
STUDY OF WIND FARM BEHAVIOUR DURING POWER
SYSTEM NETWORK DISTURBANCE
T. R. Ayodele, A. A. Jimoh, J. L. Munda and J. T. Agee
Department of Electrical Engineering, Tshwane University of Technology, Pretoria, South Africa
Keywords: Wind farm, Doubly fed induction generator, Power system, Disturbance.
Abstract: This paper studies the impact of disturbances emanating from the power system network on the behaviour
of a wind farm (WF) consisting of doubly fed induction generator (DFIG). Response of the WF to
disturbances like fault occurence, sudden change in load, sudden loss of transmission line and loss of
generation are considered in the study. The models of various systems making up the wind conversion
system are presented. Pitch control system is used for the stabilization of the wind turbine against the
disturbances. Parts of the key results show that the generator inertia, converter controller and types of
disturbance have significant effect on the response of a WF.
1 INTRODUCTION
A lot of efforts are geared towards grid integration
of renewable energies as a result of environmental
concern and energy security. Among these
renewable energies, wind energy stands out as it has
the ability to produce electricity in the MW range.
At present, the wind power growth rate stands at
20% annually and it is predicted that 12% of the
world electricity may come from wind power by the
year 2020 (El-Sayed, 2010). There is tendency to
surpass this rate with the present advancement in the
offshore wind farm techologies.
There are various types of wind turbines in use
around the world each having its own advantages
and disadvantages (Slootweg et al., 2001). The most
used one is the variable speed wind turbine with
doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) due to the
numerous advantages it offers over others et al.,
2005).
The behaviour and the characteristic of the
conventional generators for electricity generation are
well known by the utility operators. With the advent
of wind power, different types of generator
technologies are introduced to the power system.
This poses a lot of concern to most utility operators
as the response of these generators to network
disturbance is not well understood.
Most existing literature is focused on the analysis
of the behavior of power system network as a result
of wind farm integration (Eping et al., 2005; Xing et
al., 2005; Naimi and Bouktir 2008; Folly and
Sheetekela, 2009). This paper looks at it from the
other angle by studying the response of the wind
farm to disturbance in the power system network.
The study is limited to Wind farm (WF) consisting
of variable speed DFIG.
The structure of the remaing part of the paper is
as follows, section two presents the model of the
wind conversion system made of variable speed
DFIG. Section three describes the system under
study. Simulation results obtained are discussed in
section 4 while section five presents the conclusion.
2 MODELLING OF DFIG WIND
CONVERSION SYSTEM
Wind conversion system comprises of the
aerodynamic system, the mechanical shaft system,
electrical system of the induction generator, the
pitch control system, the speed control system, the
rotor side converter controller and the grid side
converter controller. All these systems are combined
together to form a unit system of a wind farm.
2.1 Aerodynamic Torque Model
Aerodynamic model involves the extraction of
241
Ayodele T., Jimoh A., Munda J. and Agee J..
STUDY OF WIND FARM BEHAVIOUR DURING POWER SYSTEM NETWORK DISTURBANCE.
DOI: 10.5220/0003576202410248
In Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH-2011), pages
241-248
ISBN: 978-989-8425-78-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
useful mechanical power from the available wind
power. Available wind power is given by
23
1
2
wind
PRV
ρπ
=
(1)
where
wind
P
,
ρ
,
R
and
V
are the available power in
the wind, air density, radius of the turbine blade and
the wind speed that reaches the rotor swept area. The
fraction of wind power that is converted to the
turbine mechanical power
m
P
is given by
()
23
1
,
2
mp
PRCV
ρπ λ β
=
(2)
where
p
C gives the fraction of available wind power
that is converted to turbine mechanical power,
λ
and
β
are the tip speed ratio and the pitch angle
respectively. The
p
C ,
λ
and
β
are related by
equation 3 and 4 (El-Sayed and Adel, 2010)
()
5
2
134 6
,
i
c
p
i
c
Ccccec
λ
λ
ββλ
λ
⎛⎞
=−− +
⎜⎟
⎝⎠
(3)
2
1 1 0.035
10.08
1
i
λβ
β
=−
+
+
(4)
Given
1
c
=0.5176,
2
c
=116,
3
c
=0.4,
4
c
=5,
5
c
=21 and
6
c
=0.0068 ,the relationship between
p
C against
λ
at various
β
is given in figure 1
Figure 1: Relationship between Power coeficient and tip
speed ratio at different pitch angle.
