client promotion to extended role of SN. Each ap-
proach/protocol is represented by a model and set of
transformation rules. All three models were tested
through 5 variations of rate x for the clients join-
ing the network. The rates assigned were ranging {
3,4,5,6,7}. For each variation we performed 9 runs
with a time unit of 4.8 hour. The results are presented
as graphs in Fig 11. In this experiment the number
of SCs with static IPs and behind firewall randomly
joins the network and their ratio is not known.
The graph in Fig 11(a) presents the percentage of
the happy peers in the network. As the graph shows
that dynamic VoIP protocol for super peer selection
approach is performing better as compared to other
two at the joining rates 3 and 4. The graph in Fig 11(a)
further shows that at joining rate 5, the number of
happy peers are almost the same but at rate 6 and 7 we
observe that, as the number of clients in the network
increases, the need based approach tends to produce
good results as compared to other two approaches.
The graph in the Fig 11(b) presents the average
number of linked clients. From graph we see that
dynamic protocol has resulted in well connected net-
work. Although, the other two protocol also managed
to link a good number of SCs to SNs. We further see
that in terms of SC connection to SN the other two
approaches are almost performing at the same level.
The graph 11(d) shows the average number of SNs
promoted in this course of simulation. The graph
results shows that there is not a big difference be-
tween the SNs promoted by all the three protocols.
Although, need based approach promoted less num-
ber of SNs but in terms of the happy peers the results
are not much different from other two protocols ap-
proach.
The third graph in the Fig 11(c) further clarify
that that all the protocol managed to result in network
nodes between 250 and 500. Although need based
protocol has slightly less number of clients in the net-
work but the difference in comparison with other two
protocol is not much. During the simulation the total
number of clients were fixed at 1000.
Th results of first experiment shows that at joining
rate 5, all the three approaches managed to produce
results which are close enough. In order to further
confirm these results we split the single rule of joining
into two as presented in Fig 8. Now we have fixed
that rate of the rule Fig 8(a), which makes clients on-
line and clients are enjoying static internet connection
without enabled firewall. The aim is to fix the number
of candidate for SN and we varied the rates for the
rule Fig 8(b) by { 3,4,5,6,7}. The aim is to increase
the number of users behind firewall. The results of
this experiment are presented as graphs in the Fig 12.
The graph in the Fig12(a) confirms that need
based protocol is performing much better as com-
pared to other two approaches when the number SCs
behind firewall increases in the model. Although we
do observe that in the start the dynamic approach is
performing better as compared to other but at joining
rate 5 where both rules are ruining at the same rate,
the results are changed and need based continues to
produce better results as the number of SCs behind
firewall increase. The second graph in Fig12(b) the
average number of SCs behind firewall in each rates,
which are almost close to each other in all the three
approaches.
7 VERIFICATION AND
VALIDATION OF SIMULATION
MODEL
Verification and validation of the simulation models
are the core entities in the modelling and simulation
study. There are various methods used in the liter-
ature for this purpose (Sargent, 1996; Whitner and
Balci, 1989). In this study we have used static and
dynamic verification techniques in order to make sure
that model has rightly been converted to VIATRA
model and the associated transformationrules are also
rightly converted. The static technique has ensured
MODEL-BASED STOCHASTIC SIMULATION OF SUPER PEER PROMOTION IN P2P VOIP USING GRAPH
TRANSFORMATION
39
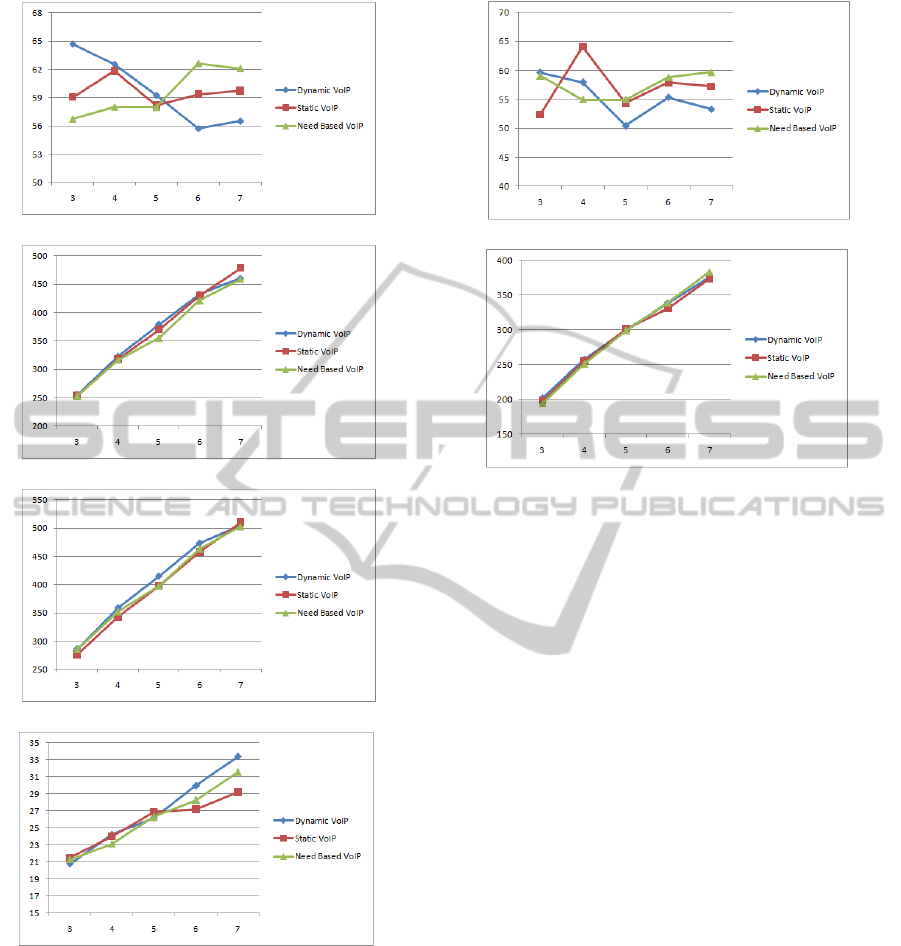
(a) Percentage of happy SCs.
