
RESEARCH ON CRITICAL CHAIN MANAGEMENT AND RISK
MANAGEMENT IN PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION
MANAGEMENT
Zhenyu Yang and Jun Jiang
UFIDA Software Co., Ltd, No.68 Beiqing Road, Haidian District, Beijing, China
Keywords: Implementation Management, Critical Chain Theory, Research on Risk Management.
Abstract: According to Standish Group’s research, more than 30% of IT projects are unfinished, and about 73% are
delayed or exceeded the budget in those completed projects. On average, the cost is 189% of the original
planned and the length of completion cycle is 222% of the planned length. This indicates that there are
shortcomings in the traditional project management mode. However, critical chain theory provides some
improvement method. This paper focuses on the application of critical chain theory to enhance the ability to
completing projects on schedule and effectively reduce cost.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to Standish Group’s research, one third of
IT projects are unfinished, and about three quarters
are delayed or exceeded the budget in those
completed projects. On average, the cost and the
length of completion cycle are nearly doubled of the
planned ones. This indicates that there are
shortcomings in the traditional project management
mode. However, critical chain theory provides some
improvement method.
TOC (Theory of Constraints) is named after
Israeli physicist and Master of Business
Administration, Dr. Eliyahu Moshe Goldratt, which
is supported by a serious of thinking method.
Figuring out the core problem and proposing a new
viewpoint of loop chain is its thinking methodology.
Loop chain is made up of several loops; it can only
enhance efficiency in the circumstances that loops
work in cooperation. Mainly used in production
management, project management and distribution
management, critical chain theory is the project
management method. This method has been utilised
successfully to guide several project. This paper
mainly focuses on application of critical chain
theory to enhance the ability to completing projects
on schedule and effectively reduce cost.
2 OVERVIEW OF CRITICAL
CHAIN THEORY
2.1 Problems in Project
Implementation Management
Project tardiness, excess budget, poor performances
are frequently confronted by project managers.
In order to change the current situation,
following advices are proposed for the improvement
of project implementation:
Leave room for each stage of projects as
uncertainty can exist in every stage.
Make timely emendations to plans according to
project situation.
Share resources with other projects.
Early detect and prevent potential risk through
statistics analysis.
Increase the input of investment.
However, do these improvements really work?
If leave room for each stage of the project, the
complete time will be postponed for a long
time.
Plan amendment is necessary, but as to those
large projects, there may be enormous changes,
affecting the regular operation of projects.
Sharing resources with other projects may also
lead to confliction in projects as the limitation
of resources, resulting in implementation delay
351
Yang Z. and Jiang J..
RESEARCH ON CRITICAL CHAIN MANAGEMENT AND RISK MANAGEMENT IN PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION MANAGEMENT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003610303510356
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (BIS-2011), pages 351-356
ISBN: 978-989-8425-54-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
of each project.
Increasing the investment blindly always means
the loss of the project.
2.2 Description of the Critical Chain
Theory through Project Plan
Schedule
How can critical chain theory used to improve the
project management? Following describes the
mechanism by comparing the traditional project
management method and critical chain management
method of a project plan. Figure1 describes the
project schedule
Figure 1: A simple project schedule.
Boxes in Figure.1 stand for different tasks. If two
tasks are connected in the horizontal direction, or
connected with arrows, it indicates that the
beginning of the latter task depends on the
completion of the former task. Resources needed for
execution are included in the boxes and the number
means the length of days to complete the task.
Current resources include one technical consultant,
one senior consultant, one implementation
consultant and a develop consultant.
As those resources may have tasks in other
projects, the time for completion is of great
uncertain. To solve this problem, adding a buffer
period in each task is proposed as stated in Figure.2,
the bold lines marked the critical path (the longest
oath to complete the task)
Figure 2: Project schedule added with buffer period.
Though added buffer period, but the outcome
seems not as reasonable as implementation
consultant is still in the contending state,
implementation consultant (6) can only start his task
after the completion of implementation (8).
