
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF THE RAILWAY
PASSENGER’S SATISFACTION BASED ON ROUGH SET
AND ENTROPY
Feng Yun-qing, Li Xue-wei
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, Haidian District, 100044 Beijing, China
Li Xue-mei
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, Haidian District, 100044 Beijing, China
Keywords: Satisfaction, Rough Set, Entropy Method, Weight.
Abstract: To assess the passenger’s satisfaction is the key to analyze the service quality of the railway sector. The
most important part of the assessment is to calculate the weight of each index which influences the
passenger’s feelings in their journey. In this paper, we choose Ticket Price, Convenience, Train speed,
Comfort and Security as the indicators to assess the passenger’s satisfaction. First, we use the rough set
theory to calculate the subjective weight of the five indicators that influences the passenger’s travel feelings.
Second, we calculate the objective weight of the same five indicators using the Entropy Method. At last, we
get the integrated weight based on the subjective weight and the objective weight through the integrated
weight calculating formula. The results indicate that the Security has the highest weight, followed by the
weight of the Ticket Price and the Convenience. The Comfort and Speed have the lowest weight.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the development of the society, Customers
have a higher requirement on the quality of their
travel. They will also have more needs in their
travel. So to meet the demand of the tourists is to
make visitors get the most satisfaction. For the
railway enterprises, improving the railway
passenger’s satisfaction not only can increase the
passenger’s loyalty in the railway transportation, but
also can bring more passenger, which can bring high
profits to the railway transport enterprise. Therefore,
to assess the railway passenger’s satisfaction can
reasonably improve the railway transport
enterprise’s service quality and level. What’s more,
it can also improve the passenger’s travel
satisfaction which can bring more income for the
transport enterprise.
2 RESEARCH STATUS
The most important part to assess the railway
passenger’s satisfaction is to ascertain each factor’s
weight which affects the passenger’s travel quality.
There are mainly two types of methods that can
ascertain the factors’ weight. These are the
subjective weighting method and the objective
weighting method. The subjective weighting method
mainly involves the AHP method, G1 method and
the expert weighting method, etc. The objective
weighting method mainly includes the principal
component analysis, entropy method and the rough
set theory and so on. These two types of methods
have their own characteristics and defects. The
subjective weighting method is mainly based on the
decision-makers’ knowledge and experience to
decide the factors’ weight, which generally
consistent with the common sense. But this method
has some subjectivity and arbitrariness, so it will
affect the accuracy and reliability of the decision.
The objective weighting method is mainly based on
629
Yun-qing F., Xue-wei L. and Xue-mei L..
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF THE RAILWAY PASSENGER’S SATISFACTION BASED ON ROUGH SET AND ENTROPY.
DOI: 10.5220/0003616506290635
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (PMSS-2011), pages 629-635
ISBN: 978-989-8425-56-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

the correlation between each index to calculate the
weight according to a certain mathematical model.
The advantage of this method is that it fully
exploited the original data’s information. The
evaluation results have a strong theoretical basis and
are more close the reality. But this method ignored
the decision-makers’ knowledge and experience,
which will have certain deviations to the
decision-makers’ feeling. Therefore, we usually use
the comprehensive evaluation method based on the
subjective weighting method and the objective
weighting method to calculate each factor’s weight.
Wu Chun-you and Liu Yan
use the
comprehensive evaluation method based on the G1
method and the entropy method to determine the
weight of the factors that impact the interests of the
city-renewable resources (Wu Chun-you, Liu Yan,
2010). Ma Xiao-ying
uses the entropy method to
assess the readers’ satisfaction in the university
library and gets the weights of different factors that
affect the readers’ satisfaction (Ma Xiao-ying,
Zhang Guo-hai, Han Shu-fen, 2007). Song Li-min
also uses the comprehensive evaluation method
based on the AHP method and the entropy method to
get the weight of different indicators between
different readers (Song Li-min, 2009). Meng Ming
uses the same comprehensive evaluation method to
assess the power customer satisfaction and get the
weights (Meng Ming, Niu Xiao-dong, Gu Zhi-hong,
2005). Peng Jin-shuan uses the comprehensive
evaluation method based on the entropy method and
the subjective weighting method to evaluate the
passenger’s satisfaction to the urban public transport
and get each factor’s weight (Peng Jin-shuan, Hao
Yi-ming, Peng Li-fang, 2007).