The tip speed ratio is given by (5)
Rt
V
ω
λ
=
(5)
The mechanical torque developed by the wind power
()
23
1
,
2
p
m
m
tt
RC V
P
T
ρπ λ β
ωω
==
(6)
where
t
ω
is the turbine speed.
For efficient wind power capture by the variable
wind turbine (Arifujjaman et al., 2009),
opt
λ
λ
=
,
therefore (5) can be re-written as
opt
Rt
V
ω
λ
=
(7)
subtituting (7) in (6), Optimum torque can be
obtained
()
23
3
1
,
2
()
popt
opt
opt
ttopt
RC R
P
T
ρπ λ β
ω
ωλ
==
(8)
Figure 2: Maximum torque tracking of a variable speed
wind turbine.
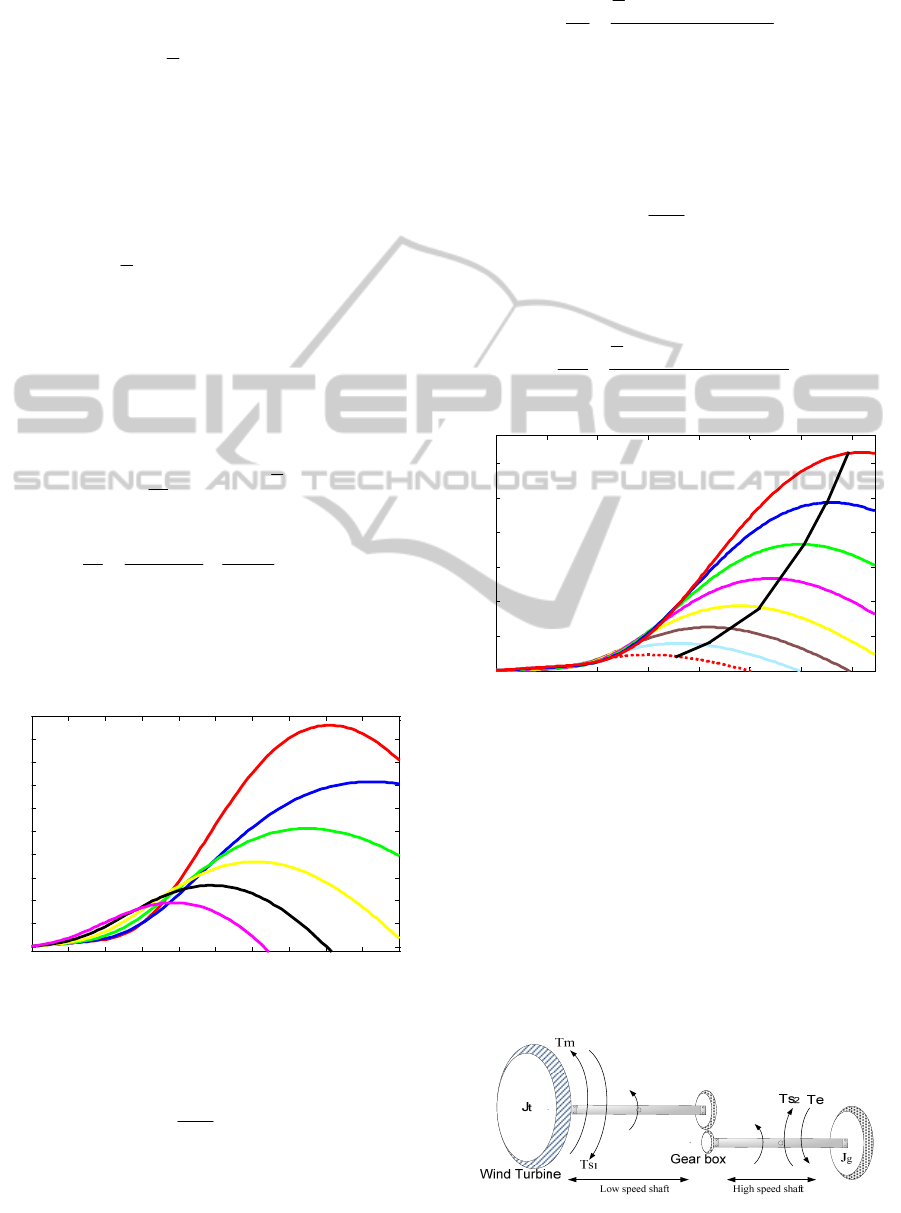
2.2 The Mechanical Shaft System
Model
Adequate model of the mechanical drive train is
required when the study involves the response of a
system to heavy disturbances. It is better to represent
the shaft by at least two- mass model (Poller, 2009).
