
STEP-BASED MODELING & SIMULATION FOR VIRTUAL
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
Li Li, Tianyuan Xiao, Wenhui Fan, Hongbo Sun and Cheng Ma
National CIMS ERC, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Keywords: Virtual Product Development, HLA, STEP.
Abstract: A novel STEP-based modeling and simulation method is proposed to improve the data consistency and the
model reusability in Virtual Product Development (VPD). Based on the proposed method, a STEP-based
product model is automatically generated from STEP files and CAD/CAE models. In the method, besides
product shape data other effective data can be extracted from STEP files and CAD/CAE models for HLA-
based simulation. An applicable prototype system is designed to support this method. A case study is
performed to demonstrate the feasibility of the method.
1 INTRODUCTION
Virtual Product Development (VPD) is the process
of designing, analyzing product and developing
Virtual Prototype in digital environment. Nowadays,
product simulations within a single discipline cannot
satisfy requirements of VPD. High Level
Architecture (HLA) is a well-known standard for
distributed simulation (IEEE Computer Society,
2001). Adopting HLA, simulation systems in VPD
could reuse existing simulation models, and
integrate different kinds of multi-disciplinary
product simulation models in one simulation task.
However, HLA-based simulations cannot
completely meet requirements of VPD. Simulation
models in HLA-based simulation are usually
independently developed without using the upstream
product information. This cannot satisfy the demand
of data consistency in VPD, and reduces the
credibility of simulation results.
As an ISO standard (ISO 10303) which is widely
used in CAD/CAE/CAM/CAPP, STEP standard
(Technical Committee 184 Sub-Committee 4, 2002)
supports data exchange in many product
development domains. Adopting STEP standard into
VPD would facilitate the reuse of CAD model
information in HLA-based simulation, and enhance
data consistency in the whole process of VPD.
Nowadays, the most representative projects
which use STEP standard to build product models
for data exchange are the Model Based Definition
(MBD) project which is proposed by Boeing (Chen
et al., 2009) and the Share-A-Share project designed
by Eurostep (Shaw, 2009). But in these projects,
STEP-based product model is mainly addressed to
resolve the problem of CAD/PDM data exchange of
complex product, and do not contain the simulation
data that are useful for multi-disciplinary
simulations. Hunten (1997) describes an approach of
CAD/FEA integration with AP209. Thurman and
Benda (2009) built a model-based enterprise
environment with AP210. The above two researches
mainly focus on information integration with single
AP, and it makes these approaches hard to extend to
other simulation domains. Li et al. (2008) define a
STEP AP203-based logical structure of a
mechatronic system using HLA, but the method of
converting STEP files to domain simulation models
is not described in details. Si et al. (2009) proposes
an application framework of Product Collaborative
Design. In this framework, STEP files are converted
into domain simulation models by specific software
interfaces. Using specific software interfaces limits
the framework for further use.
Based on the above reviews, this paper argues
that general STEP-based approach is not convenient
to be used in VPD, especially for HLA-based
simulations. A single application protocol can only
exchange data in single domain, and is lack of the
definitions of assembly constraints which are
indispensable for some specific simulation domains.
Furthermore, most researches mainly focus on the
information of product shape. Actually, there are
more useful information than product shape data
224
Li L., Xiao T., Fan W., Sun H. and Ma C..
STEP-BASED MODELING & SIMULATION FOR VIRTUAL PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003596302240227
In Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH-2011), pages
224-227
ISBN: 978-989-8425-78-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

could be reused in STEP files for VPD.
In this paper, a novel STEP-based modeling and
simulation method is proposed to improve the data
consistency and the reusability of models in VPD.
By this method, a STEP-based product model which
is suitable for HLA-based simulation would be
automatically constructed from STEP files and
domain models.
2 STEP-BASED PRODUCT
MODELING
In order to organize the data which is useful in VPD,
this paper gives a metamodel of STEP-based product
as Figure 1 shows. The metamodel specifies the
model data which must be recorded in a unified form,
and indicated basic elements of the model and their
associations. Every product model should contain
one instance of class Product, and an instance of
class Product should contain one or more instances
of class Assembly. The main information contained
in class Part is product shape data which is specified
in AP203 or AP214. An instance of class Part could
contain one or more instances of class Feature.
Class ContextData contains various application
environment and context information.
Class ProductElement which describes the
general information of product elements is
associated with class ConstrainSet and class
DesignHistory, which are used to specify the data
not represented in STEP files but useful in HLA-
based simulation. Class DesignHistory records the
data of product design processes. Including design
history in the STEP-based product model would
bring product designer’s intentions to the model.