Accordingly, the time in critical path (5+6+8+3=22
days) is not the exact time for the project. So, how to
make a more reasonable and effective project
schedule? The following four steps describe how to
apply the critical chain theory to solve this problem:
Step 1: Solve the contending situation of
resources
Firstly, the contending situation of resources
should be solved as Figure 3 demonstrated.
Figure3: The contending situation solved schedule.
There is no buffer period in this Figure.3; the
number in boxes means the average time to
complete the task. The buffer time will be added
later.
Some tasks, such as technical consultant (1) and
senior consultant (2), will start at the late starts. This
is because the start date will be advanced only when
buffer period is added, but where to add this buffer
period is still being uncertain presently.
The scheduling Figure.3 has the shortest
construction time; however, it is necessary to note
that only in the absence of any uncertainty will be
the case.
Step 2: Identify the critical chain
To fully utilise the buffer period, it is required to
identify a set of tasks which determines the cycle of
the whole project. This set of tasks is called the
Critical Chain.
Figure 4: Critical Chain.
It is easy to identify that tasks in bold boxes
determine the cycle of the whole project, as any of
those delayed will cause a delay in the project.
Step 3 and 4: Add buffer period appropriately
To avoid delay of projects is of vital importance
to project managers. To solve this problem, a buffer
period is added at the finish point, as stated in
Figure.5.
Figure 5: Schedule with buffer period.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
352
The reserve buffer period can be used in the
project; it is derived from the statistical length of
fluctuation time. It should be noted that the
protection is intended for the whole project rather
than a single task. It is still of great importance for
projects which have not generated critical chain. In
short, advance risk and postpone idleness.
Projects are protected by establishing project
buffer, but other parts of the project also need
consideration.
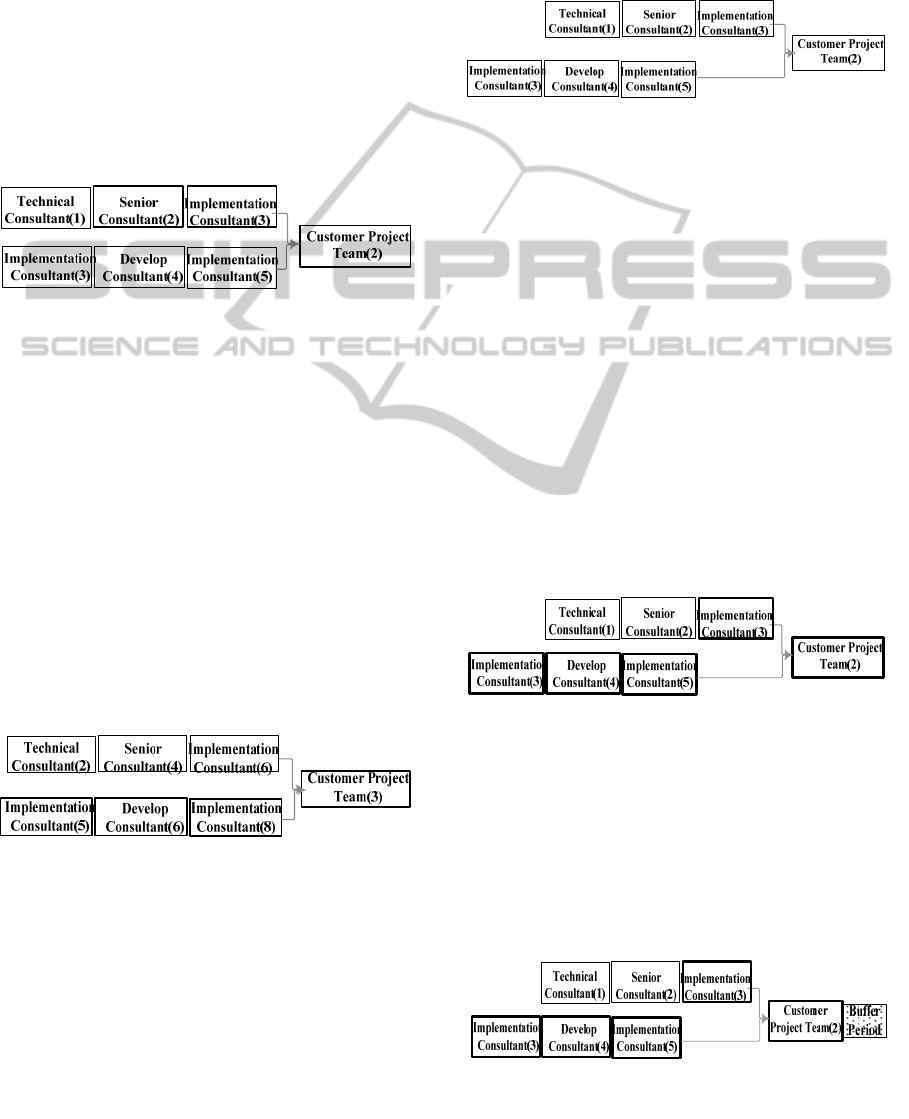
Specifically, insert vibration period at the
connection point between non-critical chain task and
critical chain task, as shown in Figure.6. Finally, we
get a practical plan not only ensure relatively short
cycle, but also consider how to avoid interference of
fluctuation.
