
STUDY ON THE EVOLUTION MECHANISMS OF THE
NETWORK PUBLIC OPINION
Honglu Liu and Zhihong Tian
Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Network public opinion, Public opinion evolution, Formation mechanism.
Abstract: Research on the formation and evolution mechanisms of network public opinion has become a very
meaningful field. Network public opinion and traditional public opinion have some similarities, but network
public opinion also has its own independent "will" and evolution which are rooted in its technical specificity.
Based on the life cycle theory, we analyze the formation path of network public opinion, and discuss its
formation mechanism. After that, we analyze the evolution mechanisms of network public opinion,
including the evolution direction mechanism of topics and mutation mechanism of network public opinion.
1 INTRODUCTION
At present, people express their views and exchange
ideas through the network, and the network media is
increasingly becoming an important social
phenomenon in China. Research on the formation
and evolution mechanisms of network public
opinion has become a very meaningful field. From a
technical perspective, the ways of human
communication are five: spoken communication,
written communication, print communication,
electronic communication and network
communication. Especially because of the network
communication, the human society has entered the
"network free communication era" from the
"original free communication era" and "gatekeeper
communication". The main features of the
communication technology are as follows: digital
transmission, network structure, multimedia
communication, interactive communication, multi
communication and global communication, and so
on. Characteristics of the interpersonal
communication are based on the technical features
of the communication. The characteristics are free,
equal, interactive, real-time, anonymous, and so on.
These features lead directly to the formation and
evolution mechanisms which are different from
network media and traditional media. Therefore,
when we are studying the network public opinion, it
is necessary to inherit the experience in the field of
traditional communication, and analyze carefully
new changes which are brought by new technologies
and new models.
2 THE FORMATION
MECHANISM OF NETWORK
PUBLIC OPINION
Public opinion is the common view of people on
recent incidents and social issues. Network public
opinion can be simply understood as the common
opinion of groups on a particular event on the
Internet. Network public opinion includes two parts.
The first one is "network news media" which is the
tendency of public opinion in the network news
media. The second one is "netizens’ views of public
opinion" which can be presented at the platform
BBS, blog, a variety of websites and online
communities.
The prerequisites for the formation of network
public opinion consist of two factors: the emergence
and the survival of topics. There are very flexible
ways for the emergence of topics, including the
original post and paste post. The original post is
published to reflect the social phenomenon or event
by forum members. However, for various reasons,
the first original post might be ignored or drowned
in the other competitive issues. Some popular topics
are rewritten, enrich, modify and recommend by
other forum users which may be called a secondary
or even multi-level communication process. A paste
444
Liu H. and Tian Z..
STUDY ON THE EVOLUTION MECHANISMS OF THE NETWORK PUBLIC OPINION.
DOI: 10.5220/0003594504440448
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (EIT-2011), pages 444-448
ISBN: 978-989-8425-55-3
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
post generally includes an event or social
phenomenon from other original post or online news
reports. In such posts, the authors often express their
attitudes and emotions.
The survival of topics means that the relative
event is attended by people. In order to be attended
continually, the topic must accumulate sufficient
posts. We can view the issues as fire, and the
survival of the fire needs combustion-supporting
agent. In practice, because there are too many posts
on the forum, the vast majority of posts become
so-called "sinking the posts ".The fire extinguishes
after burning for a short time. The fire that may
sweep through the whole network is very little.
