
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF EMERGENCY LOGISTICS
BASED ON DEA-AHP ALGORITHM
Jiyong Zhang and Shaochuan Fu
Schoole of Economics and Management, Beijing Jaotong University, Haidian District, Beijing, P.R.China
Keywords: Emergency logistics, DEA, AHP.
Abstract: In recent years, much more natural disasters, public health events and a variety of disasters, accidents have
occurred. This paper proposes an index system for the evaluation of the performance of emergency logistics.
Performance evaluation of a group of entities is frequently based on the values of several attributes and
usually requires the weights of the attributes to be set in advance. After an index of logistics system being
built and with the Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) algorithm and Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP)
algorithm being integrated. This hybrid model takes the best advantages of both AHP and DEA and at the
same time, avoids either the subjectivity of AHP or the dichotomy of DEA. The results show that the
evaluation method can measure the emergency logistics performance more effective and feasible.
1 INTRODUCTION
2011.3.11, the earthquake and tsunami disasters
have brought great suffering to the Japan. In the
process of disaster relief, the importance of
emergency logistics becomes the focus of people
again.
With the rapid development of science and
technology, the ability of predicting natural disasters
has been significantly improved. However, heaven
decides the weather. Localized, regional, even global
emergencies have occurred, serious threat to human
life and property safety.
The emergency logistics just meet the need to
complete sudden logistics demand from the various
situations.
1.1 Research Significance
The purpose of evaluating the performance of
emergency logistics is to identify the weak links of
the emergency operation in the logistics. Then, with
continuous improvement of the emergency logistics
system can make the system more efficient.
Currently, the assessment of emergency logistics
performance is still in the exploratory stage. The
most correspondingly published literature focus on
the study of response to emergency situation and the
logistics system itself. There are few studies on the
evaluation of the methods to evaluate the
performance of the emergency logistics system.
Now the main measurement methods are as follow:
Fuzzy Comprehensive Algorithm, Analytical
Hierarchy Process (AHP), Data Envelopment
Analysis (DEA). These methods are flawed during
the process.
In this text, the first step is to calculate the
weight of each layer index using the AHP method.
The second step is to obtain the relative efficiency of
each system of indicators for each layer separately
with the method of using the DEA. Finally, integrate
the weight of each index and the relative efficiency
to calculate the overall efficiency of the emergency
logistics system and sorting. The method effectively
combines the advantages of both DEA and AHP, at
the same time, is good to make up for the lack of the
two methods. All of this makes the method
applicability and operability.
2 DEA-AHP EVALUATION
PRINCIPLES
2.1 Basic DEA Methodology
Built upon the earlier work of Farrell (1957), DEA is
a well established methodology to evaluate the
relative efficiencies of a set of comparable entities
by some specific mathematical programming
527
Zhang J. and Fu S..
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF EMERGENCY LOGISTICS BASED ON DEA-AHP ALGORITHM.
DOI: 10.5220/0003589305270532
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (DMLSC-2011), pages 527-532
ISBN: 978-989-8425-55-3
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

models. These entities, often called decisions
making units (DMU
s
), perform the same function by
trans- forming multiple inputs into multiple outputs.
A main advantage of DEA is that it does not require
any prior assumptions on the underlying functional
relationships between inputs and outputs (Seiford
and Thrall, 1990). It is therefore a nonparametric
approach. In addition, DEA is a data-driven frontier
analysis technique that floats a piecewise linear
surface to rest on top of the empirical observations
(Cooper et al., 2004).
Since the work by Charnes et al. (1978), DEA
has rapidly grown into an exciting and fruitful field,
in which operations research and management
science (OR/MS) researchers, economists, and
experts from various application areas have played
their respective roles (Førsund and Sarafoglou,
2002, 2005). For DEA beginners, Ramanathan
(2003) provided an excellent introductory material.
The more comprehensive DEA expositions can be
found in the recent publication by Cooper et al.
(2006). In the sections that follow, we shall briefly
introduce the basic DEA methodology.
