
A THEORETICAL ACCESSIBLE APPROACH FOR
COLLABORATIVE LEARNING IN MOBILE DEVICES
Rocío Calvo, Ana Iglesias and Lourdes Moreno
Computer Department, UC3M University, Av. Universidad 30, Leganés, Spain
Keywords: e-Learning, Mobile learning, Collaborative, Mobile devices.
Abstract: The concept of accessing to the Internet has changed in the last decade. Nowadays, the access to the Internet
is more flexible and users are able to surf on it from different Mobile Devices. Then, why not learn through
mobile devices as mobile phones? The main aim of this paper is to propose a theoretical model of a web
collaborative module for mobile devices. It pretends to provide a list of features that all mobile Learning
Management Systems (LMSs) should have in their collaborative modules and how they should be
implemented in mobile devices.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, users access to the Internet from
different mobile devices, they use them not only for
communicating with other people through phone
calls, but also for accessing to online services such
as: publicity services, banks services, etc.
In the educational environment, teachers and
students are used to access pedagogical resources
digitally and most of educational institutions provide
Learning Management Systems (LMSs). Besides,
taking into account the number of mobile devices in
the world currently outnumbers the number of
desktop computers by three to one (CSS Insight,
2010), why not take advantage of it and allow users
to learn through mobile devices? They provide
students more flexibility to learn.
This document presents a brief summary of the
state of art of m-learning specifically in
collaborative learning and its accessibility problems
in section 2. Next, section 3 describes a theoretical
approach for collaborative learning in mobile
devices. Finally, section 4 presents the main
conclusions and further research.
2 PREVIOUS WORK
2.1 Accessibility of Mobile Devices
Mobile devices should be accessible for everybody,
as it is gathered in the W3C’s mobile guidelines
(W3C, 2008a). However, not all mobile devices
accomplish it. These devices have some restrictions
which can be similar to the accessibility problems
that users have when they access to the Internet
(Newell, 1995); it provokes accessibility limitations
to people with and without disabilities. For instance,
if the images do not have alternative text, low band
width provokes accessibility problems for a user
without disabilities. Also, some mobile devices do
not support screen readers or do not have any button
to navigate through the mobile device. These
problems will be the same as the problems that a
visual impairment person has when tries to surf on
the Internet. Also, due to the small screen size, some
people cannot read the text, so it presents the same
accessibility problems as a user with visual
impairment. As a result, some people cannot use
mobile devices regularly (Harper, 2008). Because of
that, it should be useful to consider the accessibility
problems that a mobile device could present during
the design process of learning applications.
The features that all mobile devices should have
to be accessible for everybody are explained by
(Tiresias, 2009). And, related to collaborative
learning system, (Yan, 2009) proposes some
requirements that smartphones should have. In these
two proposals is mainly based on this research.
2.2 M-Learning
These days, e-learning is deeply-rooted in our
375
Calvo R., Iglesias A. and Moreno L..
A THEORETICAL ACCESSIBLE APPROACH FOR COLLABORATIVE LEARNING IN MOBILE DEVICES.
DOI: 10.5220/0003557703750378
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CeLS-2011), pages 375-378
ISBN: 978-989-8425-50-8
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
society and it has evolved to m-learning. M-learning
is defined by some authors as “the ability to learn
everywhere at every time without permanent
physical connection to cable networks” [Georgiev,
2004]. In general, the use of m-learning refers to the
use of mobile devices to try to access to the learning
content everywhere and every time.
Comparing m-learning with e-learning, m-
learning has some advantages. For example, the
price and size of mobile devices are lower than
desktop computers and the content can be adapted to
the geographical situation of the user. But the best
advantage is users can learn when and wherever they
want, being especially useful for people with few
resources (Brown, 2008). Nevertheless, m-learning
has some disadvantages already related to the
accessibility problems described in Section 2.1. An
example of architecture of LMS in mobile devices is
proposed in (Jin, 2009).
