
RESEARCH ON LOGISTICS LOCATION OPTIMIZATION
MODEL BASED ON TIME DIMENSIONS
Jiuguo Zhao
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University
No.3 Shang Yuan Cun, Haidian District, Beijing, China
Keywords: Location model, Time-satisfaction, Time cost, Service facility.
Abstract: The classical logistics facility location models seldom lay emphasis on time, which is a critical issue for a
company to gain its competitive advantage nowadays. Some scholars study maximal covering location
problem based on time-satisfaction, but most of them have not taken the consumption of time cost into
account. This paper presents a new location model which incorporates time cost compared with previous
approaches of time satisfaction. The model is initially developed based on the integer programming, whose
objective function is subject to the maximization of total satisfaction and the minimization of total cost.
Finally, it makes precise analysis taking the case of a regional network layout optimization. The
computational result proves the feasibility and value of this model in its practical application.
1 INTRODUCTION
The competition advantage in Modern logistics is
focused on how to access to consumption with the
fastest speed, the shortest distance and lowest cost
under the premise of the satisfaction of individual
customer needs by distribution channels. So logistics
siting problem in logistic distribution centre is an
important part of the entire product supply chain
optimization.
The economic globalization and international
competition augment the frequency of location
decisions because of shortened product life cycles.
On the other hand, the decisions on the siting
problem have a growing impact on competitiveness
of enterprises. With the progress of information
technology and developing of logistics and supply
chain management in recent years, making location
decisions has become a corporate capacity trained
for business and part of changing tactical decisions.
Sometimes it is usually structured to support the
organization's daily scientific decision-making.
Therefore, the academics and managers pay close
attention to how to solve the location problem by
analysing, classifying, modelling and calculating
(Bo et al, 2008).
Nowadays, time is on the cutting edge. Time will
become the next competitive resource advantages.
Time-based competition can be a strategic tool to
gain success in many industries, especially in
logistics industry. Especially in delivery of
perishable goods and emergency services, time is
even more obvious. For the pursuit of zero-time
response to customer demand, siting problem of
various service facilities cannot be an overlooked
factor. The conventional location models of logistics
facilities have a time constraint or use time as the
main target elements, but it is still too simplified to
define time. Usually enterprises look on time of
customers demand from its own perspective, not
from the customer itself. It did not fully reflect the
importance and differentiation of time required by
people in the 2l century.
Based on the background hereinbefore, time is
even more obvious. Therefore, time effect should be
fully taken into account in the location decision-
making process of logistics distribution centre as the
key factors. Thus, this paper introduces time into
location model of logistics distribution centre. We
propose time is not considered in isolation and
shortening the time without condition is not
scientific. It should define and model time from the
perspective of the customer. In this model, we
consider not only maximizing total time satisfaction,
but also minimizing total cost of time. The time
satisfaction mentioned in this article means the
customer satisfaction of responding to the needs of
the time required. The time cost is the cost
consumed by logistics services for customers in
order to satisfy their needs.
656
Zhao J..
RESEARCH ON LOGISTICS LOCATION OPTIMIZATION MODEL BASED ON TIME DIMENSIONS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003580406560661
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (MMLM-2011), pages 656-661
ISBN: 978-989-8425-56-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 LITERATURE OVERVIEW
With the growing attention on logistics industry,
more and more enterprises are starting to focus on
logistics facilities location problem. Logistics
facility Location is a very old and classic problem,
developing of the foreign research can be divided
into three stages with different focus (Brandeau and
Chui, 1989).
① Fragmented Research Stage
This stage was from 1909 to 1960. It focused on
solving a variety of practical problems in production
and daily life. The mainly representatives was the
German economist Alfred weber. He considered a
single warehouse location problem is to determine
the location, so that total transportation distance is
the shortest between warehouse and customers.
Hotelling proposed location of two competing
suppliers in a straight line and built related models in
1929. Then Smithies, Stevens studied this problem
in more depth. Regional economist Isard also
analysed the choice of industrial location from the
perspective of land use, input and output.
② Systemic Research Stage
Hakimi went into more theoretical issues of
research on the site in 1964. For selecting for the
network location of one or more facilities, he
considers it should make the total distance or the
distance between facilities minimum. Since then, the
location problem was introduced into a broader area.
After that, the location problem of Production
centre, the transport hub and substation was
researched in succession.