Figure 6: Project scheduled according to critical chain
theory.
3 THE APPLICATION OF
CRITICAL CHAIN IN LARGE
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
3.1 Stage and Milestone in Projects
There are many reasons contribute to the delay of
project cycles and budget overrun, however, among
those reasons, not having good stages or milestones
is one of the most important. The Figure below well
illustrates this problem.
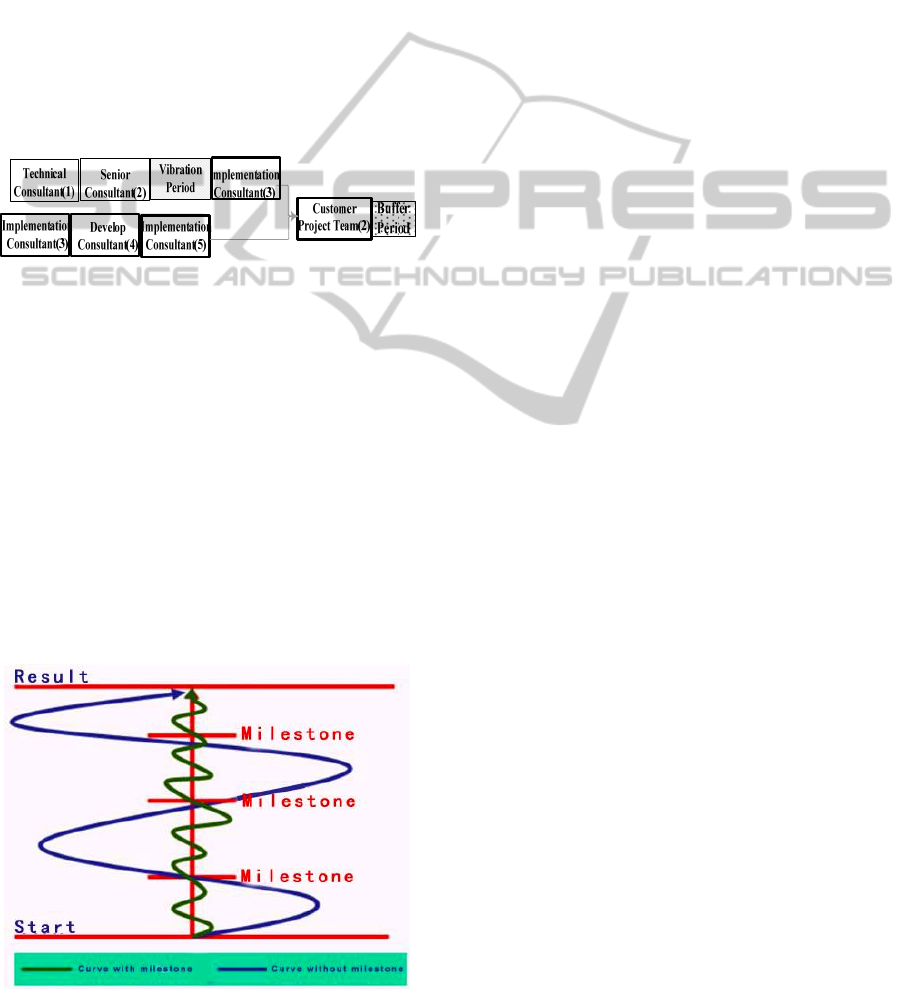
Figure 7: Comparison of executive curves.