Model of the shaft system with two mass models is
presented. The turbine is coupled to the generator
through a gearbox as shown in figure 3
1
θ
2
θ
Figure 3: Two mass model of the mechanical shaft system.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
Tip speed ratio
Power coefficient, Cp
B=20
B=25
B=15
B=10
B=5
B=0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.2 pu
6 m/s
7.2 m/s
8.4 m/s
9.6 m/s
10.8 m/s
12 m/s
13.2 m/s
14.4 m/s
Turbine speed (pu)
Turbine Torque
Turbine Torque Characteristics at various wind speed (Pitch angle beta = 0 deg)
SIMULTECH 2011 - 1st International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and
Applications
242
From the figure, the following equations can be
derived (9)-(16)
1
2
t
tm
d
HTTs
dt
ω
=−
(9)
2
2
r
e
d
H
gTsT
dt
ω
=−
(10)
where
2
2
22
and
22
g
T
gT
p
gg
J
J
HH
nP nP
ω
ω
==
(11)
1
1111
d
Ts K F
dt
θ
θ
=−
and
2
2222
d
Ts K F
dt
θ
θ
=−
(12)
12eq
θ
θθ
=−
,
12
12
*
eq
KK
K
KK
=
+
,
12
12
*
eq
Ts Ts
T
Ts Ts
=
+
(13)
eq
eq eq eq eq
d
TK F
dt
θ
θ
=+
(14)
eq
tr
d
dt
θ
ω
ω
=−
(15)
rt
eq
ωω
dt
dθ
−=
(16)
where
t
H
,
H
g
are the pu turbine and generator
inertia respectively.
g
J
and
T
J
are the inertia in
kgm
2
.
e
T
is the electromechanicl torque developed
by the induction generator,
m
T
is the pu mechanical
torque applied to the turbine by the wind as given in
(5) .
1
Ts
,
2
Ts
,
eq
T are the torques developed by the
shaft at the low speed side, torque developed by the
shaft at the high speed side and the equivalent torque
developed by the shafts respectively.
t
ω
and
r
ω
are
the pu turbine and generator rotor speed.
1
K
,
2
K
and
eq
K
,
are shaft stiffness at low speed side, shaft
stiffness at high speed side and the total shaft
stiffness.
1
F
,
2
F
and
eq
F
are the damping coefficient
of the shaft at the low speed side, high speed side
and the equivalent damping coefficient of the shaft
respectively.
1
θ
,
2
θ
and
eq
θ are the angle of twist of