③ Uncertainty Research Stage
So far into the 80s of last century, along with
great changes in the market, the static and
deterministic location model cannot meet the
development of location method. Louveaux,
Mirchandani, Weaver, Church and other scholars let
the transport time and demands as random variables
on the issue of uncertainty median. Berman and
Odoni, Berman and Leblanc let the time or
transportation costs as uncertain system variables to
study the traffic problem in random networks
(Owen
and Daskin, 1998).
The existing literatures mainly consider the
location problem of logistics from the perspective of
minimizing the cost and the time, but research on
location model of logistics facilities and distribution
considered by satisfying customer needs is not too
much. Logistic is a typical service industry,
customer satisfaction must be put in the first place.
At the same time, it is an important factor to
determine customer satisfaction. The aim of
introducing the concept of time satisfaction to
location model of logistics distribution centre is to
ensure location of services and facilities is consistent
with strategic goals and business objectives and the
expectations of customers, but few studies take into
account the cost of time caused by satisfying
customer needs when time satisfaction is considered
in the model.
3 OPTIMIZATION MODEL
TO LOGISTICS LOCATION
PROBLEM
This siting model is formulated to solve location
problem of logistics distribution centre, so as to
maximize a range of benefits. In this model, we
employ the Ma Yun-feng TSBMCLP model to
calculate the time satisfaction and establish the
frame of the time cost. We formulated model as an
integer programming under the goal of maximizing
the total satisfaction of customers and minimizing
the total cost to the service facility’s response time,
which builds respectively from the points of cost and
benefit (Daskin, 1995). The above-mentioned model
is given as follows:
3.1 Notations
ij
t
The shortest waiting time accepted by customers
between the service demand point i and the primary
service point j.
ij
c
Transportation cost per unit between service
demand point i and the primary service point j. It is
proportional to the shortest distance between two
points.
i
L
Acceptable maximum waiting time between
primary service demand point i and secondary (and
lower class) service points when customers feel very
satisfied.
i
U
The shortest waiting time between service
demand point i and secondary (and lower class)
services point when customers feel very
dissatisfied.
ii
LU
≤
.
j
c
Field processing costs per unit in primary service
point j when customers feel satisfied, including the
cost of cargo handling, sorting and etc.
i
h
Demand of service demand point i.
P
Number of primary service points.
RESEARCH ON LOGISTICS LOCATION OPTIMIZATION MODEL BASED ON TIME DIMENSIONS
657

λ
The ratio of the time and cost, it completes
conversion of time and cost. Its value depends on
specific situation. For example, if the enterprise is
more concerned about customer satisfaction and
weaken the concern of cost,
λ
will be a smaller
value.
()
ij
f
t
The satisfaction level of response time
between the secondary (and lower class) service
point i and primary service point j.
The curves of time satisfaction function is of a
variety of situations, many functions can be used to
represent the satisfaction of time (Yun-feng et al,
2006). In this paper, we use linear function of time-
satisfaction, for all
[
]
() 0,1
ij
ft ∈
.
If
ij i
tL<
,
() 1
ij
ft =
; if
ij i
tU>
,
() 0
ij
ft
=
; if
[, ]
ij i i
tLU∈
,
()
iij
ij
ii
Ut
ft
UL
−
=
−
.
3.2 Formulation of the Model
In a network G (V, A), V is a vertex set, | V | = n; A
is an edge set
iI∈
,
j
J∈
. We define
IV∈
is total
subscript set for the set of service demand points
and
J
V∈
is total subscript set for the set of primary
service points,
I
JV∪=
. The model can be
formulated as follows:
() ( )
..
1
0jJ
0, 1 j J
0, 1 j J
0
iijij ij jiij
iI jJ iI jJ
ij
jJ
j
jJ
ij j
j
j
M
ax z h f t Y c c hY
st
YiI
Xp
YX iI
X
YiI
N
λ
λλ
∈∈ ∈∈
∈
∈
=−+
=∀∈
=
−≤ ∀∈∀∈
=∀∈
=∀∈∀∈
≥∈
∑∑ ∑∑
∑
∑
,
,
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
The objective function is to maximize actual
satisfaction of services demand, while ensure the
minimum cost of time. A weight is given
to
λ
relative to the preference of the logistics
enterprises. Constraints (2) ensure every demand
point is serviced by the only one service point (this
service point can provide the best time satisfaction).