2.3 Collaborative Learning
After the evolution of Internet to Web 2.0, the
interaction between users through Internet has
changed. This concept can be extrapolated to the
electronic education too. Nowadays, students are not
static users who connect to the Internet to get
information from it; they share their own knowledge
(Peters, 1998). These days, it is important to mention
that our individual knowledge is not useful because
people need to collaborate with each other to solve
problems (Johnson, 1994). Also, there are some
researches (Yan Yu, 2010) which show that
collaborative e-learning environments provide a
huge relationship between partners. A proposal of
architecture for a collaborative learning environment
is proposed by (Wang, 2009).
2.4 Discussion
This paper is based mainly on four approaches that
are discussed in this subsection. The architecture
proposed by (Wang, 2009) which explains the main
processes and features that a collaborative learning
environment should have. However, this approach is
not adapted for mobile devices and moreover it does
not take into account how to do it accessible for
everybody. The approach presented in this paper is
based in this architecture, but taking into account
accessibility.
Related to mobile LMS, our proposal is based on
(Jin, 2009). It converts a LMS to a mobile LMS, but
it only explains some LMS’s modules and none of
them is a collaborative module. Moreover, it does
not explain how the different modules should be
implemented. The proposal presented in this paper is
based on the description of the collaborative module
in mobile devices based on this research.
Finally, although (Yan, 2009) proposes some
requirements that smartphones should have for
collaborative learning, this specification does not
take into account the accessibility problems that
people have when they use mobile devices. This
proposal is based on this research too, but adding the
accessibility point of view based on the work of
(Tiresias, 2009).
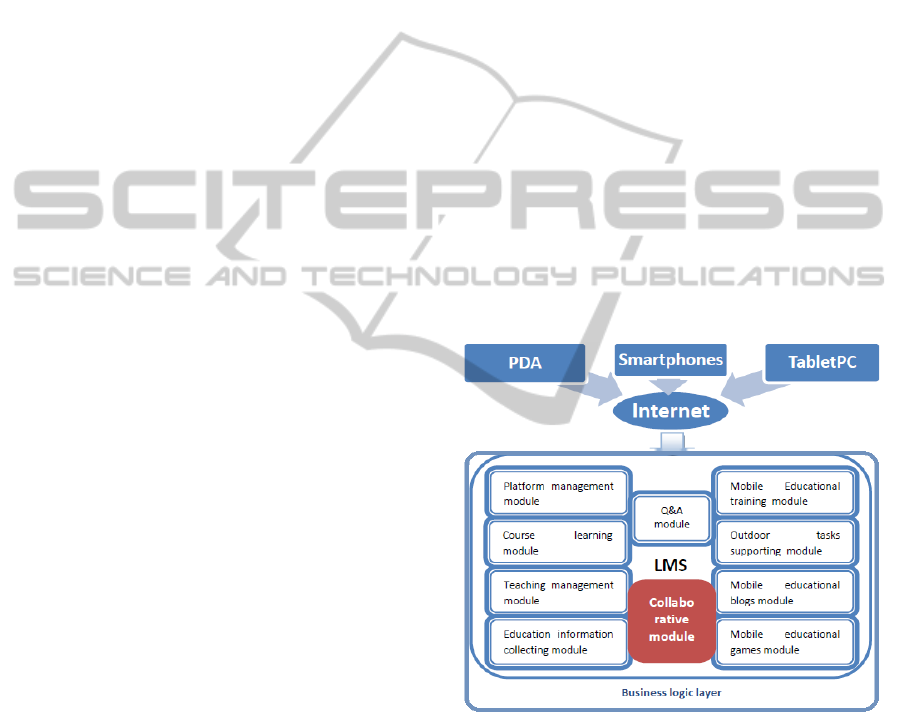
3 THEORETICAL APPROACH
3.1 Architecture
The architecture’s proposal presented in this paper
for a collaborative mobile LMS is shown in the
Figure 1. This design is based on the framework of
mobile LMS of (Jin, 2009). Trying to solve the main
drawbacks of Jin’s approach, a new collaborative
module has been added to the architecture.
Figure 1: Architecture of a collaborative mobile LMS.