(b) Average numbers of SCs linked to SNs.
(c) Total average number of clients.
(d) Total average number of SNs.
Figure 11: Simulation results first experiment.
that model and rules are error free and right syntax
has been followed. The dynamic verification tech-
nique has ensured that each rule does the task that it
was suppose to do.
Similarly for the purpose of model validation we
have used face validation, event validation as well
as compared the model with real system (Sargent,
1996; Whitner and Balci, 1989). Fore comparison
with real system we have used the study in (Guha
et al., 2006) and Skype statistics from (SkypeStatis-
(a) Percentage of happy SCs.
(b) Average numbers of SCs behind firewal.
Figure 12: Simulation results second experiment.
tics, 2011; SkypeJournal, 2010). The author analysis
in (Guha et al., 2006) is based on real system study,
their results shows that over a period 24 hour,the aver-
age number of clients that join the network varies by
over 40% of the active registered accounts, whereas
the average number of super node in this period is
below 24% of the active population. Similarity, the
author in (SkypeJournal, 2010) states that in Decem-
ber, 2010 there were 1.4 million super peer/nodes and
25 million user were on-line, when Skype network
crashed due to non availability of super peers. This
figure confirms that almost 6% of the on-line user
were super peers and still Skype network crashed.
This further confirm that Skype super peer population
must be over 6% of the on-line users, in order to make
networks stable. Based on these results we have ex-
amined our model simulation results obtained over a
period of 24 hour simulation. The simulation results
confirms that super node population in our model is
less than 24% which confirms the results of the (Guha
et al., 2006) and are over 6% which further confirms
the statement of the author in (SkypeJournal, 2010).
Our model further confirm the overall average num-
ber of population with real statistic of (SkypeStatis-
tics, 2011; Guha et al., 2006). Once we have obtained
these results we have fixed the rates of rules and var-
ied the rates of the rules where we have to make sen-
sitivity analysis.
DCNET 2011 - International Conference on Data Communication Networking
40

8 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have outlined our simulation ap-
proach based on stochastic graph transformation. We
used it to model and simulate some aspects of P2P
VoIP network protocols, and we have performed our
experiments with the GraSS/VIATRA tool (Torrini
et al., 2010). We have compared three client promo-
tion to exteded role protocols. The dynamic proto-
col does not seem to be performing better as com-
pared to the need based and static protocols in terms
of happy peers, especially when the number of clients
in the network increases over 400. The results fur-
ther confirmed that increased in super peer does not
mean that network may also result in good number of
happy clients. We further observed that need based
protocol is most suited when there are greater number
of clients, as super peer promotion costs in terms of
bandwidth use.
As future work, we are planning to extend the
model and include spatial information regarding no-
tions of jitter, packet loss and echo, along the lines
of (Khan et al., 2009), and to compare a number of
different design solutions to problems such as rout-
ing, load balancing, selfish exit, and cooperative exit
from the network, in order to investigate their trade-
offs and benefits.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is supported by Universityof Malakand,
Pakistan through faculty development programme of
HEC, Govt. of Pakistan.
REFERENCES
Adami, D., Callegari, C., Giordano, S., Pagano, M., and
Pepe, T. (2009). A real-time algorithm for skype traf-
fic detection and classification. In Lecture Notes in
Computer Science.
Baset, S. A. and Schulzrine, H. G. (2006). An analysis of
the skype peer-to-peer internet telephony protocol. In
25th INFOCOM’06.
Bergmann, G.,
˝
Okr˝os, A., R´ath, I., and Varr´o, G. (2008).