Constraints (3) ensure number of service point
is
P
. Constraints (4) limit the satisfaction of
demand points by establishment of service stations
(if service station is not established, the service
satisfaction of it is zero). Constraints (5) and (6) are
the 0-1 Constraint.
Decision variable is seen as follows:
jJ
0 not set up a service at point j
1 set up a service at point j
j
X
⎧
⎪
∀∈
⎨
⎪
⎩
=
jJ
0 customers at point i don't accept
the service from point j
1 customers at point i accept
the service from point j
ij
iIY
⎧
⎪
⎪
∀∈ ∀∈
⎨
⎪
⎪
⎩
= ,
3.3 Solving the Model
The specific target of this model is to maximize total
satisfaction of secondary (and lower class) service
points covered by primary service points, while
reducing the cost of it. The relevant algorithm is
proposed to solve the problem. With the introduction
of time satisfaction function, location model will be
more flexible and effective (Gen-gui and Yan-fei,
2008). At the same time, it will increase the
complexity of the algorithm. According to adjusting
classical algorithm of current location model, the
time-based location model can be solved. The
greedy algorithm, Ant colony algorithm, genetic
algorithm, tabu search algorithm, artificial neural
networks method and simulated annealing method
can be adjusted to solve such problems. linear
programming software can also be used for solving
of Small-scale problems, such as lindo and lingo
(Yong, 2008).
4 APPLICATION TO A CASE
STUDY
4.1 The Case
In order to verify the feasibility of modeling, we
apply this model to solve and optimize an actual
location problem. Company A is a large private
express delivery companies. It forces on customer-
oriented strategy, which pays close attention to
customer service and level of customer satisfaction.
A has three primary services points in East China
(respectively in Shanghai, Wuxi, Hangzhou) and
twenty-four secondary service points. Its annual
throughput of 591,000 tons is also the forefront of
all regions. According to the above analysis, there is
an obvious and typical site layout problem in the
region of East China. We number twenty-seven
service points, and the defined number and
Throughputs of twenty-seven service points in East
China are given in Table 1:
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
658
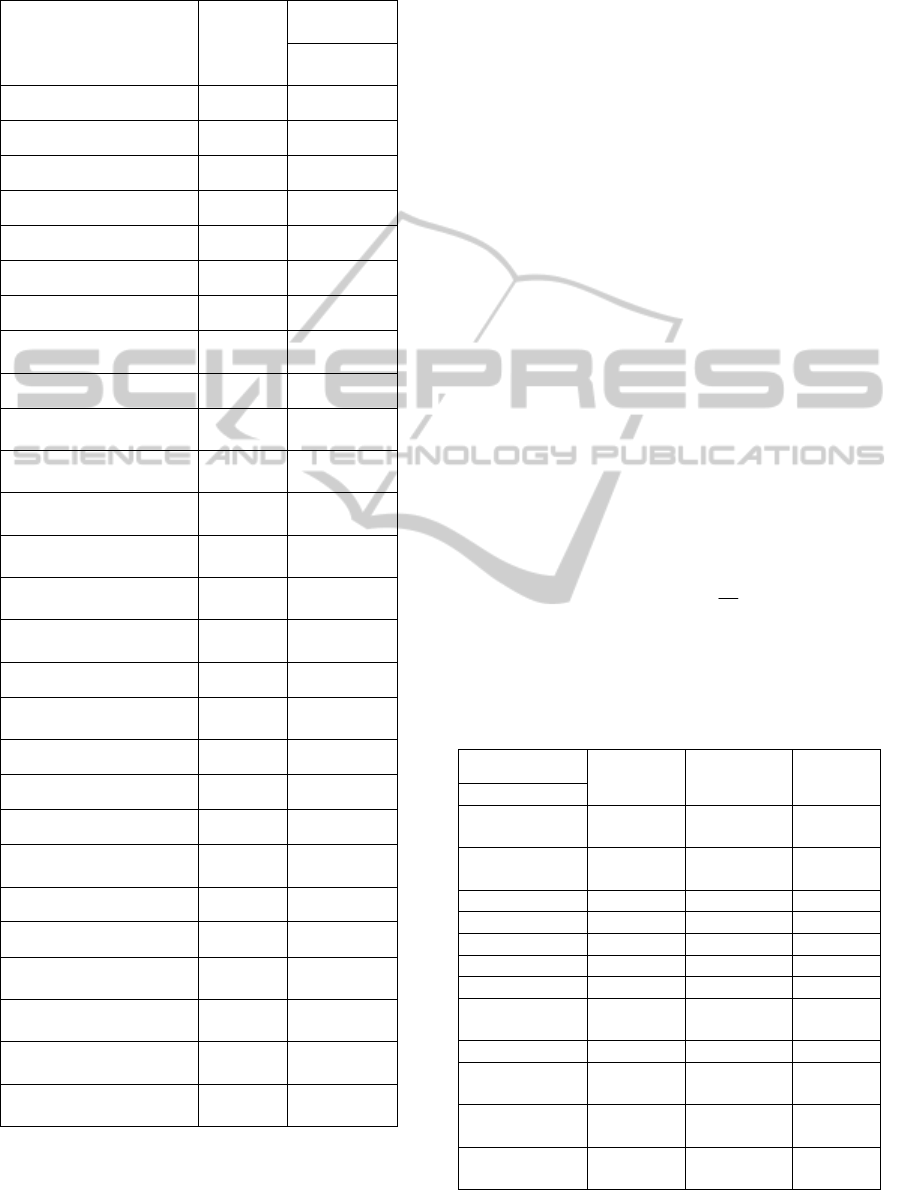
Table 1: The defined number and Throughputs of primary
