
NURSE SCHEDULING BY COOPERATIVE GA WITH PENALTY
COEFFICIENT ADJUSTMENT
Makoto Ohki and Hideaki Kinjo
Division of Information and Electronics, Graduate School of Tottori University
101, 4 Koyama Minami, Tottori, 680-8552 Japan
Keywords:
Nurse scheduling, Genecit algorithm, Cooperative genecitic algorithm, Penalty coefficient adjustment.
Abstract:
This paper describes a penalty adjustment technique for CGA applied to the nurse scheduling problem. The
nurse scheduling is very complex task, because many requirements must be considered. In real hospital, some
changes of the schedule often happen. Such a change of the shift schedule yields various inconveniences.
Such an inconvenience causes the fall of the nursing level of the whole nurse organization. Furthermore,
reoptimization of the schedule including such changes is very hard task and requires very long computing
time. To improve this problem, we propose a technique to adjust penalty coefficient through the optimization.
1 INTRODUCTION
General hospitals consist of several sections such as
the internal medicine department and the pediatrics
department. Each section is arranged by the nursing
staff of about fifty to thirty. A section manager makes
a roster, or a shift schedule, of all nurses in her/his
section every month. The manager considers more
than fifteen requirements for the scheduling. Such
the schedule arrangement, in other words, the nurse
scheduling, is very complex task. Therefore, com-
puter software for the nurse scheduling has recently
come to be strongly required.
The shift schedule generated by such the com-
mercial software is unsatisfactory. In fact, the nurse
schedule is still made by the hand of the manager in
many general hospitals. The optimization algorithm
of such the commercial software is still poor. We
discuss on generation and optimization of the nurse
schedule by using the Cooperative Genetic Algorithm
(CGA) (T. Itoga, 2003). CGA is a kind of Genetic Al-
gorithm (GA) (D. E. Goldberg, 1989), and powerful
optimizing algorithm for such a combinatorial opti-
mization problem.
Burke et al. (E. K. Burke, 2001) have proposed
a technique to evaluate the nurse schedule. How-
ever, this technique does not fit to the shift system
of our country. Therefore, we have to define the
evaluation technique of the nurse schedule. In the
real case, there are some cases that nurses attend
on a different day from the original schedule. We
have discussed such a case that the schedule has been
changed in the past weeks(M. Ohki, 2007; S. Uneme,
2008). The changed schedule must be reoptimized to
avoid various inconveniences. Such an inconvenience
causes the fall of the nursing level. Reoptimization of
the schedule including such the changes is very hard
task even by parallel computing techniques (M. Ohki,
2010b; M. Ohki, 2010a). We consider that this com-
plexity is caused by that there are many local minima
in the solution space of the nurse scheduling prob-
lem. We propose a technique adjusting penalty coef-
ficient through the optimization when the concerned
penalty function stagnate decreasing. If the optimiza-
tion is caught in the region of the local minimum,
some penalty functions stagnate decreasing. Valley
of the local minimum upheaves by increasing weight
of such the penalty function. And then, the search-
ing point of the optimization escapes from the local
minimum region.
2 NURSE SCHEDULING BY CGA
In the nurse scheduling by CGA, an individual and
a population, are defined as shown in Fig.1. The in-
dividual consists of the series of the shift symbols.
The shift series consists of 28 fields, where it means
four weeks. The i-th individual expresses one-month
schedule of the i-th nurse. In CGA, each individual
denotes the schedule of each nurse. The population
255
Ohki M. and Kinjo H..
