
SECURITY INVESTMENT ANALYSIS ON GAMING THEORY
WITH MEASUREMENTS OF COST AND DECISION BEHAVIOR
Wang Wei and Ren Ying
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Security, Investment, Gaming theory, Cost, Supervision.
Abstract: The enterprises face with problems such as coordination with the security administration, market
competition, decision-making of production, security investment and so on. With the cost of raw material
has been going up in recent years, in order to reduce the cost and maximize the profit, the enterprises are
gaming in the security investment, which results in safety accidents. Based on the gaming model with the
measurements of cost and decision behavior, this paper presents a security investment analysis for decision
maker to enhance the security supervision and improve the production and security status.
1 INTRODUCTION
From the incomplete statistics, the average
preventive investment in developed countries
accounted for 3.3% of GDP. It is estimated that the
security engineering, security facilities, and
outstanding security loans amounted to hundreds of
billions, not including the other expenditures. On the
other hand, the overall loses annually in recent years
occurred in all types of security incidents is more
than trillion dollars of direct loses, plus inestimable
indirect losses. Through the analysis of security
consciousness, security input, security legal system
and on-the-spot government, more and more
countries pay attention to the importance of security
administration and inputs. The emphasis is placed on
as strengthening enterprise's security management,
employing principle of risk concentration to arrange
invested funds for security rationally, using
risk-transfer to lower accident rates, using financial
methods reasonably to reduce losses of accident
(Dixit and Pindyck, 1994; Goeree and Holt, 2005).
Why do not companies want to invest in
security? Firstly, Let us explain this phenomenon
from the principle of minimum security cost and
maximum profit (Kort et al., 1999):
(i) Minimum Security Cost Principle
Considering security investment consists of accident
loses and security cost:
B(S)=L(S)+C(S) (1)
Where, S represents a variable for the security
production, L(S) expresses the loss function of
security; C(S) expresses the cost function of
security.
The optimal case is when B (S) is minimum. To
achieve this objective, the optimal S can be derived
through seeking dB (S) / dS = 0.
(ii) The Maximum Profit Principle
Security investment return E (S) can be expressed
as:
E(S)=F(S) - C(S) (2)
Where, F (S) is a security function which is equal to
the profit appreciated and loss saved of security
inputs. The optimal case is when E (S) the maximum.
It can be derived through setting dE (S) / dS = 0.
No matter whether it is the minimum cost
principle or maximum profit principle, the analysis
comes out from the economics perspective of a
business, and does not take into account the utility
functions of market competition, inter-firm
interaction and other constraints. This paper
introduces game theory into the analysis of
enterprise security investment from the perspective
of technology cost and the decision-making
behavior.
519
Wei W. and Ying R..
SECURITY INVESTMENT ANALYSIS ON GAMING THEORY WITH MEASUREMENTS OF COST AND DECISION BEHAVIOR.
DOI: 10.5220/0003586605190523
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (SSE-2011), pages 519-523
ISBN: 978-989-8425-53-9
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 THE MODEL OF GAMING
2.1 Utility Function
In order to study the security investment gaming
between enterprises, the constructed model involves
two entities (i, j = 1, 2) which has its own utility
function u
i
under the security investment of a
i
(a
i
≥
0), and assumed that
z the enterprise i invested in security at the level
of a
i
=0 and a
i
> 0;
z the probability P of a security accident is very
small. Otherwise, it is not attractive for a rational
investor to invest and the government would
supervise such kind of risky project. The
objective of security investment is to control the
probability of security accident so that the
accident probability decreases to a small level of
P’;
z only the price competition come out of profit
consideration is taken into account for the
market competition;
z an infinite loss of security accident would result
in a bankruptcy.
z The Security investment utility function can be
constructed as follows (
Guang-mao et al.,
2005
):
)()(),(
iiiijiii
avayaaxu −+=
(3)
Where, x
i
(a
i
,a
j
) expresses the overall profit
utility value changed for enterprise i from external
competition of security investment with other
enterprises; y
i
(a
i
) is the utility value for enterprise i
in the security investment; v
i
(a
i
) is the cost of
security investment, and v
i
(a
i
) > 0.
Taking enterprise 1 as example, and let x
1
(a
1
, a
2
)
= w
1
a
1
a
2
. Where
211
2
1
/ aaxw ∂∂∂= reflects the
contribution of x
1
to the overall utility value and the
relative impact of competition in security investment
between enterprises, its sign is the same as (a
2
– a
1
).
