
STUDY OF INFORMATION SHARING PLATFORM
IN ECO-SUPPLY CHAIN
Qinlan Tian and Xuedong Chen
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Ecological supply chain, Information sharing, Information interaction, Information sharing platform,
Algorithm.
Abstract: Based on the importance of effective information sharing in ecological supply chain, we build a logical
model of information sharing platform in eco-supply chain. After that, we expound the information sharing
mechanism and the ecological supply chain information interaction of the platform. At the same time, in
order to realize the ecological effects in the ecological supply chain, we put forward the ecological detection
algorithms of information shared and the logistics optimization algorithms of vehicle route arrangement.
1 INTRODUCTION
It is easy to produce the “bullwhip effect" of demand
enlargement, because the enterprises are unable to
realize effective information sharing in the supply
chain. However, this increases the production,
supply, inventory management and marketing risk of
the upstream suppliers, and even causes the chaos of
production, supply and marketing in the ecological
supply chain.
In addition, the demand information's
enlargement makes the production of the products
on the entire supply chain be increased exponentially
from the ecological perspective. The production of
the mass products is necessarily to consume large
amounts of water, coal, electricity and raw materials,
etc
(Wensheng, 2010). As a result, a lot of gas
pollutants would be discharged to the environment.
The production process not only wastes resources
but also causes environment damage. But, the tenet
of ecological supply chain is to make the
consumption of resources and the negative effects of
the ecological environment to the minimum. Thus,
effective information sharing is very important in the
ecological supply, and so, it is necessary to research
the information sharing platform in ecological
supply chain from the perspective of information
process.
2 STUDY OF INFORMATION
SHARING PLATFORM IN ECO-
SUPPLY CHAIN
As is mentioned above, information sharing in
ecological supply chain has very important
significance. So it is necessary for us to study how to
realize information sharing in the ecological supply
chain. In our general view, there are two kinds of
information participants in ecological supply chain.
One is the information providers. The other is the
information demanders. The realization mechanism
of sharing information is as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Realization mechanism of information sharing in
ecological supply chain.
432
Tian Q. and Chen X..
STUDY OF INFORMATION SHARING PLATFORM IN ECO-SUPPLY CHAIN .
DOI: 10.5220/0003590704320437
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (KMKSSC-2011), pages 432-437
ISBN: 978-989-8425-54-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
2.1 The Construction of Information
Sharing Platform in Ecological
Supply Chain
In fact, the information providers in the ecological
supply chain include supplier, producers, sellers,
logistics providers, government agencies.
Meanwhile, each provider is also a demander.
Therefore, for many participants, we should consider
to build an information sharing platform in
ecological supply chain to realize the above way of
information sharing.
Enterprises in supply chain set up information
platform to share information cooperate. The
construction of information sharing platform is
invested by each member enterprise in the supply
chain. At the same time, the government department
is responsible for coordination, supervision and
control. The information sharing platform in
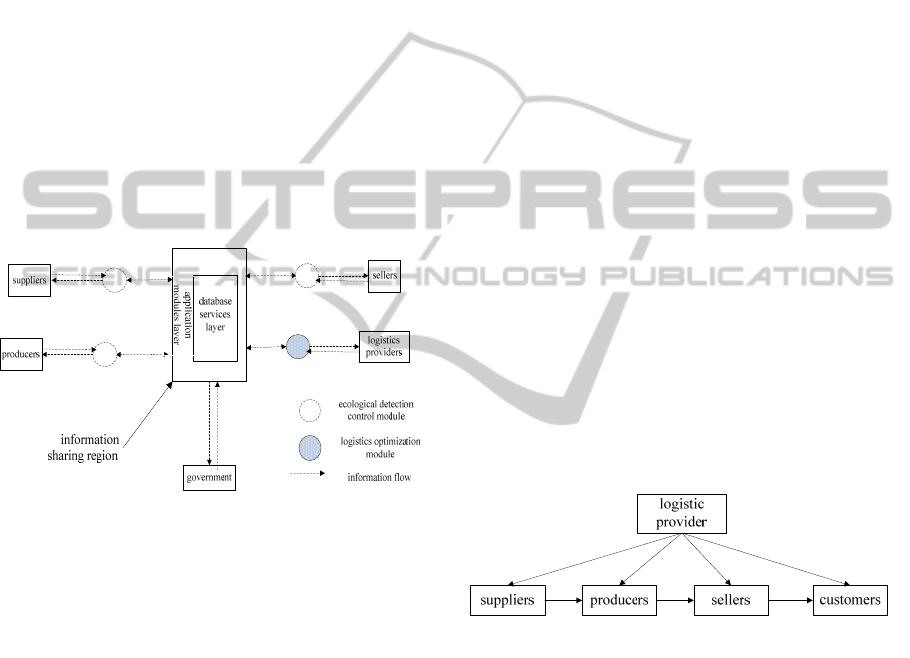
ecological supply chain follows Figure 2.
