
EMPLOYEES’ INNOVATION BEHAVIOR
The Role of External Information Awareness and Proactiveness
of Innovation Strategy
Jing Tang, Loo Geok Pee and Junichi Iijima
Department of Industrial Engineering and Management, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Keywords: Employees’ innovation behavior, External information awareness, Proactiveness of innovation strategy,
Theory of planned behaviour.
Abstract: Employees’ innovation behavior (IB), which involves developing, promoting, judging, distributing and
implementing new ideas, is the foundation for knowledge creation and diffusion in organizations. Therefore,
it is important to encourage employees’ IB in knowledge management initiatives. To better understand IB,
this study applies the theory of planned behavior (TPB). Employees’ attitude towards innovation, subjective
norm about innovation, and perceived behavioral control to innovation are expected to influence employees’
IB. In addition, the effects of organizational factors are considered. Specifically, the influence of external in-
formation awareness (EIA) and proactiveness of innovation strategy (PIS) are examined. Results from a
survey of employees in Japanese organizations show that employees’ attitude, subjective norm, and per-
ceived behavioral control not only significantly influence their innovative behavior, they also mediate the
effects of EIA and PIS. This study contributes to research by understanding what individual and organiza-
tional factors influence employees’ IB and extending TPB by considering the effects of EIA and PIS, using
data collected from an understudied yet important context. The findings also suggest that managers should
focus on improving perceived behavioral controls, EIA and PIS to encourage employees’ IB.
1 INTRODUCTION
In this information and knowledge intensive era,
innovation has become an important determinant of
competitive advantage and long-term survival for
companies. As interactivity and complexity of inno-
vation both within and across organizations, it ad-
vances new challenges in exploration and exploita-
tion knowledge, which is one cardinal foundation of
“organizational innovative potential” (Swan et al.,
1999). Growing emphasis on innovation through
knowledge management, innovation behavior (IB)
of knowledge workers, which involves developing,
promoting, judging, distributing, and implementing
new ideas at work, is the primary source for organ-
izational innovation (Jassen, 2004; Scott and Bruce,
1994; Swan et al., 1999). For example, a research of
Turgoose (2000) suggests that the acceptance rate of
ideas suggested by employees positively influences
organizational performance. The process research of
knowledge management and innovation also empha-
sizes the importance of employees’ innovation be-
havior. It suggests that innovation in organizations is
a “relay race” based on successful connection of
individual innovations along continuous stages from
new idea and knowledge initiation to implementa-
tion (De Jong and Den Hartog, 2007; King, 2002;
Swan et al., 1999). Hence, employees’ innovation is
indispensable for organization success and it is im-
portant to understand individual employees’ innova-
tion behavior.
In this study, innovation behavior is defined as
employees’ behavior “directed towards the initiation
and intentional introduction (within a work role,
group or organization) of new and useful ideas,
processes, products, or procedures” (De Jong and
Den Hartog, 2007). In order to encourage employ-
ees’ innovation behavior, prior research has tried to
identify antecedents of employees’ innovation be-
havior. Examples include leadership (De Jong and
Den Hartog, 2007; Scott and Bruce, 1994), work
groups relationship (Scott and Bruce, 1994), multi-
functionality of jobs (Dorenbosch, 2005), organiza-
tional knowledge structure (Ong et al., 2003), and
external work contacts (De Jong and Den Hartog,
2007). These studies provide many advices for man-
5
Tang J., Pee L. and Iijima J..
EMPLOYEES’ INNOVATION BEHAVIOR - The Role of External Information Awareness and Proactiveness of Innovation Strategy.
DOI: 10.5220/0003629400050017
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2011), pages 5-17
ISBN: 978-989-8425-81-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

agers, but few studies have focused on the psycho-
logical analysis of employees’ innovation behavior.
