
A STUDY ON THE ELECTRONIC SUPERVISION MODEL
OF DRUG DISTRIBUTION
Zi-Kui Lin, Zi-Sheng Dong
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China
Ying Lu
State Food and Drug Administration Information Center, Beijing, China
Key words: Drug logistics, Drug distribution, Electronic supervision, Supervision model.
Abstract: Drugs, as a special commodity, is directly related to people's lives and health, so it is essential to effectively
supervise the drug distribution process Current electronic supervision of drugs effectively regulates the
market order, but it also faces with many problems, such as high cost in the comprehensive promotion and
low efficiency of logistics operations. Therefore, this paper summarizes the principle of current electronic
supervision and analyzes the existing problems. Based on these and combined with the characteristics of
flow conservation in pharmaceutical logistics system, this paper presents a new model of electronic
supervision and compares it with the current model, in order to solve the problems in China's current
pharmaceutical distribution supervision.
1 INTRODUCTION
Drug is a special kind of goods that's related to the
health and the safety of people. In order to safeguard
people's health, maintain the society stability and
promote the healthy development of China's
pharmaceutical industry, it's very important to
strengthen the management of drugs, and ensure that
people can get safe and effective drug timely. As a
channel between the producers and patients, The
distribution of drug involves logistics, capital flow,
business flow, information flow and other
complicated process, and the supervision of it is not
only an important part of the supervision work, but
also the key to ensure the quality of drug,
standardize drug distribution channels, stop the fake
drugs’ manufacturing and selling, and promote the
reformation of drug circulation system.
In order to achieve the goal of supervising and
administrating drug distribution, State food and drug
administration has established a regulatory
mechanism for complaint, random inspection and
supervision, but these regulatory mechanisms
happen after the distribution, when most of the
counterfeit drugs have entered the market and
threatened people’s safety and health. In addition,
with the changes in the function of drug
administration and supervision, the supervising and
administrating task in the field of food and drug has
gradually increased, so the limited supervisors
cannot undertake the current heavy task, and it's no
longer suit the current work for the supervision of
drug distribution that relying on "crowd strategy"
and “large area of investigation”.
So our country urgently needs a high-efficiency
means for drug distribution that can run
automatically all the time to standardize drug
distribution channels, stop the fake drugs’
manufacturing and selling, and ensure that people
can get safe drug timely. Electronic supervision is an
innovative means that State food and drug
administration is implementing.
From the initial narcotic drugs and the first kind
of psychotropic substances in 2007 and the "four
major categories of key drugs" in 2008 to the 307
kinds of drugs in National Essential Drugs List in
2011, the implementation of the scope of electronic
supervision is gradually expanding. According to the
statistics, narcotic drugs and first kind of
378
Lin Z., Dong Z. and Lu Y..
A STUDY ON THE ELECTRONIC SUPERVISION MODEL OF DRUG DISTRIBUTION.
DOI: 10.5220/0003585903780383
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (SSSCM-2011), pages 378-383
ISBN: 978-989-8425-54-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
psychotropic substances involve of 18 drug
manufacturers, and 560 drug wholesalers; the second
kind of psychotropic drugs, blood products,
vaccines, and Chinese medicine injection, which we
call "four major categories of key drugs", involve of
568 drugs manufacturers and 13000 drug
wholesalers; the 307 essential drugs involve of 3567
drug manufacturers, accounting for 76% of all
manufacturing enterprises. Thus, the drug electronic
supervision is pushing on steadily and safely.
