
TOWARDS A COMMON UNDERSTANDING
OF THE DIGITAL PHEROMONE
Hans Dermot Doran
Institute of Embedded Systems, Zurich University of Applied Sciences, Winterthur, Switzerland
Keywords: Pheromones, Artificial intelligence, Robotics, Industrial communication, Communication theory,
Autonomous systems, Mobile robots.
Abstract: In this paper we critically evaluate the research on digital pheromones to date and conclude that the wide
variance in the understanding of what a digitised pheromone is serves to defocus research. We examine the
classical pheromone-use algorithm, the ant algorithm and conclude that as such it has not been proven
feasible for practical use. By examining the failure of proposed applications we derive an application where
pheromones appear to offer added value. On critically evaluating an initial implementation we note its
success but point out that lacking the understanding of biological pheromones serves to hinder research in
digital pheromones in general and bio-inspired robotics in particular. We propose a set of rules and urge
researchers to critically evaluate them.
1 INTRODUCTION
The general conceptual framework around this
position paper is the argument that bio-inspired
algorithms in general and pheromones in particular,
which have been suspected of bringing efficiencies
to real-world problems, are not as simply transferred
to real-world problems as the state of research
implies but require substantial applied research
which leads to a re-evaluation of previously held
opinions. In particular the paper presents the
argument that the state of the art in pheromone
research has not brought forth any applications that
can reasonably use pheromones and that the actual
implementation of these pheromones are so far
removed from the biological understanding of the
term as to mutate to mere marketing slogans. We
present an application which we believe to be as real
an application as to deserve the term pheromone but
show that even then it can be argued that the notion
of digital pheromone ought to be qualified by
quotation marks.
The paper is structured accordingly – we begin
by examining the biological definition of a
pheromone before critically reviewing the current
state of research on the digital variant of the topic.
We evaluate known use cases and construct what we
consider to be a viable use case and defend this
principle. We then presents preliminary result of an
implementation and draw the conclusions which are
then discussed in the broader context of this
argument.
Final conclusions follow with an outlook on
further work.
2 PHEROMONES
2.1 Natural Pheromones
Pheromones are well described (Wyatt, 2003) but in
summary are known to science as complex organic
compounds, and mixtures thereof, excreted by
animals and insects for message passing purposes.
Pheromones are generally, but not canonically,
classified by the reaction they invoke in receptors.
Propagation is by diffusion, accelerated by velocity
and concentration of excretion as well as the
intrinsic cohesion and medium composition
properties of the carrier (air, water). Reception is for
homogeneous message passing, apparently, an exact
science in that the receptors can be very
discriminating with respect to direction, in some
cases in three dimensions, and distance, some moths
and butterflies can famously detect potential mates
from some 10 km away. For heterogeneous
communication all or a subset of the information
intentionally transported may be, either intentionally
176
Doran H..
TOWARDS A COMMON UNDERSTANDING OF THE DIGITAL PHEROMONE.
DOI: 10.5220/0003572901760181
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2011), pages 176-181
ISBN: 978-989-8425-74-4
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

or unintentionally detected by other species.
What is known is that certain animals will re-
orientate their physical position according to
whether they wish to maximise or minimise the
reception of pheromones, what isn’t so well
discussed is whether – especially with airborne
pheromones – the act of excretion takes advantage
of ambient media conditions. There are simple
examples to suggest this is sometimes the case, dogs
and lamp posts spring to mind. More complex
examples quote bees which excrete pheromones and
accelerate movement of their wings in order to
facilitate distribution (Reinhart, 2009).
2.2 Fundamentals of Technical
Pheromones
From a technical point of view pheromone
transmission represents connectionless wireless
transmission, stochastic propagation with signal and
media dependent dispersion and attenuation.
Reception results in concentration dependent pulse
streams. Signal filtration is at point of reception.
Given that technical communication systems
depend on some form of determinism with respect to
probable area of distribution of transmitted signal,
when using pheromones we may assert:
Rule 1: Technical implementations of
pheromones must show some awareness of ambient
media conditions. If it is not otherwise possible
digital pheromones shall implement some time
based degradation profile.
Rule 2: It is acceptable for mobile units wishing
to excrete or receive pheromones to deviate from
their current path of motion to do so.
Rule 3: Pheromones serve for excreters and
receptors to interact within temporal and geographic
limits defined by the medium of choice.
As a complex chemical, sometimes a mixture
thereof it is the presence of a pheromone that
denotes the primary information value. The
secondary information is given by the concentration,
or the rate of change of concentration.
