
MANAGING INSIGHTS: A REPOSITORY FOR PROCESS
ANALYTICS, OPTIMIZATION AND DECISION SUPPORT
Florian Niedermann, Holger Schwarz and Bernhard Mitschang
Institute of Parallel and Distributed Systems, University of Stuttgart, Universit
¨
atsstrasse 38, Stuttgart, Germany
Keywords:
Process repository, Business process management, Business process decision support, Business process
optimization, Business process analytics, Analysis results sharing.
Abstract:
The success of many large businesses depends on quality of their business processes. Consequently, there
are numerous approaches to the analysis and the optimization of these processes. The focus of most of these
approaches is, however, on the generation and monitoring of basic metrics, such as the process duration.
Further, analysis results are typically considered to be ”one-off” efforts, without giving too much thought to
reuse. Together, these two factors can have a negative impact on the business process quality, as improvements
are either not discovered at all or might be not considered when the context changes. To address this issue, this
paper presents an insight-oriented process repository that centrally captures insights based on standardized
metrics, data integration and mining methods as well as graph analysis algorithms. The usefulness of this
approach is demonstrated in an application to process optimization
1 INTRODUCTION
This section first provides the paper’s motivation by
illustrating how a semantically-rich repository for
process insights can assist process optimization and
hence ultimately improve process quality. Then, it in-
troduces the platform that provides the means both for
generating the insights captured in such a repository
and for using the information contained within.
1.1 Motivation
In the past decade, businesses have moved from
tweaking individual business functions towards op-
timizing entire business processes. Originally, this
trend - then geared towards fundamental process re-
design and called Business Process Reengineering
(Hammer and Champy, 1993) - was triggered by the
growing significance of Information Technology and
the trend towards globalization (Champy, 1995). The
increasing volatility of the economic environment and
competition amongst businesses has further increased
its significance over the past years and also created the
need for faster, often incremental process improve-
ments as well as continual monitoring of process per-
formance.
To address this need, most businesses nowadays
have dedicated staff tasked with business process
deep
Business
Data
Integra-tion
(dBI)
Process
Data
Integrated DWH
Operational
Data
Match-
ing
Process Insight Repository
(PIR)
Preprocessing, Analytics
and Aggregation
deep
Business
Process
Analytics
(dBPA)
deep
Business
Process
Optimization
(dBPO)
Design Execution Analysis
Optimization stages
Focus of
this
paper
Figure 1: Platform Architecture Overview.
analysis and optimization. Despite this considerable
effort, most organizations are still looking for new
ways of further improving process performance. This
improvement can be achieved along two dimensions:
First, the analysis methods themselves can be im-
proved in order to gain more and better process in-
sights, i.e., knowledge that is useful with respect to
improving the process. This can be achieved by going
beyond the basic metrics offered by most of today’s
process design tools and including, e.g., data mining
algorithms (Zur M
¨
uhlen and Shapiro, 2009) and for-
malized domain knowledge (Niedermann et al., 2011)
in the analysis. Second, the access to the gained
insights can be improved to ensure that generated
424
Niedermann F., Schwarz H. and Mitschang B..
MANAGING INSIGHTS: A REPOSITORY FOR PROCESS ANALYTICS, OPTIMIZATION AND DECISION SUPPORT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003625604240429
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (RDBPM-2011), pages 424-429
ISBN: 978-989-8425-81-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

insights are actually applied in different situations.
While making the insights available, e.g., in basic text
documents can be a first step towards this, the lack
of semantics provided by this approach limits its use-
fulness. Instead, a semantically-rich process reposi-
tory is required that is able to capture and make avail-
able the process insights gained, e.g., through the im-
proved analytics discussed before.
1.2 Platform
To realize the improvements discussed in the pre-
vious section, a platform is required that goes be-
yond the capabilities of most of today’s process de-
sign tools, both in respect to its analytics and insight
management capabilities. For this purpose, we have
developed the deep Business Optimization Platform
(dBOP) (Niedermann et al., 2010a) shown in Figure 1
that combines three different layers aimed at improv-
ing the quality and the usability of process insights:
• Data Integration. Data that is relevant to the pro-
cess can be distributed across a number of rele-
vant sources. While the most commonly used data
source is process execution data contained in the
audit trail of the Business Process Management
System (BPMS), other relevant data is typically
contained in operational data sources. The first
layer of hence provides the facilities to integrate
heterogeneous data sources using custom schema
integration techniques.