Some scholars use the rough set theory to
evaluate the weight of different factors. Xiong Ping
proposed a new subjective weighting method based
on the information concept in rough set (Xiong Ping,
Cheng Hua-bin, Wu Xiao-ping, 2003). They
established a comprehensive optimization model to
determine the weight based on the optimization
theory. Hao Cheng uses the rough set theory to
research the weight of the effectiveness factors in
the urban rail transit project. Furthermore, they
obtained the combined weights of multiple factors
(Hao Cheng, Li Jing, Li Xue-Mei, Li Xue-wei,
2008).
Up to now, no one has used the rough set theory
to evaluate the railway passenger’s satisfaction.
Furthermore, no one has used a method based on the
rough method and the entropy method the get the
in-depth assessment for the railway passenger’s
satisfaction. First, this paper will use the rough set
theory to ascertain the factors’ subjective weight that
affects the passenger’s satisfaction. And then use the
entropy method to calculate the factors’ objective
weight. Finally, we use the comprehensive weight
formula
(Liu Jie, Li Chao-feng, Li Xiao-peng, Wen
Bang-chun, 2008) to calculate each factor’s weight
so that we can know the degree of different factors
that influence their travel choice.
3 THE SUBJECTIVE METHOD
BASED ON ROUGH SET
The rough theory, which was proposed by the Polish
mathematician Z. Pawlak in 1982, was a
mathematical method that research the
expression,learning and induction of the imprecise,
uncertain and incomplete data (China Research
Center of Industrial Safety in Beijing Jiaotong
University, 2009). The key points of this method to
blend classification and knowledge together and
then classify the data in the form of equivalence
because the knowledge comes from the human and
other species’ classification ability. The main idea of
this method is to deduce the decision-making and
classification rule of the problem through the
knowledge reduction on condition that the
classification ability doesn’t change. This method
was widely used in data analysis, data mining and
knowledge classification and other fields. This
theory which attracted wide attention from scholars
around the world in the 1990s in the 20th century
was successfully applied in the field of data analysis
and decision making, pattern recognition, machine
learning and knowledge discovery, etc.
3.1 Knowledge Definition
According to the rough set theory, a knowledge
representation system “S” can be expressed by
describing the attributes and the attribute values of
the research object (Chun-bao Chen, Li-ya Wang,
2006). So we define a equation:
(, ,,)SUCDVf
.
In this formula,
12
,,Uxx
means a collection
of objects.
12
,,Ccc
means the subjects of
the condition attributes set.
12
,,Ccc
means
the subjects of the decision attributes set. And the
conditions are
CDA
and
.CD
.
V
is
the collection of the attribute set.
:
f
UA V
is
an information function which gives each attribute
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
630

of the object an information value.
3.2 Indiscernible Relation
Suppose
R
is a series of equivalence relation in
U
.
So the
/UR
means all the equivalence class of
R
or the sets formed by the division of
U
. If
P
R
and
P
, then the intersection of all the
equivalence relation in
P
is also a equivalence
relation. We call this relation an indiscernible
relation in
P
. We record it as
().IND P
3.3 Upper and Lower Approximation
For a given knowledge
(,),
K
UR
if
X
,
X
U
and
()RINDK
, then we call
/|RX Y U R Y X
the lower approximation
of
X
about
R
and we call
/|RX Y U R Y X
the upper
approximation of
X
about
R
.
3.4 Positive, Negative and Border-field
For a given knowledge
(, ,,)SUACDVf
,
We suppose
U
is a nonempty universe and
C
is a
nonempty condition attribute set.
If
B
C
and
dD
we call
() | / ()
B
p
os d BX X U ind d
to be the
relative positive field of the decision attribute
d
for
.B
The
()
R
neg X U RX
is the negative
field of
X
for
R
. The set
()
R
bn X RX RX
is
the border-field of
.R
3.5 Weight Formula based on Rough
Set
Suppose
(, ,,)SUACDVf
is an
information system. The importance degree of the
condition attribute
i
c
can be expressed as follows.
()
() 1
()
i
i
Cc
Cc i
c
Card Pos D
Sig c
Card Pos D
(a)
i
cC
and
1, 2, 3, ,in
.
n
stands for the
number of the elements in the attribute set
C
.
()
c
Pos D
stands for the collection of objects that
can be accurately divided into the equivalence class
of relations
D
according to the information of
classification
/UC
in
.U
()
i
Cc
Pos D
stands
for the collection of objects that can be accurately
divided into the equivalence class of relations
D
according to the information of classification
/( )
i
UCc
in
.U
[]Card
stands for the number of
the elements in the set.