Under the competition condition that a security
investment would increase the cost for enterprise i,
a
1
has a negative impact and a
2
has a positive impact
on the utility value.
0,)()](1[
')'1()(
≥−−−−=
−−=
i
s
ii
c
ii
sc
ii
uapuap
upupay
γγγ
,(4)
Where, γ
i
expresses the learning ability of
security investment for enterprise i; (p-γ
i
a
i
) indicates
the probability change of accidents for a security
investment, (p-γ
i
a
i
) ≥0; u
c
is the profit for enterprise
without security accidient, u
s
is the profit loss caused
by a security accident, and u
s
→+∞. For a very small
number p, (p-γ
i
a
i
)→0.. It is hard to determine the
value of pu
s
and (p-γ
i
a
i
)u
S
which are meaningless in
the utility function. Consequently, the term (p-γ
i
a
i
)u
s
can be truncated, and the impact of security
investment is focused on the term of [1-(p-γ
i
a
i
)]u
c
.
0,
2
1
)(
2
≥+−=
iiiiiii
cacabav
, (5)
Where b
i
is security investment intention for
enterprise i, c
i
is the significance of security
investment a
i.
Under a security investment, the
utility value for enterprise 1 and enterprise 2 is:
)2,1(,
2
1
)](1[),(
2
2121
=−+
+−−+=
iacab
uapaawaau
iiii
c
iiii
γ
(6)
If enterprise i does not have a security
investment, then a
i
can be substituted by 0, and
2211
),( azazaax
jii
+=
(7)
Where, z
1
and z
2
are constant. If the impact on
enterprise 1 is negative, then the impact on
enterprise 2 would be positive, accordingly,
1
z <0
and
2
z >0.
2.2 Utility Matrix
Suppose the gaming utility matrix for two business
entities is shown in Figure 1, from equation (6),
u
1
(a
1
,a
2
) and u
2
(a
1
,a
2
) can be calculated (Wei-ying,
1996
):
c
upuu )1(),0()0,0(
21
−==
2
1111111111
2
1
)](1[)0,( acabuapazau
c
−+−−+=
γ
c
upazau )1(),0(
2221
−+=
2
2222222222
2
1
)](1[),0( acabuapazau
c
−+−−+=
γ
c
upazau )1()0,(
1112
−+=
Entity 2
0
2
a
Entity 1
0
1
a
F
Figure 1: Two entity’s security invest utility matrix.
u
1
(a
1
,a
2
),u
2
(0,0) u
1
(0,a
2
), u
2
(0,a
2
)
u
1
(a
1
,0), u
2
(a
1
,0) u
1
(a
1
,a
2
), u
2
(a
1
,a
2
)
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
520
If 0 < a
1
< 2(z
1
+b
1
+γ
1
u
c
)/c
1
,then u
1
(a
1
,0)>
u
1
(0,0). It means enterprise 1 continues to invest in
security even though enterprise stops the security
investment.
3 GAMING ANALYSIS
