
NEURAL NETWORK-BASED PROCUREMENT MODE
SELECTION OF MRO MATERIALS
Zhen Huang, Yiran Zhang
School of Business, Beijing Technology and Business University, Fucheng Road, Haidian District, Beijing, China
Haoxiong Yang, Yongsheng Zhou, Li Cui
School of Business, Beijing Technology and Business University, Beijing, China
Keywords: MRO, Procurement mode, Industrial logistics, Neural network, Clustering.
Abstract: Maintenance, Repair and operations (MRO) have following features: large sum of types, relatively low
requirement, and high transition cost. It costs companies a lot of money and human resource on MRO
procurement. In order to make MRO procurement more efficient and scientific, this paper compared the cost
of two MRO supply chain modes to get a scope for each mode. And then SOM neural networks method can
be used to cluster the materials. Different types of materials take advantage of different procurement mode.
1 INTRODUCTION
MRO is abbreviation of Maintenance Repair and
Operation, namely maintaining, repairing and
operating materials and it’s also called indirect
materials. This kind of materials includes spare
parts, machines, tools and consumables. Every
company needs certain kinds of MRO materials to
maintain their operation and business normally.
Because of the lots of kinds and specifications of
MRO materials and relatively small demand, MRO
materials procurement will inevitably lead to higher
transaction costs. According to the survey
(Wencheng Liu, 2008) , every industrial enterprise
has large sum of MRO suppliers, resulting in
inefficient MRO materials procurement, purchasing
value of total purchases accounted for only 8% of
enterprises, but it consumes more than 60% of
purchasing resources. Steve Stall (2003) mentioned
that MRO managers have come to realize that
success is no longer measured through meeting
production goals alone. They must now consider that
every purchase and maintenance decision has a
direct impact on their company's profit margin - as
well as their own department's measurement of
success. So you can see it is different from the direct
procurement of MRO materials, which involves not
only the normal production of enterprises, but also
take up a large number of enterprises of human and
financial resources. Therefore to strengthen the
management of MRO materials, procurement is very
important.
MRO study abroad is earlier, and the study
focused on e-procurement. Cade Metz (2000), Jerry
Goldstein (2001), Emily Kay (2001), Abbas
ForoughiMehmet C. Kocakülah (2003) mentioned
that MRO e-procurement can save time, improves
efficiency and reduces paper work. The domestic
study started from 2006. On the mode of
procurement of MRO materials, MRO materials
procurement study focused on the integration of
mode-based, Minjie Wu (2007) proposed integration
of the domestic industrial enterprises in international
MRO procurement. Kongji Li, Yue Li (2009)
proposed centralized procurement by the integration
of procurement service providers. Si Chen (2010)
mentioned that third party logistics providers
undertake procurement, sales and logistics role of
MRO supply chain to achieve integrated supply and
demand. But Xiaoyu Xu, Daoli Zhu (2001) thought
small and medium company can only take MRO
procurement market mode.
The earliest scholars believed that MRO material
should be obtained through the market, but in recent
years, scholars have generally agreed that MRO
materials procurement should be integrated.
However, the literatures in these two modes are not
theoretical or mathematical in-depth analysis to
523
Huang Z., Zhang Y., Yang H., Zhou Y. and Cui L..
NEURAL NETWORK-BASED PROCUREMENT MODE SELECTION OF MRO MATERIALS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003589205230526
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (DMLSC-2011), pages 523-526
ISBN: 978-989-8425-55-3
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

clarify the scope of these two modes. According to
large sum of types and specifications of MRO
materials, taking all the materials the same mode is
not economic, so this paper is on the basis of
previous research, in-depth comparative analysis of
the two modes to propose the scope of the different
mode and provide the basis of procurement channel
for choosing.
2 ANALYSIS OF PROCUREMENT
MODES
There are two supply chain modes of procurement,
which are “manufacturers - companies” and
“manufacturer - distributor - companies “. For the
bulk procurement of raw materials, companies
usually select the "manufacturers - companies"
procurement mode. But according to MRO
materials’ special feature of variety of types and
specifications, if only selecting one of these two
modes, will inevitably result in uneconomical MRO
procurement management, So companies should
analyze and compare of the scopes of these two
modes, and then take a different mode to meet
different types of MRO materials’ requirements.
2.1 “Manufacturers - Companies”
Mode
"Manufacturers - companies” mode refers that
enterprises (the ultimate consumers) procure
materials from the manufacturer directly in
commerce flow. In logistics, MRO materials are sent
directly from the manufacturer to the enterprises (the
ultimate consumer).
The cost of this mode as following:
Assumption:
1
y ——Total cost of procurement in this
mode,
n ——Number of manufacturers,
i
c ——
Manufacturing cost ,
i
r ——Manufacturer’s
profits,
i
t ——Transaction costs.
