
Implementing a Transformation from BPMN to CSP+T
with ATL: Lessons Learnt
Aleksander González
1
, Luis E. Mendoza
1
, Manuel I. Capel
2
and María A. Pérez
1
1
Processes and Systems Department, Simón Bolivar University
PO Box 89000, Caracas, 1080-A, Venezuela
2
Software Engineering Department, University of Granada
Aynadamar Campus, 18071, Granada, Spain
Abstract. Among the challenges to face in order to promote the use of tech-
niques of formal verification in organizational environments, there is the possi-
bility of offering the integration of features provided by a Model Transforma-
tion Language (MTL) as part of a tool very used by business analysts, and from
which formal specifications of a model can be generated. This article presents
the use of MTL ATLAS Transformation Language (ATL) as a transformation
artefact within the domains of Business Process Modelling Notation (BPMN)
and Communicating Sequential Processes + Time (CSP+T). It discusses the
main difficulties encountered and the lessons learnt when building
BT
RANSFORMER; a tool developed for the Eclipse platform, which allows us to
generate a formal specification in the CSP+T notation from a business process
model designed with BPMN. This learning is valid for those who are interested
in formalizing a Business Process Modelling Language (BPML) by means of a
process calculus or another formal notation.
1 Introduction
Business Processes (BP) must be properly and formally specified in order to be able
to verify properties, such as scope, structure, performance, capacity, structural consis-
tency and concurrency, i.e., those properties of BP which can provide support to the
critical success factors of any organization. Formal specification languages and proc-
ess algebras, which allow for the exhaustive verification of BP behaviour [17], are
used to carry out the formalization of models obtained from Business Process Model-
ling (BPM). Not only require these notations an understanding of the business rules,
but of the formal notation’s descriptive capacity, within this specific interpretation
domain, by the business modeller. Moreover, there exists reluctance from industry to
adopt formal methods. An alternative way to directly using process algebras is to
automate the formal representation of BP models, and thus we propose a set of trans-
formation rules that generate a formal Process Calculus (PC)-based notation specifi-
cation from a BP model.
Two types of tools for formal verification of business artefacts are generally of-
fered to business analysts at moment, those within the first one provide answers to the
González A., Mendoza L., Capel M. and Pérez M..
Implementing a Transformation from BPMN to CSP+T with ATL: Lessons Learnt.
DOI: 10.5220/0003581100510060
In Proceedings of the International Joint Workshop on Information Value Management, Future Trends of Model-Driven Development, Recent Trends in
SOA Based Information Systems and Modelling and Simulation, Verification and Validation (MSVVEIS-2011), pages 51-60
ISBN: 978-989-8425-60-7
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

user directly [8], they are generally aimed at a small universe of users, and the formal
representation of the verification mechanism is implicit in the response; whereas tools
in the second one offer a response to the user through making use of a programming
language, thereby the transformation rule is specified by programming in this lan-
guage. In both cases the development and support of all functions (modelling and
verification) falls in the responsibility of the developer entity that offers the tool.
Aiming at the automatic verification of BPM, the Laboratory for Research in In-
formation Systems (LISI) at Simón Bolívar University and the research group in
Concurrent Systems (SC) at the University of Granada created the BT
RANSFORMER
tool. The Model Transformation Language (MTL) ATLAS Transformation Language
(ATL) has been selected to implement this tool. BT
RANSFORMER allows us to gener-
ate a formal specification of a BP model described with Business Process Modelling
Notation (BPMN) [10] notation. Communicating Sequential Processes + Time
(CSP+T) [18], based in Communicating Sequential Processes (CSP) [14], is used here
to describe the formal model generated.
The BT
RANSFORMER tool seeks to promote the use of MTL in verification envi-
ronments, and thus modelling tools and model-checkers can be separately supported.
MTL allows us to make use of the benefits of both kinds of tools, without specifically
supporting any of the two. As a result of this strategy, the development support effort
and further maintenance of the models becomes significantly reduced. This tool was
developed as part of a research that seeks to accomplish the following goals,
1. (a) to determine which MTL and tool are more appropriate for being used in a
given context, and (b) to provide access to the benefits of a MTL to business analysts.
2. How can we express the syntactic relationship, in a specific MTL, between two
domains to be made correspondent.