• Process Analytics. Based on the integrated
source data and the process model, process in-
sights can be generated. For that purpose, the
platform combines a set of standardized process
metrics with graph analysis and data mining algo-
rithms. The results of the insight generation are
stored in the Process Insight Repository (PIR).
• Process Optimization. Finally, the insights
stored in the PIR are used by one or several appli-
cations for the improvement of the process qual-
ity. This can be either while (manually) analyz-
ing the process, while conducting an optimization
with a specific goal in mind or for decision sup-
port during the execution of the process.
The main contribution of this paper is the stor-
age and the management of process insights within
the PIR. It introduces the meta-model that is used to
describe semantically-rich processes within the PIR,
discusses which insights are contributing to the goals
of the PIR and provides the information model that is
used to integrate the insights with the process models.
Other aspects of the platform have been discussed ex-
tensively in previous work of the authors. This paper
Insight-augmented Model
Derive Data Mining Models
4
Identify special Constructs
3
Analyze Dependencies
2
Dec
3 min
100%
7 min
100%
4 min
30%
3 min
20%
7 min
50%
4 min
100%
Initial Process Model
Compute Metrics
1
3 min
100%
Dec-
ision
Dec
Control Data Resource
Execu-
tion
Ana-
lysis
Model
Ana-
lysis
Figure 2: Process Analysis Conceptual Overview.
will hence only cover them as far as they are necessary
to further the understanding of the PIR’s role and de-
pendencies within the platform. For this purpose, the
paper is structured as follows. First, Section 2 gives a
brief overview of the analysis methods used to popu-
late the PIR. Next, Section 3 introduces both the types
of insights captured in the PIR and the model used for
doing so. Section 4 then proceeds to explain how the
PIR manages access to and changes of the insights
contained within. Next, Section 5 illustrates the use-
fulness of the insights contained in the PIR through a
sample application scenario. Finally, Section 6 dis-
cusses related work before concluding the paper in
Section 7.
2 PROCESS ANALYTICS
To provide the data contained in the process knowl-
edge component of the PIR, both the process mod-
els and their execution data need to be analyzed, as
shown in Figure 2.
As the first step, execution data is aggregated us-
ing a set of process metrics which are discussed in
more detail in the next section. Next, the dependen-
cies within the process model that might allow or dis-
allow certain optimizations of the process, e.g., par-
allelization or the relocation of knockout sequences
(Van der Aalst, 2001), are assessed. Based on the
metrics and the initial model result, so called ”spe-
cial process constructs” are identified in the third step.
These are activities or sub-processes that warrant spe-
cial further examination by additional analysis tech-
niques. One example for that step is the identification
of decisions within the process, as they are a prime
candidate for analytical support or even automation
(Rozinat and van der Aalst, 2006b) based on data min-
ing models. Finally, Data Mining models are con-
MANAGING INSIGHTS: A REPOSITORY FOR PROCESS ANALYTICS, OPTIMIZATION AND DECISION
SUPPORT
425
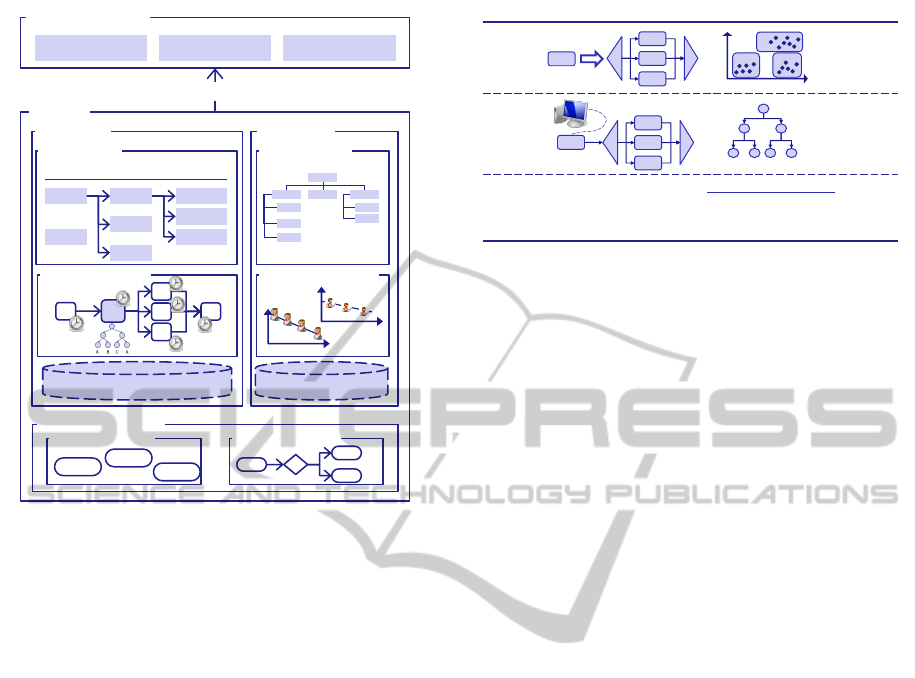
Business Domain
Context
Manufacturing Procurement Logistics
Processes Resources
Template Objects
Implements
Model Variant Version
M1
M2
Var11
Var12
Var13
V11_1
V11_2
V11_3
Resource DB
Resource Model
Activity Templates Process Fragments
AcT1
AcT2
AcT3
x
Process Model
Resource Knowledge
Process DB
Process Knowledge
Dec
3 min
100%
7 min
100%
4 min
30%
3 min
20%
7 min
50%
4 min
100%
Figure 3: PIR Content Overview.