and secondary service points in East China.
Name of Service point Number
Throughput
s(h
i
)
kiloton
Shanghai (primary) 1 24
Hangzhou (primary) 2 120
Wuxi (primary) 3 23
Minhang 4 7
Qingpu 5 28
Pudong 6 14
Zhuanqiao 7 8
Huzhou
Wuxing
8 5
Nanhu 9 22
Ningbo
Gaoqiao
10 33
Yuyao
Lanjiang
11 15
Wenzhou
Ouhai
12 44
Suzhou
Wuzhong
13 22
Nantong
Yongxing
14 8
Wuxi
Shuofang
15 13
Jindong 16 23
Yiwu
Heye Tang
17 14
Huangyan 18 11
Keqiao 19 4
Zhuji 20 1
Shaoxing
Donghu
21 25
Xiaoshan 22 64
Xiacheng 23 10
Changzhou
Hengshan Bridge
24 22
Nanjing
Guanghua
25 13
Zhenjiang
Danyang
26 9
Huaian
Wangying
27 11
4.2 Solving of Case
① Numbering
In the given network G (V, A), | V | = n = 27.
Shanghai, Hangzhou, Wuxi are three original
primary service points among them, so their current
handling capacity ranks first in major cities in East
China. After considering the fixed costs of set up a
new primary service point, carrying capacity of
cities and distribution of airports, we assume
Shanghai, Hangzhou and Wuxi are candidate
primary service points.
j
X
is set as follows:
1
X
: Primary service point in Shanghai;
2
X
: Primary service point in Hangzhou;
3
X
: Primary service point in Wuxi;
Actually, A Company has realized two location
problems: ① the layout of three primary service
points mentioned above is not suitable; ②the scope
of their distribution is not unreasonable because the
relatively distance between them is short. Therefore,
we reduce number of primary service points. We
assume p = 2.
② Time-satisfaction Function
()
ij
f
t
If V is the average speed and
ij
S
is the distance
between two service points,
ij
ij
S
t
v
=
. The time can be
figured out by the linear distance between two
service points.
ij
S
is showed in Table 2:
Table 2: The distance between primary service point i and
secondary service point j.
Distance
ij
S
Shanghai
1
X
Hangzhou
2
X
Wuxi
3
X
km
Shanghai
(primary)
— 166.9 120.3
Hangzhou
(primary)
166.9 — 188.7
Wuxi (primary) 120.3 188.7 —
Minhang 15.6 151.1 113.7
Qingpu 34.2 136.4 90.1
Pudong 32.5 171.1 121.8
Zhuanqiao 17.8 149.0 117.0
Huzhou
Wuxing
134.6 78.7 120.2
Nanhu 85.8 81.6 105.9
Ningbo
Gaoqiao
286.6 126.7 312.7
Yuyao
Lanjiang
250.5 93.8 270.6
Wenzhou
Ouhai
444.6 306.7 466.7
RESEARCH ON LOGISTICS LOCATION OPTIMIZATION MODEL BASED ON TIME DIMENSIONS
659

Table 2: The distance between primary service point i an
d
secondary service point j (cont.).
