
THE OPTIMIZATION OF ROAD NETWORK IN LOGISTICS
HUB BASED ON LOW-CARBON ASPECT
Yisong Li and Mengna Lai
Beijing Jiaotong University, Haidian District, Beijing, China
Keywords: Low carbon, Logistics Hub, Road network.
Abstract: Carbon emission is becoming a more and more popular issue recently. It is important to design a reasonable
road network within logistics hub to reduce the whole carbon emissions. Previous studies have targeted as
maximum economics benefits or least time consumed, which ignored the environmental effects. This paper
uses the model of minimum cost maximum flow to optimize the road network, in the model, “cost” is
defined as carbon emissions, so we can finally achieve the goal, then classify the type of road according to
the capacity, the decreasing order is trunk road, secondary road and slip road. The above classification can
help with arranging transportation and guiding the traffic flow. The paper lists the specific optimal plan to
the logistics hub in Luan County. However the factors concluded in the model is not adequate, we should
consider the factor of road length, and it is also a factor affected carbon emission.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the development of the logistics industry in
China, the domestic Logistics Hus are expanded, the
number is increasing to about 600 recently.
According to related data, the CO
2
emission during
transportation is accounted for 40% of the whole
logistics process. Apparently the main reason which
leads into carbon pollution in Logistics Hub is
transportation. Some studies show that CO
2
emissions is related to traffic volume, road
congestion, and therefore a reasonable layout of
Logistics Hub are helpful to reduce carbon
emissions, such as controlling the traffic volume in
trunk road and improving the road condition.
The design of the Logistics Hub network include
choosing the form of road network, planning red
line(the direction and location of trunk road and
secondary roads and the functional division of
them),green belts and road node planning. Previous
studies are aimed at the minimum of the total cost of
the transportation or the shortest transit time, but
environmental issues is not taking into
consideration, for instance, total carbon emissions.
This paper is to improve road network then increase
the efficiency of trunk road and realize the low
carbon transportation in the Logistics Hub, and
finally reduce total carbon emissions.
The procedure of road network in Logistics Hub
are as follows: 1, Forecasting the main logistics
volume and the road capacity, then translate the
logistic capacity into traffic volume. 2, Select the
entrance of the Logistics Hub from the railway
entrance, highway entrance, link entrance and other
locations around the Logistics Hub which
accumulate cargo flow. Then optimize road network
within them. 3, Using EcoTransIT tool to calculate
the volume of carbon emissions of each unit distance
and weight, with the minimum cost maximum flow
model to optimize the road network, the specific
process are as follows:
Figure 1: The steps of optimizing road network.
2 THE LOGISTICS HUB
NETWORK OPTIMIZATION
FACTOR ANALYSIS AND
MODEL SELECTION
Logistics Hub road network is composed of different
666
Li Y. and Lai M..
THE OPTIMIZATION OF ROAD NETWORK IN LOGISTICS HUB BASED ON LOW-CARBON ASPECT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003594406660670
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (MMLM-2011), pages 666-670
ISBN: 978-989-8425-56-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

levels of city roads and railways. The road network
planning should determine the form of road network;
then determine the nature of roads, width, the form
of road cross section, the location of intersection and
the parking lots and the receipt of road network
maps. The current form of the existing road system
can be summarized into four main types: grid-type,
ring radial, freestyle, and hybrid. Then use model to
plan direction and capacity of roads which make the
overall road network release less emissions.
Optimization methods of road network are
consisted of four-stage method, the total control
method and graph theory method. They are mostly
targeted as maximum economic benefits and least
time consumed, they distributes the predicted traffic
flow to the road after considering these factors,
which are the layout of road network, traffic flow in
the direction and distribution of goods. Further,
according to the amount of traffic flow to determine
technical level, the direction of the selected roads,
extension angle and optimal points to the line.
However, the above methodologies ignore the
environmental effects. Carbon emissions are related
to traffic volume and road resistance coefficient,
while considering carbon emission, there are
four-stage method and graph theory method can be
selected.
Four-stage method is based on investigation, and
then predicts the future distribution at the base of
traffic condition. The basic steps are traffic
generation, traffic distribution, traffic model
selected, traffic assignment. We can gain some
parameters about cargo flow through investigation.
But it is difficult to implement, it will cost a lot of
manpower, material and financial resources, so the
minimum cost maximum flow is practical to
optimize the road network. The so-called minimum
cost maximum flow problem is to find a maximum
flow f; simultaneously the total cost is minimum.