structed for various process elements. This includes
the determination of process variants using clustering
techniques, or, as in Figure 2, the automation of deci-
sions with decision or model trees (Han and Kamber,
2006).
3 PROCESS INSIGHTS
After the previous section has introduced the meth-
ods to generate the insights contained in the PIR, this
section will focus on discussing its actual contents.
First, we will give an overview of the PIR contents.
Next, the contained metrics are discussed. Finally, we
discuss how further process insights can be derived
through the use of Data Mining models.
3.1 Content Overview
The top structuring element of the PIR is, as shown
in Figure 3, the process context. A process context
groups processes that are executed in a similar envi-
ronment and that, e.g., share access to a common set
of resources. A process context belongs to one or sev-
eral business domains. These business domains pro-
vide template objects, sample optimization patterns
(see Section 5) and other domain-specific function-
ality that can be reused by a context.
Within a context, information about the processes
Task Illustration Data Mining Technique
Detect
Process/
Activity
Variants
Decision
Automation/
Support
Rule
Identifi-
cation
Attributes
Dura-
tion
A B C A
A1 A2
A3
A
A2
A1
A3
X X
B
A
C
X X
D
Clus-
tering
Deci-
sion/
Model
Tree
IF Status =“GOLD”
AND Volume > EUR 5.000
THEN Discount = “TRUE”
Set Support Conf.
Asso-
ciation
Rule
Mining
{G,>5k,TRUE} 0,4 0,90
{G,>5k,FALSE} 0,04 0,10
{G,<5k,TRUE} 0,1 0,50
Figure 4: Data Mining Algorithms matched to Analysis
Tasks.
and the resources belonging to that context are stored.
Further, it is possible to store template objects, e.g.,
sub processes that are frequently used and shared
across a number of processes, within a context. Both
processes and resources are described by their re-
spective models, additional knowledge captured, e.g.
through data mining or metrics and through a process-
or resource-centric view on the instance data which is
stored in the integrated Data Warehouse of the plat-
form shown in Figure 1. The PIR additionally con-
tains meta-information required to effectively store
and query the information contained within, that is
used in the next section to query the repository.
3.2 Metrics
Process and resource metrics seek to explain certain
aspects of the business process through the aggrega-
tion of some numerical properties. While the most
common process metrics are activity/process duration
and frequency and the most common resource metric
usually refers to utilization, other metrics can be quite
relevant for the analysis as well. Hence, we have com-
piled for the PIR a metrics catalogue from a number
of different sources. The core catalogue contains only
domain-independent metrics such as duration or fre-
quency. Domain-specific metrics, such as energy ef-
ficiency in a manufacturing context, are provided by
the business domains, as explained in Section 3.1.
3.3 Data Mining
While metrics are well-suited for capturing basic pro-
cess properties, they do not perform well when it
comes to explaining more complex behavior and de-
pendencies. For that purpose, Data Mining tech-
niques are required (Zur M
¨
uhlen and Shapiro, 2009).
Data Mining models can further be used to automate
or assist with decision activities (Rozinat and van der
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
426

Aalst, 2006a). Hence, Data Mining results are an im-
portant source of insights for the PIR.