NURSE SCHEDULING BY COOPERATIVE GA WITH PENALTY COEFFICIENT ADJUSTMENT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003618902550258
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications (ECTA-2011), pages 255-258
ISBN: 978-989-8425-83-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
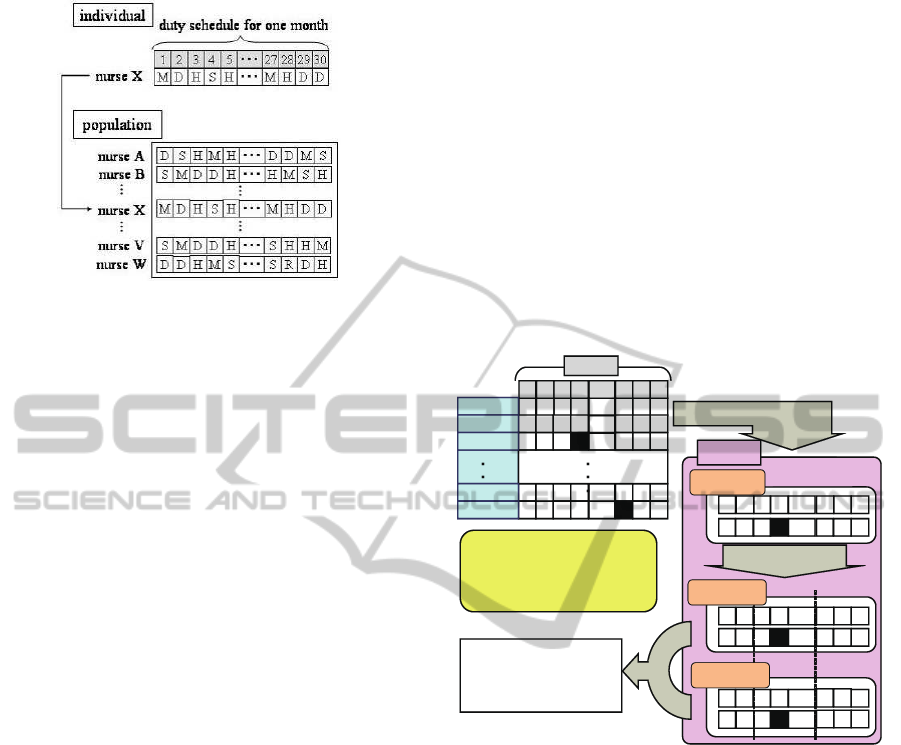
Figure 1: The individual and the population.
denotes one-month schedule.
We have summarized all the requirements into the
13 penalty functions to evaluate the population. De-
tail of these penalties has been shown in the previous
research work (M. Ohki, 2010a). We describe an out-
line of each penalty.
The following penalty functions evaluate work
load of each nurse. A penalty function F
1i
evalutates
the work loard of each nurse i for three consecutive
days. A penalty function F
2i
evaluates to prohibit the
X night shift or more for the consecutive Y days. A
penalty function F
3i
evaluates specific prohibited shift
pattern.
The following penalty functions evalute the num-
ber of the shifts impartially assigned. Penalty func-
tions F
4i
, F
5i
supress unevenness of the number of
shifts among nurses on the holidays and the night
shifts. A penalty function F
6i
restrains assignment of
the shift on many consecutive shift days.
In our CGA, the number of nurses in each work-
ing hours is preserved in any case. We define penalty
functions F
7j
, F
8j
and F
9j
to evaluate the nursing level
on the day time shift, the semi-night shift and the mid-
night shift respectively.
The following penalty functions evaluate about
the combination of the nurses. A penalty function F
10j
restrains unfavorable affinity of nurses. A penalty
function F
11j
restrains unfavorable situation that too
many new faces are assigned on the midnight shift. A
penalty function F
12j
restrains unfavorable situation
that one or more expert or more skilled nurses are not
assigned to the daytime shift and the midnight shift.
A penalty function F
13
performs the difference be-
tween the original schedule and the newly optimized
schedule of the remainder of the current month to
restrain the falls of the nursing level because of the
change of the schedule.
Finaly, we perform the shift schedule by the fol-
lowing total penalty function at g-th generation,
E(g) =
∑
i
(h
1
F
1i
+ h
2
F
2i
+ h
3
F
3i
)
+
∑
i
(h
4
F
4i
+ h
5
F
5i
+ h
6
F
6i
)
+
∑
j
(h
7
F
7j
+ h
8
F
8j
+ h
9
F
9j
)
+
∑
j
(h
10
F
10j
+ h
11
F
11j
+ h
12
F
12j
) + h
13
F
13
, (1)
where h
1
—h
13
denote penalty coefficients.
The basic algorithm of the CGA is as shown in
Fig.2 (M. Ohki, 2006; M. Ohki, 2007; S. Uneme,
2008). CGA applies the crossoveroperator to the pop-
ulation and searches so that a penalty of the whole
population becomes small.