Studying this problem is trying to find out: In order
to achieve minimum cost, how to choose the path
and assign traffic flow from A to B. The meaning of
cost can be defined as carbon emissions in this
model.
3 THE ESTABLISHMENT OF
THE OPTIMIZE MODEL OF
ROAD NETWORK IN
LOGISTICS HUB
3.1 The Establishment Mind
While the initial road network planning is finished,
then we can use EcoTransIT tool to obtain carbon
emissions’ weight, as we get the parameters about
the minimum cost maximum flow, the road network
can be optimized. Network planning is to reach the
minimum carbon emissions based on meeting
logistics requirements and rational distribution
network. At the condition of knowing the total
demand in a cycle, the permitted maximum capacity
of each road, and carbon emissions of unit weight on
different road type, we can determine which can be
used as the trunk roads, secondary roads and slip
roads for two random entrances of Logistics Hub.
3.2 Mathematical Model
If f whose flow is v(f) is the minimum cost flow of
all feasible flow, and u is the smallest-cost
augmented chain of all the augmented chain
contained f, then adjust f along u, we will get f’,
which is the minimum cost flow of all the feasible
flow. Thus, when f’ is the maximum flow, it is what
required minimum cost maximum flow.
As b
≥0, so f=0 must be the minimum cost
flow whose flow is 0. This always starts from f=0.
Generally, it also sets f is the minimum cost flow,
and its flow is v (f), the remaining problem is how to
find the augmented chain of minimum cost about f.
So we can construct a weighted diagraph w(f), its
vertices are vertices of the original network D, and
change arc included in D into two arcs in opposite
directions (vi,vj) and (vj,vi). We define the
weights of arcs in the w (f) as:
Wij=
b
,
<
+∞,
=
(1)
W
=
−b
,
>0
+∞,
=0
(2)
So seek the minimum cost flow in network D is
equivalent to find the shortest paths in the weighted
diagraph. Therefore, the following algorithm is:
Firstly, it can setf
(
0
)
=0, if at the (k-1) step we
get the minimum cost flowf(k − 1), then construct a
THE OPTIMIZATION OF ROAD NETWORK IN LOGISTICS HUB BASED ON LOW-CARBON ASPECT
667

weighted diagraph W(f(k − 1), and seek the shortest
paths in W(f(k − 1)). If the shortest paths are not
existed, and then f(k − 1) is the minimum cost
maximum flow; if existed, we can get corresponding
augmented chain u, and adjust f(k − 1) on u, the
adjusted volume is:
() ()
11
= min min min
kk
ij ij ij
uu
cf f
+−
−−
⎧⎫
⎛⎞⎛⎞
⎪⎪
θ−⏐
⎨⎬
⎜⎟⎜⎟
⎪⎪
⎝⎠⎝⎠
⎩⎭
F
(
)
=
f
(
)
+
θ
v
v
∈u
f
(
)
−
θ
v
v
∈u
f
(
)
v
v
∉ u
(3)
We get new feasible flow, and then repeat the
above steps.
Then use EcoTransIT (Ecological Transport
Information) tools to predict the relevant index, and
calculate carbon emission of the unit mile and
weight in different types of road. The tool is
developed by Heidelberg’s energy and
environmental agencies and Cink Company, if we
input related data in the software, we can obtain the
amount of total energy consumption which include
production and transportation, and gas emissions
including CO
2
, NO
X
and SO
2
NMHC, and PM10
and so on.
The tool mentioned the road resistance
coefficient of different road levels; it can be
recognized as the carbon emissions standards.
Table 1: Related index about model.
The trunk
road
Secondary
road
Slip road Rail
way
road
resistance
coefficient
3 4 5 2
Traffic
volume per
day
6000~10000 4500~8000 2500~5500 10000
Unit carbon
emission
index
3 4 5 2
Capacity
index
11 5 2 25
Therefore, the specific model is as follows:
Object: making the maximum road network flow
and minimum carbon emissions on transportation.
Constraints:
The capacity of each arc is greater than the total
amount of logistics.
The traffic volume on each arc is less than the
road capacity.
Related variables:
Total logistics cycle Q,
Capacity and flow of each road are C
and f
.
Carbon emissions of unit mile and weight are b
.
The functions are:
MinZ=bij ∗ ij
(4)
Constraints: (1)
∑
ij≥Q;
(2) ij≤Cij .