the shaft at low speed, high speed and the equivalent
angle of twist of the shaft respectively.
p
n is the
number of pole pair, n is the gear ratio,
g
P is the
generator active power,
ω
is
2
f
π
where
f
is the
frequency.
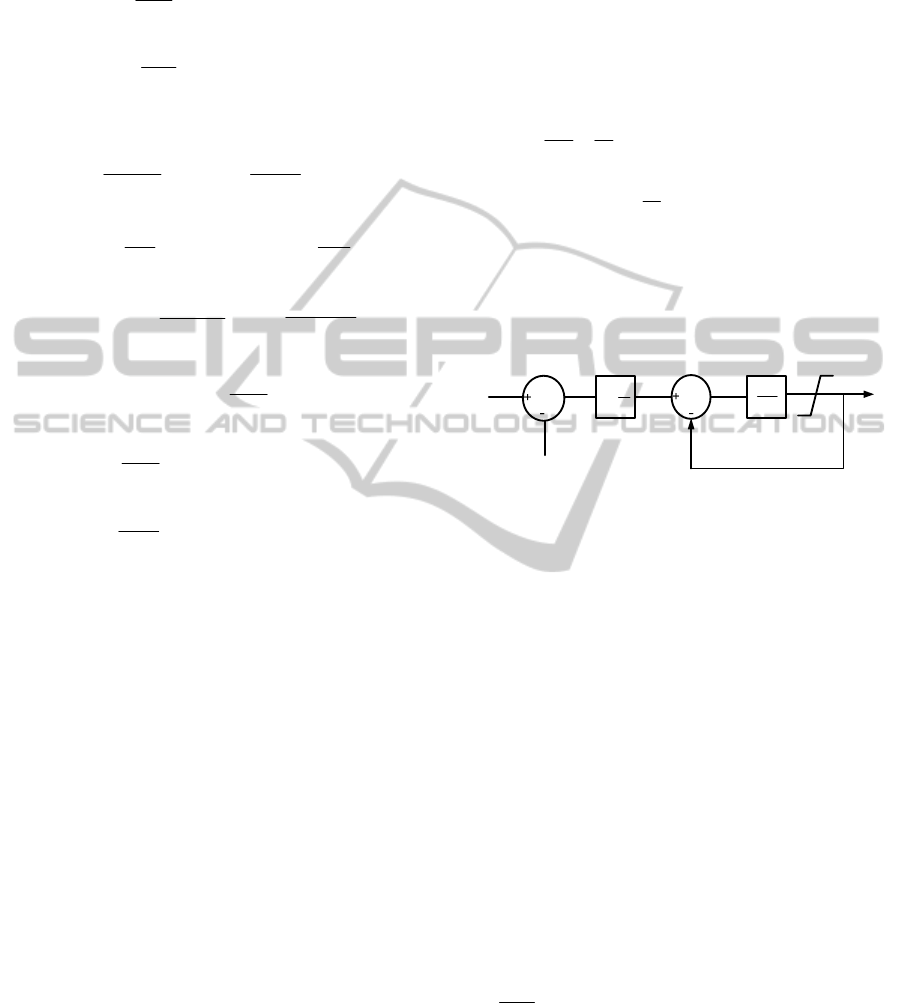
2.3 Pitch Angle Controller Model
Pitch angle controller majorly serves a purpose of
limiting the generated power to the rated power in
the time of high wind speed. It also limits the speed
of the generator during heavy disturbances. The
pitch controller based on PI is given by (17) (El-
Sattar et al., 2008)
()
()
1
ref
s
i
ref P ref m
d
dt
k
kPP
s
β
ββ
τ
β
=−
⎛⎞
=+ −
⎜⎟
⎝⎠
(17)
where
ref
β
is the reference pitch control,
P
k
and
i
k
are
the proportional and integral parameter of the PI
controller,
ref
P is the reference turbine power
Figure 4: Pitch angle controller.
2.4 Wind Generator Model
Most wind farms are made of induction generators
because they are cheap and robust. The dq stator and
rotor voltage equations model in generating mode
are as follows (Lipo 2000; Krause et al., 2002). The
equation presented is a fifth order model. Third
order model is obtained by neglecting the transient
term in the stator voltage equation.
qs s qs qs qs
vri p
ω
λλ
=
−− −
(18)
ds s ds qs ds
vri p
ω
λλ
=
−+ −
(19)
(
)
qr r qr r qr qr
vri p
ω
ωλ λ
=− − − −
(20)
(
)
dr r dr r qr dr
vri p
ω
ωλ λ
=− + − −
(21)
where
s
r
,
r
r
are the stator and rotor speed resistance,
p
is
(
)
.d
dt
term.
The stator and rotor flux equations are
qs s qs m qr
Li L i
λ
=
+
(22)
ds s ds m dr
Li L i
λ
=
+
(23)
P
K
i
K
s
+
m
P
Re
f
P
Re f
β
1
s
τ
0
max
90
β
=
0
mi n
0
β
=
β
STUDY OF WIND FARM BEHAVIOUR DURING POWER SYSTEM NETWORK DISTURBANCE
243

qr r qr m qs
Li L i
λ
=+
(24)
dr r dr m ds
Li L i
λ
=+
(25)
where
s
L
,
r
L
,
m
L
are the stator, rotor and magnetzing
inductance respectively.
ds
i
, ,
qs
i
dr
i
and
qr
i
are the
stator and rotor d-axis and q-axis.