Assume that there are K DMU
s
, e.g. electricity
distribution utilities, to be evaluated that covert N
inputs to M outputs. Further assume that DMU
k
consumes x
nk
>=0 of input n to produce y
mk
>=0 of
output m and each DMU has at least one positive
input and one positive output (Fare et al., 1994b;
Cooper et al., 2004). Based on the efficiency
concept. in engineering, the efficiency of a DMU,
says DMU
o
(o=1,2,...,K), can be estimated by the
ratio of its virtual output(weighted combination of
outputs) to its virtual input(weighted combination of
inputs). To avoid the arbitrariness in assigning the
weights for inputs and outputs, Charnes et al. (1978)
developed an optimization model known as the CCR
in ratio form to determine the optimal weights for
DMU
o
by maximizing its ratio of virtual output to
virtual input while keeping the ratios for all the
DMU
s
not more than one.
2.2 Basic AHP Methodology
Analytic Hierarchy Process(AHP) is theorized by
U.S. Operations Research Professor Saaty TL. It is a
simple, flexible and practical method for multiple
criteria decisions making. It is based on a hierarchy
of multi-objective, subjective judgments based on a
range of options for calculating the relative
importance, followed by a top down basis, through
the decision-makers for each sub-index layer and
index layer provided by the importance of subjective
judgments in pairs, for each unit down to the
pairwise comparison matrix to establish.
Comparison of first through calculating the feature
vector matrix elements get the same level on a level
for the relative importance of the same unit, and then
in accordance with the order from the bottom up
Yici, calculate aggregate importance, end up ranking
value of each option. AHP process was people's
thinking process by fully reflect the preferences of
decision makers, decision makers experience will be
quantified, so as to provide decision makers with
quantitative forms of decisions making. But its
limitations can not be ignored: it relies heavily on
people's experience, subjective factors is large, it can
only rule out the thought process up to the serious
non-compliance, but can not rule out the possible
existence of individual decision-makers A serious
one-sidedness.
2.3 Evaluation of the Significance
of AHP-DEA
The above method of DEA-AHP method described
shows, DEA methods for assessing the results of the
program is totally dependent on the objective
evaluation of indicator data, without considering the
preferences of decision makers, and can only be
divided into units based on the dichotomy of
decision-making both active and inactive Part of
effective decision-making unit of the information
given is too small, can not be a reasonable sort; and
simple AHP, due to the characteristics of semi-
qualitative semi-quantitative determined by its lack
of strict objectivity, subjective factors, too. Taking
into account the practical problems of evaluation
reflects the degree of importance among may vary,
so the decision makers in order to reflect the
preferences of the different level of evaluation, so
that the evaluation of a more comprehensive and
reasonable, considering the above two methods the
author Advantages and disadvantages in use of data
envelopment analysis and analytic hierarchy process
method are combined to establish the subjective and
objective integrated multi-objective comprehensive
evaluation model. The model make up the traditional
method of data envelopment analysis does not
consider the lack of decision-makers preferences,
and overcome the many levels of analysis and
decision making the current weakness of
subjectivity, the evaluation results more
comprehensive and more realistic.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
528
3 THE STEPS OF OPERATION
3.1 Determine the Comprehensive
Evaluation Index System
After the disaster, need to provide emergency
support by emergency logistics. Information systems
in the process of the establishment may be abreast of
the situation and help the government and relief
workers to better organize the relief work. After the
disaster, a different geographic location should adopt
different means of transportation, but they are time
efficient in order to achieve the ultimate goal.
Organize and direct the work of the emergency
logistics, largely depends on the functioning of the
Government, pragmatic and efficient government
departments to organize and command the
emergency key to the success of logistics.