A study of Scott and Bruce (1994) suggests that, at
individual level, employees’ innovation behavior is a
primary response to cognitive meaningful and feasi-
ble interpretation of situations, which is more inte-
grative, rather than to the situations per se. So there
is a path model of individual innovation from situ-
ational and personal characteristics to psychological
factors, and to behavior sequentially. Hence, we
consider a structured study of employees’ innovation
behavior’s psychological antecedents is important,
because it helps to improve management efficiency
by focusing on those factors related to the more ef-
fective psychological antecedents of employees’
innovation instead of paying attention to everything.
In this paper, the theory of planned behavior (TPB),
which is a social psychological model, is used to
explain employees’ innovation behaviour. It identi-
fies three antecedents of intention: attitude towards
innovation (ATT), subjective norm about innovation
(SN) and perceived behavioral control to innovation
(PBC). TPB is a well-conceived psychological theo-
retical framework that provides a useful lens for the
intervention of a wide range of behaviors.
The organization provides basic conditional en-
vironment for individual behaviors, so organiza-
tional characteristics have potential influence on
employees’ innovation behavior (De Jong and Den
Hartog, 2007; Krueger Jr, 2007; Scott and Bruce,
1994). In this study, we consider two factors that
have been neglected in prior research: external in-
formation awareness (EIA) and proactiveness of
innovation strategy (PIS). Now, in the highly com-
petitive Internet economy, while lots of innovative
firms have extended their search for new ideas by
involving “the use of a wide range of external actors
and sources to help them achieve and sustain inno-
vation”, openness is becoming a key approach for
innovation (Laursen and Salter, 2006). An open or-
ganization is likely to have high external information
awareness of customer requirements and markets
trends, which could raise employees’ consciousness
of the importance of innovation. On the other hand,
on the basis of resource-based view (RBV), proac-
tive strategy is positive with firm performance when
proactiveness bolsters firms to develop some com-
petitive advantages (Arogon-Correa and Sharma,
2003). As the highly-qualified innovative employee
is treated as one important strategic resourse for
firms in terms of knowledge creation and diffusion
to keep long-term competitive advantage (Lieber-
man, 1988), there is a lack of research considering
the relationship between proactiveness of innovation
strategy and employees’ innovation. We posit that
proactiveness of innovation strategy could prompt
employees to engage in innovation behavior. Overall,
the organizational characteristics of external infor-
mation awareness and proactiveness of innovation
strategy may improve the explanatory power of TPB
for employees’ innovation behavior.
It has been observed that most empirical research
on innovation behavior has been mainly conducted
in western countries such as US (Scott and Bruce,
1994, 1998), Netherlands (De Jong and Den Hartog,
2007; Pieterse et al., 2010) and Spain (Martin et al,
2007). This study addresses the gap by collecting
data from employees in Japanese companies to un-
derstand their innovation behavior. As a leader in the
global market of automobiles and electronics
(Fagerberg, 2005), Japanese companies are among
the most innovative. It is therefore a suitable context
for studying employees’ innovation behavior. In
general, Japanese companies view innovation as a
collaboration of all employees, regardless of organ-
izational levels, rather than a task for limited part of
the organization (Forrester, 2000). It is therefore
interesting to examine what motivates Japanese em-
ployees to engage in innovation behavior.
In sum, the research questions addressed in this
study are:
RQ1: What are the social psychological factors
influencing employees’ innovation behavior?
RQ2: Does organizational external information
awareness and proactiveness of innovation strategy
influence employees’ innovation behavior?
Based on a survey of 127 employees of Japanese
organizations, we found that employees’ attitude,
subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control
are positively related to their innovation behavior as
predicted by TPB. More interestingly, they mediate
the influences of external information awareness and
proactive innovation strategy. This study potentially
contributes to research and practice in several ways.
First, this is the first study to apply TPB to study
employees’ innovation behavior. The findings indi-
cate that the theory is suitable for understanding the
behavior. Second, we examine how the factors in the
TPB mediate the influences of organizational factors
on employees’ innovation behavior. This provides
explanations for how organizational factors influ-
ence employees’ innovation behavior. Together,
these findings offer insights into how innovation
behavior may be promoted in organizations. Third,
this is the first study to examine the innovation be-
havior of employees in Japanese companies, which
is a highly relevant but understudied context.