2 PRINCIPLE OF CURRENT
DRUG ELECTRONIC
SUPERVISION
Current drug electronic supervision mainly rely on
China's drug electronic supervision network, which
is an information net the State food and drug
administration adopts to supervise the drugs
manufacturing and circulation enterprises. Moreover,
it is also a net system based on the Public
information service platform which covers all over
the country, and the methods and tools by which the
State food and drug administration implement for
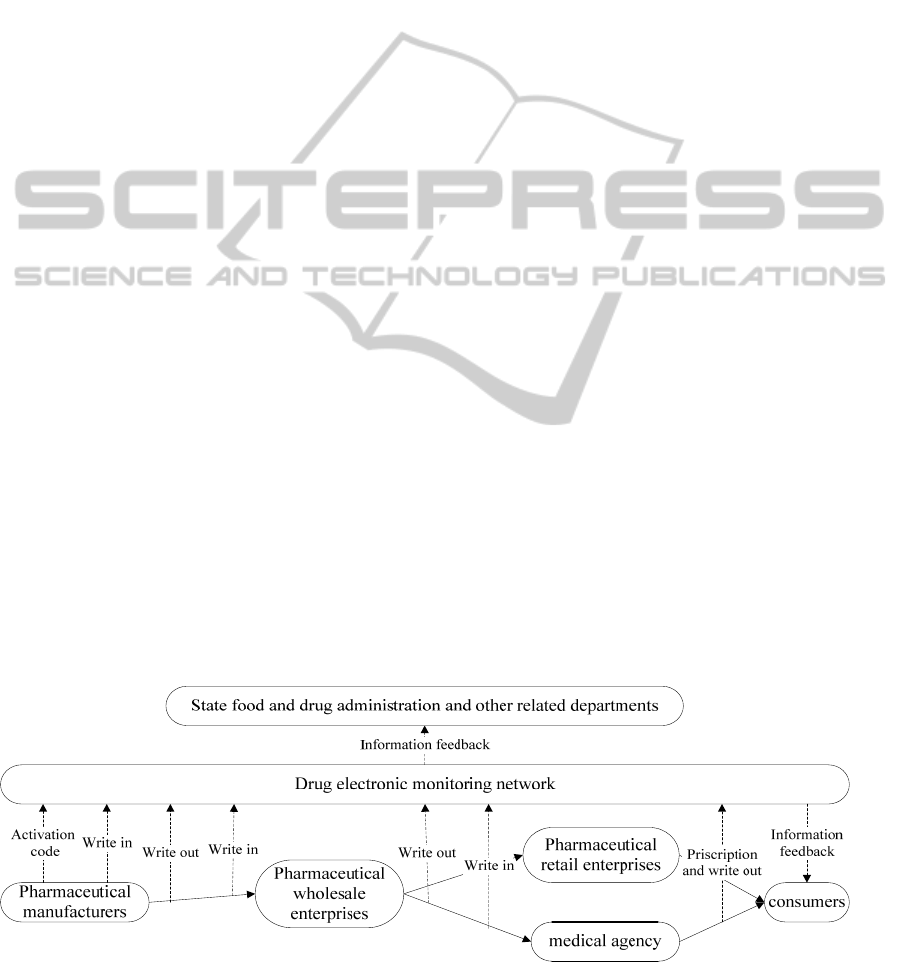
electric supervision. Their working principle can be
concluded as “One code throughout, all process
supervised”.
2.1 One Code Throughout
By the rules of State food and drug administration,
the drugs which are listed on the China’s drug
electronic supervision network to implement electric
supervision have to be pasted one universal drug
electric supervision code, which is called “E-ID”.
Otherwise any kinds of drug are not allowed to be
put on the shelves of pharmacy agent. The electric
supervision code will accompany with the drug
during the whole flow process.
2.2 All Process Supervised
The registered drug manufacturers should apply for
drug electric supervision code from China's drug
electronic supervision network before they produce
drugs. Then the code should be adhered to drug’s
minimum sale unit. Before the drug’s entrance to the
warehouse of manufacturers, these codes will keep
the state of being “not activated”, the corresponding
drugs cannot be searched on the drug electronic
supervision network, and the drug can't circulate.
Initially, the enterprises will scan and upload the
information of the code before the single drug with
electric supervision code entering the warehouse of
drug manufactures. Soon the corresponding drug can
be searched on China’s drug electronic supervision
network, thus these kinds of drugs come into effect,
and then the flow was legal. It is just by the working
theory of “write in” and “write out” that those drugs’
process supervision comes into reality. As is showed
in figure 1. (Note: Nowadays, China’s drug
electronic supervision network has not covered all
the nation’s drug agents and consumers.)
Taking pharmaceutical wholesale enterprise as
an example, pharmaceutical wholesale enterprise
must scan each electronic supervision code and
upload the information to China's drug electronic
supervision network as soon as it receives the drugs
from manufacturers. The system will check the
information one by one automatically with the" write
off" information from manufacturers, until
confirming all medicines arrived are correct. Then
pharmaceutical wholesale enterprise records the
Figure 1: Principle of current drug electronic supervision.
A STUDY ON THE ELECTRONIC SUPERVISION MODEL OF DRUG DISTRIBUTION
379

information in their own "account book", and we call
this process "write in"; When delivery, the
pharmaceutical wholesale enterprises must scan each
electronic supervision code, and upload the
information The system will check the information
one by one automatically with the" account book",
until confirming all medicines outbound are correct.