Total cost of procurement in this mode as
following:
()
∑
=
++=
n
i
iii
trcy
1
1
2.2 “Manufacturers - Distributors –
Companies” Mode
"Manufacturers - Distributors - Companies” mode
refers that companies (the ultimate consumer)
procure a variety of MRO materials from a
distributor in commerce flow. In logistics, MRO
materials are sent from the distributor (namely
integrated MRO materials distributor, such as
Grainger, Yao Shun and other companies) directly to
the company (the ultimate consumer).
The cost of this mode as following:
Assumption:
2
y ——Total cost of procurement in this
mode ,
m ——Number of manufacturers ,
nm
<
,
i
c ——Manufacturing cost ,
i
r ——
Manufacturer’s profits,
i
t ——Transaction costs,
i
s ——Distributor’s profits.
Total cost of procurement in this mode as
following:
()()
∑∑
==
+++=
m
i
ii
n
i
ii
strcy
11
2
2.3 Modes Comparison
The difference between the two modes’ cost can be
used to illustrate which mode is more economic.
Namely,
∑∑
==
+−=−
m
i
ii
n
i
i
sttyy
11
21
)(
Assumption:
∑
=
=
n
i
i
tQ
1
1
,
∑
=
+=
m
i
ii
stQ
1
2
)(
,
The functions of
1
Q and
2
Q are shown in figure
1. In figure 1,
0
q is the intersection of
1
Q and
2
Q ,
when
0
qq < , companies should select the
"Manufacturers - Distributors - Companies” mode.
When
0
qq > , companies should select the
"Manufacturers - Companies” mode.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
524
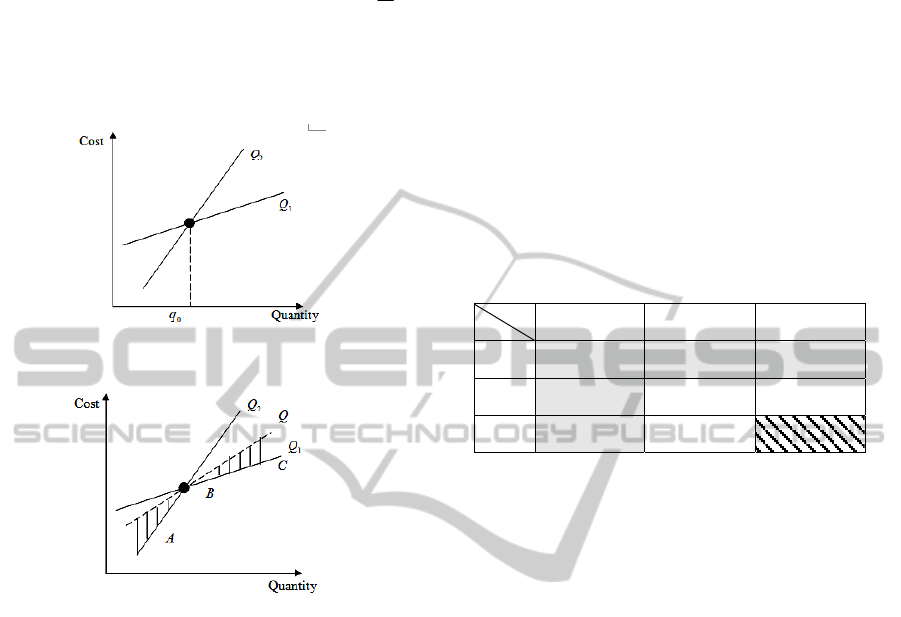
So the function of cost when companies combine
the two modes is ABC in Figure 2. If the enterprise
fails to combine the two modes, while using only
one mode, the average cost function is
Q .
Obviously, combining the two modes can cut cost
and the cost saving is in the area of the shaded in
figure 2.
Figure 1: Cost Functions of Two Modes.
Figure 2: Cost Savings.
3 SELECTION OF
PROCUREMENT MODES
3.1 Theoretical Methods
In reality, transaction costs, the profits of the
manufacturers and distributors are hard to be
separated. So direct calculating of the cost of the two
modes is hardly realized. For this reason, here are
trying to analyze the causes of cost to find the
obvious characteristics of different modes, so that
companies can use the scientific method to classify
MRO materials according to these characteristics. It
can easily and accurately identify different types of
MRO procurement mode to be applied.
In figure 3, the intersection of the functions
depends on purchasing quantity, which is to say the
choice of procurement mode is depends on
purchasing quantity. As MRO material has the
characteristics of demand uncertainty, so enterprises
generally sign a certain time frame contract of the
total procurement quantity of one year to the
supplier, which is the annual procurement volume.
Annual procurement volume is equal to material’s
value multiple quantity. Therefore, the product of
number and value of the purchasing material decides
the enterprise’s MRO procurement mode.
The number of materials’ value and quantity can
be classified by large, medium and small categories,
so that there are nine situations of the product, see
Table 1:
P represents the value of materials; Q represents
the number of procurement; A represents large
number; B represents medium number and C
represents small number.
Table 1: Nine situations.