3 TECHNICAL
IMPLEMENTATIONS
OF PHEROMONES
3.1 “Virtual” Pheromones
Payton et. al’s. work is well cited with respect to
their pherobot project during which he coined the
phrase “Virtual Pheromone”. (Payton, 2001, 2003,
2004) They envisioned the search and rescue use
case and whilst they begin promisingly, detailing
some of the simpler characteristics of pheromones, it
becomes hard to reconcile priority transmission,
message passing and data request primitives with the
concept of a bio-inspired pheromone. Although the
term “Virtual Pheromone” found use with other
researchers, in essence his solution reduces to a
mixture of a directed transmission/re-transmission
service combined with elements of embodied and
situated communication.
The message complexity suggested by Payton
et.al. was vastly reduced by Campo et.al (Campo,
2010). to three message types who, following other
authors (Ducatelli, 2008), conceptualised message
passing as an ant which laid pheromones along a
chain of robots whilst being passed along this chain
by the robots themselves. The concept has much
merit, but is an abstraction removed from the
physicality of laying down a trail and acting on it
like the bio-inspired counterparts.
3.2 Pheromone Storage
Storage of these imagined pheromones is always an
issue. Most research that requires a bio-inspired
model and a pheromone tends towards research in
swarm robotics which in turn generally means that
short and medium term coordination is the task to be
solved by the use of these pheromones. Meng
(2008). built a map of swarm participants and their
respective pheromone densities. Borzello and
Merkle (2005) deposit a “pheromone”, whose
structure is unclear, on an uncompleted task by a
robot who then attempts to find another task leaving
the next random-walking robot to chance across the
task and attempt to complete it. The work, located
solely in the virtual world, attempts to use the ant
algorithm in an attempt to prevent task-deadlock in
multi-robot cooperative scenarios. As such the
pheromone loosely corresponds to a signal
pheromone, a pheromone designed to trigger a short-
term behaviour alteration. In this case the
pheromone triggers a state change in a state
machine, the behavioural pattern itself is not
changed and the pheromone does not serve to attract
the mobile robot nor does it induce any kind of
cooperative behaviour making it difficult to consider
it a “proper” pheromone. Both Susnea et.al (2009)
and Gunzinger and Pffifner (2008) use a central
server to map the pheromones onto virtual space and
provide these details to real-world requesting robots.
The use of air as a medium has also been
researched. Kuwana et.al, (1995) in earlier work
attached live moth antenna to a mobile robot to
TOWARDS A COMMON UNDERSTANDING OF THE DIGITAL PHEROMONE
177

follow moth pheromones. A practical application of
this technique would however depend on both
keeping the moth antenna alive over a longer period
of time and being able to generate the moth
pheromone in some manner. Russell and his
researchers (Purnamadjaja, 2004) tackled this
problem by using inorganic chemicals and gas
sensors for pheromone generation/detection.
Fujisawa et al. (2008) use ethanol as a pheromone.
There are other deposition media considered
such as ink on substrate (Svennebring, 2004) or UV
on phosphorescent coating (Mayet, 2010) but whilst
general feasibility may have been shown these do
not represent solutions that are likely to be taken up
by industry. Several researchers including Mamei
et.al. (2005) Heiranto (2009) and Doran et.al.
(2009b) have experimented with the idea of using
RFID tags. Heiranto concentrates on imagining a
floor of RFID tags whilst Doran and Mamei imagine
discretely positioned tags within a building.
3.3 Pheromones and Methodology
Interestingly enough Gunzinger found that the ant
algorithm was, for his particular scenario noticeably
less efficient than the Dijkstra algorithm in finding a
path with the help of pheromones but unfortunately
failed to quantify this. The use of a bio-inspired
model in conjunction with a mathematical algorithm
is not new and but does lead us to several questions.
The first is as to the general methodology
concerning the use of bio-inspired models. The
author has experienced in other projects, notably the
implementation of fish swarming algorithm that the
algorithm appears to need continual refinement
which is generally mathematical in nature, before
being implementable in hardware. This may be due
to the fact that a bio-inspired algorithm must
generally be expressed mathematically before initial
implementation therefore further refinement is by
default mathematical and the Gunzinger case is
merely the extreme case where the refinement of a
bio-inspired algorithm is simply not efficient given
known mathematical alternatives. It may also be due
to the fact that researchers are trained to research in
this way and that a lack of methodological flexibility
precludes the discovery of alternatives. In either case
it would thus appear probable that the act of
observation and expression of a bio-behaviour in
mathematical terms causes the algorithm to lose the
robustness that the observer wished to capture in the
first place.