Figure 2: Information sharing platform in ecological
supply chain.
2.2 The Illustration of Information
Sharing Platform in Ecological
Supply Chain
The participants of the platform are suppliers,
producers, sellers (retailers and distributors
collectively), logistics providers, and government
departments. With customer's products as the core,
they form a net chain structure, in which the
suppliers are mainly responsible for raw material
purchase, the producers are responsible for the
product production and manufacturing, sellers are
responsible for product sales, logistics providers are
in charge of the whole supply chain transportation.
They have formed upstream and downstream
relations which is shown in the below Figure 3. Each
participant is given certain privileges and provided
an interface to get into the platform. The platform is
made of four layers. They are customer layer,
control layer, application layer, and the database
service layer. The customer layer provides each
node enterprises an interface for registration. The
control layer comprises some modules including
logistics optimization and ecological detection
modules. The application layer manages the shared
information. While the database service layer
provides data support for the operation of whole
platform. The whole platform is based on the
Internet. So, the participants can obtain and send
relevant information after they login in the platform.
Each node enterprise should share information
which has been detected by ecological detection
module to this platform except the government
departments and logistics providers. The ecological
detection modules are used to detect whether the
information shared to the platform conforms to the
ecological requirements. Each ecological detection
module includes some different detection
algorithms. The enterprises in the same role
correspond to the same ecological detection module,
while enterprises in different roles correspond to
different ecological detection module, because the
information shared by them need to detect different
kinds of ecological indices. For example, the
detection control module of producers is more
concerned about the recycling and utilization rate of
waste, the utilization rate of raw materials and so on.
But the detection control module of suppliers is
more concerned about the recycling and utilization
rate of purchasing materials.
Figure 3: The upstream and downstream relations in the
supply chain.
2.3 Information Interaction in
Ecological Supply Chain
Information Sharing Platform
The information shared in ecological supply chain
not only includes the information of the traditional
supply chain, but also the ecological information of
each enterprise and the government's eco-policy
information. The convenient, timely, accurate
information interaction among enterprises in
ecological supply chain improves each other’s
operation efficiency. Information interaction among
enterprises in ecological supply chain is as follows.
STUDY OF INFORMATION SHARING PLATFORM IN ECO-SUPPLY CHAIN
433

2.3.1 The Information Interaction of
Government
The information shared among government
department and other node enterprises consists of
related environmental protection laws and
regulations, environmental protection policy and
environmental protection practice achievement of
the enterprises. The government will provide the
latest environment evaluation indices standard to the
platform at any time, such as energy utilization rate
index, equipment and material utilization rate index,
recycling index of waste, etc. Meanwhile, the
government departments share ecological
information of other enterprises from the platform,
such as the amount of waste recycling, the utilization
rate of energy, emissions intensity of waste gas, etc.
This behavior is necessary for the enterprise and
government to understand the present reverse
logistics in supply chain promptly. So, they can
identify problems timely and modulate the operation
procedure in ecological supply chain to promote
waste recycling utilization effectively.
2.3.2 The Information Interaction of
Suppliers
The information flow of suppliers mainly includes
information that suppliers share with other node
enterprises. The suppliers provide materials demand
and supply information for logistics providers. The
suppliers provide quality, order of producers, order
implementation, products and technology
improvement information for producers. The
suppliers provide various ecological indices
information for supply chain platform. Meanwhile,
suppliers obtain from the platform producers’
demand, inventory, production planning
information, etc. They also receive feedback
information of its ecological information. Then they
adjust their production ways of products to accord
with ecological requirements according to the
feedback information timely. So, they can control
ecological level of the whole supply chain from the
source.