We normalize the importance degree data of each
attribute according to the formula and get the weight
of each attribute. The results are as follows.
1
()
()
i
Cc i
i
n
Ck
k
Sig c
Wc
Sig c
(b)
4 ENTROPY METHOD
4.1 The Definition of Entropy
Entropy is a concept derived from thermodynamics
(China Research Center of Industrial Safety in
Beijing Jiaotong University, 2009). Shannon,
founder of the information theory, used the entropy
theory to describe the uncertainty of the source
signal for the first time in 1948. Now this method is
widely used in the engineering, socio-economic and
other fields. Shannon gives the definition of the
source’s information entropy to us by the
probabilistic method. The definition of the
information entropy is as follows:
The System may be in
n
different states, and
the probability of each state is
i
p
(1,2,,)in
. If
01
i
p
and
1
1
n
i
i
p
, the entropy of the system
is
H
.
1
ln
n
ii
i
Hpp
(c)
The entropy is a measure of the degree of
disorder on the system and the information entropy
is a measure of the degree of order on the system.
The smaller the value of the index’s information
entropy is, the greater the variability is. Therefore,
we can use the information entropy to calculate the
weight of each index by
the
variation of each
indicator.
4.2 Entropy Calculation Steps
In a system with
m
indexes and
n
objects, the
steps of the entropy calculation
( Don-Lin Mon,
Ching-Hsue Cheng, Jiann-Chern Lin, 1994; Hong
Zhang, Chao-lin Gu, Lu-wen Gu, Yan Zhang, 2011.)
are as follows:
(1)
The Standardization of the indexes membership
matrix. The valuation value of the
m
indexes
for the
n
objects constitute the membership
evaluation matrix which is expressed by
R
.
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF THE RAILWAY PASSENGER'S SATISFACTION BASED ON ROUGH SET
AND ENTROPY
631

11 12 1
21 22 2
12
m
m
nn nm
rr r
rr r
R
rr r
(d)
Then we standardize the evaluation matrix
R
and get the matrix
'
R
.
'
'()
ij n m
Rr
(e)
ij
r
stands for the membership of the evaluation
indexes.
(2)
Normalize all the indexes and calculate the
indicator values of the
i
evaluation objects for
the
j
indexes.
1
ij
ij
n
ij
i
r
p
r
(f)
(3)
Calculate the entropy of the index
j
.
Given
1/lnKn
(0,0 1)
ij
Kp
and
ln 0
ij ij
pp
if
0
ij
p
. The entropy formula is:
1
ln ( 1, 2, )
n
jijij
i
HKppj n
(g)
(4)
Calculate the coefficient of variation of index
j
.
1
jj
H
(h)
(5)
Calculate the weight of the index
j
.
1
j
j
m
j
k
w
(i)
5 COMPREHENSIVE WEIGHT
If the subject weight to index
i
is
s
i
w
and the
object weight is
oi
w
, the comprehensive weight
formula (Wu Chun-you, Liu Yan, 2010; Hong Zhang,
Chao-lin Gu, Lu-wen Gu, Yan Zhang, 2011) to the
index
i
is as follows.
1
s
ioi
i
m
s
ioi
i
ww
w
ww
(j)
6 EMPIRICAL STUDY
In this paper, we choose Ticket Price,
Convenience,
Train speed,
Comfort and Security as the indicators
to assess the passenger’s satisfaction. We analysis
the 1051 questionnaires surveyed in January in the
year 2010 and calculate the subject weight and
object weight of the five indexes by the rough set
theory and the Entropy theory. Finally we obtain the
comprehensive weight of the five indexes by using
the comprehensive weight formula.
6.1 Subject Weight based on Rough Set
According to the rough set theory, the 1051
questionnaires surveyed constitute the set of the
objects. That is
1 2 1051
,,Uxx x
. The evaluation
of the passenger to the five indexes Ticket Price,
Convenience, Train speed, Comfort and Security
constitute the set of the condition attributes. That is
12345
,,,,C ccccc
. In this set, the sign
1
c
stands
for the index of Ticket Price. The sign
2
c
stands for
the index of Convenience. The sign
3
c
stands for
the index of Train speed. The sign
4
c
stands for the
index of Comfort. The sign
5
c
stands for the index
of Security. The overall satisfaction evaluation
constitutes the decision attribute which is expressed
by
D
.
There are seven evaluation grades for each index.