Distance
ij
S
Shanghai
1
X
Hangzhou
2
X
Wuxi
3
X
km
Suzhou
Wuzhong
79.3 144.8 45.7
Nantong
Yongxing
115.8 237.6 127.7
Wuxi
Shuofang
112.1 170.2 13.4
Jindong 298.8 133.5 326.2
Yiwu
Heye Tang
256.3 93.5 261.3
Huangyan 233.4 70.5 248.5
Keqiao 184.6 38.5 211.3
Zhuji 217.4 55.3 241.5
Shaoxing
Donghu
201.2 47.6 225.8
Xiaoshan 165.8 17.5 187.7
Xiacheng 167.4 25.0 183.2
Changzhou
HengshanBridge
142.0 188.2 28.1
Nanjing
Guanghua
271.6 248.4 158.5
Zhenjiang
Danyang
197.7 228.5 82.7
Huaian
Wangying
356.4 423.4 271.6
Data is measured by Google Maps
③ The Cost
The value of cost parameters
j
c
and
ij
c
is given by
the actual data analysis.
j
c
=34.3 and
ij
c
=35.4.
We assume customers can accept service
provided by primary service points and secondary
service points in East China. So the time-satisfaction
is not zero. According to customer-focused strategic
analysis of private express delivery companies, we
give same weight to time and cost.
0.014
λ
=
.
4.3 Illustrative Results and Analysis
We solve this model based on the branch and bound
algorithms and lingo software. The lingo result
showed as follows:
①
36.234Max z =
② The site selection resulting of primary service
point is A transit output is
2
X
,
3
X
. The final
selection is Hangzhou and Wuxi. Shanghai is
changed into secondary service point. The specific
service scope is showed in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The optimized layout of regional network.
This result shows an optimized layout of
regional networks. It reselects two primary service
points: Hangzhou and Wuxi, and reorganizes the
regional scope. The new program can not only meet
growing business needs, but also improve the
relatively dense layout. It achieves a high level of
customer satisfaction because customers can obtain
service in shorter time. Company A can gain
competitive advantages by improving time-
satisfaction, while cost of services is deceased.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper discusses location model of logistics
distribution and service centre based on time
dimensions. The main value added of this study is
the development of the new location model, in
which, both time satisfaction and time cost are taken
into account. We formulated the model as an integer
programming under the goal of maximizing the total
satisfaction and minimizing the total cost. According
to analysing the optimized layout of regional
networks which is solved by this model, we confirm
the model has usage value for the location problem
of logistics facility. Nevertheless, a more research is
needed to develop the model. The following step of
this research could be to replace a part or all of
relevant expressions about transportation cost with
time cost accurately in objective function or
constraints. At the same time, more factors need to
be considered in this model so as to reflect actual
situation.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
660

REFERENCES
Qu Bo, Yang Chao, Ma Yun-feng, Weng Ke-rui, 2008.
Time-satisfaction-based covering location problem
and the application of Hybrid Genetic Algorithm.
Industrial Engineering and Management.
Brandeau ML, Chui SS, 1989. An overview of
representative problems in location research.
Management Science, 35(6), 645-674.
Susan Hesse Owen, Mark S. Daskin, 1998. Strategic
facility location: A review. European Journal of
Operation Research, 111, 423-447.
Mark S. Daskin, 1995. Network and discrete location:
models, algorithms and applications. New York,
Wiley Interscience.
Ma Yun-feng, Yang Chao, Zhang Min, Hao Chun-yan,
2006. Time-satisfaction-based maximal covering
location problem. Chinese Journal of Management
Science, 2 (14).
Zhou Gen-gui, Hen Yan-fei, 2008. Research on logistics
siting problem in logistic distribution center based on
time satisfaction. Journal of Zhejiang University of
Technology, 4 (36).
Liu Yong, Ma Yun-feng, Yang Chao, 2008. Study on the
telecom business outlet location optimization model
Based on the Time-Satisfaction. Industrial
Engineering and Management.
RESEARCH ON LOGISTICS LOCATION OPTIMIZATION MODEL BASED ON TIME DIMENSIONS
661