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
6

2 CONCEPTUAL BACKGROUND
2.1 Innovation Behavior
In this study, innovation behavior is defined as em-
ployees’ behavior “directed towards the initiation
and intentional introduction (within a work role,
group, or organization) of new and useful ideas,
processes, products, or procedures” (De Jong and
Den Hartog, 2007). Unlike individual creativity,
which focuses on the production of novel and useful
ideas, innovation behavior also includes the produc-
tion or adoption of useful ideas and idea implemen-
tation (Scott and Bruce, 1994). Prior research on
innovation behavior has identified many individual
and organizational antecedents from different per-
spectives, such as proactivity, self-confidence, prob-
lem-solving style, leadership, work group relation-
ship, job autonomy, organizational knowledge struc-
ture, and organizational support (De Jong and Den
Hartog, 2007; Dorenbosch et al., 2005; Ong et al.,
2003; Scott and Bruce, 1994; Unsworth and Parker,
2003).
However, few prior studies have focused on the
psychological antecedents of employees’ innovation
behavior. As behavior is a result of rational decision
of individuals based on the judgment of “perceived”
existence of related preconditions, the associated
psychological process and psychological factors are
important (Ajzen, 1991). So, “perceived” psycho-
logical antecedents are more directly related to inno-
vation behavior rather than other organizational and
environmental factors. It addresses the importance of
social psychological analysis of employees’ innova-
tion behavior. This study proposes a structural psy-
chological model of employees’ innovation behavior,
and considers how psychological behavioral antece-
dents mediate the influence of organizational factors
(i.e., external information awareness and proactive-
ness of innovation strategy) on employee’s IB. TPB
and the organizational factors are described next.
2.2 Theory of Planned Behavior
The theory of planned behavior provides explana-
tions of social and psychological influences on be-
havior (Ajzen, 1991). It is a deliberative processing
model in which individuals make behavioral deci-
sions based on careful consideration of available
information. The theory posits that human behavior
is preceded by intention formation and that intention
is determined by individuals’ attitude, subjective
norm, and perceived behavioral control. Since this
study is cross-sectional, we focus on actual behavior
rather than intention. Attitude is a personal evalua-
tion or interest about performing the target behavior
by an individual. Subjective norm reflects the indi-
vidual’s perception of social influence and pressure
from relevant social constituents such as peers and
superiors about the necessity to perform the target
behavior. Perceived behavioral control reflects the
perceived existence of necessary facilitators (e.g.
time, ability) to successfully perform the target be-
havior. In other words, perceived behavioral control
is an assessment of the ability to overcome possible
obstacles for performing the target behavior (Ajzen,
1991). TPB has been shown to be an effective model
for predicting employee behaviors such as individual
technology adoption (Morris et al., 2005), participa-
tion in learning and training (Wiethoff, 2004), iden-
tification of environment opportunities (Krueger Jr
1998), and support for organization change (Jim-
mieson et al., 2008). For the high predictive power
of TPB, we use TPB to understand employees’ in-
novation behavior in this study.
Some prior studies have examined the effects of
these three antecedents separately. For example,
employees’ attitude is an important predictor for
their creative performance (William, 2004). Percep-
tion of innovation climate, as an important dimen-
sion of perceived behavioral control, is studied in
Scott and Bruce (1994). Perceived opinion of “im-
portant others”, which is similar to subjective norm,
has been examined to be important for nurses’ inno-
vation behavior in Amo’s study of health care indus-
try (2006). This study contributes by examining
these aspects together and comparing their relative
importance to employees’ innovation behavior in an
empirical study. This is the first study to examine
their relative effects.