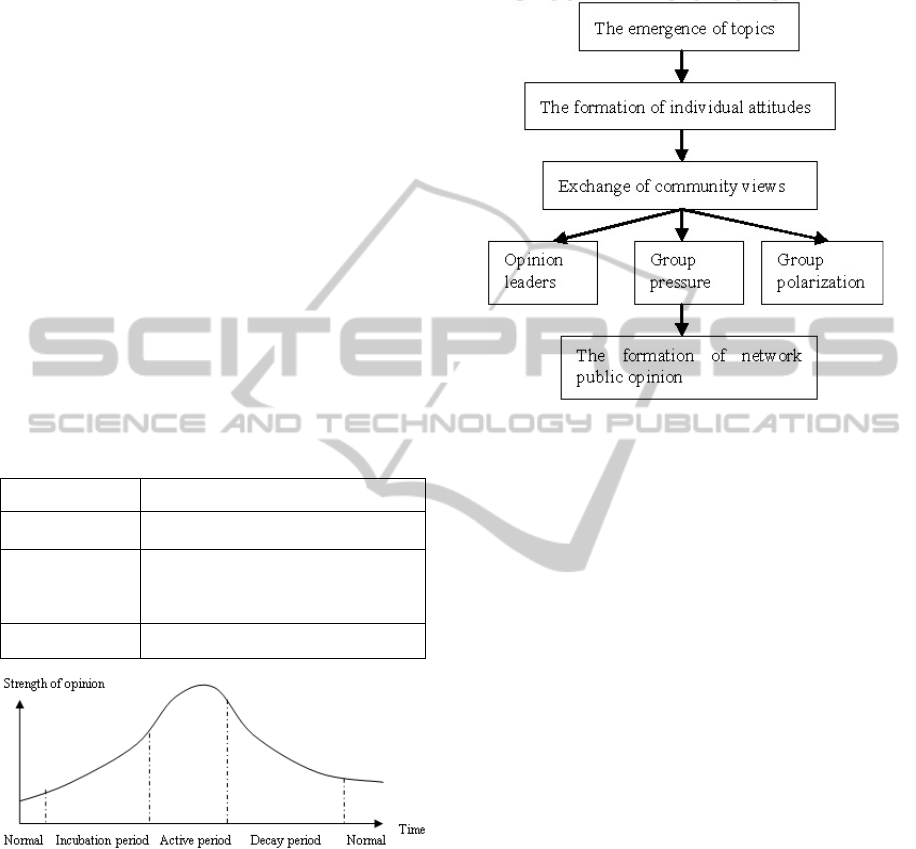
The life cycle of network public opinion
generally includes three stages-incubation period,
active period and decay period, which is shown in
Table 1 and Figure 1. When a large-scale discussion
of an event of individuals or groups formats, the
incubation period is over. The life cycle enters active
phase, which also marks that the public opinion will
gradually form in the specific environment.
Table 1: The life cycle of network public opinion.
The life cycle Status
Incubation period Attention slowly increases, the views
slowly gather
Active period Attention sharply increases,
All kinds of opinions emerge
After evolution, the mainstream opinion
has formatted
Decay period Attention reduces
Figure 1: The life cycle of network public opinion.
The formation path of network public opinion
passes through three phases—individual expression,
the collision of community views and formation of
the network public opinion, which is shown in
Figure 2. When topics appear and constant attention
of the individuals and the comments and attitudes
gradually accumulate in frequent interaction, one or
more opinion leaders. Several camps representing
different views emerge. There is polarization in the
camps. When the camp's size reaches a certain level,
it can be said that a network public opinion has
formed. We can see that, in the formation of network
public opinion, the opinion leaders, group pressure
and group polarization play very important roles.
Figure 2: The formation path of network public opinion.
2.1 The Mechanism of "Opinion
Leaders"
In the communication, the persons who are active in
the interpersonal communication networks, who
often provide information, opinions or suggestions
for others, and influent others are known as the
"opinion leaders ". In the traditional media era, mass
media takes of (or monopolies) the role of "opinion
leader". They guide and control the activities of
public opinion. In the Internet Age, due to the digital
communication network and star network
communication, and other special communication
technology, there is more freedom, equality and
interaction in network communication. Any Internet
users could become "opinion leaders ".
Internet opinion leaders emerge gradually from
participants in the process of exchange of views.
The basic properties of Internet opinion leaders are
the frequency of the debate, ability of debate, and
self-adhere.