3.1 Graphical Analysis of Gaming
Zones
By means of a game graphics with gaming zones,
the gaming can be divided into two situations
(Jun-jie et al., 2006; Li and Sun, 2005):
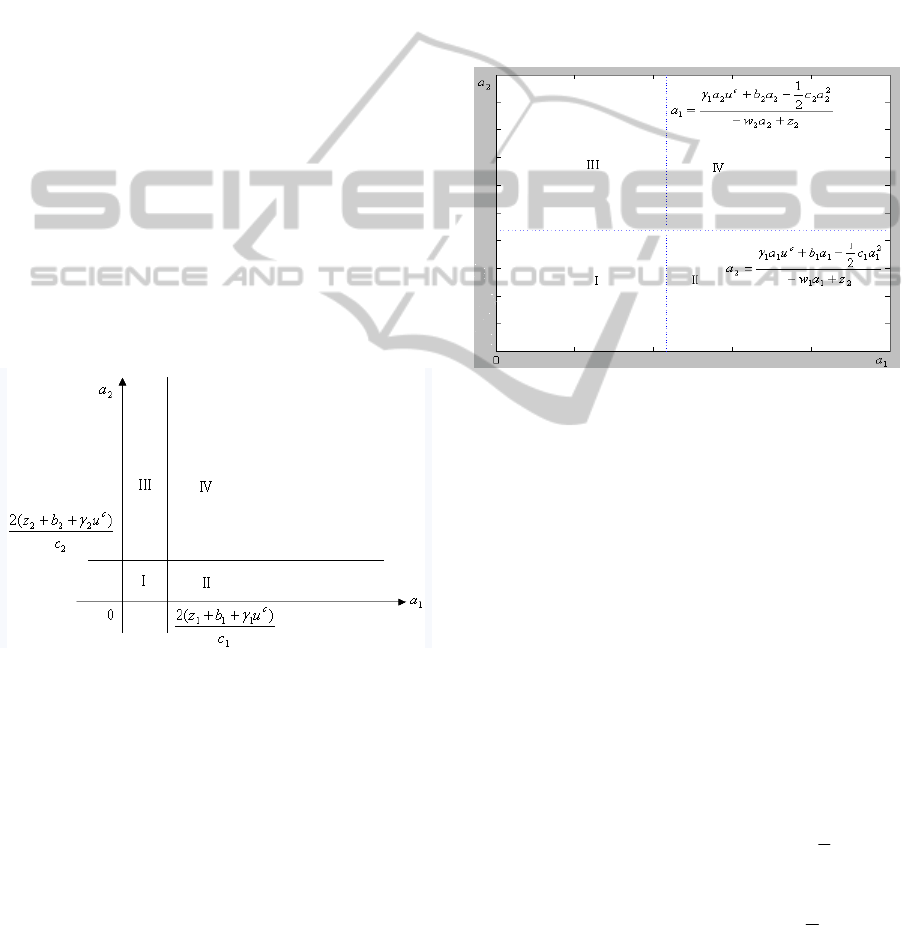
Situation 1:
Corresponding to u
1
(0,0)=u
1
(a
1
,0) and u
2
(0,0) =
u
2
(0,a
2
),there are four gaming zones (I, II, III, IV)
divided by the cross lines of a
1
=2(z
1
+b
1
+γ
1
u
c
)/c
1
and
a
2
= 2(z
2
+b
2
+γ
2
u
c
)/c
2
, which is shown in Figure 2.
In zone I,u
1
(0,0) < u
1
(a
1
,0) and u
2
(0,0) <
u
2
(0,a
2
) , the security investment choices for the two
enterprises are(a
1
,a
2
). Similarly, in zone II, III, IV the
security investment choices are (0,a
2
), (a
1
,0) and
(0,0).
Figure 2: Graphics for gaming situation 1.
Situation 2:
Corresponding to u
1
(a
1
,a
2
)=u
1
(0,a
2
) and u
2
(a
1
,a
2
) =
u
2
(a
1
,0), the four gaming zones (I, II, III, IV) are
divided by the cross lines of
a
1
=(γ
2
a
2
u
c
+b
2
a
2
-0.5c
2
a
2
2
)/(-w
2
a
2
+z
2
)
and
a
2
=(γ
1
a
1
u
c
+b
1
a
1
-0.5c
1
a
1
2
)/(-w
1
a
1
+z
1
)
,
which is shown in Figure 3. Through an iterative
calculation, the gaming zones can be obtained and
shown briefly as Figure 3. Any change of the
parameters can only affect the size of the zones but
not the relationship between zones. The security
investment choices for gaming zone I, II, III, IV are
(0,0), (0,a
2
), (a
1
,0), (a
1
,a
2
), respectively.
Combining Figure 2 with Figure 3 into one
coordinate frame, there are nine gaming zones
available in Figure 4.
It should be noted that the relative location of
gaming zones in Figure 4 might be changed based
on the value of (z
1
+b
1
+γ
1
u
c
)/c
1
, (z
2
+b
2
+γ
2
u
c
)/c
2,
(γ
2
a
2
u
c
+ b
2
a
2
- 0.5c
2
a
2
2
)/(-w
2
a
2
+ z
2
),
and (γ
1
a
1
u
c
+
b
1
a
1
- 0.5c
1
a
1
2
)/(-w
1
a
1
+ z
1
)
.
It can also be observed
from Figure 4 that the gaming results are always the
same for zone IV, V, and VII, which are (0,0), (0, a
2
),
(a
1
, 0), respectively. The gaming results for the other
zones might vary from different gaming situations.
Figure 3: Graphics for gaming situation 2.
3.2 Gaming Analysis for Security
Investment
Another observation from the gaming model and
gaming zone analysis is that the security investment
is very much dependent upon the parameters.