The electromechanical torque,
e
T
developed by
the induction generator in pu can be derived as (26)
given by
()
1
eqsdrqrds
T
λ
λλλ
σ
=−
(26)
where
2
1
m
rs
L
LL
σ
=−
The equation is completed by the mechanical
coupling equation in pu between the turbine and the
generator using two mass model as derived in (9)-
(16)
()
2
1
2
r
e
g
d
Ts T
dt H
ω
=−
the active and reactive power generated by the
induction generator is given as
()
3
2
s
qs qs ds ds
Pvivi=+
(27)
()
3
2
s
qs ds ds qs
Qvivi=−
(28)
2.5 Grid Connection of DFIG Wind
Farm
DFIG technology makes use of wound rotor. The
stator is directly connected to the grid while the rotor
is coupled to the grid through a Pulse width
modulation (PWM) frequency converter as shown in
figure 4. The converter carries only the rotor slip
power typically in the range of 10-15% of the
generated power (Veganzones et al., 2005).
Figure 5: DFIG with PWM converter control system.
For dynamic study of DFIG, the converter
controller model is important. Stator flux oriented
control is commonly used in the decoupled control
of DFIG.
2.6 DFIG Rotor Side Converter
Controller
The control of the DFIG rotor is done in a
synchronous rotating reference frame i.e
e
ω
ω
=
in
equation (18)-(21). The rotor side converter controls
the stator active and reactive power of the DFIG. By
alligning the dq reference frame in the stator flux
reference frame, then
0
ds
v =
,
qs s
vv= ,0
qs
λ
=
and
ds s
λ
λ
=
. Subtituting these in (22)-(25), (27), (28)
and re-arranging, we obtain
*
3
2
m
s
sqr
s
L
P
vi
L
=−
(29)
2
*
3
2
s
s
smdr
ss
v
QvLi
L
ω
⎛⎞
=−
⎜⎟
⎝⎠
(30)
The rotor voltage equation governing the active
and reactive power control can be obtained by
rearranging equation (18)-(25) and is given by (31)
and (32) (Krause et al., 2002)
()
()
**
di
dr dp dr dr e r r qr
k
vk ii Li
s
ωωσ
⎛⎞
=+ −−−
⎜⎟
⎝⎠
(31)
(32)
where,
dp
k ,
di
k
are the PI proportional and integral
constant for the d-axis for the control of reactive
power while gain
qp
k
,
qi
k
are the PI constant for
controlling the active power.
*
qr
i
and
*
dr
i
are the
reference current for the active and reactive power
respectively.
*
dr
v
and
*
qr
v
are the dq reference voltage
which will be converted to a-b-c frame to generate
command for the rotor end PWM converter. The
block diagram is shown in figure 6a and 6b
2.7 DFIG Grid Side Converter
Controller
The main objective of grid side controller is to
maintain the dc link between the back to back PWM
converters at constant voltage irrespective of the
direction of power flow (Krause et al., 2002). The dq
=
=
,ref ref
P
Q
,dcref ref
VQ
=
()
()
**
qi
m
qr qp qr qr e r r dr S
s
k
L
vk ii Li
sL
ω
ωσ λ
⎛⎞⎛⎞
=+ −+− −
⎜⎟
⎜⎟
⎝⎠ ⎝ ⎠
SIMULTECH 2011 - 1st International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and
Applications
244

dr
i
−
+
+
*
qr
i
qr
i
qi
qp
k
k
s
+
*
qr
v
()
er
L
ω
ωσ
−
*
S
P
S
P
PI
−
+
()a
+
()
m
er s
s
L
L
ω
ωλ
−
*
S
Q
S
Q
PI
d
d
i
p
k
k
s
+
dr
i
*
dr
v
(
)
er r
L
ω
ωσ
−
qr
i
−
+
−
+
+
−
*
dr
i
()b
Figure 6: Rotor side Controller system.
voltage for the grid side converter is represented by
(33) (Soares et al., 2009)
1
1
q
qq eidq
d
dd eiqd
di
vRiL Lv
dt
di
vRiL Lv
dt
ω
ω
=+ + +
=+ − +
(33)
Re-arranging 33 with 0
qs
v
=
, the governing voltage
equation for the grid side converter can be obtained
()
()
**
1
11
**
2
12
i
qp qqeid
i
dpddeiqd
k
vk iiL
s
k
vk iiLv
s
ω
ω
⎛⎞
=− + − −
⎜⎟
⎝⎠
⎛⎞
=− + − + +
⎜⎟
⎝⎠
(34)
where
1 p
k ,
1i
k
are the q axis PI propornal and the
integral constant.
2 p
k ,
2i
k
are the d axis PI
proportionality and integral constant respectively.
*
1q
v
and
*
1d
v
are the reference voltage that generates
the command for the grid side PWM converter after
conversion to abc frame.