2.3 External Information Awareness
External information is an important driver of inno-
vation that provides signals of market trend and ex-
tends limited internal innovation capability (Cooper
et al., 1995; Frishammar et al., 2005). In a volatile
environment where customer needs and technology
changes rapidly, organizations need to maintain
strong relationships with their environmental con-
stituents in their innovation endeavour. It has been
emphasized that firms should openly “use external
ideas as well as internal ideas”, especially those
from key customers, suppliers, competitors, research
organizations and market to accelerate innovation.
This approach is named open innovation (Ches-
brough, 2003). These suggest that it is important for
organizations to have strong external information
EMPLOYEES' INNOVATION BEHAVIOR - The Role of External Information Awareness and Proactiveness of
Innovation Strategy
7

awareness.
External information awareness refers to the ex-
tent to which organizations track best performers,
main competitors and technologies in the industries,
and maintain contact with suppliers, customers, and
the government to gather information from the ex-
ternal environment (Mendelson, 2000; Von Hippel,
1988). In firms with active network to access both
internal and external knowledge and expertise, em-
ployees’ awareness and access of external knowl-
edge and knowledge sharing among employees will
be strengthened also (Cohen and Levinthal, 1990).
Even many scholars certified empirical linkage be-
tween external information awareness and innova-
tion performance on the organizational level (Tambe
et al., 2009), however, few prior studies have con-
sidered the potential influence from external infor-
mation awareness to employees’ innovation behav-
ior for its capability to bolster employees’ external
information and knowledge access. This study pro-
vides new insights by examining how external in-
formation awareness influences innovation behavior
through affecting employees’ attitude, subjective
norm, and perceived behavioral control.
2.4 Proactiveness of Innovation
Strategy
Innovation strategy guides organizations’ innovation
endeavor (Lumpkin, 1996; Saleh, 1993). An impor-
tant aspect of innovation strategy is proactiveness.
Proactiveness “implies taking initiative, aggressively
pursuing ventures, and being at the forefront of ef-
forts to shape the environment in ways that benefit
the firm,” which is opposite with reactiveness
(Knight, 2000). In other words, proactiveness of
innovation strategy refers to the organization’s
quickness to innovate and to introduce new products
or services. According to the resource-based view
(RBV), proactiveness is posited to be positively re-
lated to firm performance when firms some develop
competitive advantages from proactive stratgy,
while a reactive strategy of innovation is considered
to be not effective to keep long-term success in a
dynamic and sophisticated environment (Arogon-
Correa and Sharma, 2003; Souder, 1987).
A proactive innovation firm is likely to be a
leader rather than a follower (Lumpkin, 1996). Slater
(2006) identified four types of innovation strategy:
early market innovator, early adopter, mainstream
market, and conservationist (late majority and slug-
gards). Early market innovators are those organiza-
tions which “appreciate innovation for its own sake”
and continuously focus on discovering new needs of
customers. Early adopters are those that are sensitive
to new market trends and actively “adopt and use
innovation to achieve a revolutionary improvement”.
Organizations in the mainstream market are those
that are sensitive to innovation risks and prefer to
conduct a “mature” innovation that already con-
firmed by the market and with low risk. Conserva-
tionists are those organizations that are highly con-
servative or averse to innovation.
As highly-qualified innovative employees and
tacit innovation processes are considered as hard-to-
imitate strategic resources for firms to get and main-
tain innovation advantages (Lieberman, 1988), the
potential linkage between proactiveness of innova-
tion strategy and employees’ innovation behavior
can deepen our understanding of the positive influ-
ence from proactiveness on firm performance. How-
ever, there has been a lack of research considering
this potential linkage. This research seeks to address
this gap.
3 PROPOSED MODEL AND
HYPOTHESES
Figure 1 shows the proposed model of employees’
innovation behavior. Based on TPB, employee’s
innovation behavior is a function of attitude towards
innovation, subjective norm about innovation, and
perceived behavioral control to innovation. These
three antecedents are expected to mediate the influ-
ence of proactiveness of innovation strategy and
external information awareness on employees’ inno-
vation behavior. Additionally, industry, firm size,
department and job position are included as a control
variable that may influence employees’ innovation
behavior. The hypotheses are explained next.