Also, by observation, the author has noticed that
the necessary input to enact a behavioural pattern
generally cannot be solely received from one
sensory input - is a second or third sensory input is
required. For example fish schooling can be
simulated by using an interpretation of the lateral
line but the creation or breakup of a school requires
either a short-cut using either, for instance, a random
walk or optical species recognition. Given that
neither a real nor artificial fish will grow and utilise
eyes solely for swarming purposes but as
Lichtensteiger (2005) shows, albeit for flies,
artificial evolution of eye morphology leads to
single-use optimisation. It is unfortunate he omitted
to test quality of second and third priority tasks.
These observations inevitably lead to the question as
to whether, and if so with what methodology,
behavioural patterns can be isolated and
implemented whilst avoiding a holistic approach to
robot development.
3.4 Implementation Architectures
Controller architectures also play an important role.
In many experimental systems standard controllers
using some form of state machine are used. Whilst
state machines are often used in embedded systems
mapping a behavioural pattern into a state machine
is the engineering equivalent of expressing an
observed algorithm in a mathematical form, the
essence is bound to get “lost in translation”. The use
of state machines to switch between behavioural
patterns has, according to the authors research, not
yet been researched, but given the experience at the
sensor level where some convolution of sensor
inputs produces an output, it is unlikely to work very
well. Other controller architectures use neural
networks and evolve behaviour. Neural networks
have so far, by and large, failed to impress industry
due to the fact that training is lengthy and is both
non-deterministic and non-reproducible in output.
Whilst self-modelling, as shown by Bongard et.al.
(2006), is promising, it will be some time before we
see such architectures implemented.
Ants are relatively easy things to conceptualise
but, the drive towards cheap microbots
notwithstanding, robots cost money, ants don’t and a
lost ant won’t be missed whereas a lost robot will.
Therefore the task that the robot must fulfil should
be equivalent to the complexity (and by proxy cost)
of the robot. If we orientate ourselves to animals
which can be used in various scenarios then we need
something at least of the relative complexity of a
dog (Doran, 2009a). On the other hand there doesn’t
seem to be any reason why one can’t borrow the
sensor system of an ant and graft it onto a robot dog.
Given a pheromone is intimately connected with
a behavioural pattern (searching for and identifying
ICINCO 2011 - 8th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
178
pheromones) and the switch between behavioural
patterns this must be reflected in the controller
architecture. Therefore the robot designer must be
able to combine the behavioural patterns of various
models to make one robot.
In conclusion and summary:
Rule 4: A pheromone may be used to switch
from one behavioural pattern to another, or prevent
such a switch taking place, should it be present in
sufficient concentrations.
4 DEFINING AND
EXPERIMENTING WITH A
REAL-WORLD USE CASE
4.1 Deriving the Scenario
Gunzinger’s work represented an attempt to assess
whether the ant algorithm could be used for real-
world navigation scenarios. What it clearly showed
was that ant type algorithms are wildly inefficient if
the environment is even only partially known. On
this insight it is possible to narrow down the purpose
of an autonomous search by a robot to the case when
a known route is blocked and a second or third
passable route must be found. Formally this problem
can be expressed as the robot knowing a route at
time t0 which is invalid at time t1, discovered by the
robot to be invalid at time t2 and that a new route is
discovered by the robot at time t3 with t0 < t1 < t2 <
t3. The optimisation an ant routing algorithm can
achieve is by directing the following robot to the
correct route without it going through the discovery
phase already performed by its predecessor.