Incremental pattern matching in the VIATRA model
transformation system. In GraMoT’08.
Biondi, P. and Desclaux, F. (2006). Silver needle in the
skype. Technical report, EADS Corporate Research
Centre, Suresnes, France.
Dabek, F. (2001). Building peer-to-peer systems with
chord, a distributed lookup service. In Proceedings
of the Eighth Workshop on Hot Topics in Operating
Systems. 8th HotOS, IEEE Computer Society.
Guha, S., Daswani, N., and Jain, R. (2006). An experimen-
tal study of the skype peer-to-peer voip system. In 5th
IPTPS06.
Gupta, R. and Somani, A. K. (2004). Pricing strategy for
incentivizing selfish nodes to share resources in peer-
to-peer (p2p) networks. In 12th (ICON04).
Heckel, R. (2005). Stochastic analysis of graph transfor-
mation systems: A case study in p2p networks. In
ICTAC05. Springer-Verlag.
Heckel, R., Lajios, G., and Menge, S. (2006). Stochastic
graph transformation systems. Fundamenta Informat-
icae.
Idrees, F. and Khan, U. A. (2008). A generic technique
for voice over internet protocol (voip) traffic detec-
tion. International Journal of Computer Science and
Network Security.
Ji, L. C. (2004). Computation in peer-to-peer networks.
Technical report, Department of Computer Science,
University of Saskatchewan, Canada.
Khan, A., Heckel, R., Torrini, P., and Rth, I. (2010). Model-
based stochastic simulation of p2p voip using graph
transformation system. In 17th Int. Conf. Analyti-
cal and Stochastic Modeling Techniques and Applica-
tions, ASMTA (2010).
Khan, A., Torrini, P., and Heckel, R. (2009). Model-
based simulation of voip network reconfigura-
tion using graph transformation system. In
Vol.17,(ICGT)EASST.
Lara, J. D. (2007). Attributed graph transformation with
node type inheritance. Theor. Comput. Sci. In Funda-
mental Aspects of Software Engineering.
L’Ecuyer, P. L., Meliani, L., and Vaucher, J. (2002). SSJ:a
framework for stochastic simulation in Java. In Winter
Simulation Conference.
Lo, V., Zhou, D., Liu, Y., Dickey, C. G., and Li, J. (2005).
Scalable super node selection in peer-to-peer overlay
networks. In 2nd HOT-P2P Workshop.
Lysne, O., Montaana, J., Pinkston, T., Duato, J., Skeie, T.,
and Flich, J. (2005). Simple deadlock-free dynamic
network reconfiguration. In Boug, L. and Prasanna,
V., editors, High Performance Computing - HiPC
2004, volume 3296 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 277–316. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Milojicic, D. S. (2002). Peer-to-peer computing. Technical
report, HP Labs, Palo Alto.
Montresor, A. (2004). A robust protocol for building super
peer overlay topologies. Technical report, University
of Bologna, Italy.
NS2 (2008). The Network Simulator-NS2,
http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/.
Oneil, H., Jeong, J. K., and Kwon, D. (2000). Transport
layer identification of p2p super node. In hhhhhhhh.
Ren, S., Guo, L., and Zhang, X. (2006). Asap: an as-aware
peer-relay protocol for high quality voip. In 26th Int.
Conf. on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS’06),
Lisbon, Portugal.
Rowstron, A. and Druschel, P. (Nov. 2001). Pastry:scalable,
decentralized object location and routing for large-
scale peer-to-peer systems. In 8th Int. Conf. on Dis-
tributed Systems Platforms. Heidelberg, Germany.
MODEL-BASED STOCHASTIC SIMULATION OF SUPER PEER PROMOTION IN P2P VOIP USING GRAPH
TRANSFORMATION
41

Sargent, R. G. (1996). Verifying and validating simulation
models. In Winter Simulation Conference.
Skype (2011). The Skype Ltd, http://www.skype.com.
SkypeJournal (2010). Skype sn crashed.
http://skypejournal.com.
SkypeStatistics (2011). Skype statistics. http://aaytch.com.
Stutzbach, D. and Rejaie, R. (2006). Understanding churn
in peer-to-peer networks. In Proceedings of the 6th
ACM SIGCOMM conference on Internet measure-
ment.
Torrini, P., Heckel, R., and Rath, I. (2010). Stochastic simu-
lation of graph transformation systems. In FACE2010.
Whitner, B. and Balci, O. (1989). Guidelines for selecting
and using simulation model verification techniques. In
Winter Simulation Conference.
Yang, B. and Garcia-Molina, H. (2003). Designing a super-
peer network. In 19th Int. Conf. on Data Engineering
(ICDE),Bangalore, India.
Zhao, B. (2003). Tapestry: A resilient global-scale over-
lay for service deployment. IEEE Journal on Selected
Areas in Communications.
DCNET 2011 - International Conference on Data Communication Networking
42