2.2 The Role of Network Group
Pressure
There is a lot of previous research on how does
groups pressure influent on mood and attitude. In
1972, in the study of the relationship between public
opinion and mass communication, the German
scholar Neumann proposed a "spiral of silence"
STUDY ON THE EVOLUTION MECHANISMS OF THE NETWORK PUBLIC OPINION
445
hypothesis. She believes that the strength of public
opinion is from the nature of our society, from
draconian laws for the prohibited views and
behaviors, and from the individual fear of isolation
from others. People express favor when the voice of
favor is rising, and are silent when the voice is
falling.
Group norms can lead to the generation of group
pressure, thereby change the direction of network
public opinions. Group norms refer to considered
behavior expectations in specific group activities for
members, which is a standardized concept
established by a group. In Internet, there are also
norms to follow by net groups. These specifications
and guidelines have invisible binding for members
of groups. Only complying with group norms,
people can communicate smoothly with each other,
and people can be accepted and recognized.
Otherwise, people may be suppressed, marginalized
or even expulsed. Appropriate normative guidelines
can influence and control members, and can
effectively change their attitudes.
2.3 Group Polarization Mechanism
In 1961, the earliest group polarization is proposed
by Stoner who is from MIT. Through empirical
researches, he discovered as follows: In the group
decision-making situations, opinions or decisions of
individuals, are often influenced by inter-group
discussion, and consistent results produce which are
usually more adventure than the earlier ones of
individual. Stoner calls it risk shift. Risk shift was
eventually called group polarization by other
scholars, because they found that after a group
discussion the views or a decision of individuals
sometimes tend to one end of adventure, and in
some cases tend to the conservative end. Therefore,
group polarization is defined as: at the beginning,
there has been some bias of views in the team. After
discussion, views continue to move toward the
direction of bias, and finally an extreme view
format.
The phenomenon of group polarization is more
vulnerable for network public opinion. Internet users
who have the same interests will form virtual groups
on the network, and will have a strong group identity,
so it is prone to the polarization of views. Compared
to the face to face groups, the polarization of
network groups are more pronounced.
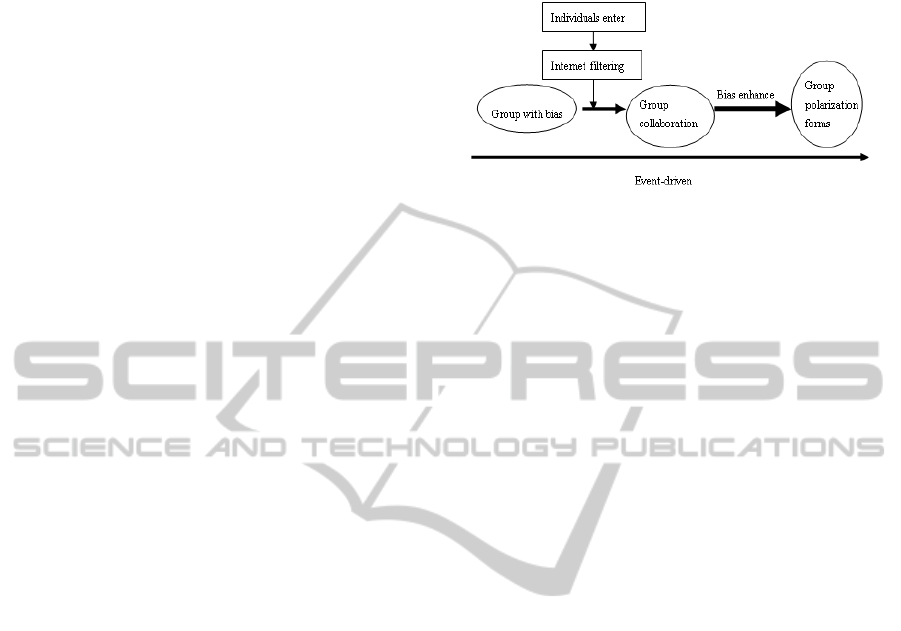
The factors that promote group polarization of
network public opinion include a number of aspects,
both the direct stimulation of public events, but also
the filtering effect of network media, but also from
the nature of coherence within groups. The process
of group polarization is shown as figure 3.
Figure 3: The process of group polarization.