4.2 Deriving the Use Case
Landhuis and Terwellen’s work (2010), which
attempted precisely this, plays an important part in
the development of this papers argument. Based on
the premise that mobile robots making deliveries on
known routes may be blocked for periods of time
long enough for it to be more efficient for the robot
to spend its time searching for a new route, the work
also presumed that the robot would be given tasks,
and a route, by a job server but would not have
continuous contact with the job server via a house-
intern WLAN network and therefore requires partial
autonomy. Given a set of RFID tags which, being
cheaper by far than a WLAN access point and can
be spread redundantly across the corridors of a
building, can be used to store pheromones, a robot
searching for a new route can deposit re-
enforcement or detractor pheromones depending on
whether it is tracing or re-tracing its tracks. Whilst
Gunzinger (and Payton) had to invent pheromone
types to fulfil their respective tasks – and hence
severely compromise the quality of their
conclusions, Landhuis was able to call on the
precedent of the Pharaohs Ant (Robinson, 2008)
which, unlike other ant species, deposits detractor
pheromones to cancel out re-enforcement
pheromones. Given the scenario that the robot used a
local, non recognising, navigation (in this case
ultrasound transducers) and an extended Braitenberg
architecture (Lambrinos, 1995) with three active
inputs, the job/map, the local navigation and the
pheromones, Landhuis and Terwellen were able to
show that in the case of a blockage in the parcours
the use of pheromones was not inefficient with
respect to a robot always connected to a server or
one which returned to base when faced with a
blockage. Landhuis and Terwellen were also able to
show that using pheromones to mark routes brought
efficiencies with respect to using random walk
methods.
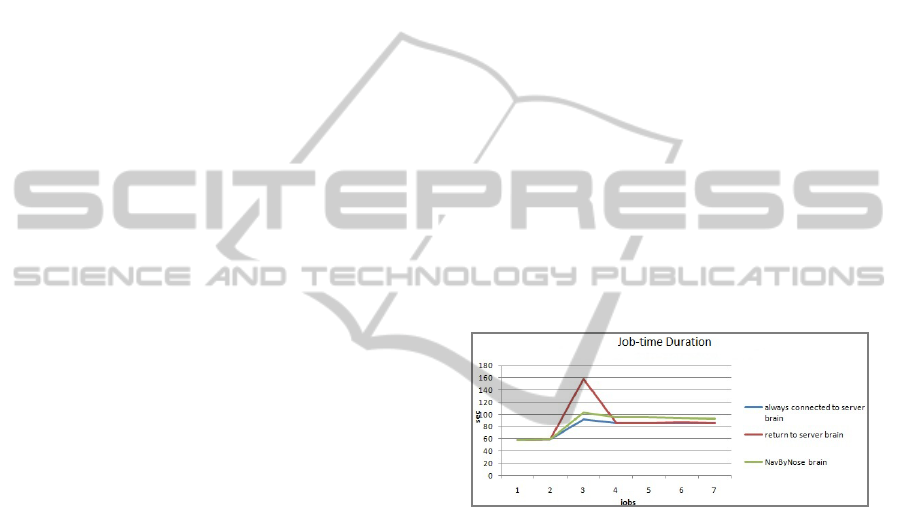
Figure 1: Simulation results for a robot's response to a
blockage. On job 3 a robot responds to a blockage by
either returning to base (red), or finding another route with
the help of RFID pheromones (green). The blue line shows
the response if the robot is always connected to a server.
Most importantly however Landhuis and
Terwellen were able to show that pheromones and
anonymous local navigation are not sufficient to
avoid positive feedback loops. They therefore
conceived their pheromone to include a direction
and destination factor, on the basis that the set of
active robots were not necessarily following the
same trail and that pheromone deposit on corridor
corners could otherwise be misleading. Equally it
may be asserted that a functioning local navigation
system should have noticed the robot was running
around in circles and judicious placement of RFID
tags, or some clever tag manipulation, may have
helped alleviate the need for the direction
component. The pheromone itself was represented
by the obligatory time-degrading signed integer
TOWARDS A COMMON UNDERSTANDING OF THE DIGITAL PHEROMONE
179

representing concentration and thus represents the
closest attempt so far to emulate a natural
pheromone.
Figure 2: Response times to a blockage (Job 3) given
random walk (red) or pheromones (gblue) or increased
density of RFID tags (green).
4.3 Results Analysis
It’s difficult to conceive of search and rescue
operations using tens hundreds of microbots as a
viable use-case let alone one requiring pheromones.
A trail finding application in a known environment
where short term obstacles can occur – hospitals,
manufacturing plants, warehouses etc spring readily
to mind – does sound like a viable use case and can
be shown to have some merit.
Landhuis and Terwellen show that it is possible
– given adherence to a fundamentalist view of
pheromones – to create a viable application for the
industrial arena that functions whilst retaining their
essential characteristics – which is, or should be, the
reason their emulation was chosen for an application
in the first place. In contrast Payton’s, and others,
rather lackadaisical interpretation of communication
theory in general and pheromones in particular,
serves only to mask the potential this
communication methodology possesses.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Even more dangerous by far is the ad-hock
modification or invention of further pheromone
properties which serves in practice to get something
to work but in fact only serves to mask conceptual
failings in the implementation of the research work.