Pharmaceutical wholesale enterprise eliminates the
drugs from its "account book", and we call this
process "write off." If a single product goes wrong,
the system will alarm, and "write in" or "write off"
will not proceed. Through the "write in" and "write
off" process of the entire circulation, the background
database system of China's drug electronic
supervision network records every single product’s
major pharmaceutical logistics "path" from the
manufacturer to the final sale, so that consumers can
inquire the basic information of the drugs he bought,
while the food and drug administration departments’
real-time supervision of the whole process of drug
distribution can be achieved.
3 THE PROBLEMS EXISTING
IN CURRENT DRUG
ELECTRONIC SUPERVISION
MODE
The current model of drug electronic supervision
resolves many problems that exist in the traditional
supervision, makes the automatic and real-time
supervision to the circulation process possible,
ensures in stipulated time to complete the recall of
problem drugs, improves the extent of
comprehensive utilization supervision resources,
promotes the drug regulatory departments’ work
efficiency at all levels , effectively regulates the drug
distribution market order, and guarantees people's
safe drug use. The current drug electronic
supervision mode takes the minimum sale unit as
drug regulatory object, which is "an object, a code",
and it also records most of the logistics "path" of a
single product from drug manufacturers to the final
sale of drug companies. However, with the gradual
expansion of the supervision scope, current drug
electronic supervision will face more and more
challenges.
3.1 High Cost of Comprehensive
Promotion
In current electronic supervision mode, the cost
includes enterprises’ annuity of access key, labelling
system renovation cost of drug manufacturers’
production line, information collection equipments
cost of drug circulation, and maintenance cost of
electronic supervision network system.
Drug product and business enterprises need to
apply for access key to join the electronic
supervision network; and the key digital certificate’s
annual service fee is 300 Yuan per enterprise.
Taking 3850000 drug enterprises to calculate, the
current drugs electronic supervision annual
enterprise access key fee will reach 116 million
Yuan. To meet the requirements of electronic
supervision drugs, the manufacturers which have
accessed to the network must affix electronic
supervision code to each single product, which
requires transformation of the original production
line to increase the labelling system. If each drug
manufacturer production line labelling system
transformation needs a million Yuan, the full
implementation of current electronic supervision
mode will at least cost 47 million Yuan. The current
drug electronic supervision model for each single
product needs the circulation process "write in",
"write out" operation, which requires all links in
drug circulation use information collection devices
to collect and unload information. If each enterprise
purchasing information collection device needs to
spend 100 Yuan, the full implementation of current
electronic supervision mode will at least cost 380
million Yuan.
In addition, considering China’s electronic
supervision network system’s upgrade and
maintenance cost, at least millions Yuan per year
will need.
3.2 Heavy Load of Information System
The number of annual drug sales is about 150
million. If we adopt current electronic supervision
mode to supervise all drugs sold in China, the
electronic supervision network system will have to
handle at least ten billions of "write in" and "write
out" data. Coupled with data from previous years,
electronic supervision network data processing
system will face a huge challenge. With hundreds of
millions information stored in the background
system of China’s electronic supervision network, it
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
380

may lead to the system’s slowly run thereby to
reduce the supervision efficiency, meanwhile it also
increases the risk of system crash or paralyze. Once
the system is paralytic, drug product and business
enterprises will be unable to carry out normal
inbound and outbound work, business operations
will be affected, and drug supply will be suffered,
which even bring about serious social problems.
3.3 Low Efficiency of Enterprise
Logistics
Current drug electronic supervision model requires
drug product and business enterprises must collect
and unload each single drug’s information in order to
complete the process of "write in", and “write out".
For large scale drug product and business
enterprises, the information collection operation will
directly affect the efficiency of logistics, and
one-dimensional code in the form of drug electronic
supervision makes it difficult to achieve mass of
information collection, which severely limits the
enterprises’ operational efficiency.
Overall, current drug electronic supervision
mode has a high cost of comprehensive, and the
benefits are limited, so the foreground is not
optimistic. Therefore, China still needs to explore
others effective technological means to supervise the
drug distribution, rectify market order, curb the fake
drugs’ manufacturing and selling, and ensure that
people can get safe and effective drug timely.
4 NEW MODEL OF
ELECTRONIC SUPERVISION
FOR DRUG DISTRIBUTION
In China, each kind of drug on sale has a
corresponding drug approval number. A drug
approval number corresponds to a production of a
pharmaceutical manufacturer. Therefore, if you want
to supervise the distribution process of a certain kind
of drugs, in theory the supervision of effective drug
approval number can be enough.