Emergency funds management, resource
availability, quality, utilization, efficiency is the
focus of government management. The performance
of government logistics performance directly affects
the level of emergency. Greater chance of sudden
disasters, as in emergency logistics will face many
problems can not be predicted, which requires the
strain relief workers have the ability to act
decisively, through peacetime training and exercises
in dealing with real problems can be quickly and
effectively. A state of emergency to deal with
emergency incidents is the key to effective
functioning of government functions and
coordination. When the disaster occurred, the
government needs through statistical property loss
rate, affected by the number and scope of post-
disaster disaster feedback, documentation kept
facilitate future reference to justice. We can set up
an emergency measure logistics performance
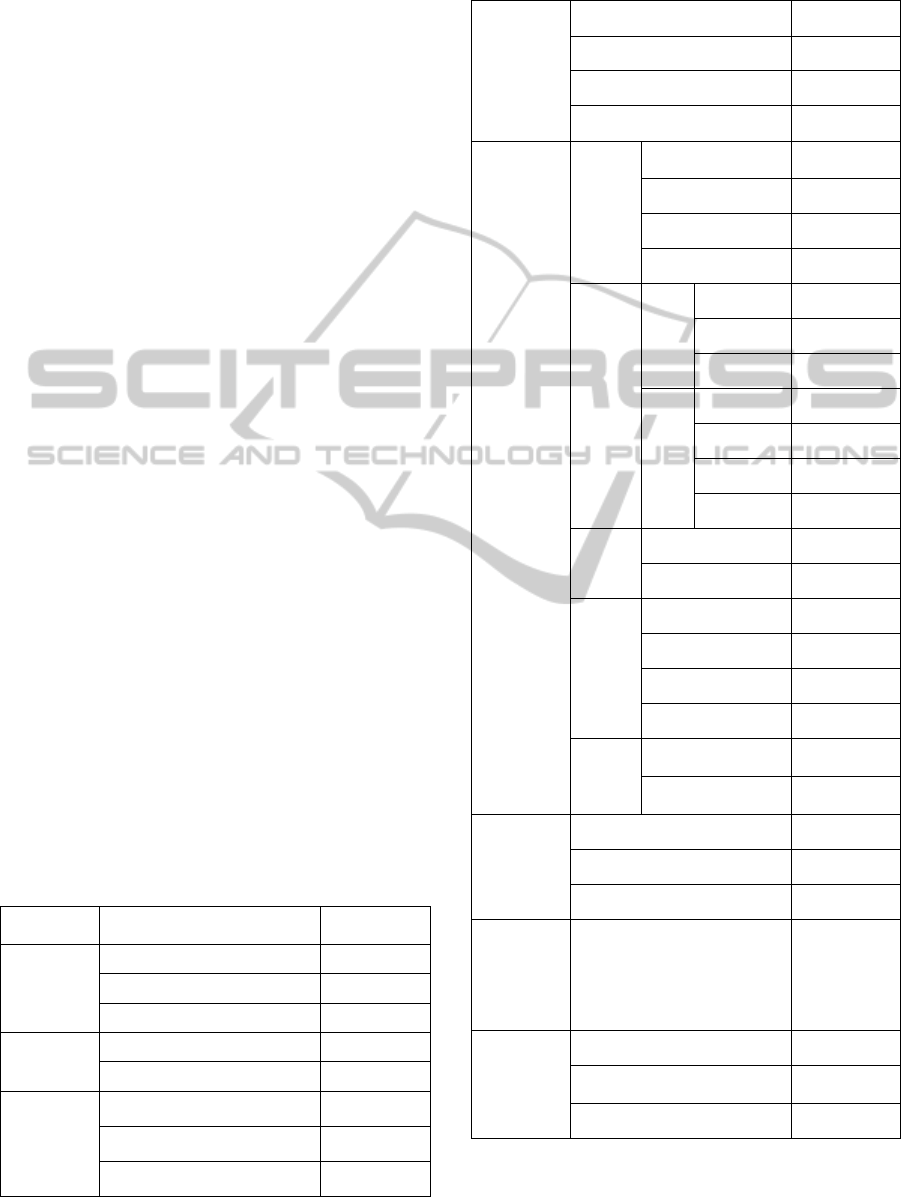
evaluation system, see Table 1.
Table 1: Emergency Evaluation System of logistics
performance measurement.
Framework
Elements
Index name
Form and
Content
Emergency
Information
System A
1
Normative B
11
Index
Timely feedback B
12
Index
Safety and secrecy B
13
Index
Condition
Of Disaster
A
2
Natural Factors B
21
Level
Human factors B
22
Level
Location A
3
City B
31
Index
Rural B
32
Index
Natural Area B
33
Index
Table 1: Emergency Evaluation System of logistics
performance measurement (cont.).