Figure 2: The model of minimum cost maximum flow.
2 CASE STUDY
We take example about Luan county’s Logistics
Hub planning, then show the procedure of
optimizing road network. Luan County is 260 km
west from Beijing, 84 km east from Qinhuangdao,
adjacent to northeast old industrial base in the north,
access to Cao Feidian National industrial Park. From
the point of location, Luan city is in the development
area of Beijing, Tianjin, it has close relationship
with the main cities, and also inseparable from
Tangshan industrial equipment manufacturing base,
it is the only way which connected Northeast
Economic Zone and North Economic Zone. It is
Datong-Qinhuangdao railway that makes it through
the western region, Luan county becomes an
important transit node.
Luan county has a superior transportation, there
are totally about 6 railways travel through it, and
locates about 11 rail way stations .102 State Road,
State Road 205, Provincial Road S 252 and
Beijing-Shenyang Expressway runs through the
county (Figure 3). Luan county connects with
Tianjin port and Qinhuangdao port and Jing Tang
port and other port by railway or highways, so
shipping is very convenient. While choosing Luan
County as a logistics transit point, it can display the
advantage of transportation, reduce regional logistics
costs and improve the efficiency of regional logistics
and promote regional development of related
industries.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
668
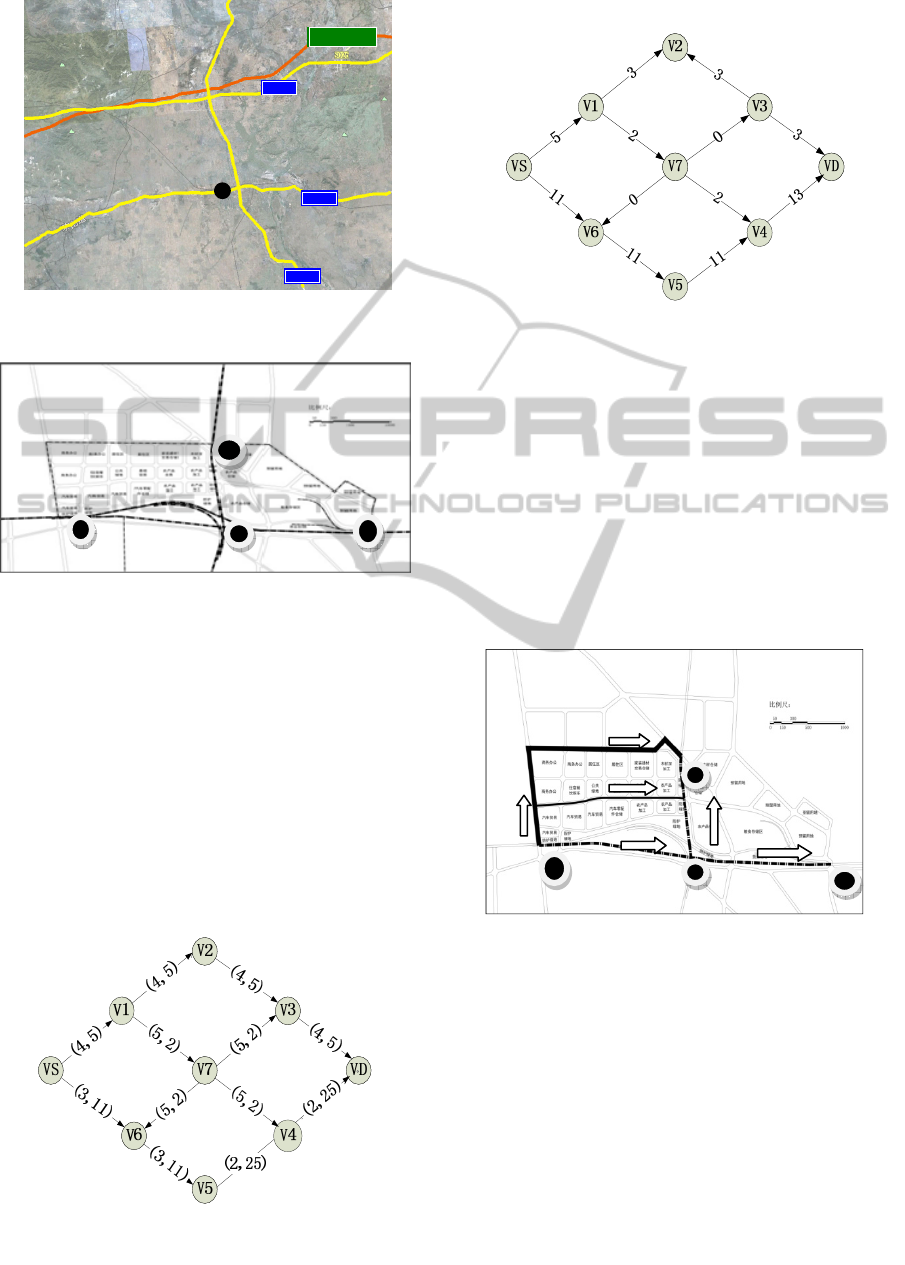
Figure 3: Traffic map in Luan County.