Drug manufacturers, who obtain a drug approval
number, can be drug’s legitimate pharmaceutical
manufacturers. Meanwhile, in order to supervise the
drugs quality of pharmaceutical manufacturers, and
trace and review of the marketed drugs production
history, we use “batch number" to identify the drugs
in the same production cycle. Therefore, drugs with
the same approval number and the same batch
number can be considered by the same manufacturer
who use the same materials in the same production
process, and the nature and quality can be considered
to be basically the same only installed in the
different sub-drug sale unit. In this case, China's
drug supervision and management departments can
use the same batch number and the approval number
of drugs as a whole in supervising drug distribution.
According to the relevant provisions of China's
current electronic supervision, for the drug product
and business enterprises, once drugs’ purchasing or
selling occurs, the two parties must scan the
electronic supervision code of each single product
and upload the electronic supervision code, trading
notes and other related information to China's drug
electronic supervision network. Therefore, if we
implement electronic supervision for all kinds of
drugs, all systems’ inflow and outflow can be
supervised in real time in the pharmaceutical
logistics system, including manufacturers,
wholesalers, and retailers.
When there are no illegal drugs between the
distribution and no problem of logistics activities,
for the drugs with the same approval number and
batch number, the flow monitored in the
pharmaceutical logistics system should be
conserved, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Flow conservation in pharmaceutical logistics
systems.
In Figure 2, beginning from the drugs flow into
the pharmaceutical logistics system to a certain
moment, the cumulative amount of manufacturer
sending to the pharmaceutical logistics system
should equal the sum of the cumulative amount
returning from the logistics system to manufacturer,
the cumulative sales to consumers and inventory of
drug logistics system of the present moment.
It can
be
expressed by an equation:
Delivery amount=Return amount+Sales+Inventory
For each constituent in the supervision system,
the system’s cumulative input flow is equal to the
cumulative output flow and the current inventory of
system. An equation can be showed as follows:
A STUDY ON THE ELECTRONIC SUPERVISION MODEL OF DRUG DISTRIBUTION
381

Input flow=Out flow+Inventory
Here, we call the equation "addition sum
relationship", and the difference of the "total input
flow" minus the "total output flow" and "the current
system inventory", which we call "supervision
coefficient of pharmaceutical logistics system total
network flow", being expressed with
γ.
For the drugs with the same approval number
and batch number, the initial inventory of each
constituent in the supervision system is zero before
distribution. When China's drug electronic
supervision network receives the information
uploaded by the constituents in pharmaceutical
logistics system, the system will automatically
calculate the “supervision coefficient of
pharmaceutical logistics system total network flow”
and calculate each constituent’s current inventory
based on "addition sum relationship", and then the
result will be compared with zero. In this way, we
can monitor the drug logistics system timely and
automatically. The inventory of each constituent
should not be less than zero in pharmaceutical
logistics system.
(1) When
γequal to zero, there are two cases:
1) If each constituent’s current inventory of the
monitored system is nonnegative, it means there are
no illegal drugs mixed, that’s to say, the drugs are in
normal circulation.
2) If a constituent’s current inventory of the
monitored system is negative, it means this
constituent (wholesaler or retailer) have a more
cumulative outflows than inflows, that is to say this
constituent produced and sold illegal of drugs, or this
constituent did not report the inflow information, and
drugs distribute abnormal in this condition.
(2) When
γis less than zero, it means there are
illegal drugs mixed, drugs distribute abnormally.
This is because one constituent (wholesaler or
retailer) in the network of the pharmaceutical
logistics system purchased illegal drugs, then
uploaded the inflow information, the supervision
system calculates the constituent’s current inventory
through "addition sum" relationship and finds it
increase, so the current inventory of the
pharmaceutical logistics system will equal the
increase, resulting in cumulative inflows will be less
than the sum of cumulative outflows and current
inventory, making the “supervision coefficient of
pharmaceutical logistics system total network flow”
is less than zero.
(3) When
γis greater than zero, it means some
drugs have not flowed into the monitored system, or
there is a constituent sold drugs to other enterprises
out of this system, although both cases belong to
illegal operations, but no matter what kind of
situation, the drugs flowing are legal drugs, no
illegal drugs mixed.
It is necessary to indicate that this new model of
electronic supervision for drug distribution is only
applicable to the drugs with the same approval
number and batch number, if we want to apply this
mechanism to monitor all drugs, just using the above
mechanism respectively for all the drugs with the
same approval number and batch number.
5 THE COMPARISON OF TWO
DRUG ELECTRONIC
SUPERVISION MODES
The new mode of electronic supervision on drug
circulation put forward in this paper is based on
China’s current drug electronic supervision; it is an
innovation of electronic supervision. Compared with
China’s current drug electronic supervision mode,
both similarities and differences exist.