However, the actual security investment decision for
an enterprise is not complicated, in most of the cases,
it is dependent upon the cost and technology
instrument.
For enterprise 1, obviously, the investment
choices could be (0,0), (a
1
, 0), (0, a
2
), (a
1
,a
2
). The
decision can be made after the comparison
of
u
1
(0, 0) and u
1
(a
1
, 0), as well as u
1
(0, a
2
) and
u
1
(a
1
, a
2
). From (6) we can obtain (Liang-qiao,
2007):
2
11111111111
2
1
)0,0()0,( acabuaazuau
c
−++=−
γ
(8)
2
111111
2221121211
2
1
),0(),(
acabua
azaawauaau
c
−++
+−=−
γ
(9)
In (8), z
1
a
1
<0. From the presupposition of
security investment cost v
i
(a
i
) > 0, we can know:
SECURITY INVESTMENT ANALYSIS ON GAMING THEORY WITH MEASUREMENTS OF COST AND
DECISION BEHAVIOR
521
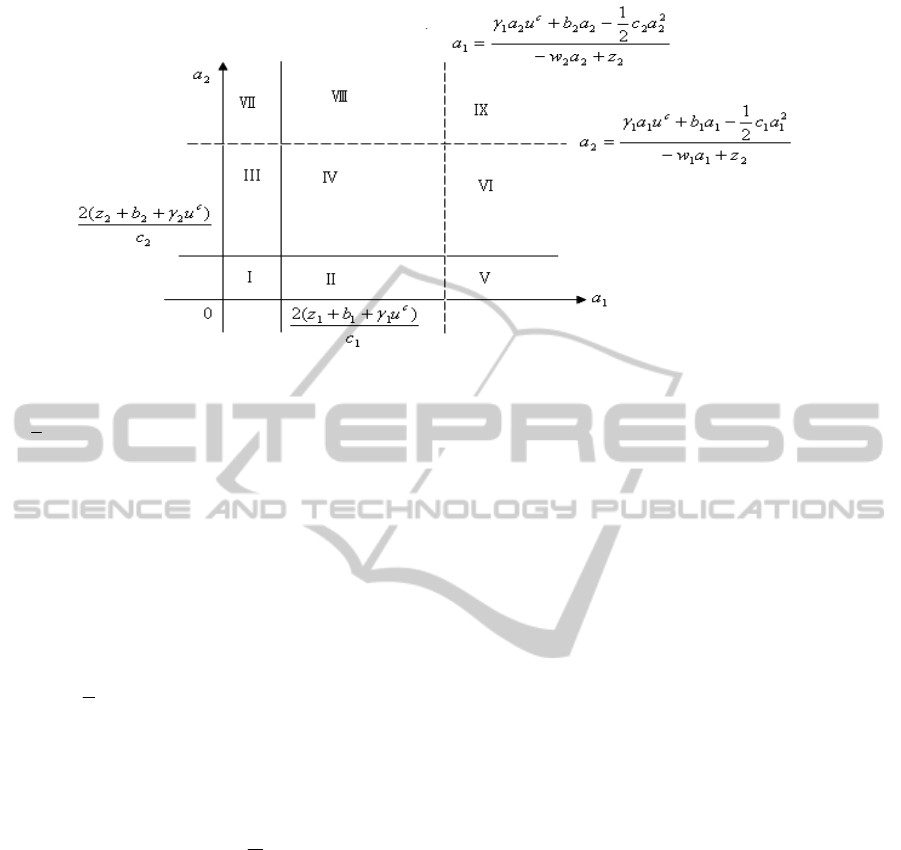
Figure 4: Integrated gaming zones.
0
2
1
2
1111
<− acab
. Under a certain level of investment
a
1
,γ
1
a
1
u
c
depends on the value ofγ
1
and u
c
. γ
1
is
mainly affected by business environment and
technology level, the higher the technical level
requires, the greater value
γ
1
from the impact of
security probability would be. u
c
is related to the
enterprise cost, a lower cost reflects a higher value
of u
c
. From the viewpoint of technology and cost
components, a lower level of technology would
cause a higher investment cost. Compared with z
a
a
1
and
)
2
1
(
2
1111
acab −
, the value ofγ
1
a
1
u
c
is very small
and can be ignored. Therefore, u
1
(a
1
, 0) - u
1
(0, 0) <
0. In the situations of
(0,0)and (a
1
, 0), enterprise 1
would not make a security investment until an
improvement of technology and profit occurs.