1) Event-driven. In essence, events are the basis
and momentum of group polarization of network
public opinion.
2) Internet Filtering. Compared with the real world,
the network provides a systematic filtering natural
environment of information, which makes the
network easy to form homogeneous members within
groups and heterogeneity members intergroup. The
network Helps and strengthens the gathering of
people who have similar interests but are at different
place. Meanwhile, the information on the network is
unlimited, but the information accepted by users is
limited. Internet users have to choose the
information that is valuable and interesting for them.
The network technologies, such as hyperlinks, help
them filter their seen, read and hear things, and
enhance the select ability of information, so they can
selectively access and continually strengthen the
same information. Therefore, the seemingly
personalized information filtering eventually leads
to a "narrowing of information". More and more
Internet users can only hear their own echo, and the
network interaction becomes a "whispering gallery".
The speed of polarization of network public opinion
greatly accelerates.
3) Group Collaboration. The nature and
characteristics of network groups determine the
emergence of group polarization of network public
opinion. The research on social psychology shows
as follows: because of the role of mechanisms in the
collective unconscious, when individuals access to
groups, their psychology will produce a change of
which can not help but lose self-consciousness.
Individuals’ personalities are under varying degrees
of repression, so, even without any external
compulsion, individuals will instead their own
spirits of the groups’ spirits.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
446
3 THE EVOLUTION
MECHANISM OF NETWORK
PUBLIC OPINION
3.1 The Evolution Direction
Mechanism of Topics and the
Change of Network Public Opinion
Direction
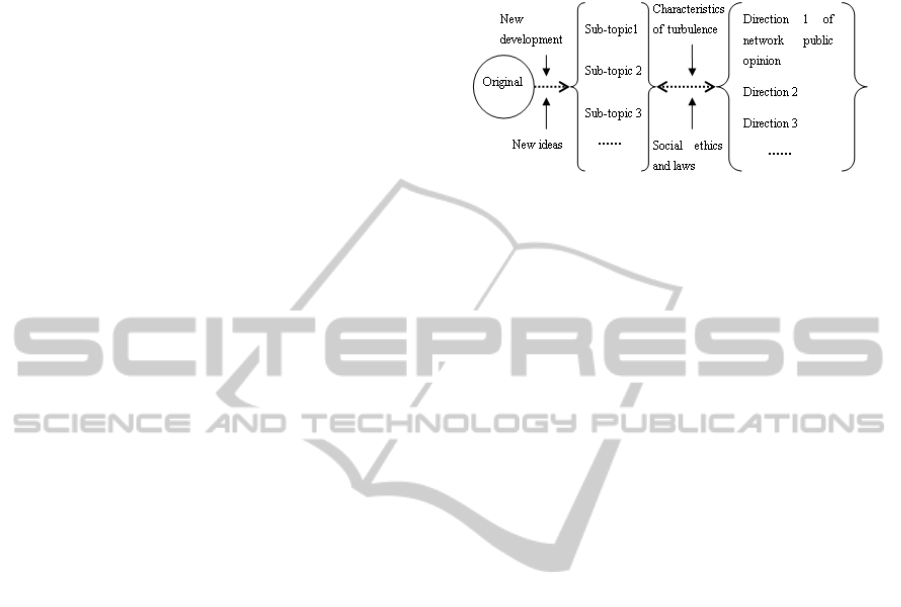
An original topic may be just a post or a news report.
While the attention is increasing to the topic, the
topic will show as a collection concluding series of
news reports, website reviews, forum posts, blog
and others. This change may be due to the
emergence of new developments of the events
discussed or the addition of new ideas. At this time,
the topic will change and sub-topics and new issues
center will format. Because of the lack of network
communicators, network public opinion may move
in any one direction in the dissemination process,
which led to new topics that are even unrelated with
the original public opinion. There are two situations
about this change. First, with the development of
events, the concerns of public opinion are changing.
Second, only for an event, the network public
opinion disperses from the point to the surface. The
evolution of topics and the evolution of network
public opinion are complementary and inseparable
processes.