Attitude
towards
Innovation
Perceived
Behavioral
Control to
Innovation
Subjective
Norm about
Innovation
Employee’s
Innovation
Behavior
External
Information
Awareness
H1b
H1c
H2a
H2b
H2c
H1a
Proactiveness
of Innovation
Strategy
H3a
H3b
H3c
H4
Figure 1: Proposed Model.
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
8

3.1 The Effects of Attitude, Subjective
Norm, and Perceived Behavioral
Control
According to TPB, attitude, subjective norm, and
perceived behavioral control are positively related to
individuals’ behavior. We expect these relationships
for employees’ innovation behavior as well.
Attitude is a person’s evaluation or interest about
performing the target behavior by an individual,
which is strongly related to the perception of behav-
ior-associated outcomes and “the strength of these
associates” (Ajzen, 2005). Based on the “principle of
compatibility”, employees’ innovation behavior
should be anticipated by their attitude toward inno-
vation (Ajzen, 2005). That is to say, as a general rule,
employees tend to do innovation when they view it
as beneficial or favorable, as it has high possibility
of increasing their job efficiency and reputation in
the workplace. A study of Lee and Wong (2006)
demonstrated the positive relationship between atti-
tudes and performance of R&D scientists and engi-
neers. William (2004) also certified the empirical
link between attitudes toward divergent thinking,
which is “an integral process in creativity”, and em-
ployees’ creation. Meanwhile, in general, innovators
are treated to be with higher attitude toward innova-
tion than non-innovators (Pizam, 1972). So, we posit
that:
Hypothesis 1a: Employees’ attitude toward inno-
vation is positively associated with their innovation
behavior.
Subjective norm reflects an individual’s percep-
tion of social encouragement and pressure from
relevant social referents such as peers and superiors
about the necessity to perform the target behavior
(Ajzen, 2005). When employees’ key social refer-
ents in the workplace seem to all “suggest” them to
conduct innovation behavior, employees are likely to
feel pressured to engage in innovation. For example,
Amobile (1988) considers that leaders’ expectations
are important for employees’ creative work, and
Amo (2006) indicates that the perceived opinion of
“important others” such as managers and colleagues
influence health-care workers’ innovation behavior.
Meanwhile, CEOs’ commitment toward innovation
indicates the importance of innovation in firm’s de-
velopment strategy and customers’ new service or
product requirements and expectations and they
compel employees to innovate continuously. In addi-
tion, from the process view of innovation, the im-
plementation of new innovation ideas demands
heavily on the engagement of these key social refer-
ents (Van de Ven et al., 1989). Accordingly, we hy-
pothesize that:
Hypothesis 1b: Employees’ subjective norm
about innovation is positively associated to their
innovation behavior.
Perceived behavioral control reflects the per-
ceived existence or absence of necessary facilitators
(e.g. time, ability) to successfully perform the target
behavior (Ajzen, 2005). Facilitators such as oppor-
tunities for innovation, freedom to innovate, and
resources provided by organization are important, as
they provide the basic “physical” preconditions for
employees to carry out innovation. Hence, the exis-
tence of these facilitators is another independent
factor which will be considered when employees
make a rational decision of conducting innovation
behavior. In support, it has been found that percep-
tion of organizational innovation support and re-
source supply, which is an important part of PBC,
has strong positive effects on employees’ innovation
behavior (Scott and Bruce, 1994). Then we postulate
that:
Hypothesis 1c: Employees’ perceived behav-
ioral control to innovation is positively associated
with their innovation behavior.