Traffic A
4
Port Facilities B
41
Level
Road Facilities B
42
Level
Aviation facilities B
43
Level
Pipeline facilities B
44
Level
Governmen
t
Administrat
i-on A
5
Emerge-
ncy
Logisti-
cs Costs
B
51
Transportation
costs
Proportion
Warehousing costs Proportion
Handling costs Proportion
Labor costs Proportion
Avail-
ability
of
Suppl-
ies
B
52
Avai
labili
ty
Convenience
Index
Timely
Index
Complete
Index
Reso
urce
call
Usually
reserves
Proportion
Proportion
Proportion
Social
contributions
Proportion
Emergency
Procurement
Proportion
Quality
B
53
Quality materials Index
Shipping Quality Index
Utilizati
on of
Supplies
B
54
Type Proportion
Quantity Proportion
Specifications Index
Recycling Rate
Efficien
-cy B
55
Material Delivery
Time
Time
People Arrival
Time
Time
Rescue
workers A
6
Organizers B
61
Index
Training B
62
Level
Experts B
63
Proportion
Governmen
t
coordinatio
n
mechanism
A
7
Advantage of Government
Coordination B
71
Index
Aftermath
A8
Loss of Property B
81
Proportion
Number of People Affected
B
82
Proportion
Areas B
83
Proportion
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF EMERGENCY LOGISTICS BASED ON DEA-AHP ALGORITHM
529
3.2 Determine the Weight of Each
Index System
As the special nature of emergency logistics,
emergency logistics management capabilities in
building evaluation system should be strengthened
in terms of speed indicators, and weakening
economic indicators system, it can be reflected by
the weight.
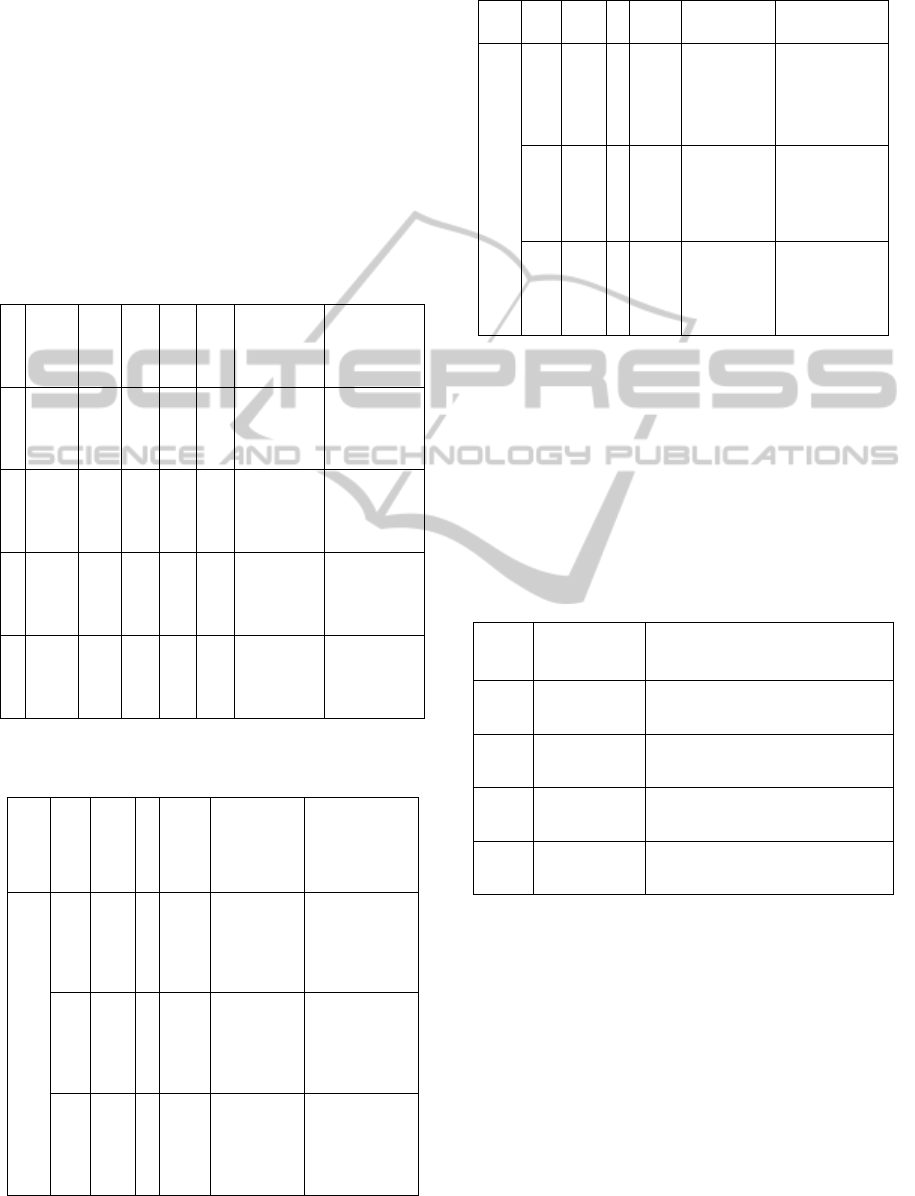
The index weight was determined by expert
evaluation of. The determination of one, two weight
is show in Table 2, Table 3.