Once the issue survives, the subsequent
development will depend on a number of factors and
balances. On the one hand, the characteristics of
turbulence are from the publicity and release of
Internet users. On the other hand, when the topic
survive and become the "Climate "of public opinion
that is attended by many users and even mass media,
social ethics and even laws and regulations will be
involved in the process, and become important
constraint factors of network public opinion.
Since then, the forum posts that reflect the
reaction to the events and practices of the relevant
people, including users and the media are
significantly more and more. This phenomenon
reflects that the network of the forum itself is not a
closed system, and it connects with social system
and the Internet. On the other hand, the phenomenon
reflects that the forum itself has a self-purification
mechanism or "quasi-life body function". In other
words, whether the pressure is from the outside or
inside, in a relatively mature, rational forum space,
with the event gradually reflecting actual situation,
people's views and comments on the event will
become objective, fair and rational. The mechanism
of topics evolution direction and the change of
network public opinion direction are shown as figure
4.
Figure 4: The mechanism of topics evolution direction and
the change of network public opinion direction.
3.2 Mutation Mechanism of Network
Public Opinion
Mutation of network public opinion of public crisis
is a system evolution. Specifically, the basic
mutation modes in the dissemination of network
public opinion are three types: assimilation, that is,
Internet users interpret and disseminate information
of events using their knowledge and experience;
alienation, that is, understanding of the information
appears different versions; simplification, that is, a
lot of details which are helpful for understanding the
truth are omitted.
In the network environment, the modes of
dissemination of information are different from the
common "one on one" or "one to many" in real life,
but "many to many" or "mesh" form. Therefore,
taking into account the different interests of the
communication actors, the network public opinion
will assimilate and alienate which is an inevitable
situation. These variations may include disaster
panic, political rumors, and economic profit and so
on.
Disaster panic is common in panic and public
health events. As the incident instantly destroys the
life and production order, people are shrouded by a
sudden and inexplicable fear, and they will
intentionally or unintentionally disseminate
information of panic. In fact, Internet users are
expressing moods or attitudes in the transmission of
information, which is a kind of subconscious release.
As a result of this kind of subconscious, the
composition of event information is continually
changing. In the development process of the public
opinion, users will forward their own explanation to
the fuzzy part of the event information which leads
to enhance the variance of the information.
Thus, the network public opinion and the
interests of the participators of dissemination have
STUDY ON THE EVOLUTION MECHANISMS OF THE NETWORK PUBLIC OPINION
447

closely relationship. The power of mutation is the
different interests of different Internet participators.
These differences led to mutation or twist of the
event information and make network public opinion
deviate from the truth.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Network public opinion and traditional public
opinion have some similarities, but network public
opinion also has its own independent "will" and
evolution which are rooted in its technical specificity.
In this paper, based on the life cycle theory, we
analyze the formation path of network public
opinion, and then, we discuss its formation
mechanism. After that, we study the evolution
mechanisms of network public opinion, including
the evolution direction mechanism of topics and
mutation mechanism of network public opinion.
REFERENCES
Tippins M J, R SSohi. IT Competency and Firm
Performance: Is Organizational Learning a Missing
link[J].Strategic Management Journal, 2003, 24(8):
745-761.
Qin Y, Rao J N K, Ren Q. Confidence interval for
marginal parameters under fractional linear
regression imputation for missing data[J] . J
Multivariate Anal, 2008, 99: 1232-1259.
Fortunato S. Damage spreading and opinion dynamics on
scale free networks[J]. Physic A, 2004, 348: 683-690.
S. P. Borgatti, A. J. Mehra, D. J. Brass, G. Labianca.
Network Analysis in the Social Sciences. Science 323
(2009) 892.
L.-N. Wang, J.-L. Guo, H.-X. Yang, T. Zhou. Local
preferential attachment model for hierarchical
networks. Physica A 388 (2009)
Gao G, Gu B, Lin M. The dynamics of online consumer
reviews[C]. WISE 2006, Evanston, Illinois, USA,
2006.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
448