3. How to determine inconsistencies in a non-formal model by making use of a for-
mal notation.
This article describes the challenges and solutions for succeeding with the develop-
ment of BT
RANSFORMER tool. Section 2 describes the challenges faced. Section 3
presents a brief description of ATL. In section 4, it is discussed how to improve the
expressiveness of the rules. Section 6 discusses the integration of components under
the Eclipse platform and section 7 presents the creation of the deployment environ-
ment. Finally, some conclusions and recommendations for future work are presented.
2 BTransformer: Background and Challenges
There are currently tools that allow the generation of distinct specifications, written in
different versions of CSP, of a BPMN model. OWorkflow [11] is a tool that allows
transforming a BPMN (ILOG JViews BPMN Modeler) model into a Timed CSP
specification [17] and then to verify it with FDR [4]. This tool is implemented in
Haskell. In addition, we can also mention a plugin that uses the editor of Intalio [3] to
verify a BPMN model with the PAT model checker [15].
However, all these tools are specific to FDR and other specific software verifica-
tion tools, and in none of them an MTL has been used for the definition of the trans-
52
formation rules. Now, BTRANSFORMER, which is based on using an MTL, can be
considered a tool that promotes the maintainability and portability of transformation
rules between models and development platforms, respectively. Within the proposed
transformation method, we use an intermediate CSP+T model that will allow us to
work with different verification tools, following an incremental mode, in the future.
Additionally, our proposal allows time management during the transformation phase
without using external elements to standard BPMN 2.0 and with a complexity less
than of the Timed CSP formalism.
At moment, it is possible to generate a formal specification to determine (with the
help of a Model-Checker —MC) whether two collaborative processes are consistent
or not according to [5]. In the future, it is expected to additionally generate the input
specification of a MC and, based on the model checker response, to suggest changes
in the model.
From the implementation side, BT
RANSFORMER has been designed as a plugin for
the Eclipse platform, and it is capable of transforming BPMN models designed with
Intalio and to generate a text file with its specification written in CSP+T.
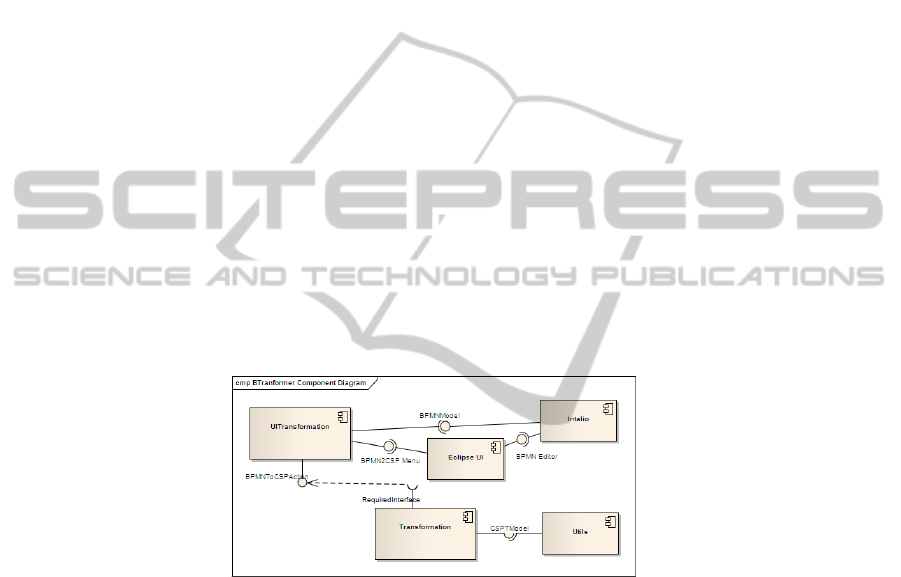
BT
RANSFORMER consists of three components (see Fig. 1):
UITransformation, which makes use of the facilities for platform’s inter-
faces extension, and the Intalio editor for creating BPMN models.
Utils, consisting of a set of classes to handle the persistence and format evalua-
tion, so that the user can additionally specify them in more detail.
Transformation, which makes use of ATL language interpretation services to
define the correspondence between BPMN and CSP domains.