D S
S M
1 2
h
D
M
D
3 4
nurse A
nurse B
S
D
D
D D
h
M
M
D M S
M S
h
26 27 28
h
h M
H
D
h
䊶䊶䊶
䊶䊶䊶
䊶䊶䊶
䊶䊶䊶
䊶䊶䊶
M h D Hnurse C
S h
D
䊶䊶䊶
nurse Y
nurse Z
date
D S h M D M S
䊶䊶䊶
M h D H
S h
D
䊶䊶䊶
crossover
D S
h
M D M S
䊶䊶䊶
M h
D
H
S h
D
䊶䊶䊶
D S
h M
D M S
䊶䊶䊶
M h
D H
S h
D
䊶䊶䊶
two-point crossover
Each pair is taken back to
the original position of
their parents and whole
population is performed.
select two individuals
parent pair
child pair 1
child pair 2
This procedure is repeated for
100 parent pairs. One pair
giving best performance is
selected for the next generation.
Figure 2: One generation cycle by the crossover operator.
When the optimization stagnates for long genera-
tion cycles, it is effectiveto forcibly give small change
to the population. Therefore we have proposed a mu-
tation operator activated depending on the optimiza-
tion speed V
E
(g). When V
E
becomes less than or
equeal to a speedo-thleshold ε
E
, the mutation is ac-
tivated. We have defined two parameters, a guard
interval G
g
to prevent the activation of the mutation
operator for G
g
generation cycles right after the last
activation.
We also have proposed a periodic mutation opera-
tor activated periodically in G
M
generation cycles(M.
Ohki, 2010b). This mutation is advantage on the point
that fewer parameter is required to define itself.
3 PENALTY ADJUSTMENT
The shape of the solution space is defined by the pen-
ECTA 2011 - International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
256

alty function E(g). By changing the penalty coeffi-
cients, the shape of the solution space is also changed.
Valley of the local minimum upheaves by increasing
weight of such the penalty function. And then, the
searching point of the optimization escapes from the
local minimum region. The optimization flow with
Penalty coefficient Adjustment (PA) is as shown in
Figure 3.
START
C
M
=N
M
?
Y
N
mutation
operator
N
Y
crossover operator
initialize
END
PA
?0%
M
=∨< Ggv
EE
ε
)13,,2,1(1:
,0:,
L==
=++
kh
NC
k
gM
++
++
g
N
g ,
Figure 3: Optimization flow with the penalty adjustment.
First, all the penalty coefficients h
1
—h
13
are ini-
tialized to 1. The decreasing speed of each penalty
function at the generation cycle g, V
k
(g), is calculated
in PA by the following equations,
A
k
(g) =
1
N
g
N
g
−1
∑
h=0
M
∑
i=1
F
ki
(g− h) (k ≤ 6),
1
N
g
N
g
−1
∑
h=0
D
∑
j=1
F
kj
(g− h) (k > 6),
(2)
V
k
(g) = A
k
(g− 1) − A
k
(g). (3)
As shown in Figure 4, when the decreasing speed of
the k-th penalty function, V
k
, becomes less than or
equal to a speed threshold ε
F
, the penalty coefficient
h
k
is increased by multiplying with parameter α. In
this research, the values of ε
F
and α are defined as
0.01 and 1.01 respectively. When the mutation is ac-
tivated, all the penalty coefficients h
1
—h
13
are initial-
ized to 1 again.
4 PRACTICAL EXPERIMENT
We have tried computational experiment of the nurse
scheduling with practical data. In order to compare
exactly, we have tried to optimize the ten times un-
der each condition. Figures 5 (a)—(c) show examples
13 penalty coefficients
PA
F
tv ε≤)(
2
22
: hh ⋅= α
Y
N
F
tv ε≤)(
13
1313
: hh ⋅= α
Y
N
F
tv ε≤)(
1
11
: hh ⋅= α
Y
N
Figure 4: Primitive operation of the penalty coefficient ad-
justment.
of the variation of the penalty coefficients modified
by PA. In the initinal stage of the optimization, sev-
eral coefficients are increased extremely. While the
optimization progresses, the penalty coefficients wig-
gle for long term of the generation cycle. In these
generation cycles, the mutation is activated in a short
period. In other words, the optimization stagnates fre-
quently. This means that the optimization is caught
in the local minimum region. Approaching the end of
the optimization, we can find several generation inter-
vals which the mutation is not activatedand then some
of coefficients are increased extremely. In these inter-
vals, the optimization progresses for a long generation
interval. In the final stage of the optimization, the pro-
gression of the optimization clearly represented. This
suggests that the optimization goes towards conver-
gence.