Table 2: Logistics performance indicators weight
determination of level 1.
N
.
Mea-
sure
E1 E2
…
En Mean Normalized
1 A
1
A
11
a
12
…
a
1n
a
1=
na
n
i
i
/
1
1
∑
=
c
1
=
∑
=
8
1
1
/
i
i
aa
2 A
2
a
21
a
22
…
a
2n
a
2=
na
n
i
i
/
1
2
∑
=
c
2
=
∑
=
8
1
2
/
i
i
aa
… … … … … … … …
8 A
8
a
81
a
82
…
a
8n
a
8=
na
n
i
ni
/
1
∑
=
c
8
=
∑
=
8
1
3
/
i
i
aa
Table 3: Logistics performance indicators weight
determination of level 2.
L1
L
2
E1
…
En Mean Normalized
A
1
B
1
1
b
11
1
…
b
11n
b
11=
nb
n
j
j
/
1
11
∑
=
d
11
=
∑
=
3
1
111
/
j
j
bb
B
1
2
b
12
1
…
b
12n
b
12=
nb
n
j
j
/
1
12
∑
=
d
12
=
∑
=
3
1
112
/
j
j
bb
B
1
3
b
13
1
b
13n
b
13=
nb
n
j
j
/
1
13
∑
=
d
13
=
∑
=
3
1
1
/3
j
j
bb
Table 3: Logistics performance indicators weight
determination of level 2 (cont).
… … …
…
… … …
A
8
B
8
1
b
81
1
…
b
81n
b
81=
nb
n
j
j
/
1
81
∑
=
d
81
=
∑
=
3
1
881
/
j
j
bb
B
8
2
b
82
1
…
b
82n
b
82=
nb
n
j
j
/
1
82
∑
=
d
82
=
∑
=
3
1
882
/
j
j
bb
B
8
3
b
83
1
…
b
83n
b
83=
nb
n
j
j
/
1
83
∑
=
d
83
=
∑
=
3
1
883
/
j
j
bb
3.3 Quantify the Indicators of Level2
Use interval [0, 1] as indicate the pros and cons of
each index. 0 is the worst, 1 is the best.
Index system can calculate the value of the index
should be calculated by using actual data, for data
can not be quantified or non-comparable should deal
with expert evaluation.
Table 4: Logistics performance measurement indicators of
level 2.
NO. Indicators Pros and cons of degree
1 B
11
e
11
2 B
12
e
12
… … …
24 B
83
E
83
The value of A
1
, A
2
, …, A
8
are set with Q
01
, Q
02
,
…, Q
08
.
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
•=
11
13
12
),,(
13121101
e
e
e
dddQ
…
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
•=
81
83
82
),,(
83828108
e
e
e
dddQ
Q
0
= (Q
01
, Q
02
, …, Q
`
)
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
530

This problem can be further transformed into an
equivalent output maximization linear programming
problem as follows:
∑
=
=
M
m
mom
yu
1
max
s.t.
0
11
≤−
∑∑
==
N
n
nkn
M
m
mkm
xvyu
k=1,2,…,K.
1
1
0
=
∑
=
N
n
nn
xv (1)
u
m
, v
n
≥
0, m= 1,2,…,M;
n= 1,2,…,N.
Model (1) is known as the CCR in multiplier
form. The efficiency scores of DMU
1
to DMU
K
can
be derived by solving K such models. Despite the
linear form of (1), efficiency score is usually
calculated based on its dual problem:
Min
θ
s.t.
∑
=
≤
N
n
nknk
xx
1
0
ϑλ
n=1,2,…,N;
∑
=
≥
M
m
mkmk
yy
1
0
λ
m=1,2,…,M; (2)
0≥
k
λ
k=1,2,…,K.
Input units include A
1
-A
7
, Output unit includes
A
`
. Bring the data into the formula (2).
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, the establishment of logistics system
performance bases on evaluation index system.