*
q
i
is derived from the grid
reactive power error while
*
d
i
is derived from the dc
link voltage error as shown in figure 7a and 7b
respectively.
3 SYSTEM UNDER STUDY
The system considered for the study is shown in
figure 8. It consists of 110MW, 50MVAR
synchronous generator (SG) connected to bus 4
through a 20/400kV transformer.
d
i
−
+
−
+
*
q
i
q
i
1
1
i
p
k
k
s
+
*
1q
v
e
L
ω
*
s
Q
s
Q
PI
−
+
()a
Figure 7: Grid side controller system.
S
G
DFIG
Turbine
0.69 / 20K
V
20 / 400
K
V
1
B
2B
P
CC
4B
5
B
20 / 400
K
V
Figure 8: The system under study.
The wind farm (WF) is made up of 40 wind
turbines of 2MW, 0.69kV each modelled as an
aggregate wind turbine. Aggregate model reduces
simulation time required by detailed multi turbine
system (Conroy and Watson 2009). It is assumed
that the wind farms are located far from the point of
common connection (PCC) where the wind
resources are abundantly located as the case for most
real wind farms. The WF is connected to the PCC
through two 20km line (to allow disconnection of a
line) and 69/20KV transformer. The WF is feeding a
60MW, 25MVAR local load connected to bus2
(B2). Another 100MVA, 30MVAR load is
connected to the high voltage bus (B4). The whole
system is connected to a strong grid through a two
400kV, 100km transmission lines.
4 THE SIMULATION RESULT
AND DISCUSSION
Different scenarios were created to get insight into
the response of WF to disturbances from the grid.
First, the response of the wind farm was studied
when there is a step change of 20% in the local load
connected to B2 at 1s. The results with the rotor
controller in place and out of place are depicted in
*
dc
v
dc
v
PI
2
2
i
p
k
k
s
+
d
i
d
v
d
v
*
1d
v
e
L
ω
qr
i
−
+
−
+
+
+
+
*
d
i
()
b
STUDY OF WIND FARM BEHAVIOUR DURING POWER SYSTEM NETWORK DISTURBANCE
245

figure 9. From the figure it can be observed that with
the controller in place, the active power (the
negative values indicate a power injected into the
grid) and the electrical torque are immediately
returned to the pre-disturbance level. The step
increase in the local load resulted in a dip in the
terminal voltage and an increase in the speed of the
generator, however, it stabilizes to a new value
almost immedately. This is as a result of change in
the system configuration. With the rotor controller
out, the system is stable but it takes about 3s for the
wind farm to stabilize.
Figure 9: The response of (a) DFIG speed (b) Active
power, (c) Electrical torque (d) Terminal voltage to 20%
step change in local load at 1s.
The response of the wind farm to different fault
type of duration 200ms was investigated. The fault
considered are three phase fault, two phase to
ground fault, phase to phase fault and single phase to
ground fault. The fault was created at 1s at the
middle of 100km, 400kV line. The results are
presented in figure 9. The severity of the impact of
these faults is in the order listed in the legend. This
is evident in the speed, the active power, the
electrical torque and the rotor current in figure 10.
The speed of the generator is limited by the pitch
angle. The first swing of the rotor current reached a
value of 2pu from the prefault value of 0.8pu for a
three phase fault, 1.5pu for two phases to ground
fault, 1.3pu for phase to phase fault and 1pu for
phase to ground fault.
The response of the wind farm to different fault
locations was examined. To get insight into this
scenario, a three phase fault of 200ms duration was
created at different location on the 50km, 20kV line.
The result is shown in figure 11. From the result, the
impact of fault at different location has almost the
same impact on the response of the wind farm.
However, the impact is visibly different at the PCC.
The closer the fault location to the PCC, the more
the dip in voltage and the more the deviation from
the nominal grid frequency.
Figure 10: Response of the wind farm (a) speed (b) Active
power (c) pitch controller (d) Turbine power (e) rotor
current to different types of fault.
Figure 11: Response of (a) DFIG speed (b) DFIG active
power (c) PCC frequency and (d) PCC voltage to 3 phase
fault (200ms duration) at different location on the 20kV
line.