For example, for the index Ticket Price, the seven
evaluation grades are extremely dissatisfied, very
dissatisfied, slightly dissatisfied, general, slightly
satisfied, very satisfied and extremely satisfied. The
satisfaction degree of the seven evaluation grades
deepens gradually. We use the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6 and 7 to stand for the seven evaluation grades
correspondingly. For instance, 1stands for extremely
dissatisfied, 2 stands for very dissatisfied and so on.
The other indexes such as Convenience,
Train speed,
Comfort, Security and the overall satisfaction
evaluation have the same evaluation grades and
expression in numbers. The evaluation scores are
shown in
Table 1.
According to the weight calculation formula in
the rough set theory, we use the ” Matlab” software
to program the appropriate procedures and get the
correspondingly evaluation results as follows. The
1
Wc
,
2
Wc
,
3
Wc
,
4
Wc
and
5
Wc
stand for the
subjective weight of Ticket Price,
Convenience,
Train speed, Comfort and Security correspondingly.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
632

Table 1: Passenger satisfaction evaluation score sheet.
Data
ID
Condition Attribute
Decision
Attribute
1
c
2
c
3
c
4
c
5
c
D
1
x
2 4 4 4 5 4
2
x
3 5 2 4 5 5
1051
x
2 4 2 3 5 3
Note: the dates come from the survey questionnaire in
January in 2010.
( ) 446
C
Card pos D
,
1
( ) 219
Cc
Card pos D
,
1
1
1
()
227
() 1
() 446
Cc
Cc
C
Card pos D
Sig c
Card pos D
,
2
() 196
Cc
Card pos D
,
2
2
2
()
250
()1
( ) 446
Cc
Cc
C
Card pos D
Sig c
Card pos D
,
3
() 186
Cc
Card pos D
,
3
3
3
()
260
()1
( ) 446
Cc
Cc
C
Card pos D
Sig c
Card pos D
,
4
( ) 234
Cc
Card pos D
,
4
4
4
()
212
()1
() 446
Cc
Cc
C
Card pos D
Sig c
Card pos D
,
5
() 181
Cc
Card pos D
,
5
5
5
()
265
()1
( ) 446
Cc
Cc
C
Card pos D
Sig c
Card pos D
,
1
1
1
5
1
()
227
0.186985,
1214
()
k
Cc
Cc k
k
Sig c
Wc
Sig c
2
2
2
5
1
()
250
0.205931,
1214
()
k
Cc
Cc k
k
Sig c
Wc
Sig c
3
3
3
5
1
()
260
0.214168,
1214
()
k
Cc
Cc k
k
Sig c
Wc
Sig c
4
4
4
5
1
()
265
0.174629,
1214
()
k
Cc
Cc k
k
Sig c
Wc
Sig c
5
5
5
5
1
()
265
0.218287,
1214
()
k
Cc
Cc k
k
Sig c
Wc
Sig c
According to the results above we get the
subjective weight of the five indexes using the rough
set theory. The subjective weight of the Ticket Price
is 0.186985. The subjective weight of the
Convenience is 0.205931.The subjective weight of
the Train speed is 0.214168. The subjective weight
of the Comfort is 0.174629. The subjective weight of
the Security is 0.218287. The weight of the Security
is the highest in all the five weights. And then is the
weight of the Train speed and the weight of
Convenience. So in the subjective aspects the
passengers pay the most attention on their security in
the travel because the security is the premise of
human existence. Besides, with the development of
the society, people are increasingly concerning more
about the time value which is affect a lot by the
Train speed and the Convenience in their travel. So
the results show that the weights of the Train speed
and Convenience are a little higher than the weights
of Ticket Price and Comfort subjectively.
6.2 Objective Weight based
on Entropy
Different evaluation grades of each index has
different number of people. We process the data and
calculate the number of people in different
evaluation grades. the distribution results are listed
below in Table 2.