Fig. 1. UML Component Diagram of BTRANSFORMER tool.
To successfully implement the developed components, it has been necessary to
face the following three challenges:
1. To ensure that the transformation rules are expressive. In this way, it is promoted
that the rules are expressed correctly and it improves their readability for the purpose
of maintainability.
2. To evaluate different components and integrate them. Thus, the reuse of compo-
nents and the interoperability assurance between components and with the new ones
to be developed are promoted.
3. To create the deployment environment that allows the user to apply the transforma-
tion. It has been crucial to have found a familiar environment to the BP analysts in
order to ensure the usability of our tool.
53

3 ATLAS Transformation Language
ATLAS Transformation Language (ATL) is a proposal of ATLAS Group at INRIA &
LINA at the University of Nantes and it was developed as part of the AMMA
(ATLAS Model Management Architecture) platform [1, 2]. ATL shares common
characteristics and the same set of requirements that have been defined in QVT RFP
[2]. Compatible with the OMG standards, ATL makes it possible to describe model to
model transformations and defines pre and post conditions in Object Constraint Lan-
guage (OCL) [6]. ATL allows applying the transformation pattern of Fig. 2. In this
pattern a source model Ma is transformed into a target model Mb, and the transforma-
tion is defined by a definition or program (mma2mmb.atl). Source and objective
models conform to the metamodels Mma and Mmb. In their turn, the metamodels con-
form to the Meta Object Facility (MOF) Metamodel [1, 2].
Fig. 2. Overview of ATL transformational approach [2].
BTRANSFORMER allows the implementation in ATL of the rules for transforming a
BPMN model into a specification written in CSP+T. It has been possible to define
these rules thanks to the ATL development environment within Eclipse.
There are different metamodels of BPMN [7], which also capture a range process
concepts, shared with other languages of business process modelling. We selected the
BPMN
1
metamodel proposed by OMG because, besides being implemented by sever-
al tools, it focuses on the syntax of the language and not on the concepts represented
by the language (semantics). Additionally, the chosen metamodel allows us to select
the right subset of the metamodel elements, with which we have worked, and not the
entire metamodel that also includes concepts related to the Eclipse platform. Accord-
ing to the BPMN metamodel used by the Eclipse consortium shown in Fig. 3, it is
possible to link elements Activity with SequenceEdges. Task, Event and
Gateways elements are of the class Activity. A class Activity may be asso-
ciated with one or more Subprocess classes, and with one Lane (or none at all). A
Pool can be composed of one or more lanes.
Each of these classes is represented by a corresponding Meta Object Facility
(MOF) element that is used by the ATL language. The MOF element of an Activity is
bpmn!Activity, that of the SequenceEdges, is bpmn!SequenceEdges,
and so on for each one of the elements.
1
Although this metamodel was initially proposed for version 1.2 of BPMN, it still remains valid for the
transformation of BPMN in version 2.0 [12], since the latter is an extension of the former one.
54

Fig. 3. BPMN metamodel. Adapted from Eclipse.org.
As for CSP, there is already a metamodel accepted for this process algebra [13,
16]. Figure 4 shows the metamodel adapted for this proposal to consider messages, as
well as temporal operators of CSP+T, as additional operators of CSP.
Fig. 4. CSP+T metamodel. Adapted from [13, 16].
ATL maps each class element to a corresponding expression type. Thus the
Process element in the metamodel becomes a csp data!Process data type, the
element ProcessExpression is a csp!ProcessExpression and so on. Using
these types of elements it is now possible to map the BPMN metamodel elements to a
ProcessExpression of CSP. In order to be able to generate a specification in
CSP+T from a BPMN model the following set of rules has been defined:
The transformation of any BPMN activity is a CSP+T process.
The Transformation of a sequence flow between BPMN activities becomes a
sequence of terms in CSP+T.
Transformation of Gateway becomes a concurrence operator in CSP+T.
Messages are transformed into CSP+T messages.
Transformations of (temporal) annotations are transformed into CSP+T associated
intervals.
A verification process is made of two stages: the first one is to validate that the model
is correctly and completely defined. In the second one the definition is translated to
CSP+T, from which the specification for an MC can be obtained. This work focuses
on the translation between BPMN and CSP+T, and it is assumed that the business
process model is correct and complete before transforming it. This transformation
assumes the semantics of BPMN proposed by Wong and Gibbons [4].