From table 1, we know that the new mode can
achieve the same results with China’s current
electronic supervision, but because of the new
mode’s regulatory precision expands to the varieties
grade (namely the drugs with the same approval
number and batch number) from the single grade, it
will reduce the regulatory costs greatly.
At the same time, using the new mode, China’s
drug electronic supervision network just needs to
record the flow information in each constituent
(manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers) of drugs with
the same approval number and batch number, which
greatly reduces drug electronic supervision’s
information processing load, and makes it possible
to achieve mass of information collection, thereby
enhancing the efficiency of enterprise logistics.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Using the new mode of drug electronic
supervision, the problems existing in current drug
circulation electronic supervision such as high cost
of comprehensive promotion, heavy load system
information, and low efficiency of business logistics,
all have been solved very well. In order to enhance
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
382
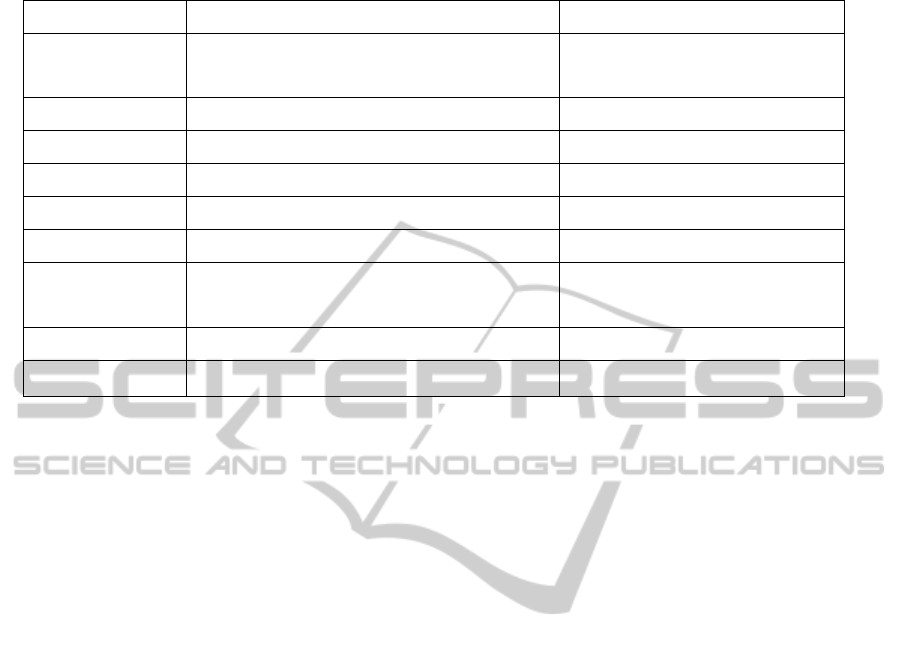
Table 1: The comparison of two drug electronic supervision modes.
Items Current drug electronic supervision mode New mode of drug electronic supervision
Regulatory scope The whole country
An administrative areas or the whole
country
Control mode General investigation, beforehand control General investigation, beforehand control
Regulatory precision Single drug The same batch number
Regulatory cost High Low
Regulatory efficiency High High
Drug identification Drug electronic supervision code approval number and batch number
Anomaly judgment
Whether the information of “write in” and “write out”
completely match
Whether the flow of drug logistics system
is conservative
Drug recall Support Support
Process supervision Realizable Realizable
the efficiency of State food and drug administration
at all levels, standardize the market order of drug
circulation, and guarantee people's safe drug use in a
better way, our country should carry out the new
mode of drug electronic supervision vigorously.
REFERENCES
State food and drug administration. The announcement of
reiterating the relevant regulations about new
pharmaceutical manufacturers and business enterprises.
[EB/OL].2000, 6. http://www.sda.gov.cn/WS01/CL00
55/9610. html.
Netease. 307 kind of basic drugs labeled "id", involving
76 % of Chinese enterprises [EB/OL]. 2010, 8. http://
news.163.com/10/0804/08/6D7SGRNM000146BC.ht
ml.
State food and drug administration. The announcement
about implementing electronic supervision of all
varieties of basic drugs. [EB/OL]. 2010, 6. http://www.
sda.gov.cn/ WS01/ CL0055/ 50136.html.
APPENDIX
This paper is supported by the fund “RFID
technology research of drug safety retroactive
management” (Number: 2008BAI55B07)
A STUDY ON THE ELECTRONIC SUPERVISION MODEL OF DRUG DISTRIBUTION
383