For expression (9),
2
1111
2
1
acab −
<0, w
1
a
1
a
2
–
z
2
a
2
= (w
1
a
1
– z
2
)a
2
. As a matter of experience, under
the unique condition of competition, the choice of
(0,a
2
)is better than(a
1
,a
2
) for enterprise 1 to
improve the competition, this conclusion can also be
derived from the analysis of utility functions.
Compared with the case of (0, a
2
), the case (a
1
, a
2
)
implies a smaller impact of the overall utility value
for enterprise 1, and w
1
a
1
a
2
– z
2
a
2
< 0. The value of
γ
1
a
1
u
c
is very small compared with that of z
1
a
1
and
w
1
a
1
a
2
– z
2
a
2
, so it can be ignored. u
1
(a
1
, a
2
) - u
1
(0, a
2
)
<0, so we have the same conclusion for the
situations of (0,0) and (a
1
, 0) that enterprise 1 would
not make a security investment until an
improvement of safety instruments.
From the analysis of (8) and (9), under the
condition of a low technology level and a high
security investment cost, the enterprise 1 thought it
is not necessary to make a security investment
because of the low utility value in the short run.
Without a change of business environment,
enterprise 1 would be gaming forever. Similarly,
enterprise 2 also gets the same conclusion and does
not want to invest neither. Consequently, the choices
for enterprise 1 and enterprise 2 would be (0, 0)
which located at zone IV in Figure 4, both
enterprises are unwilling to make a security
investment.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The reason why enterprises are reluctant to make a
security investment is partially due to a low level of
technology, high investment cost as well as a result
of ineffective supervision, thereof the problems of
low input and technology instrument are not difficult
to solve. However, the fact of inadequate
government supervision and the pursuit of maximum
profit leads to the enterprises’ gaming behavior. To
improve the security investment efficiency, some
suggestions are summarized as follows:
z The managerial principle of profit
maximization results in a shortage of security
input, irrational gaming, inappropriate
supervision, and even corruption. A task of top
priority is to strengthen security supervision,
add impetus to the marketization of public
utilities, improve funds efficiency, and
establish a rational institutional system. The
enterprises may have to provide detailed
statements timely to the administrative
agencies.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
522

z The government should encourage the
enterprises to improve the technology level
through making more R&D investment and
accelerating the pace of imports and
international cooperation in advanced
technology.
z Facing with the problems of high security input
cost and capital shortage in the context of the
recent crisis in global financial markets and
weakening of global economic activity, the
government should make an effort to adjust the
policy, including the government subvention
,
public subsidy, tax exemption and reduction.
z The enterprises must identify the objective and
the use of security investment funds, including
government subsidies, R&D, and the security
fee deducted, setting up a proactive investment
mechanism and risk preventive system.
z The enterprises should establish a budget and
check framework to monitor progress and
effectiveness of the security funds, as well as
create an internal performance reporting
structure to ensure the funds are in a virtuous
cycle.
REFERENCES
Dixit, A . K. and Pindyck, R. S., Investment under
Uncertainty, Princeton University Press, Princeton
,
N J
,1994
Goeree and Holt (2005)
:An experimental study of costly
coordination
.games and economics behavior.(51),
349—364
.
P.M. Kort; J. L. Haunschmied; G Feichtinger, “Optimal
firm investment in security”, Annals of Operations
Research 1999(1):81_98
Annals of Operations Research
Dong Guang-mao, Yuan Li, LIAO Xiu-wu. “The failure
of strategic alliances Game Analysis: coordination
failures perspective”, Journal of Systems Engineering,
2005, 23 (8): 91_ 95.
Zhang Wei-ying. Game Theory and Information
Economics, Shanghai People's Press, 1996.
Lu Jun- jie, Chiu Wan-hua, WANG Yuan-Zhuo. “Based
on the interdependence of information security
investment in the game”, Journal of China
Management Science, 2006 (3).
Meng Li, Wei Sun. “On the competitive power generation
business under the conditions of the investment
strategy of the game options research”, Journal of
contemporary economic management, 2005 (3).
Zhang Liang-qiao. “Coordination game with a balanced
selection”, Journal of Explorations, 2007 (5).
SECURITY INVESTMENT ANALYSIS ON GAMING THEORY WITH MEASUREMENTS OF COST AND
DECISION BEHAVIOR
523