Class DomainElement is an abstract class which
could be instantiated with domain-specific
information. In order to store the mappings between
domain elements and product part, class
MappingData is associated with both class Part and
class DomainElement. Based on class
HLAModelData, users could define which data
should be published and which data are needed in
the HLA-based simulation. Several attribute data of
the class HLAModelData, such as dataUnitType, are
dependent on class ContextData, which improves
the data consistency in HLA-based simulations.
Because of the complexity of EXPRESS
language, STEP files may not contain an explicit
data structure. Therefore, analyzing a STEP file to
get explicit data structure is still a difficult job.
Furthermore, there are many entity instances that do
not contain any useful information in STEP files
which are exported by upstream systems. When
extracting information from STEP files, these
useless instances are usually ignored manually. This
paper proposes a user-friendly method which could
automatically analyze STEP files with the rules
defined by users and convert them into the STEP-
based product model. The process of the method can
be described as follows:
• Construct preliminary STEP file information set.
The method makes search rules first, which
contain an entity as start point and an entity as
end point defined by users. Each search rule
would lead to a file traversal of the STEP file in
the shortest path between the points, and produce
a search result whose data are stored in an
appropriate sequence. The search result can be
generated as Figure 2 shows. This process could
be seen as a data preprocessing which would
facilitate the information analysis of STEP files.
Each search result is deemed as a data block, then
they form a preliminary STEP file information set
which contains all the information needed in
VPD.
Figure 1: STEP-based product metamodel.
STEP-BASED MODELING & SIMULATION FOR VIRTUAL PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
225

Figure 2: The search result of STEP files.
• Analyze the information set and construct the
STEP-based product model. In this process, the
instances of class Product, class Assembly and
class Part in the model would be generated first,
as well as their relationships. Then instances of
other classes defined in the metamodel are added
to the STEP-based product model. After the
process, useless entity instances are removed
according to the requirements of users.
• Use specific interfaces to access domain specific
information from domain product models, such as
product assembly constrains and design history
data, and attach them to the STEP-based product
model based on the architecture of the metamodel.
This process would be varied in different specific
domains.
For the purpose of describing and completing the
processes in detail, this paper develops a grammar to
describe the information set.
Table 1: Grammar of information set.
No. Grammar rules
1
S→P
2
P
→D
R
D
P
D
D
D
ϵ
……
76
ϵ→/
77
ϵ→/δ
78
δ →an
y
string does not contain ternimal
ϵ and δ are deem as terminals, and this paper
denotes “<product>” as θ, “<attribute type =δ δ>” as
α and so on. Handles such as D
and R
represent
data blocks in the information set. Users could
define new handles if they want to introduce new
data blocks into the set. Based on rule 2, a gross
deterministic finite state automata (Figure 3) could
be built to describe the grammar.
Figure 3: Gross deterministic finite state automata.
Rule 3 to 12 represent the grammar of the data
block shows in Figure 2. This paper takes this data
block as an example to demonstrate the process of
information transformation. The augmented
grammar of the data block is listed as follows:
Table 2: Augmented Grammar of the data block.
No. Augmented Grammar rules
1
S′ →S
2
S→P
ϵ
3
P
→P
P
4
P
→P
5
P
→ P
PNP
Pϵ
6
P→θA
ϵ
7
P
→ ηA
ϵ
8
N→γA
ϵ
9
A
→AA
10
A
→A
11
A → δ δ ϵ
Using the rules mentioned above, the reachable
item sets and the transitions between them can be
found. A state machine can be represented as Figure
4. For brevity, the parsing table and attached actions
for generating the STEP-based product model are
not represented. Because of the serial structure of the
gross finite state automata, users could easily add or
remove data blocks in the information set, and
modify the states in the finite state automata as well
as the attach actions in order to analyze the STEP
files in their own rules.
2
0
2
3
2
2
2
5
2
1
S
β
P
RS
P
R
ζ
P
R
2
7
P
RS
2
4
∈
2
6
ζ
2
8
N
2
9
γ
2
15
2
16
A
S
∈
2
11
A
2
13
2
14
2
10
2
17
2
18
∈
∈
η
α
α
2
19
P
DF
2
23
2
24
2
25
2
26
2
27
P
N
P
DF
P
∈
2
20
A
θ
2
21
2
22
∈
γ
θ
α
A
S
A
A
η
A
S
Figure 4: State machine of search result data.
3 CASE STUDY
This case is part of the research project of the
National High Technology Research Development
Program of China (863 Program). A prototype
system is developed based on the proposed method.