55

4 Expressiveness of the Proposed Rules
When the declarative style of ATL is used, a correspondence rule consists of a rela-
tionship between two metamodels, rather than a set of instructions, and cannot be
considered a set of programming sentences (for, while, among others). A rule of
transformation under the paradigm of a Model Transformation Language (MTL),
such as ATL one, is an association between two metamodels. In the rule presented, a
bpmn element!Sequence, between two bpmn!Activity, is related to a
csp!BinaryOperator, which expresses the sequencing between two processes
(each process is the representation of an activity).
Activity sequencing is expressed in the CSP+T metamodel as a Binary Condition
instance that uses the infix operator “;” to connect both parts. This specification is
written in a resource or file rule.atl. Fig. 5 includes the specification of the CSP+T
expression proposed by the metamodel, so that the reader can identify a variable for
each MOF element of the metamodel. With these variables the desired element is
specified, which conforms to a CSP+T model.
Fig. 5. Condition operator specified within the CSP+T metamodel.
In ATL this rule is expressed in the following way:
rule Secuency2Relations {
from BPMN3 : bpmn!SequenceEdge
to i1 : csp!ProcessIdentifier(name <- BPMN3.source.processName),
i2 : csp!ProcessIdentifier(name <- BPMN3.target.processName),
i : csp!ProcessIdentifier(name <- ';'),
p1 : csp!Process( processIdentifier <- i1),
p2 : csp!Process(processIdentifier <- i2),
p : csp!Condition(expression <- ';',leftHandSide <- p1,
rightHandSide <- p2),
pAssig : csp!ProcessAssignment(processIdentifier <- i, process
<- p),
cspContainer : csp!CspContainer(name <- 'Container',
processAssignments <- pAssig, expression <-
BPMN3.source.name + ';' + BPMN3.target.name) }
We can then see the declaration of the csp!Condition expression, in which
leftHandSide and rightHandSide are assigned to processes p1 and p2, re-
spectively. Each one of these processes has its respective processIdentifier.
And finally, pAssig and cspContainer are declared to assign process p to the
container. It should be noted that ATL is a hybrid language, which eased to perform
some testing, following an imperative style, before obtaining a dominance of the
declarative style of this language. It is not always possible to use a declarative style
for transformation rules.
56

5 Evaluation and Integration of Different Components
Although the Eclipse platform allows working under the component-based software
development model, a considerable effort is required to integrate and choose the right
different components or plugins. This is because vendors provide varying degrees of
support and conditions for their plugins, and because they must be well adapted to the
target platform, and thus these conditions are not always satisfactory. Table 1 presents
a brief comparison of the evaluated components.
Table 1. Components evaluated.
Plugin Eclipse version Advantages Disadvantages
TGG Interpreter 3.4 Visual language
Lack of documentation for carrying
out the deployment
SMART QVT 3.5.1 Declarative language Minimum Integration support
ATL 3.6.1
Plugin integrated with a recent
version of Eclipse
Significant effort needed for construc-
tion of the integration environment
Intalio
2
3.6.1
Plugin integrated with a recent
version of Eclipse
The only plugin found for editing
BPMN models.
In Table 1, a comparative of components addressing some representative MTL
(TGG, QVT and hybrids [2]), under the Eclipse platform, can be seen. The plugins of
ATL and Intalio developed for the latest version of the platform were selected, which
in their turn facilitated the installation of both components. The documentation for the
deployment of ATL is available, whilst for the rest is quite limited. Although this is
not the case described here, should another transformation be selected, and no plugin
to handle some of source or target models involved can be found, the MTL plugin
must be migrated to another version of the platform in which it exists, or it has to be
developed anew in any other case.
6 Deployment Environment Construction
In order for the end-user to make use of the proposed software tool, a set of deploy-
able components must be built, in addition to integrate the different components,
which belong to the development environment, into a unique version of the platform.
To accomplish that it must not be necessary to use the entire development environ-
ment, but to only run a set of rules.