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF THE RAILWAY PASSENGER'S SATISFACTION BASED ON ROUGH SET
AND ENTROPY
633
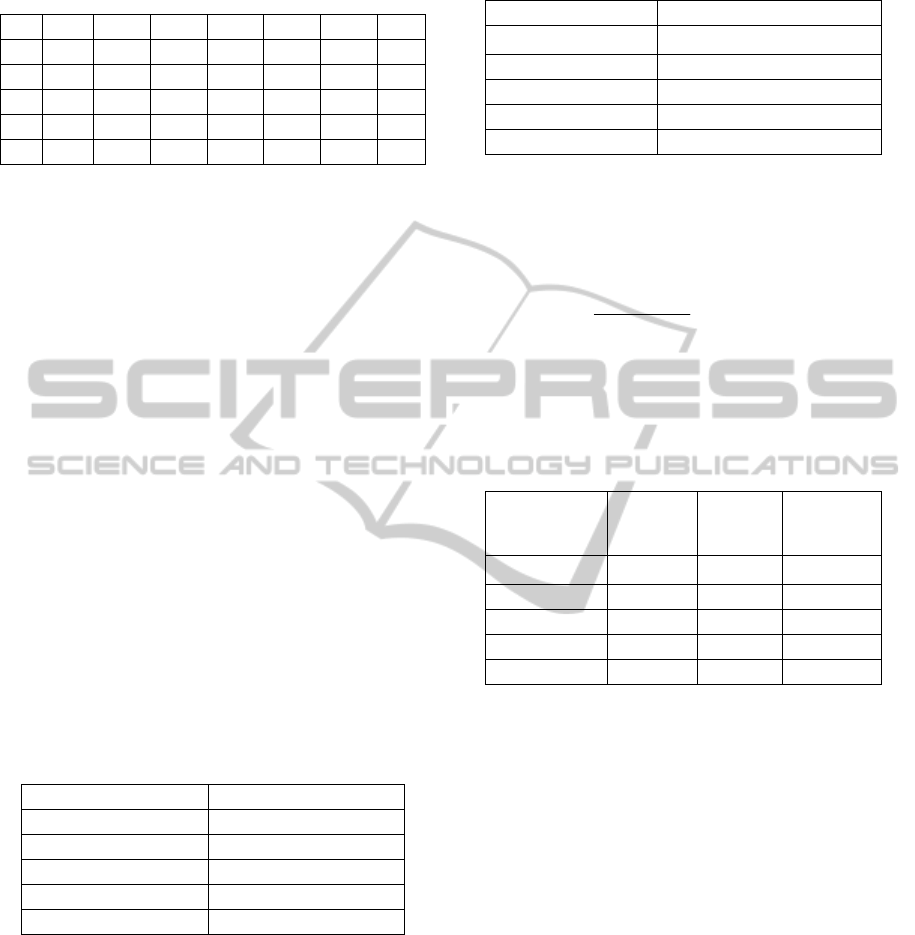
Table 2: Distribution tables of different people in different
evaluation grades.
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
I1 4 19 203 404 349 69 3
I2 21 62 151 378 315 87 37
I3 55 108 204 293 266 88 37
I4 33 69 197 363 256 104 29
I5 2 5 36 141 520 277 70
The
I1, I2, I3, I4 and I5 stand for the Ticket
Price, Convenience, Train Speed, Comfort
and
Security
correspondingly.
We Standardize and normalize the membership
matrix composed of the evaluation form in Table
2.Then we calculate the Distribution matrix of
different people. The result is as follows.
75
0.0038 0.0200 0.0523 0.0314 0.0019
0.0181 0.0590 0.1028 0.0657 0.0048
0.1931 0.1437 0.1941 0.1874 0.0343
( ) 0.3844 0.3597 0.2788 0.3454 0.1342
0.3321 0.2997 0
ij
p
.
.2531 0.2436 0.4948
0.0657 0.0828 0.0837 0.0990 0.2636
0.0029 0.0352 0.0352 0.0276 0.0666
According to the entropy formula:
1
ln ( 1, 2, ).
n
jijij
i
HKppj n
We calculate the entropy of each index in
Table 3.
Table 3: Entropy of each index.
Entropy
()
j
H
Ticket Price
1
()
c
0.2838
Convenience
2
()
c
0.173
Train Speed
3
()
c
0.0985
Comfort
4
()
c
0.1432
Security
5
()
c
0.3016
According to the formula of the coefficient of
variation, we get the final objective weight of each
index. The results are as follows in Table 4.
Table 4: Objective weight of each index.
Objective Weight
()
j
w
Ticket Price
1
()c
0.2838
Convenience
2
()
c
0.173
Train Speed
3
()
c
0.0985
Comfort
4
()
c
0.1432
Security
5
()
c
0.3016
6.3 Calculate the Comprehensive
Weight
Finally, according to the comprehensive weight
formula:
1
.
si oi
i
m
s
ioi
i
ww
w
ww
We get the comprehensive weight of each index
in Table 5.
Table 5: Comprehensive weight of each index.