Figure 4: Initial road network in Logistics Hub.
According to the traffic condition of Luan
County, We set four logistics nodes. They are node 1,
node 2, node 3 and 4 from top to bottom and left to
right. Generally, the nodes locate in the point of
large amount of traffic flow, so the nodes are in the
junction of railway and state road or the junction of
state road and provincial road.
Node 1 and Node 4 are regarded as the entrance;
node 2 and node 3 are regarded as exports. We set
node 1 and node 2 as OD points, there are following
path, the weights and capacity index are given in
table 1. The initial paths are:
Figure 5: The initial paths.
The flow after adjusted are:
Figure 6: The traffic flow in different kind of road after
adjusted.
As the figure shows, the path V
S
—>V
6
—>V
5
—>V
4
—>V
D
has the largest amount of traffic flow,
so we set it as the trunk road.
The path V
S
—>V
1
—>V
2
—>V
3
—>V
D
has the
traffic volume. So it can be used as secondary roads.
The smallest traffic volume is V
S
—>V
1
—>V
7
—>V
4
—>V
D
, so it is the slip road.
Then we can choose every two nodes in the
Logistics Hub to plan the grade of road, finally
optimize the whole network, the planning chart is:
Figure 7: Schematic diagram of optimized network.
The two thickest arrows are represented the trunk
road, the three dotted arrows are represented
secondary road; the thin arrow in the middle are
represented slip road. And the affiliated hollow
arrows are the direction of them.
5 CONCLUSIONS
With the intensification of the greenhouse effect,
carbon dioxide emissions reduction is increasingly
G102
G205
S252
京沈高速公路
滦县
THE OPTIMIZATION OF ROAD NETWORK IN LOGISTICS HUB BASED ON LOW-CARBON ASPECT
669

becoming the focus of activities related to
warehouse, transportation, distribution, information
process and other process of logistics. Each process
will have carbon emissions, but transportation is
main factor, so the most important thing is how to
optimize the road network to achieve minimum
carbon emissions, this paper use minimum cost
maximum flow model to optimize the road network,
then define road grade and guide traffic. This paper
takes Luan County for example, using simulated
data which is deduced by EcoTransIT tool to
optimize the existing network, in order to make the
Logistics Hub’s carbon emissions reduced. But the
model is just take the factor of carbon emissions and
traffic volume into consideration, carbon emission is
also related with the length of road, how to combine
them is to be solved.
REFERENCES
Mo Yi Kui, Yan Kefei, Chengfeng. The study of
optimization urban mixed network based on genetic
algorithm [J]. Computer Engineering and Applications,
2007, 43(14):240~243.
XuDunchu. City road and traffic planning [M]. Beijing:
China Building Industry Press, 2007.
Fan Decheng, WangTingjian. The analysis of current
situation and problems in construction of Logistics
Hub [J]. Technology of Logistics, 2004, 28(113).
Lianye, ChenDapeng, Wangzhiyun. The road network
planning of circular economy industrial park based on
logistics optimization [J]. Chemical Industry, 2009,
(11).
Li Hongbing, Sun Zhiyuan, GeXijun. Traffic impact
analysis of urban Logistics Hub based on S-Paramics
micro-simulation technology [J]. Technology of
logistics, 2009, 28(4).
Gaofei, Zhangbaoyu, Luoligao.The application of DEA in
the development of road network [J]. Shanxi
Architecture, 2010, 36(13).
Liu Shiduo, Wu Qunqi. The availably study of road
network which based on the transport demand [J].
Learned journal of Chang’an University, 2010, 12(1).
Dai Yue, Lu jian.The study of prediction of traffic flow in
Logistics Hub [J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2008, 4(36).
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
670