In the case of the BT
RANSFORMER tool, the rules stated so far allow us to generate
the model CSP+T associated with a BPMN model. As shown in Fig. 6, through an
additional transformation, named CSPT2Latex.atl, the set of instructions associ-
ated with each one of the elements of the model CSP+T is obtained. This set of ex-
pressions is used by the Utils component to generate a specification in LaTeX.
Finally, a service that runs the transformations using the Eclipse interface must be
built. This service is defined overriding one of the classes that correspond to a button
2
Although this plugin works with BPMN version 1.2; the specifications that it generates comply with
version 2.0 [12].
57

located in the component Eclipse UI. This button invokes a plugin that executes the
transformations within an Eclipse environment generated with ATL Wizard. In Fig-
ure 7, the result of a model and its specification can be seen.
BPMN
CSPT
LATEX
MMBPMN MMCSPT
MMInstructions
MOF
ATL
ATL
BPMN2CSP.atl
CSPT2Latex.atl
Source
Source
Target Target
Conforms to
Executes
Transform
Fig. 6. How the metamodels are involved in the transformation.
Fig. 7. Screenshot of BTRANSFORMER tool invocation and fragment of results.
7 Lessons Learnt
Among the lessons learnt, we can say that promoting the use of declarative expres-
sions when writing the rules must be considered mandatory. In this way, to under-
stand and maintain the code in the future becomes easier. Additionally, the developer
can then focus more on what the transformation means, and not on how it executes. In
this way a better understanding of the rules will be achieved, and it also facilitates the
transformation into another MTL, where necessary.
Secondly, the tools that implement an MTL must offer facilities for executing
transformations outside the programming environment. In this sense ATL presents
two advantages: (1) it is built on a well-known platform and easy to use for any Java
58

developer, and (2) there are various examples
3
that include this deployment. How-
ever, it has been necessary to adapt the proposed plugin for the ATL Wizard in order
to produce a sequence of transformations, as well as to link it to the Eclipse interface.
Finally, component-based platforms facilitate the development of the MTL devel-
opment environment; it is due to the fact that model editing and manipulation will
remain the responsibility of the third party, as well as all the difficulties in doing so
might arise.
8 Conclusions
A software tool named BTRANSFORMER that helps the verification of business process
models (BPM) has been proposed in this article. Initially described in the Eclipse
platform and its editor Intalio [3], BT
RANSFORMER automatically transforms BPM
into the formal specification language CSP+T [18] (an extension with discrete-time of
the CSP process algebra [14]). From a technological point of view, several challenges
have been confronted in this work. They mainly consisted of extending, adapting and
making work together several software components: BPMN editor, MTL, plugins
previously available and which are supported by the common platform Eclipse.
ATLAS language services [1] have been adjusted to work with the selected plu-
gins to carry out the transformation from BPMN models into CSP+T process terms.
In this respect, the declarative style of the ATLAS language allowed us to carry out
the definition of the correspondence rules between models in a way that is unders-
tandable, easy to modify and transport; and therefore useful if we want to experiment
with another MTL in the future. A friendly configuration of the environment, useful
to its foreseeable users (business analyst, stakeholder, etc.), has been developed,
which saves the CSP+T output models according to various formats.
The creation of BPMN models using Intalio has allowed us to easily check, before
transformation, their consistency by using the correspondence rules declared in
ATLAS. The generation of the output according to various formats has been facili-
tated by the flexibility that presents the Eclipse platform to integrate different compo-
nents and software tools.
BT
RANSFORMER is currently working as a pre-processing tool of a “state of the
art” model-checker that accepts the CSP [14] process algebra as the system’s model
formal specification language. An example of these model-checkers is FDR2 [4]. In
the future, we plan B
TRANSFORMER can collaboratively work with other model-
checkers, within an environment of business process modelling that allows a partial
and incremental modification of these models. As well as to facilitate the modular
verification using an infrastructure of compositional verification, called Formal Com-
positional Verification Approach (FCVA) [9], [10].
As future work we plan to evaluate the migration of the tool into some of the plu-
gins launched by OMG for the 2011 version of BPMN
4
.
3
See http://www.eclipse.org/m2m/atl/atlTransformations/ for more detail.
4
http://planet.jboss.org/post/new_bpmn_2_0_eclipse_editor.
http://docs.codehaus.org/display/ACT/Activiti+BPMN+2.0+Eclipse+Plugin.