As shown in Figure.7, there is a long way to go
for the success of the project, and there is not a
readily available method to draw on. If project
manager wants to settle the project at one go and not
divide the project into several stages, it is easily take
unperceived detours. When realised, it has been far
from the targets. Even corrected, it is easily deviate
to another unperceived direction. Repeating like this,
become the blue track in Figure.7. If divide the
whole implementation into several stages and each
stage has its symbolic milestones, though detours
cannot be avoided, it does not go far and forming the
green track in figure. It can be easily seen from the
figure that these two tracks have different length,
and the blue one longer than the green one, which
indicates that the former spend more cost and time
than the latter, indicates the budget overrun and
schedule delay.
Having long cycle spans, it is not realistic to
foresee and make plans of future in advance.
Accordingly, the best way to solve this problem is to
divide the whole project reasonably and set up
milestones at the appropriate positions. As for the
subdivision of project, it can utilise the seven steps
of implementation methodology as the basis and
subdivide the project according to the practical
situation of each project. Following methods can be
considered in subdivision:
Large projects usually implemented for several
stages, for example, implementing financial
accounting in the first stage, implementing
supply chain in the second stage and
implementing administrative accounting in the
third stage.
After the division of large stages, divide the
project into detailed stages according to the
practical situation of each project.
Detail the task planning and milestones for each
stage.
3.2 Adopting the Principles of Risk
Advancing and Idleness Postponing
Detailing the Project Schedule
The core principle of critical chain theory is to
advance risk and postpone idleness.
Figure.8 describes the relation of complete time
and complete probability of a project, the difference
in projects and the ability and experience of team are
certain to have impact on the shape of curves.
We can draw conclusion from the figure that the
possibility of completing tasks in advance or delayed
is very low, but it really exists. Usually, the
consultant will choose the corresponding complete
RESEARCH ON CRITICAL CHAIN MANAGEMENT AND RISK MANAGEMENT IN PROJECT
IMPLEMENTATION MANAGEMENT
353
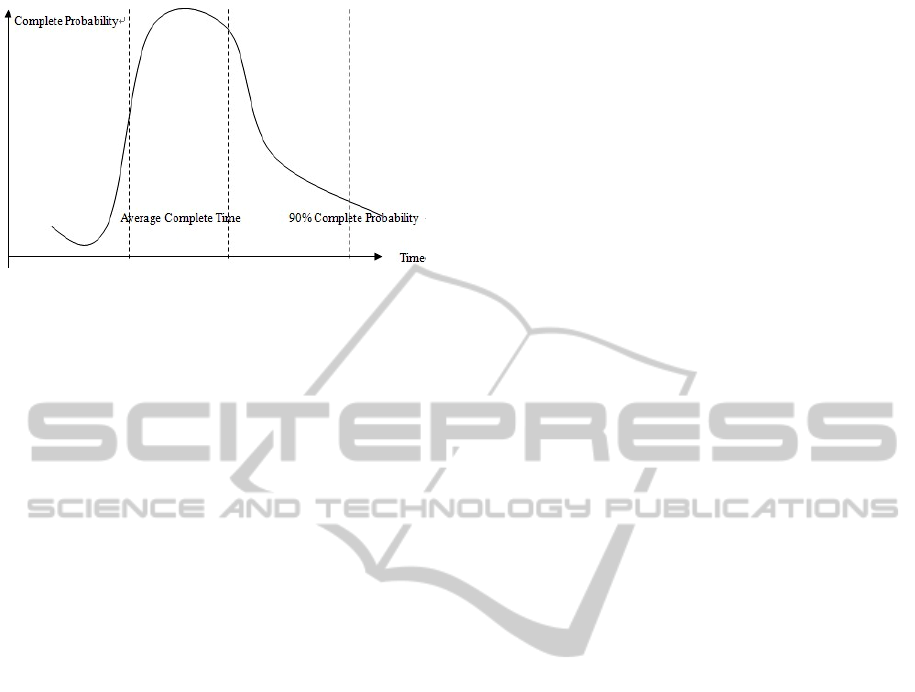
Figure 8: Curve of project complete probability and
complete time.
time of the 90% complete probability, meanwhile,
there is still possibility that the project cannot be
completed timely. However, according to the critical
chain management method, all the safe time of each
task will be taken away and add it at the completion
point of the whole stage, working as the buffer time
of this stage, protecting the critical chain.