3.2 The Effects of Organizational
Context
On the basis of Scott and Bruce’s study (1994), at
individual level, employees’ innovation behavior is a
primary response to cognitive meaningful and feasi-
ble interpretation of situations, which is more inte-
grative, rather than to the situations per se, so there
is a path model of individual innovation from situ-
ational and personal characteristics to psychological
factors, and to behavior sequentially. TPB suggest
that many personal, social, and informational back-
ground factors are related to attitude, subjective
norm, and perceived behavior control, and in turn to
behaviors (Ajzen, 2005). Although organizations
provide the basic environment for employees’ be-
havior, there is a lack of empirical studies testing the
effects of organizational factors on employees’ be-
havior (Morries et al., 2005). In this research, we
expect two organizational factors: external informa-
tion awareness and proactiveness of innovation
strategy to be important to employees’ innovation
behavior, and their influences are mediated by atti-
tude, subjective norm, and perceived behavior con-
trol.
EMPLOYEES' INNOVATION BEHAVIOR - The Role of External Information Awareness and Proactiveness of
Innovation Strategy
9

3.2.1 The Effects of External Information
Awareness
Nowadays, with increased globalization, innovation
requires firms utilize both internal and external in-
novation sources to advance their R&D capability
(Chesbrough, 2003). High external information
awareness means organizations tend to be highly
open to environment to absorb external knowledge
or gain complementary resources. Since these ex-
ternal sources accesses compensate the lack of inter-
nal ability, external information awareness enhances
the employees’ perception of innovation success and
support innovative initiatives, especially for em-
ployees in innovation-adopter firms. Meanwhile,
external information awareness will improve em-
ployees’ perception of innovation necessity. Hence
employees in organizations with strong external in-
formation awareness will develop a positive attitude
towards innovation.
Hypothesis 2a: External information awareness
is positively associated with employees’ attitude
towards innovation.
As external information awareness could also
improve CEO and senior managers’ perceived ne-
cessity to innovate, they will tend to persuade and
require employees to do innovation through assign-
ing more innovation-related tasks and giving more
innovation rewards. At the same time, employees
may also feel more innovative pressure from direct
contact with external stakeholders such as customers.
In addition, the closely cooperation among employ-
ees is always needed in the innovation project corre-
sponding to external customer requirements, so the
innovation pressure from colleagues will be en-
hanced sequentially.
Hypothesis 2b: External information awareness
is positively associated with employees’ subjective
norm about innovation.
External information awareness is associated
with a wider knowledge and technology base to
achieve and sustain innovation. Hence, employees
are likely to get more innovation support and free-
dom. Meanwhile, the external information about
customers, suppliers and competitors is a trigger of
employees’ innovation to provide innovation hints,
and the external resource may extend employees’
research and development capability.
Hypothesis 2c: External information awareness
is positively associated with employees’ perceived
behavioral control to innovation.
3.2.2 The Effects of Proactiveness of Innova-
tion Strategy
Proactiveness of innovation strategy refers to an
organization’s quickness to innovate and the speed
to introduce new products or services according to
new market opportunities (Lumpkin, 1996). Proac-
tiveness of innovation strategy reflects the high pri-
ority of innovation inside organizations. In proactive
organizations, employees’ proactive innovation is
more appreciated than in reactive organizations.
According to the theory of organizational alignment
(Sender, 2007), rewards system should be aligned
with the strategic goals and values, so innovators are
expected to receive more formal or informal organ-
izational rewards. Hence, employees will develop
more positive attitude toward their innovation be-
haviors.
Hypothesis 3a: Proactiveness of innovation
strategy is positively associated with employees’
attitude towards innovation.
Innovation strategy directly reflects administra-
tors’ expectation of employees’ work, and the high-
light of innovation management. Managers in or-
ganizations with proactive innovation strategy are
likely to focus more on continuous generation and
implementation of new ideas actively to react to new
market trends quickly. Consequently, employees are
likely to feel more pressure from social referents to
innovate.
Hypothesis 3b: Proactiveness of innovation
strategy is positively associated with employees’
subjective norm about innovation.