Figure 12 shows the response of the wind
generator with different rotor inertia to a three phase
fault created at the middle of 400kV line. The effect
0 1 2 3 4 5
1.18
1.2
1.22
1.24
(a) Time (s)
DFIG Speed (pu)
0 1 2 3 4 5
-1
-0.9
-0.8
-0.7
-0.6
(b) Time (s)
Active power (pu)
0 1 2 3 4 5
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
(c) Time (s)
Electrical torque (pu)
0 1 2 3 4 5
0.645
0.65
0.655
0.66
(d) Time (s)
Terminal voltage (kV)
With rotor side controller Without rotor side contoller
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
1.15
1.25
1.35
(a) Time (s)
DFIG Speed (pu)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
(b) Time (s)
Active Power (pu)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
-0.5
0
0.5
1
(d) Time (s)
Electrical torque (pu)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
0
2
4
6
(c) Time (s)
Pitch angle
0 1 2 3
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
(e) Time (s)
Rotor current (pu)
3-phase fault
2 phase to ground fault
Phase to phase fault
Phase to ground fault
Legend
0 1 2 3
1.15
1.2
1.25
1.3
1.35
(a) Time (s)
DFIG Speed (pu)
0 1 2 3
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
(b) Time (s)
Active power (pu)
0 1 2 3
49
50
51
52
(c) Time (s)
Freq at PCC (Hz)
0 1 2 3
0
5
10
15
20
(d) Time (s)
PCC Voltage (kV)
0% 30% 70% 100%
SIMULTECH 2011 - 1st International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and
Applications
246

of inertia can be noticed in the speed of the
generator. The generators with larger inertia are
more stable in case of fault compared to the
generator with smaller inertia. The first swing in
rotor speed for 50kgm
2
is 1.28pu, 1.26pu for
100kgm
2
, 1.24pu for 150kgm
2
and 1.22pu for
200kgm
2 .
No distict difference in the response of the
active power, electrical torque and the terminal
voltage are seen.
Figure 12: Wind farm with DFIG of different inertia.
The effect of a loss of transmission line (TL) and
generation was studied. For the TL, the circuit
breaker at both ends of the lines were opened at 1s
for the 400kV, 100km line and then for 20kV, 50km
line. The circuit breaker at bus 4 connecting the
synchronous generator (SG) to the bus was opened
at 1s to disconnect the SG from the power system.
The results are shown in figure 13. A loss of line
causes a surge in the system frequency at the PCC,
this caused a reduction of active power to the
network by the WF to restore the frequency to the
prefault value. The 20kV, 50km line has a severe
impact compared to the 400kV, 100km line due to
close proximity to the WF. At the instant the SG
(generation) was lost; a sudden dip in the system
frequency was experienced, this in turn resulted into
an instant injection of active power from the WF to
the grid to restore the system frequency. The
terminal voltage reduces from the prefault value of
0.655kV to a new value of 0.638kV, 0.641kV and
0.650kV for the loss of 50km line, 100km line and
SG respectively as a result of change in the system
configuration.
Figure 13: Response to loss of transmission line.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The behaviour of wind farm consisting of DFIG in
response to different disturbance emanating from the
power system has been studied. From the study, the
effect of the rotor controller on the stability of a
wind farm has been shown to be significant to the
stability of the wind farm following a disturbance.
Without controller, prefault condition was achieved
after about 3s. With controller, the prefault condition
was achieved almost immediately.
The type of fault on the power system has
different significant impact on the behaviour of the
wind farm with three phase fault being the most
severe fault. The location of the fault occurence is
seen to have little effect on the wind farm. However
the location of fault occurence has significant effect
on the frequency and the voltage at the PCC.
The inertia of wind generators has influence on
the response of the WF to a disturbance. The larger
the inertia the lesser the magnitude of oscillation of
the generator speed. A larger inertia enhances good
stability. The WF responds to the sudden loss of
transmission line and generation in such a way as to
restore the system frequency. The rotor current and
the terminal voltage assume a new value due to the
change in the network configuration.
This paper is useful to the ultility operators in
understanding the probable response of a wind farm
during disturbance in the power system.However, a
qualitative study mainly is carried out on a small test
system. Further investigation is necessary for a large
power system.