3.2 Mobile Device’s Requirements
In order to ensure the accessibility of a mobile
device, a subset of technological requirements based
on (Tiresias, 2009). These ones are listed next:
1) Able to install assistive technologies such as:
screen readers, screen magnificients, etc
2) Alerts should be showed with a visual, audio,
voice and vibrant signal.
3) Color, type size, contrast, audio and illumination
should be customized by the user.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
376

4) Screen touch sensitive areas are enough big to
avoid the activation by mistake.
5) Information and help should be clear and simple.
6) Provide a front camera for video-conferences.
7) The size and weight should be appropriate to be
portable.
8) The design of all mobile components such as:
card, battery and battery charger, easy to connect
and use in a fixed way.
3.3 Design of the Collaborative Module
for Mobile Devices
The main issue to create accessible content for
mobile devices is to adapt the task to the common
characteristics of mobile devices and consider the
different accessibility problems that a user can have
when s/he navigates through a LMS. For instance,
there are some tasks which are hard to complete in a
small screen such as modify or create a document.
Therefore, it has been considered that the
processes of the Wang’s study (Wang, 2009) can be
implemented in a mobile LMS tool, even in an
accessible way. Thus, the mobile collaborative
module should have next components:
Social Network (SN): the user should have the
possibility to choose who his friends are and decide
which people can see or discus his documents.
Exchange Files (EF): it is useful for users to
provide a tool for exchanging files between peers
and save them. This task is divided into three main
subtasks: upload, download and share files.
Save the Evolution of each document (SE): the
user will be informed about the different changes
produced in the document and it will show the next
changes that should be done.
Document Version Storage (DVS): each version of
all documents should be stored. It provides a great
control for the user because s/he can compare the
different versions and decide the best approaches for
the document.
Then, the main characteristics that all tasks
should accomplish to be accessible are shown next:
F1) The design of the controls must be accessible.
So they should be big enough to be pressed and
selected by a usual finger. Also, they should be
created according to WCAG 2.0 guidelines (W3C,
2008b) because screen readers and
Table 1: Main accessible steps for the mobile collaborative learning.
Task Steps ¿How to make it accessible?
SN Search the name of his friends
The text area where the user has to write the friend’s name and the confirmation
button should be designed according to feature F1.
SN Select friend/s
The friends are showed according to feature F2.
Each friend’s name has associated a check control that is checked by the user. This
check and the confirmation button should be designed according to feature F1.
SN
The system sends a message/email
for the possible friend
A message is sent as described in feature F4. After that, an alert is showed as
described in feature F3.
SN
The invitation is confirmed by the
friend
The friend should press a confirmation button designed according to feature F1.
SN
The user receives a message/email
to inform him about the friend’s
confirmation
Idem to the task “Social network / The system sends a message/email for the
possible friend”.
EF Select the folder
The folders are showed according to feature F2.
Each folder’s name has associated a check control. This check and the confirmation
button should be designed according to feature F1.
EF Select the file
The files are showed according to feature F2.
Each file’s name has associated a check control. This check and the confirmation
button should be designed according to feature F1.
Share
files
Press the button for sharing The button should be designed according to feature F1.
Share
files
Select friends to share the file. Idem to the task “Social network/ Select friend/s”
SE Select the file Idem to the task “Upload files/ Select file task”
SE
Fill a form to explain the evolution
of the document
The form should be designed according to feature F1.
DVS Upload file
This task has the same steps as the task “Upload file”. So it is divided into: select
folders and upload files. As a result, the way for make it accessible is the same as
described before
A THEORETICAL ACCESSIBLE APPROACH FOR COLLABORATIVE LEARNING IN MOBILE DEVICES
377

screen magnificients could interpret the elements in
a good way. F2) The information must be shown in
small groups. For example, if a list is shown, it
should be divided into small groups of five or ten
elements.
F3) The system has to inform the user about all
completed tasks or the status of some tasks with an
alert. These alerts should be shown by the system in
a visual, audio, voice and vibration way to be
realized by the user.