Accordingly, we should tell consultant to estimate
each task based on 50% complete probability time,
namely the average complete time in Figure.8. Try
the best to complete the plan, if cannot finished
timely, adjust the task utilising the buffer time of
this stage.
3.3 Scheduling Plan and Resources in
Accordance with Critical Chain
In the view of resource allocation manager, plan
means two sheets; one is the task sheet, which gives
an overall view of what recourses are needed from
the perspective of project manager. This sheet can be
generated by PROJECT, stating, I need a financial
consultant from 8 to 12 in April to conduct the
financial requirement investigation in preparation for
Project A. The other one real-time priority
arrangement, usually, this sheet stating, do this
immediately or why Project A gets nowhere. The
first sheet changes with the project, maybe once a
week, however, the second sheet changes more
frequently, maybe every hour a change, especially in
large projects.
Traditional project management method also
needs to arrange project plan, allocate resources and
schedule. Following will demonstrate the advantages
and improvements of critical chain theory:
Making detailed project plan and scheduling
resources with critical chain theory is mainly
aimed at current detailed stage targets and
milestones.
Leave no room for buffer time for each task.
In the critical chain method, task scheduling
outlines priority but there is no exact time to
complete the task. This is a significant
difference between traditional theory and
critical chain theory. In the circumstances that
fluctuation cannot be avoided, it is better not
giving the exact start time rather than
estimating the start and finish time and adjust
when fluctuation occurs. So it is critical to
strictly adhere to one rule: Finish your job as
soon as possible when you are assigned with
tasks.
The most significant difference with traditional
project management method lies in scheduling
plans and resources according to the critical
chain rather than non-critical chain. In the
process of scheduling, we should pay particular
attention to the over-loaded bottleneck
resources rather than try to solve every
problem concerning resource contention.
Unless significant changes occur, we do not
rearrange plans frequently, in other words, not
changing the priority of tasks frequently.
Considering the tasks in non-critical chain, we
should also pay certain attention to them. In
order to ensure that non-critical tasks do not
affect the overall progress of the project to the
largest extent, it is strongly recommended that
arrange the start time as early as possible and
leave adequate vibration period between
critical chain tasks and non-critical chain tasks.
As all the safe time in each task has been taken
away and the tasks in non-critical chain have
been brought forward, the problem of resource
contention is more outstanding than traditional
ones.
3.4 Establish Project Tracking
Mechanism
Contingencies are inevitable in the project
implementation process, establishing a tracking
mechanism to monitor the execution of projects is
also of great importance.
This tracking mechanism is called “Buffer Period
Management”. According to the situation task
completion, we can easily monitor how much of the
buffer time has been used. For example, as to
schedule in Figure.5, after 8 days work, technical
consultant (1), senior consultant (2), and
implementation consultant (3) all have finished their
tasks and develop consultant has nearly completed.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
354

In Figure.9, we use the blue line stands for the
completion of tasks. It can be seen from the figure
that technical consultant (1) and senior consultant
(2) have delayed for one day, as there is vibration
period so the delay does not impact the project
progress. However, tasks in critical chain,
implementation consultant (3) and develop
consultant (4), also delay a day, accounting for a day
of the buffer period in Customer Project (2), as
stated in Figure.9.
Figure 9: Buffer period state.
The establishment of tracking mechanism is of great
importance to projects. Following are some
suggestions on how to establish tracking
mechanism:
Establish weekly meeting system to monitor the
implementation the projects.
Regarding those critical tasks in critical chain,
weekly tracking cycle is too long, daily tracking
system is necessary.