A
P
B
P
C
P
A
Q
AA
QP ×
AB
QP ×
AC
QP ×
B
Q
BA
QP ×
BB
QP ×
BC
QP ×
C
Q
CA
QP ×
CC
QP ×
CC
QP ×
In order to achieve optimal benefit, companies
should choose a suitable procurement strategy for
each case in Table 1. Nine cases in Table 1 can be
divided into three categories, namely the different
three patents in Table 1:
① Gray Area
Gray area is on behalf of the large quantity of
procurement or high value materials. It is very easy
to be hand-selected in practice. The product is large
obviously. So in this case, companies should select
the "manufacturers - companies” mode.
② Slash Area
Slash area is on behalf of the small quantity and
value of material purchasing. It’s also very easy to
be hand-selected in practice. The product is small
obviously. So in this case, companies should select
"Manufacturers - Distributors - Companies” mode.
③ White Area
White area is on behalf of the medium or small
quantity or value. Because there are many kinds of
MRO materials and the demand relatively less, so in
manual work, a lot of material will be fall into this
category. And this kind of materials do not have a
typical product (relative maximum or relative
minimum), it is difficult to determine the
procurement mode by people.
In summary, the theoretical method is using
quantity and value of procurement as a characteristic
mark to select the MRO materials procurement
NEURAL NETWORK-BASED PROCUREMENT MODE SELECTION OF MRO MATERIALS
525

mode. However, in many cases, the feature can not
be man-made classified (cases in white area),
requiring a scientific and effective method to replace
the manual classification.
3.2 Actual Operation Method
In order to solve the above-mentioned problem that
artificially cannot be classified, this paper chooses
neural network of self-organizing feature mapping
network (SOM) algorithm for classification. The
SOM algorithm provides an effective way and
general framework for this type of problem, and it is
a kind of advanced artificially intelligent algorithm.
Self-organizing feature map (SOM, Self -
Organizing Feature Map) is also called the Kohonen
network, which is put forward by the Dutch scholar
Teuvo Kohonen in 1981. Kohonen think that a
neural network will be divided into different regions
when accept outside input mode, and each region
has a different input mode response characteristics
and this process is done automatically. Therefore,
SOM network is widely used for clustering research.
Based on the analysis of procurement, MRO
materials procurement model selection should be
based on the annual purchasing quantity
n
Q and
value of the procurement for clustering. In this
paper, we choose the plotsom neural network
function in the Matlab to implement clustering, and
the learning rate and other variables will use the
default values in Matlab.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper focus on the characteristics of MRO, that
the material type specification is so much while
purchase quantity relatively small, by comparing the
cost structure of the two modes of MRO materials’
supply chain, the scope of application of these two
types are obtained, and use the purchase quantity
and value as characteristic value, we know that
different kinds of materials should choose different
purchase mode. In order to put the theory into
practice, this paper use SOM neural network
classification of MRO materials, to solve the
problem that can’t solve manually, and select
different purchase model for different types of MRO
materials, which make the procurement of MRO
more efficiently. In this paper, the annual purchase
quantity and the value are used as the characteristic
value to establish the model. The method is simple,
convenient and feasible and provides an effective
way for enterprises to select the MRO materials
procurement model.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by “Dynamic Allocation of
City Logistics Resource Based on the City
Sustainable Development Perspective”, a research
project of the humanities and social sciences of the
Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of
China (No. 10YJC630324), and supported by
“Allocation of City Logistics Resource”, a project of
the Beijing Municipal Commission of Education
(No. PHR20110877).
REFERENCES
Abbas ForoughiMehmet C. Kocakülah, 2003. E-
procurement: Extending E-supply Chain Benefits to
MRO. Annual meeting of the decision sciences
institute, 20031122-25
Cade Metz, 2000. Purchasing Power. PC Magazine, 2000,
19 (20).
Emily Kay, 2001. Cut the Paperwork With Online
Procurement or MRO. Managing Automation, 2 001,
16 (3).
Jerry Goldstein, 2001. Heed These 10 Points When
Buying MRO Items Online. AFE Facilities
Engineering Journal, 2001, 28 (2).
Jili Kong, Yue Li, 2009. Research on Inventory
Management System of integrated Procurement
Service Providers of MRO Materials of Industrial
Enterprises. Logistics Engineering and Management,
2009, 12.
Minjie Wu, 2006. Transnational Integration of MRO
procurement. Modern Management Science, 2006, 10.
Si Chen, 2010. Research on the applications of integration
of supply and demand in the third-party MRO logistics
business. Market Modernization, 2010, 6.
Steve Stall, 2003. Making the Business Case for MRO
Initiatives. Technical Conference and 3rd Annual
Emerging Technologies Conference.
Wencheng Liu, 2008. MRO Procurement and Supply
Management - Discussing the Management of MRO
Applications in energy industry. China's bidding, (32):
25 -29.
Xiaoyu Xu, Daoli Zhu, 2001. Internet-based e-
Procurement Model. Logistics Technology, 2001, 5.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
526