The prototype system could convert the information
in STEP files and domain models into the STEP-
SIMULTECH 2011 - 1st International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and
Applications
226
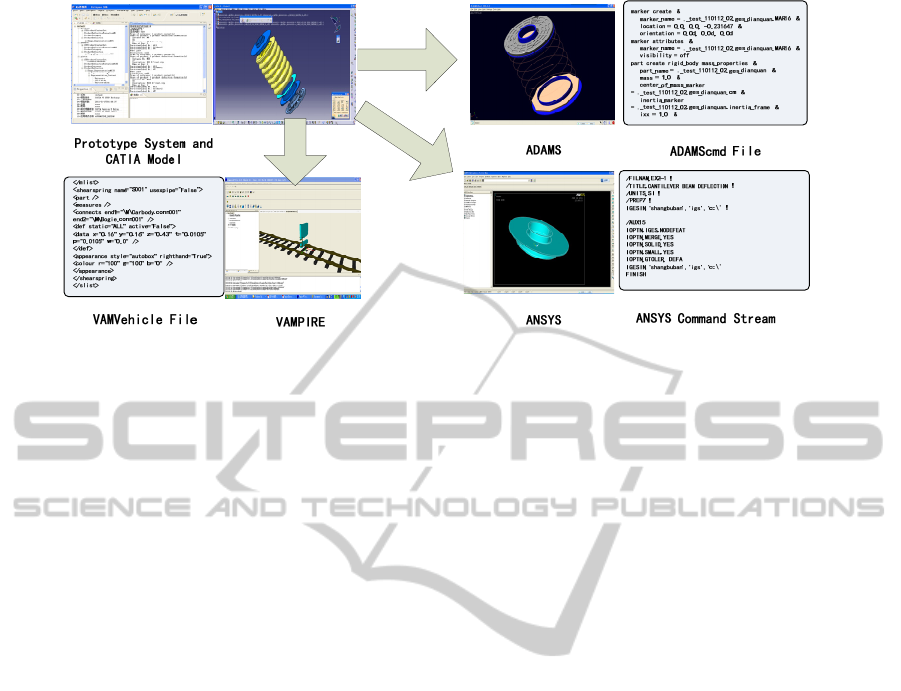
Figure 5: Part of the codes of simulation models and the prototype system.
based product models, and transform the model to
several kinds of simulation domain models for HLA-
based simulations. This paper mainly focus on the
information extracting, so we do not describe the
method of converting the STEP-based product
model into several kinds of domain simulation
models (such as ADAMS model, VAMPIRE
model). The prototype system and part of the codes
of these models are shown in Figure 5.
Compared to other approaches, the proposed
method could integrate more useful information in
STEP files than product shape data for simulation,
and the information of domain models are also
integrated. So the STEP-based product model could
provide all the necessary information for design and
multi-disciplinary simulations in VPD. Moreover,
the method of extracting information from STEP
files are more flexible and user friendly, this could
facilitate simulation modeling for VPD in a more
effective way.
REFERENCES
Chen, T. C. and McGowan, T. (2009). MBD Data
Exchange. In PDE2009, the 11th NASA-ESA
Workshop on Product Data Exchange, Kent,
Washington.
Hunten, K. A. (1997). CAD/FEA Integration with STEP
AP209 Technology and Implementation. Retrieved
from http://www.mscsoftware.com/ support/library/
conf/auc97/p01297.pdf
IEEE Computer Society. (2001). IEEE standard for
modeling and simulation (M&S) high level
architecture (HLA)- object model template (OMT)
specification (IEEE Std 1516.2- 2000). NewYork: The
Institute of Electrical and Engineers.
Li, X., Li, X. and Chen, L. (2008). Research on
collaboration simulation of complex mechatronic
system based on HLA. In ICMA'08, Mechatronics and
Automation, 2008, Takamatsu, Japan.
Park, J., Moraga, R., Rabelo, L., Dawson, J., Marin, M. N.
and Sepulveda, J. (2005). Addressing complexity
using distributed simulation: a case study in spaceport
modelling. In SWC’05, Simulation Conference,
Proceedings of the 2005 Winter Simulation
Conference, Orlando, USA.
Shaw, N. (2009). Experience with a standards based
product data collaboration hub. In PDE2009, the 11th
NASA-ESA Workshop on Product Data Exchange,
Kent, Washington.
Si, N., Zhang, L., Laili, Y., Zhang H. and Cong, K. (2009).
Study on Semantic SOA Based Product Collaborative
Design. In ICICTA'09, Intelligent Computation
Technology and Automation, 2009, Zhangjiajie, China.
Technical Committee 184, Sub-Committee 4. (2002).
Industrial automation systems and integration -
Product data representation and exchange - Part 21:
Implementation methods: Clear text encoding of the
exchange structure. International Organization for
Standardization.
Thurman, T. and Benda, M. (2009). From Paper Based
Analysis to Model Based Analysis: Applications of
AP 210 at Rockwell Collins. In PDE2009, the 11th
NASA-ESA Workshop on Product Data Exchange,
Kent, Washington.
STEP-BASED MODELING & SIMULATION FOR VIRTUAL PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
227