F4) The message could be a text message and/or
an email. If an email is sent then it should contain
text, well-formed links and images with alternative-
text only.
Table 1 shows the different tasks and steps that
users should perform when they want to complete a
task. The first column shows the name of the task,
the second column shows the steps to perform in
each task and the third column explains how to make
each step accessible for everybody. This explanation
takes into account the features described in section
3.3 classified as F1, F2, F3 y F4.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FURTHER
RESEARCH
This paper presents a theoretical approach for
creating to create accessible collaborative learning
modules for mobile devices. This approach has as a
starting point some previous studies of m-learning,
accessibility in mobile devices and collaborative
learning for personal computers.
This research is centered in the collaborative
module which would allow teachers and students to
collaborate in the learning process through mobile
phones. Our study provides the architecture of a
mobile LMS which includes a collaborative module.
It specifies the main features that a collaborative
learning module should have to be accessible in
mobile devices. Finally, this approach specifies the
different features that a mobile device should have
to be accessible for everybody.
Currently, we are working on implementing and
evaluating the theoretical approach.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work presented in this paper has been partially
founded by GEMMA (TSI-020302-2010-141)
research projects.
REFERENCES
Brown, 2008, Brown T. M-Learning in Africa: Doing the
Unthinkable and Reaching the Unreachable.
International Handbook of Information Technology in
Primary and Secondary Education 2008 Springer
International Handbooks of Education (2008)
CSS Insight, 2010, CSS Insight Global Mobile Phone
Market Analysis. http://www.ccsinsight.com/our-
services/publications/35-global-mobile-phone-market-
analysis
Georgiev, 2004, Georgiev T., Georgieva E. and
Smrikarov A. M-Learning - a New Stage of Е-
Learning International Conference on Computer
Systems and Technologies - CompSysTech’2004 - IV.
(2004)
Harper, 2008, Harper, S. Mobile Web: Reinventing the
Wheel? ACM SIGACCESS Accessibility and
Computing - 20 years after Dexter Hypertext
Reference Model, vol. pp16.-18. Jan. 2008
Johnson, 1994, Johnson, D. , Johnson, R. Learning
Together and Alone. Cooperative, Competitive, and
Individualistic Learning. Allyn and Bacon (1994)
Newell, 1995, Newell, A.F., Extra-ordinary Human
Computer Operation, in Extra-ordinary Human-
Computer Interactions by A. D. N. Edwards (Ed.),
Cambridge University Press (1995)
Peters, 1998, Peters, J. and Armstrong, J. Collaborative
Learning: People Laboring Together to Construct
Knowledge. New directions for adult and continuing
education. September 1998.
Tiresias, 2009, Tiresias. Design Guidelines for Accessible
Information Communication Technology Systems.
Available in:http://www.tiresias.org
/research/guidelines/checklists/index.htm
W3C, 2008a, World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
Mobile Web Best Practices 2.0. Available in:
http://www.w3.org/2005/MWI/BPWG/Group/Drafts/
BestPractices-2.0/ED-mobile-bp2-20080327
W3C, 2008b, World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). Web
Content Accessible Guidelines 2.0. Available in:
http://www.w3.org/TR/WCAG20/
Wang, 2009, Wang, Q. Design and evaluation of a
collaborative learning environment. Computers &
Education Learning with ICT: New perspectives on
help seeking and information searching. (2009)
Yan, 2009, Yan, C., How to implement collaborative
learning in Web2.0: Take three applications for
example IT in Medicine & Education, 2009. ITIME
'09. IEEE International Symposium on , vol.1, no.,
pp.627-631, 14-16 Aug. 2009
Yan Yu, 2010, Yan Yu, A. , Wen S., Vogel D. , Chi-wai
Ron. Can learning be virtually boosted? An
investigation of online social networking impacts.
Journal Computers and Education (2010)
Jin, 2009, Yi Jin, "Research of One Mobile Learning
System," wnis, pp.162-165, 2009 International
Conference on Wireless Networks and Information
Systems, 2009
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
378