2.3.3 The Information Interaction of
Producers
Producers have a direct link with suppliers, sellers,
logistics service providers from. Producers provide
the material information needed by the future
production cycle, real-time updating inventory
information and production planning information for
the suppliers. To ensure the enterprises of the supply
chain develop coordinately, producers are also
required to share the new product’s development
information with the suppliers, which includes new
craft, new technology and new material information.
The producers share sellers with the product ,order
and order executive information. They also share the
goods supply information with the logistics
providers. At last, they send out kinds of ecological
indices information to ecological supply chain
platform. Meanwhile, the producers can obtain
information shared form other node enterprises in
the platform. After receiving the feedback
information, the producers adjust their production
ways of products to conform to ecological
manufacturing, such as craft, design, packaging, etc.
2.3.4 The Information Interaction of Sellers
Aiming at reducing supply chain cost and preventing
upstream enterprise from overstocking products,
sellers should share theirs inventory information
with suppliers, so that the suppliers can organize
flexible production, especially when the uncertainty
brought by demand fluctuation and occasional
glitches in production and transportation is evitable ,
sharing the inventory information is particularly
important. At the same time, sellers would also share
logistics demand information. Just like other role of
member enterprises, the sellers also share kinds of
ecological indices information to ecological supply
chain platform and receive information from the
platform. Based on the feedback information from
the platform, the sellers try their best to achieve
ecological marketing standard.
2.3.5 The Information Interaction of
Logistics Providers
The information flow is composed by the
information the logistics providers send to the
platform and prepare to share with other members of
eco-supply chain, such as the optimal route schemes,
logistics route, vehicles information, etc. The
logistics providers are the important link in the
entire eco-supply chain, because the logistics
providers are responsible for the material, product
transportation and the feedback of order information
of the entire supply chain. If it is necessary, the
logistics providers will keep certain inventory for the
producers. At last, Logistics providers also share
kinds of ecological indices information to ecological
supply chain platform.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
434

3 THE ALGORITHM RESEARCH
OF INFORMATION SHARING
PLATFORM IN ECOLOGICAL
SUPPLY CHAIN
The ecological detection modules comprise some
different ecological detection algorithms and the
logistics optimization module consists of some route
optimization algorithms in the platform. The
platform can maintain its ecological characteristics
because of these modules that play a control
function. In the following, we choose two algorithms
of these modules to explain the control process.
3.1 Logistics Optimization Algorithm
of Vehicle Route Arrangement
Ecological supply chain means that we would take
advanced logistics technology to reduce
environment pollution and resources consumption
caused by logistics and that we should make the
processes of logistics activities and environmental
protection coordinate and unified in promoting the
development of economy, under the guidance of the
sustainable development concept (Hock, 1999).
After the ecological supply chain information
sharing platform is established, logistics providers
can make a comprehensive consideration of logistics
service request in the supply chain. Then, they could
find the optimal logistics arrangement strategy to
minimize the logistics cost and reduce the
environment damage caused by logistics process by
means of the logistics optimization module.
3.1.1 Algorithm Statement
The optimization problems of logistics distribution
vehicle route are called Vehicle Routing Problem,
which is called VPR for short abroad. The classical
Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) involves a set of
delivery customers to be serviced by a homogeneous
fleet of vehicles housed at a central depot. The
objective of the problem is to develop a set of
vehicle routes originating and terminating at the
depot such that all customers are serviced, the
demands of the customers assigned to each route do
not exceed the capacity of the vehicle that services
the route, and the total distance traveled by all
vehicles is minimized (Jun and Yaohuang, 2001). In
this paper we consider an easy optimization
algorithm with constraints of vehicle capacity, the
distance between each two demanders and the
demanders’ goods weight in the logistics
optimization module.
3.1.2 Description and Flow Charts of the
Algorithm
With the delivery of directly round trip used by all
demanders as the initial feasible arrangements, the
algorithm is designed to find the two demanders of
the largest savings:
① connecting the two demanders when their
total freight volumes are no more than the volumes
of the vehicle's load carrying ability; adding the
demander of the largest savings ,when connecting
with the former two demanders, to the line until the
total amounts of the freights in the line equal or
surpass the limit of the vehicle load, then adding the
final demander when the sum of its demand and the
previously total freight volumes surpasses the limit
of the vehicle. The line generated through the
method above ensures that the freight volumes
provided for the demanders just equal the vehicles'
full load.