0 1 2 3
1.1
1.15
1.2
1.25
1.3
(a) Time (s)
DFIG Speed (pu)
0 1 2 3
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
(b) Time (s)
Active power (pu)
0 1 2 3
-0.5
0
0.5
1
(c) Time (s)
Electrical torque (pu)
0 1 2 3
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
(d) Time (s)
Term inal voltage (kV)
50kgm
2
100kgm
2
150kgm
2
200kgm
2
0 1 2 3
-0.72
-0.7
-0.68
-0.66
-0.64
Time (s)
Active power (pu)
0 1 2 3
0.63
0.64
0.65
0.66
Time (s)
Terminal voltage (kV)
0 1 2 3
49.95
50
50.05
50.1
50.15
Time (s)
Frequency at (Hz)
0 1 2 3
0.76
0.78
0.8
0.82
Time (s)
Rotor current (pu)
20kV,50km line loss 400kV,100km line loss SG loss
STUDY OF WIND FARM BEHAVIOUR DURING POWER SYSTEM NETWORK DISTURBANCE
247

REFERENCES
Arifujjaman, M. D., M. T. Iqbal, et al. (2009). Vector
Control of a DFIG Based Wind Turbine, "Journal Of
Electrical & Electronics Engineering." 9(2):1057-1066.
Conroy, J. and R. Watson (2009). "Aggregate Modelling
of Wind Farms Containing Full-Converter Wind
Turbine Generators with Permanent Magnet
Synchronous Machines: Transient Stability Studies."
IET Renewable Power Generation 3(1): 39-52.
El-Sattar, A. A., N. H. Saad, et al. (2008). "Dynamic
Response of Doubly Fed Induction Generator Variable
Speed Wind Turbine Under Fault." Electric Power
Systems Research 78: 1240-1246.
El-Sayed, M. A. (2010). Integrating Wind Energy into
Weak Power Grid Using Fuzzy Controlled TSC
Compensator. International Conference on Renewable
Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ,
,
2010),
Granada, Spain.
El-Sayed, M. A. and M. S. Adel (2010). Wind Energy-
Grid Stabilization using a Dynamic Filter
Compensator. International Conference on Renewable
and Power Quality (ICRPQ 2010), Spain.
Eping, C., J. Stenzel, et al. (2005). Impact of Large Scale
Wind Power on Power System Stability. 5th
International Workshop on Large-Scale Integration of
Wind Power and Transmission Networks for Offshore
Wind Farms, Glasgow, Scoland.
Folly, K. A. and S. Sheetekela (2009). Impact of fixed and
variable speed wind generators on the transient
stability of a power system network. Power Systems
Conference and Exposition, 2009. PSCE '09.
IEEE/PES.
Krause, P. C., O.Wasynczuk, et al., Eds. (2002). Analysis
of Electric Machinery and Drive Systems Second
Edition, A John Wiley and Sons,Inc.Publication.
Lipo, T. A. (2000). Electric Machine Analysis and
Simulation. Research Report. W. E. M. a. P. E.
Consortium. Madison, Wisconsin Power Electronic
Research Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Naimi, D. and T. Bouktir (2008). "Impact of Wind Power
on the Angular Stability of a Power System."
Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and
Technologies 12: 83-94.
Poller, M. A. (2009). Doubly_FEd Induction Machine
Models for Stability Assessment of Wind Farms,
http://www.digsilent.de/consulting/publication/DFIG
modelling date accesed, 28th Sept.
Slootweg, J. G., S. W. H. de Haan, et al. (2001). Modeling
wind turbines in power system dynamics simulations.
Power Engineering Society Summer Meeting, 2001.
IEEE.
Soares, O. M., H. N. Gocalves, et al. (2009). Analysis and
NN-Based Control of Doubly Fed Induction Generator
in Wind Power Generation. International Conference
on Renewable Energies and Power Quality
(ICREPQ
,
2009), Valencia(Spain).
Veganzones, C., S. Martinez, et al. (2005). Large Scale
Integration of Wind Energy into Power Systems.
Electrical Power Quality and Utilisation, Magazine.
Spain. 1: 15-22.
Xing, Z., Q. Zheng, et al. (2005). "Integration of Large
Double-Fed Wind Power Generator System into Grid."
8th international Conference on Electrical Machines
and System.: 1000-1004.
APPENDIX
TABLE: DFIG Parameters.
Description Values
Active power ,P 2MW
Rated voltage 0.69kV
Stator resistance Rs 0.01pu
Stator reactance, Xs 0.1pu
Rotor resiatance, Rr 0.01pu
Rotor reactance, Xr 0.1pu
Magnetizing reactance,Xm 3.5pu
Inertia 75Kgm
2
SIMULTECH 2011 - 1st International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and
Applications
248