If there were serious problem during the
tracking process, it is necessary that rearrange
the project plans and resources allocation, in
order to ensure the completion of whole project.
4 APPLICATION ANALYSIS
OF THE PROMOTION
OF CRITICAL CHAIN
4.1 Problems and Strategy in the
Application of Critical Chain
In the implementation of critical chain, there are
some inevitable problems, following are detained
analysis of these problems and corresponding
strategy:
Table 1: Problems and strategy in the implementation of
critical chain.
Problem
Category
Problem
description
Strategy and
Analysis
Cognition
Inertia determines
that project
managers are
reluctant to change
the previous
method, even
though they are
proved to be
ineffective.
Strengthen the
training in project
plan scheduling and
critical chain theory,
enhancing the
cognition of project
managers.
Organization
The application of
critical chain is
more demanding, it
is vital to identify
the urgent degree of
resources in order
to allocate
effectively.
When resources
cannot be
coordinated within
teams, department
manager should
communicate with
other teams to solve
the problem.
In the
implementation of
critical chain, the
main task is to
ensure the tasks in
the critical chain,
repeating tasks in
the non-critical
chain should
coordinate with
other resources.
1. Establish echelon
team ability in the
implementation
department, with both
senior consultant and
assisted consultant.
2. Develop
implementation
partners, make then
undertake the on-tech
tasks in busy period.
Assessment
Team members
work harder to
ensure the
completion of
tasks, but project
manager and
consultant may be
thinking: why
should we work so
hard, there is buffer
period, and even
finished, there are
other continue
tasks.
1. Taking task
completion time and
input cost as
measuring indicators.
2. Project manager
and consultant
promote mutually,
project manager has
the right the assess
consultant, which is
beneficial to find out
problems and solve
them timely.
4.2 Proposed Steps for the Promotion
of Critical Chain
As the implementation system is divided into three
levels, enterprises, regions and branches, and
different branch offices have significant differences
in implementation ability, accordingly, different
focus on different points in the implementation of
critical chain. In the level of enterprises and large
regions, most of the project managers have relatively
stronger ability and most of the projects are large
RESEARCH ON CRITICAL CHAIN MANAGEMENT AND RISK MANAGEMENT IN PROJECT
IMPLEMENTATION MANAGEMENT
355

projects, which can be promoted in large scale. The
key branch offices in Beijing, Shanghai and
Shenzhen not only have capable project managers
who can be responsible for large projects, but also
have project managers being responsible for medium
and small projects. When carrying out the critical
chain, we can choose the appropriate ones for the
project according to the ability of managers and the
scale the projects. As for the small branch offices,
due to the relatively low ability in project
management, even though large projects were
signed, usually, the project manager was dispatched
by enterprises or large regions.
4.3 Summary of the Prospects of the
Application of Critical Chain
In the light of the previous analysis, in order to
promote the critical chain in implementation
systems, we can conduct the work from the
following aspects:
Strengthen the training for large project managers.
Select appropriate project managers to conduct
projects, summarizing and accumulating
experience on a trial basis.
Make modest adjustment in terms of
organizations, resources allocation ratio and
development cooperation partners in
implementation.
Match assessment system with corresponding
large projects.
If promoted smoothly, it can bring following values
for enterprises:
Enhance the management ability of large
project managers.
Effectively improve the on time delivery rate in
the implementation of large projects.
Effectively control the input cost and increase
profits in the implementation of large projects.
Improve customer satisfaction to a certain
extent.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper analyzes the critical chain theory,
implementation steps, how to implement in projects
and how to promote within implementation systems.
On the premise of fixed project resources capability,
this paper mainly discusses how to utilize critical
chain to solve the problems, such as project delay,
resources contention, in traditional project
management.
REFERENCES
Eliyahu, Goldratt., 2006. Critical Chain. Beijing:
Electronic Industry Press.
Qunting, Liu., Zhibin, Jiang., Zhiying, Zhang., 2008,
Project Manufacturing Planning Control Process
Models and Critical Issues, Industrial Engineering and
Management.
Goldratt, E. M., 1997, Critical Chain. New York:North
River Press,1997.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
356