The first failing is not to realise that it has not been
proven that a bio-property can be abstracted out of
its natural eco-system and transplanted into some
arbitrary technical solution. The refusal to consider
or acknowledge this failure results in
implementations of bio-inspired properties are
condemned to endless research cycles of abstracted
refinement, usually totally ignoring the fact that this
particular property resulted from generations of
embodied refinement in the first place. In short there
exists a serious methodological issue with which
much of research is conducted in this area which,
whilst touched on by previous literature (Pfeiffer
1999), needs to be better acknowledged in future.
Current natural science understanding of
pheromones tends to categorise them by the
behaviours they trigger. Current technical
understanding categorises them under
communication methods. The two don’t fit. The
triggering of a behavioural pattern is deeply
connected with the control architecture of the robot,
itself a subject where the jury is still in consideration
(Gershenson, 2005
). Whilst researchers using close-
to-life pheromones (gas, light) implicitly
acknowledge this through the limitations their
medium imposes on them others don’t and therefore
spend research time chasing issues that would have
been better avoided by an appreciation of this inter-
connectivity.
There appears to be an unfortunate element of
chance regarding the technicalisation of bio-inspired
properties. From a methodological point of view a
behaviour was specified and a bio-inspired tool was
found, it could equally have been that Landhuis and
Terwellen remained ignorant of the existence of the
Pharaohs ant and hence could have invented some
message passing system that functioned more or less
as well, in their case the increased robustness of the
bio-inspiredness of the solution has not been proven
but its relative simplicity certainly has.
Therefore it might be worth investigating the
creation of a list of biological behavioural patterns
so that technical researchers can better visualise
what kind of beast they wish to emulate and more
importantly what kind of sensor and actuators are
required. There is of course a sizeable ethical
dimension to building one’s own beast out of a
collection of behaviours like some modern day Dr.
Frankenstein and, given that scientific method seeks
to establish boundary conditions and work inwards
to the solution core, a new methodology must be
established to ensure that the behavioural patterns do
not express themselves all too negatively given some
hitherto unknown and unfortunate set of input
values.
In conclusion we would like to see a better
theoretical appreciation or possibly formal definition
of pheromones possibly based on the general rules
asserted earlier in the paper on which technical
researcher can base their work on and so better
understand their advantages and disadvantages.
ICINCO 2011 - 8th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
180

REFERENCES
Bongard, J., Zykov, V., Lipson, H. 2006. Resilient
machines through continuous self-modeling. Science,
314: 1118-1121.
Borzelloi, E., Merkle, L. D., 2005. Multi-Robot
Cooperation Using the Ant Algorithm with Variable
Pheromone Placement. In: Proc. IEEE Congress on
Evolutionary Computation.
Campo A, Gutiérrez A, Nouyan S, Pinciroli C,
Longchamp V, Garnier S, Dorigo M. 2010. Artificial
pheromone for path selection by a foraging swarm of
robots. In: Biological Cybernetics. Nov;103(5):339-
52. Nov. 2010.
Gershenson, C., 2005. Cognitive paradigms: which one is
the best? In: Cognitive Systems Research. Volume 5,
Issue 2, June 2004, Pages 135-156.
Doran, H., D. 2009a A Communication Technique for
Swarm-Capable Autonomous Agents. In: Proceedings
of Second International Conference on Robot
Communication and Coordination:
Doran, H. D., Meli, M. 2009b Verbesserung autonomer
Roboternavigation mit RFID basierten Pheromonen.
In Tagungsband 11th Wireless Technologies
Kongress. - Stuttgart: VDE,
Ducatelli, F., DeCaro, G.A., Gambdradella, L.M. 2008.
Robot Navigation in a Networked Swarm. In: Proc.
First International Conference on Intelligent Robotics
and Applications. Berlin.
Dünner, S., Kern, D., 2008. Ethernet POWERLINK as a
Communication System Internal to and Between
Autonomous Agents. In Proc. IEEE International
Symposium on Industrial Electronics.
Fujisawa, R., Imamura, H., Hashimoto, T., Matsuno, F.
2008. Communication Using Pheromone Field for
Multiple Robots, In: Proc. IEEE/RSJ International
Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems.
Gershenson, C., 2005. Cognitive paradigms: which one is
the best? In Cognitive Systems Research. Volume 5,
Issue 2, June 2004, Pages 135-156.