Propose the method DEA-AHP. Firstly, use AHP to
assessment the weights of the indicators of the
performance. Secondly, use DEA to calculate the
relative efficiency of indicators for each level of the
system. Last, sort the weight of each index and the
relative efficiency of the logistics system. The
method combines well the advantages of DEA and
AHP. Make up the problem of DEA method which
can not consider the preferences of decision maker,
and the problem of AHP is too subjective. Further
analysis of the results of evaluation of each program
can be obtained and the corresponding improvement
of weak links in each program.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Our thanks go to everyone who supported our work,
and who provided us lots of material. We also thank
the team members from the company who sponsored
this work, whose support is greatly appreciated.
REFERENCES
Cooper, W.W., Seiford, L.M., Zhu, J., 2004. Data
envelopment analysis: History, models and
interpretations. In: Cooper, L.M., Seiford, L.M., Zhu,
J. (Eds.), Handbook on Data Envelopment Analysis.
Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp. 1–39.
Cooper, W.W., Seiford, L.M., Tone, T., 2006.
Introduction to Data Envelopment Analysis and Its
Uses: With DEA-Solver Software and References.
Springer, New York.
Chang qi, Yun Jun, 2009, Theoretical Issues About
Constructing an Emergency Logistics Management
System for Natural Disasters, Journal of wuhan
university of technology, 18-22.
Chen Chang-bin , Miu Li-xin, 2009, An Analysis of
Supply — chain Classification, vulnerability and
Management Method, business economy, 98-101.
Førsund, F.R., Sarafoglou, N., 2002. On the origins of data
envelopment analysis. Journal of Productivity
Analysis 17, 23–40.
Førsund, F.R., Sarafoglou, N., 2005. The tale of two
research communities: The diffusion of research on
productive efficiency. International Journal of
Production Economics 98, 17–40.
Fa¨re, R., Grosskopf, S., Lovell, C.A.K., 1994b.
Production frontiers. Cambridge University Press,
Cambridge.
Gan ming, Wang feng, 2010, Performance Evaluation of
Emergency Logistics Based On Fuzzy Oustermg
Algorithm, Logistics technology, 75-77.
Hilary Cheng, Yi-Chuan Lu, Jen-Tsung Chung, 2010,
Improved slack-based context-dependent DEA–A
study of international tourist hotels in Taiwan, Expert
systems with applications, 6452-6458.
Liu sin, Zhao qingzhen, 2009, DEA based AHP analysis
on emergency logistics distribution destination
selection, Logistics sci-tech, 32-48.
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF EMERGENCY LOGISTICS BASED ON DEA-AHP ALGORITHM
531

Linet Ozdamamr, Ediz Ekinci, 2004, Emergency Logistics
Planning in Natural Disaster, Annals of Operation
Research, 217-245.
Li zhongcai, Li lihong, 2007, The Study on Choosing the
Supplier Based on the Methods of DEA/AHP,
Logistics sci-tech, 165-168.
P.Zhou, B.W.Ang,K.L.Poh, 2008, A survey of data
envelopment analysis in energy and environmental
studies, European journal of operational research, 1-
18.
Qu Long, Li Shuqing,Feng Shaohai,2010, Performance
Evaluation Method of Emergency Logistics Based on
Fuzzy Mathematics, Computer and communication,
65-68.
Ramanathan, R., 2003. An Introduction to Data
Envelopment Analysis: A Tool for Performance
Measurement. Sage Pub lications, New Delhi.
R. Eglin, 2003, Can suppliers bring down your firm?
Sunday Times (London), appointments sec., p. 6.
Seiford, L.M., Thrall, R.M., 1990. Recent developments in
DEA: The mathematical programming approach to
frontier analysis. Journal of Econometrics 46, 7–38.
Scott C. Ellis, Raymond M. Henry, Jeff Shockley, 2009,
Buyer perceptions of supply disruption risk: A
behavioural view and empirical assessment, Journal of
Operations Management 28, 34-36.
Song xiaoyu, Liu chunguang, 2010 , Gray programming
model for emergency material dispatch, Application
research of computers ,1259-1262.
Wu anji, 2010, Bring into Full Play the Main Role of
Logistic Parking in Emergency Logistic Operation
Systems, Logistics engineering and management, 88-
89.
Wang xuping, Fu kejun, 2005, Research on emergency
logistics system and its emergent response mechanism,
China soft science, 127-131.
Wu qi, Wu Chunyou, 2009, Research on Evaluation
Model of Energy Efficiency Based on DEA, Journal of
management sciences, 103-112.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
532