Figure 6 shows optimization progress by using the
periodic mutation operator and PA respectively. The
red dotted lines and blue solid lines denote maximum,
average and minimum value of the penalty function E
given by the periodic mutation and PA respectively. In
one trial, the optimization is executed for N
M
= 500
mutation cycles. By means of PA, the optimization
finishes in about one-tenth generation cycles by the
periodic mutation.
Figure 7 shows comparison of the maximum, the
average and the minimum value of the ten results un-
der each technique. Compared to the periodic muta-
tion operator, PA is slightly worse. Both results are,
however, within the range between 169—174. This
means that both results are almost regarded as satis-
factory.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has shown a technique of nurse scheduling
by using CGA. We have discussed the case that the
nurse schedule has been changed in the past weeks.
To reoptimize the changed schedule, we have de-
NURSE SCHEDULING BY COOPERATIVE GA WITH PENALTY COEFFICIENT ADJUSTMENT
257

1
10
100
1000
10000
100000
1000000
10000000
100000000
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000
penalty coefficient
generation cycle
h1
h2
h3
h4
h5
h6
h7
h8
h9
h10
h11
h12
h13
(a) from 0-th generation to 10000-th generation
1
10
100
1000
10000
100000
1000000
10000000
30000 32000 34000 36000 38000 40000
penalty coefficient
generation cycle
h1
h2
h3
h4
h5
h6
h7
h8
h9
h10
h11
h12
(b) from 30000-th generation to 40000-th generation
1
10
100
1000
10000
100000
1000000
10000000
penalty coefficient
generation cycle
h1
h2
h3
h4
h5
h6
h7
h8
h9
h10
h11
h12
h13
(c) from 100000-th generation to the final generation
Figure 5: The variation of the penalty coefficients. Each
vertical axis shows on a logarithmic scale.
165
170
175
180
185
190
0 200000 400000 600000 800000 1000000
penalty E
genera!on cycle g
Figure 6: Comparison of the optimization progress between
CGA with the periodic mutation and CGA with PA.
168
170
172
174
convenonal
PA
Penalty Funcon E
Figure 7: Comparison of the optimization result between
the periodic mutation and PA.
fined a penalty function performing the difference be-
tween the original schedule and the optimizing sched-
ule. Therefore we need new techniques to search for
good schedule effectively. We have proposed a tech-
nique adjusting the penalty coefficient depending on
the optimization progress, PA. This technique is im-
plemented with the mutation depending on the opti-
mization speed. By means of PA, the optimizationfin-
ishes within one-tenth generation cycles by the con-
ventional periodic mutation technique.Thus, the ef-
fectiveness of PA is confirmed.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research work has been supported by Tot-
tori University Electronic Display Research Center
(TEDREC).
REFERENCES
D. E. Goldberg (1989). Genetic Algorithm in Search, Opti-
mization and Machine Learning. New York.
E. K. Burke, P.De Causmaecker, S. G. (2001). Fitness eval-
uation for nurse scheduling problems. In Proceedings
of the 2001 Congress on Evolutionary Computation.
M. Ohki (2010a). Effective mutation operator for nurse
scheduling by cooperative ga and its parallel process-
ing. In 19th Int. ACM Workshop on Parallel Architec-
tures and Bioinspired Algorithms, pages 1–8.
M. Ohki, S.Uneme, H. (2010b). Effective mutation operator
and parallel processing for nurse scheduling. In Stud-
ies in Computational Intelligence, volume 299, pages
229–242. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-13428-9 10.
M. Ohki, A. Morimoto, K. (2006). Nurse scheduling
by using cooperative ga with efficient mutation and
mountain-climbing operators. In 3rd Int. IEEE Con-
ference Intelligent Systems, pp.164-169.
M. Ohki, S. Uneme, S. M. (2007). Effective genetic
operators of cooperative genetic algorithm for nurse
scheduling. In 4th Int. INSTICC Conference on In-
formatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages
347–350.
S. Uneme, H. Kawano, M. (2008). Nurse scheduling by co-
operative ga with variable mutation operator. In Proc.
of 10th ICEIS, INSTICC, pages 249–252.
T. Itoga, N. Taniguchi, Y. K. (2003). An improvement on
search efficiency of cooperative ga and application on
nurse scheduling problem. In Proc. of 12th Intelligent
System Symposium, pages 146–149.
ECTA 2011 - International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
258