② connecting the two demanders when their
total freight volumes is equal to the volumes of the
vehicle's load carrying ability;
③ connecting the two demanders when their
total freight volumes surpass the volumes of the
vehicle's load carrying ability, which ensures the
vehicle fully loaded. Then the remaining demanders
and the distributing vectors are organized into a new
distribution route planning; the results of the
solution by adopting the above method repeatedly
until all the possible demanders are connected
completely will be the optimal solution.
The flowchart of optimization algorithm in
vehicle routing is as shown in the following Figure
4.
3.1.3 Algorithm Examples
As the following, the table 1 gives the shipments of
each logistics demander and the table 2 gives the
distance between logistics provider and demanders.
Here, we assume the capacity of the vehicles is 1.
LP-- logistics provider, D — demanders.
Table 1: Shipments of each logistics demander.
LP 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
freight 0.3 0.35 0.3 0.2 0.6 0.3 0.5 0.4
STUDY OF INFORMATION SHARING PLATFORM IN ECO-SUPPLY CHAIN
435

Figure 4: The flowchart of optimization algorithm (Xuezhi
and Gongyu, 2008).
Table 2: Distance between logistics provider and
demanders.
LP
D1 9 D1
D2 14 5 D2
D3 21 12 7 D3
D4 23 22 17 10 D4
D5 32 31 26 27 25 D5
D6 40 41 36 31 29 10 D6
D7 50 49 44 37 31 18 8 D7
D8 52 51 46 39 29 20 10 10 D8
We take the delivery of directly round trip used
by all demanders as the initial feasible arrangement.
As a result, we need eight vehicles and the total
transportation distance is 486. If the logistics
optimization algorithm is used to optimize the
transportation, the final route arrangement is like
this: R1=(0 1 2 3 0); R2= (0 4 5 6 0); R3=(0 6 7 8 0).
Taking logistics optimization algorithm, we only
need 3 vehicles for the distribution and the total
transportation distance is 257.
3.2 Ecological Detection Algorithm of
Sharing Information
As is mentioned above, the information shared to the
platform from the enterprises in different roles
should be detected by ecological detection module.
In the following, we take a simple specific example
to illustrate the ecological detection process.
3.2.1 Algorithm Statement
The ecological detection algorithms are designed to
keep the platform ecological. And different kinds of
information from different roles of the platform
correspond to different ecological detection
algorithms. Although the ecological detection
algorithms are different, the design ideas of them are
the same. The following algorithm is based on the
customer order information shared by the sellers of
the auto industry.
3.2.2 Description and Flow Charts of the
Algorithm
The sellers register the platform through the
platform’s interface. After that they send out the
information they want to share with other
enterprises. Before the information goes into the
platform, it must to be tested by the ecological
detection module. The ecological detection module
detects whether the customer order information
shared complies with the ecological standard,
referring to the latest policies issued by government.
If it complies with the ecological indices it will go
into the information sharing region of platform
directly. If it does not conform to ecological indices,
first, the ecological detection module will send the
detection result to sellers and ask them to take some
improvement measures; second, the module send the
information to the information sharing region.
The flowchart of ecological detection algorithms
about customer order information shared is as shown
in the following Figure 5..
4 CONCLUSIONS
The information shared in the ecological supply
chain not only involves the information shared in the
traditional supply chain, but also ecological
information. In order to realize the effective
information transfer and sharing, we consider
building ecological supply chain information sharing
platform. Compared with the traditional supply
chain information sharing platform, we add some
control modules that contain some different
algorithms, in order to guarantee the information
shared ecological. Different roles in the platform
send different kinds of information to the platform,
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
436

Figure 5: flowchart of ecological detection algorithms
all of which need to be detected. So, there should be
a lot of algorithms. This needs our further study.
REFERENCES
Hou Wensheng. The Research of Information Sharing
Degree in the Regional Ecological Supply Chain [J].
Beijing Jiaotong University. 2010.
Hock. From reversed Logistics to Green Supply Chain [J].
Supply Chain Management, 1999, 4(3):129-134.
Li Jun, Guo Yaohuang. Logistics distribution vehicles
optimized scheduling theory and method [M]. Beijing:
China materials press, 2001.
Zhang Xuezhi, Chen Gongyu. An Improved Saving
Method of the Vehicle Routing Problem [J]. Systems
Engineering, 2008 (11):68-70.
STUDY OF INFORMATION SHARING PLATFORM IN ECO-SUPPLY CHAIN
437