Gunzinger, D., Pfiffner, S. 2008. How to Motivate a
Robot. Diploma Thesis. Zürich University of Applied
Sciences. Unpublished.
Herianto,K. D. 2009 Realization of an artificial
pheromone system in random data carriers using RFID
tags for autonomous navigation. In: Proc. IEEE
International Conference on Robotics and
Automation.
Kuwana, Y. Shimoyama, I. Miura, H. 1995, Steering
control of a mobile robot using insect antennae. In:
Proc. IEEE Int. Con. Intelligent Robots and Systems
95. 'Human Robot Interaction and Cooperative
Robots', Proceedings. 1995.
Lambrinos, D., Scheir, C., 1995. Extended Braitenberg
Architectures.http://www8.cs.umu.se/kurser/TDBD17/
VT04/dl/Assignment%20Papers/Extended%20Braiten
berg%20Architectures.pdf Last viewed March 2011.
Landhuis, P., Terwellen, C., 2010 Navigation by Nose:
Implementing Pheromone Communication for
Autonomous Mobile Navigation Applications.
Navigation. BA Thesis. Zürich University of Applied
Sciences , Saxion University of Applied Sciences.
Unpublished.
Lichtensteiger, L., 2005 Bodies that think quickly and
learn fast: on the interdependence of morphology and
control for intelligent behaviour. Shaker, Aachen
Mayet, R., Roberz, J., Schmickl, T., Crailsheim K., 2010.
Antbots: A Feasible Visual Emulation of Pheromone
Trails for Swarm Robots. In: Proc. 7th international
conference on Swarm intelligence. Springer, Berlin.
Mamei, M. Zambonelli, F. 2005. Physical deployment of
digital pheromones through RFID technology. In:
Proc. IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium.
Meng, Y. 2008 Q-Learning Adjusted Bio-Inspired Multi-
Robot Coordination. In: Lazinica , A. (Ed.) Recent
Advances in Multi-Robot Systems, pp. 139-152, May
2008. I-Tech Education and Publishing, Vienna,
Austria.
Payton, D., Daly, M, Estkowski, R., Howard, R., Lee, C.
2001. Pheromone robotics. Autonomous Robots,
11(3):319-324, Nov. 2001.
Payton, D. Estkowski, R., Howard, R., 2003 Compound
Behaviors in Pheromone Robotics, Robotics and
Autonomous Systems, 44 (3-4): 229-240, Sept. 2003.
Payton, D., Estkowski, R, Howard, M. 2004. Pheromone
Robotics and the Logic of Virtual Pheromones. In:
Swarm Robotics. SAB 2004 International Workshop
LNCS 3342, Springer, New York.
Pfeiffer, R. Scheier, C. 1999 Understanding Intelligence.
MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Purnamadjaja, A. H. Russell, R. A. 2004. Pheromone
communication: implementation of necrophoric bee
behaviour in a robot swarm. In: Proc. IEEE
Conference on Robotics, Automation and
Mechatronics,
Reinhart, J., Sirnivasn, M., V., 2009 The Role of Scents in
Honey Bee Foraging and Recruitment. In Jarau, S.,
Hrncir, M. (Eds) Food Exploitation by Social Insects.
Ecological Behavioural and Theoretical Approaches.
CRC Press.
Robinson, E. J. H., Ratnieks, F. L. W., Holcombe, M..
(2008) An agent-based model to investigate the roles
of attractive and repel-lent pheromones in ant decision
making during foraging. In: Journal of Theoretical
Biology, Vol. 255, 2008, pp.250-258.
Susnea, I. Vasiliu, G. Filipescu, A. Serbencu, A.
Radaschin, A. 2009. Virtual pheromones to control
mobile robots. A neural network approach. In: Proc.
IEEE International Conference on Automation and
Logistics. ICAL '09.
Svennebring, J., Koenig, S. 2004. Building Terrain
Covering Ant Robots: a Feasibility Study,
Autonomous Robots, 16 (3): 313-332, May 2004.
Nicholas R. Hoff, N.R., Sagoff, A., Wood, R.J., Nagpal,
R., 2010. Two Foraging Algorithms for Robot Swarms
Using Only Local Communication. In: Proc IEEE Int.
Conf. on Robotics and Biomimetics, Tianjin, China.
Wyatt, T.D. 2003 . Pheromones and animal behaviour,
communication by smell and taste. Cambridge
University Press.
TOWARDS A COMMON UNDERSTANDING OF THE DIGITAL PHEROMONE
181