Our platform provides a range of customized min-
ing algorithms adapted from the WEKA suite (Hall
et al., 2009). Depending on the types of process in-
sights to be gained, different Data Mining techniques
are applied as shown in Figure 4. For example, C4.5
decision trees and M5 model trees are used to auto-
matically predict the outcomes of activities. Other
mining techniques employed include association rule
mining for the identification and validation of busi-
ness rules and clustering for the identification of pro-
cess or activity variants.
4 REPOSITORY CAPABILITIES
After the previous section discussed the content of the
repository in detail, this section introduces various ca-
pabilities that the PIR offers for accessing and mod-
ifying the contained information. We focus on three
important features: Version and variant management,
repository querying and model modification.
4.1 Version and Variant Management
Like standard version management tools (Collins-
Sussman et al., 2004), the PIR supports two modes
for adapting existing processes. Through the creation
of a process version, a process designer declares that
he wants to create a refined version of that process.
As such, a new version is likely to (eventually) re-
place the process it was derived from. Versions are
implicitly created whenever a process is modified and
checked in back to the repository. The creation of
a process variant, on the other hand, is an explicit
act. By declaring a new process adaption to be a vari-
ant, the process designer explicitly creates a process
model that is based on the existing one, however, does
not supplant it. In the scenario we use for demonstrat-
ing the insight application (Section 5), this could, e.g.,
mean to create a specialized loan process for high-
value assets. When creating a new version or variant,
the insights related to the original process model are
retained. Further, changes (either manual or pattern-
based, see Section 5) are tracked to allow for later
insight mining (see Section 7).
4.2 Respository Access
The contents of the PIR can be accessed in two ways:
The basic access mode is just browsing through its
contents. While this might be sufficient for basic
applications and small repositories, access to large
Pattern Scope Category
Patterns
Activity
(Sub-)Process
Resource
Composition
Sequencing
Automation
Variants
Assignment
Org. Structure
Control
Supported Decision
Automated Decision
Task Automation
Decomposition
Composition
Activity Elimination
Parallelization
Serialization
Early Knockout
Standardization
Variant Elimination
Resource Selection
Split Workload
Specialization
Generalization
Case Manager
Rework Elimination
Knockout Elimination
Triage
Figure 5: Sample Optimization Patterns.
repositories additionally require a query interface.
The query interface of the PIR hereby allows queries
to address any of the properties that are part of the
meta-model. To accommodate for different require-
ments, the PIR supports two query modes. The exact
mode retrieves only PIR elements that fully match the
given query. This can be, e.g., used to retrieve insights
during process execution for a given activity.
The more complex and powerful fuzzy mode on
the other hand retrieves all activities, process frag-
ments or entire processes that exceed a certain sim-
ilarity threshold with regards to the given query. This
is achieved using process similarity measurements
(Niedermann et al., 2010b).
4.3 Model Modification
The models contained in the PIR can be modified in
two ways. The first way is through basic operators
that enable the insertion, deletion or modification of
model elements just as in standard process modelling
tools. The second way is by using the optimization
patterns, such as the ones shown in Figure 5, which
we briefly already mentioned in the discussion of the
role of business domains. These optimization pat-
terns are a formalization of process design best prac-
tices such as the ones described in (Reijers and Li-
man Mansar, 2005) and contain both a detection and
a modification component, which enable process de-
signers to modify processes in a goal-oriented fash-
ion. The patterns are described using the same meta-
model as the PIR. As the detection of a pattern is
based on the insights contained in the PIR, it can be
conducted automatically. Section 5 shows an exam-
ple of both the pattern detection and their application
in a case scenario.