59

References
1. Allilaire, F., Bėzivin, J., Jouault, F., Kurtev, I.: ATL – Eclipse Support for Model Trans-
formation. In: Proceedings of the Eclipse Technology eXchange workshop (eTX) at the
ECOOP 2006 Conference, Nantes, France (2007).
2. Correa, N. Giandini. R.: Lenguajes de Transformación de Modelos. Un análisis comparati-
vo. XIII Congreso Argentino de Ciencias de la computación. Universidad Nac. del Nordes-
te Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales y Agrimensura (2007).
3. Flavio, C., Alberto, P., Barbara, R. and Damiano, F.: An ECLIPSE Plugin for Formal
Verification of BPMN Processes. In Proceedings of the 2010 Third International Confe-
rence on Communication Theory, Reliability, and Quality of Service (CTRQ '10). IEEE
Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA (2010) 144-149.
4. Failures Divergences Refinement. www.fsel.com/.
5. Wong, P., Gibbons, J.: A Relative Timed Semantics for BPMN. Electronic Notes in Theo-
retical Computer Science (ENTCS), v.229 n.2, (2009) 59-75.
6. Joault, F., Allilaire, F., Bézivin, J., Kurtev, I. Atl: A model transformation tool. Science of
Computer Programming 72(1–2) Elsevier New York (2008) 31–39.
7. List, B. and Korherr, B. An evaluation of conceptual business process modelling languages.
In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM symposium on Applied computting. ACM, New York,
NY, USA, (2006) 1532-1539. http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1141277.1141633.
8. Leuxner, C., Sitou, W., and Spanfelner, B.: A Formal Model for Work Flows (doi:
http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/SEFM.2010.27.
9. Mendoza, L. E., Capel, M. I., Pérez, M. A.: Compositional Verification of Business
Processes by Model–Checking. In: Capel-Tuñón, M., Garbajosa, J. (eds.): Modelling, Si-
mulation, Verification and Validation of Enterprise Information Systems. Proc. 8th Interna-
tional Workshop on Modelling, Simulation, Verification and Validation of Enterprise In-
formation Systems - MSVVEIS 2010. SciTePress, Funchal (2010) 60–69.
10. Mendoza, L. E., Capel, M. I., Pérez, M. A.: A Formalization Proposal of Timed BPMN for
Compositional Verification of Business Processes. In: Filipe, J., Cordeiro, J. (eds.): Enter-
prise Information Systems. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, Vol. 73.
Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg (2011) 388–403.
11. OworkFlow. http://www.comlab.ox.ac.uk/peter.wong/bpmn/index.html.
12. OMG: Business Process Modeling Notation – version 2. Object Management Group, Mas-
sachusetts, USA (2011).
13. Varró, D. Asztalos, M. Bisztray, D. Boronat, A. Dang, D. Geiss, R. Greenyer, J. Pieter Van
Gorp, Ole Kniemeyer, O. Narayanan, A. Rencis, E. y Weinell, E. Transformation of UML
Models to CSP: A Case Study for Graph Transformation Tools. In Schürr, A. Nagl, M. and
Zündorf, A. editors, Proc. 3rd Int. Workshop Applications of Graph Transformation with
Industrial Relevance. Springer, Berlin, LNCS (2008).
14. Roscoe, A. (2005). The theory and practice of concurrency. London: Prentice Hall.
15. Sun, J. Liu, Y., Song J., D. & Pang, J. PAT: Towards Flexible Verification under Fairness.
The 21th Intern. Conf. on Computer Aided Verification, France (2009).
16. Treharne, H. Turner, E., «Paige, R. F. & Kolovos, D. S. Automatic generation of integrated
formal models corresponding to UML system models. In TOOLS Europe '09, Lecture
Notes in Business Information Processing, Vol. 33. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Germany (2009) 357–367.
17. Yeh, W., Young, M. Compositional reachability analysis using process algebra, in: TAV4:
Proc. of the Symp. on Testing, Analysis, and Verification (1991) 49–59.
18. Žic, J. Time-constrained buffer specifications in csp + t and timed csp, ACM Trans. Pro-
gram. Lang. Syst. 16(69), New York (1994) 1661–1674.
60