Subject
()
s
i
w
Object
()
oi
w
Complex
()
j
w
Ticket Price
0.186985 0.2838 0.2645
Convenience 0.205931 0.173 0.1776
Train Speed 0.214168 0.0985 0.1052
Comfort 0.174629 0.1432 0.1246
Security 0.218287 0.3016 0.3282
7 CONCLUSIONS
The result of the objective weight calculated by the
entropy theory is that the weight of the Security is
the highest which is the same to the subjective
weight of Security calculated by the rough set theory.
That is to say all the people consider their personal
security as the most important part in their travel, no
matter subjectively or objectively. Besides,
passengers pay more attention on the Train Speed
and Convenience than the Ticket Price and the
Comfort subjectively. But objectively passengers
usually think the Ticket Price and Convenience are
more important than the Comfort and the Train
Speed. In general, the results of the comprehensive
weights show that the passengers pay the most
attention on Security. The followed indexes are the
Ticket Price and the Convenience. The Comfort and
Train Speed are not important enough to arouse too
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
634

much attention of passengers in their travel generally.
So based on this result the railway department
should try their best to ensure the passengers’
personal and property safety. They should improve
the safety of train operation and reduce the accident
rate so that they can more passenger flows.
Moreover, the railway department should make more
appropriate strategies which are more diversified
and flexible to provide the passengers more choice
in the ticket price make them feel more satisfied.
What’s more, the railway department should
improve the convenience of the passenger transfer
between the railway and the other ways so that they
can reduce the passengers’ transfer times and lower
their burden. At last we should provide a more
comfortable environment and raise the travel speed
reasonably to give the passengers a more convenient
and comfortable service.
REFERENCES
Wu Chun-you, Liu Yan, 2010. Urban renewable resources
stakeholders satisfaction evaluation model and
empirical research. China’s population - Environment
and Resources. 20 (30). 117-123.
Ma Xiao-ying, Zhang Guo-hai, Han Shu-fen, 2007.5. The
university library reader’s comprehensive fuzzy
satisfaction evaluation based on the entropy.
Information science. 25 (25). 715-719.
Song Li-min, 2009.4. Reader’s comprehensive fuzzy
satisfaction evaluation based on the AHP and entropy
method. Modern information. 29(4). 58-61.
Meng Ming, Niu Xiao-dong, Gu Zhi-hong, 2005.7. Power
customer’s satisfaction evaluation model based on the
fuzzy entropy theory. Journal of North China Electric
Power University. 32 (4). 68-70.
Peng Jin-shuan, Hao Yi-ming, Peng Li-fang, 2007. The
public transportation fuzzy comprehensive satisfaction
evaluation based on the entropy theory. Shan Xi
Construction.
Xiong Ping, Cheng Hua-bin, Wu Xiao-ping, 2003. A
comprehensive weighting method based on the rough
set theory. Journal of Naval University of Engineering.
Hao Cheng, Li Jing, Li Xue-Mei, Li Xue-wei, 2008. The
research of the weight of the effectiveness factors in
the urban rail transit project based on the rough set. 29
(6). 121-125.
Liu Jie, Li Chao-feng, Li Xiao-peng, Wen Bang-chun,
2008. Product generalized quality evaluation and
application based on matter element and the combined
weights. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural
Science Edition). 29 (9). 1314-1317.
China Research Center of Industrial Safety in Beijing
Jiaotong University, 2009.Report of China Financial
Industry Security in 2009. Publisher of Beijing
Jiaotong University. 138-148.
Chun-bao Chen, Li-ya Wang, 2006. Rough Set-Based
Clustering with Refinement Using Shannon’s Entropy
Theory.Computers and Mathematics with Applications.
1563-1576.
Don-Lin Mon, Ching-Hsue Cheng, Jiann-Chern Lin, 1994.
Evaluating weapon system using fuzzy analytic
hierarchy process based onentropy weight. Fuzzy Sets
and Systems.127-134.
Hong Zhang, Chao-lin Gu, Lu-wen Gu, Yan Zhang, 2011.
The evaluation of tourism destination competitiveness
by TOPSIS & information entropy —A case in the
Yangtze River Delta of China. Tourism Management.
APPENDIX
This paper was supported by “National Science and
Technology Support Projects (2009BAG12A10-1)”
and “Railway Ministry Projects (2010Z012)”.
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF THE RAILWAY PASSENGER'S SATISFACTION BASED ON ROUGH SET
AND ENTROPY
635