MANAGING INSIGHTS: A REPOSITORY FOR PROCESS ANALYTICS, OPTIMIZATION AND DECISION
SUPPORT
427

Not Available
Initial Process
Duration:
23,1 minutes
Detected
patterns
1
3
Early Knockout
Supported Decision
✔
Optimized
Process
Duration:
16,1 minutes
Analyst
Plat-
form
Review
Proposal
Set Goal:
Time
Confirm
Selection
Review &
Commit
Model
Conduct
Analysis
Select
Patterns
Receive
Changes
Propose
Changes
Update
Model
Enter Loan
and
Collateral
Volume
Enter
Customer
Information
Assess
Loan
Risk
Review
Condition
Proposal
Offer Dis-
counted
Rate
Offer Low
Rate
Enter
Customer
Infor-
mation
4 min
100%
4 min 70%
3 min
70%
2,5 min
70%
2 min 50%
2 min 20%
3 min 70%
Good
Nor-
mal
Check
Collat-
eral
Ratio
Cancel
Loan
Ok
Not
Ok
1 min
100%
2 min 30%
Propose
Loan
Condit-
ions
0,5 min
70%
Updated by
optimizer
Enter
Loan and
Collateral
Volume
Enter
Customer
Infor-
mation
Assess
Loan
Risk
Check
Collat-
eral
Ratio
Decide on Loan
Conditions
Cancel
Loan
Offer Dis-
counted
Rate
Offer Low
Rate
Enter
Customer
Infor-
mation
Ok
Not Ok
4 min
100%
4 min
100%
3 min
100%
1 min
100%
10 min 70%
2 min
30%
2 min 50%
2 min
20%
3 min
70%
Good
Normal
Assess
Loan
Risk
Check
Collateral
Ratio
Enter
Cust.
Info.
2
Automated Decision
✘
Decide on Loan
Conditions
✔
1
2 3
Decide on Loan
Conditions
Propose Loan
Conditions
Figure 6: Loan Process Optimization Example.
5 INSIGHT APPLICATION
This section briefly demonstrates the application of
the insights contained in the PIR for a sample pro-
cess scenario. As the applications to process analysis
are fairly obvious (i.e., largely revolve around queries
to the PIR as described above) we will focus on the
applications of the PIR to process optimization and
decision support.
For the demonstration, the (greatly simplified)
loan handling process shown in the upper part of Fig-
ure 6 is used. In it, a bank clerk first enters all the
customer’s details as well as the details of the loan
being requested. After it has been verified that the ra-
tio of loan volume to collateral exceeds a certain mini-
mum, the loan risk is assessed and the loan conditions
are set accordingly. As the process has already been
analyzed, the upper part of Figure 6 already shows
the activity durations and frequencies. Not shown in
Figure 6, the analyzer has also identified two special
process constructs: ”Check Collateral Ratio” initiates
a knockout sequence, while ”Decide on Loan Condi-
tions” is the decision node of a corresponding deci-
sion.
The optimization of the process is depicted
throughout Figure 6. First, the business analyst de-
cides on the optimization goal ”process duration”.
The optimizer then selects patterns that are conduc-
tive to this goal and determines which of these pat-
terns are applicable.
In this scenario, the optimizer can identify three
applicable patterns from the catalogue of standard
patterns. First, the knockout sequence ”Check Collat-
eral Ratio” → ”Cancel Loan” can be executed right
after the loan and collateral volume have been en-
tered. Hence, the Early Knockout pattern can be ap-
plied, moving the knockout sequence and reducing
average process duration by 2,1 minutes, as the subse-
quent activities are only executed in 70% of the cases.
Second, as the ”Decide on Loan Condition” deci-
sion takes up considerable time and there is a high-
quality decision tree available in the PIR, the opti-
mizer proposed to either automate or support the deci-
sion with said classifier, respectively using the Auto-
mated Decision or the Supported Decision patterns.
In our scenario, the process analyst decides not to
fully automate, but instead support the decision of the
clerk by providing the clerk with a model-based solu-
tion proposal. The clerk then only has to check that
everything is in order (which, in this case scenario,
is assumed to reduce the activity duration by 75%).
Overall, this additionally reduces the process dura-
tion by 4,9 minutes. Hence, the optimized process,
as shown in the lower part of Figure 6, now requires
on average 7 minutes less in total than the original
process
6 RELATED WORK
The Process Insight Repository (PIR) presented in
this paper is part of our ongoing work on creating
a platform for the (semi-)automated, analytical opti-
mization of business processes, please see (Nieder-
mann et al., 2011) for an overview of both the plat-
form and of related work.
Both the importance of using analytics in process
optimization and the need for managing process mod-
els in a central repository has been (separately) widely
recognized both in research and in practice. However,
the combination of these two concepts so far is not
widely covered. Closest to the approach presented
is the work on integrated process warehouses (Casati
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
428

et al., 2007), Business Process Intelligence (Grigori
et al., 2004), Business Process Analytics (Zur M
¨
uhlen
and Shapiro, 2009) and some variants of Process Min-
ing (Van der Aalst et al., 2010). However, these ap-
proaches typically focus on data integration and anal-
ysis issues and less on the representation and sharing
of process-centric insights.
Various approaches deal with enhancing the de-
sign of process repositories. (Ma et al., 2007) pro-
poses a semantic business process repository, that
uses in-built reasoning capabilities for retrieving
process models for a given (semantic) user query.
(Shahzad et al., 2009) discusses various requirements
for process repositories and provides an evaluation
of some existing implementations, however, without
giving significant consideration to the analytical di-
mension.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND
CURRENT WORK
This paper has presented a semantically rich Process
Insight Repository (PIR). The PIR provides a central
place for the storage of aggregated process insights
and provides the facilities to access these insights both
at process design, execution and analysis time. Be-
yond improving the sharing of insights across an orga-
nization, the PIR also enables increased efficiency and
effectiveness of business process optimization. This
is achieved by combining the insights contained in
the PIR with so called optimization patterns, which
represent formalized process best practice for the ap-
plication domain of the given process.
Our current work on the PIR is concerned with
two major topics. First, we are working on the im-
plementation of additional business domains, with a
special focus on the manufacturing domain. Second,
we are exploring the possibilities of insight mining,
i.e., the application of data mining techniques to the
models contained in the PIR.
REFERENCES
Casati, F., Castellanos, M., Dayal, U., and Salazar, N.
(2007). A generic solution for warehousing business
process data. In Proceedings of the 33rd international
conference on Very large data bases, pages 1128–
1137.
Champy, J. (1995). Reengineering Management. Harper-
Collins.
Collins-Sussman, B., Fitzpatrick, B., and Pilato, C. (2004).
Version control with subversion. O’Reilly Media, Inc.
Grigori, D., Casati, F., Castellanos, M., Dayal, U., Sayal,
M., and Shan, M. (2004). Business process intelli-
gence. Computers in Industry, 53(3):321–343.
Hall, M., Frank, E., Holmes, G., Pfahringer, B., Reutemann,
P., and Witten, I. (2009). The WEKA data mining
software: An update. ACM SIGKDD Explorations
Newsletter, 11(1):10–18.
Hammer, M. and Champy, J. (1993). Reengineering the
corporation: a manifesto for business revolution.
Brealey, London.
Han, J. and Kamber, M. (2006). Data mining: concepts and
techniques. Morgan Kaufmann.
Ma, Z., Wetzstein, B., Anicic, D., Heymans, S., and Ley-
mann, F. (2007). Semantic business process repos-
itory. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Semantic
Business Process and Product Lifecycle Management
(SBPM 2007), volume 251, pages 92–100.
Niedermann, F., Radesch
¨
utz, S., and Mitschang, B. (2010a).
Deep business optimization: A platform for auto-
mated process optimization. In Proceedings BPSC
2010.
Niedermann, F., Radesch
¨
utz, S., and Mitschang, B.
(2010b). Design-time process optimization through
optimization patterns and process model matching. In
Proceedings of the 12th IEEE Conference on Com-
merce and Enterprise Computing.
Niedermann, F., Radesch
¨
utz, S., and Mitschang, B. (2011).
Business process optimization using formalized pat-
terns. In Proceedings BIS 2011.
Reijers, H. and Liman Mansar, S. (2005). Best practices
in business process redesign: an overview and qual-
itative evaluation of successful redesign heuristics.
Omega, 33(4):283–306.
Rozinat, A. and van der Aalst, W. (2006a). Decision mining
in business processes. In Business Process Manage-
ment.
Rozinat, A. and van der Aalst, W. (2006b). Decision mining
in ProM. Business Process Management, pages 420–
425.
Shahzad, K., Andersson, B., Bergholtz, M., Edirisuriya,
A., Ilayperuma, T., Jayaweera, P., and Johannesson,
P. (2009). Elicitation of Requirements for a Business
Process Model Repository. In Business Process Man-
agement Workshops, pages 44–55. Springer.
Van der Aalst, W. (2001). Re-engineering knock-out pro-
cesses. Decision Support Systems, 30(4):451–468.
Van der Aalst, W., Pesic, M., and Song, M. (2010). Beyond
process mining: from the past to present and future.
In Advanced Information Systems Engineering, pages
38–52. Springer.
Zur M
¨
uhlen, M. and Shapiro, R. (2009). Business process
analytics. Handbook on Business Process Manage-
ment, 2.
MANAGING INSIGHTS: A REPOSITORY FOR PROCESS ANALYTICS, OPTIMIZATION AND DECISION
SUPPORT
429