Proactive organizations invest more in R&D and
human capital than reactive ones (Arogon-Correa
and Sharma, 2003), so they are likely to provide
more support (i.e., money, times, and opportunities)
for employees’ innovation. With the aim to innovate
quickly, proactive organizations are likely to give
faster feedback, and implement employees’ idea
bravely.
Hypothesis 3c: Proactiveness of innovation
strategy is positively associated with employees’
perceived behavioral control to innovation.
Additionally, we expect proactiveness of innova-
tion strategy to increase organizations’ external in-
formation awareness. Proactive firms are likely to
actively recognize and catch the value of new prod-
ucts design and marketing opportunity, even with
high potential risks (Lumpkin, 1996). So, continuous
focus of external information is likely to be one of
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
10

the tactics utilized by top managers (Shoukry, 1993).
Early market innovators and early adopters need a
close communication and cooperation with external
partners such as suppliers, customers, and govern-
ment to capture new market trends. Successful envi-
ronmental information scanning and gathering is a
primary prerequisite for implementing proactive
strategy (Goodman, 1989).
Hypothesis 4: Proactiveness of innovation strat-
egy is positively associated with external informa-
tion awareness.
4 RESEARCH METHOD
4.1 Survey Instrument Development
The proposed model was assessed with data col-
lected in a survey. The questions related to attitude,
subjective norm, perceived behavioral control and
employees’ innovation behavior were adapted from
prior studies applying TPB (Bock et al., 2005;
Fishbein and Ajzen, 1981; Lin and Lee, 2004; Price
and Mueller, 1986; Robinson and Shaver, 1973).
Attitude was assessed with four questions:
“...engaging in innovation behavior is enjoyable”,
“...innovation behavior is valuable”, “...innovation
behavior is beneficial”, and “...innovation behavior
is favorable”. Subjective norm was measured in
terms of perceived innovation encouragement and
pressure from CEOs, supervisors, colleagues, and
customers (e.g., “...receive innovation encourage-
ment and competitive pressure from CEOs/direct
supervisors/colleagues/customers to innovate”).
Perceived behavioral control was assessed in terms
of perceived existence of resources for innovation
(e.g., technology, financial support), opportunities
for innovation, freedom to innovate, and feedback,
such as “there are many opportunities for employees
to innovate in my company” and “employees in my
company are given the freedom to innovate at work”.
Employees’ innovation behavior was measured with
four questions related to frequency of innovation,
time spent on innovation, activeness in innovation,
and participation in innovation projects. Examples
include “…innovate actively” and “…spend signifi-
cant time innovating at work”. Measures for external
information awareness were developed based on
prior studies (Freel, 2000; Kaufmann et al., 2002;
Mendelson, 2000; Souitaris, 2001) and focuses on
the capture and sharing of information about market
trend, government policy, customers, suppliers,
competitors, and strategic partners such as research
and development institutes and consultants. All
items were measured on a five-point Likert scale
anchored by “strongly disagree” (1) and “strongly
agree” (5).
Proactiveness of innovation strategy was meas-
ured by four multiplicative measures. The multipli-
cative measures were based on the forms of proac-
tive innovation strategy identified by Slater (2006):
early market innovator, early adopter, mainstream
market, and conservationist (late majority and slug-
gards). Early market strategy is perceived when
firms continuously consider expressed and latent
customers needs in conducting innovation to create
new market trends (item PIS1). Early adaption strat-
egy is perceived when firms are sensitive to follow
new market trends that created by competitors (item
PIS2). Mainstream strategy is perceived when firms
prefer to capture external market trend, but postpone
implementing innovation until it becomes mature
inside organization (item PIS3). Conservation strat-
egy is perceived when firms develop non-active atti-
tude toward innovation (item PIS4). Among these
designs, early market strategy is the highest level of
proactiveness of innovation strategy, while conser-
vation strategy is the lowest one. These four items
form a Guttman-type scale. Actually, these four
strategies are on a development continuum for firms
to accommodate environment changes. Firms mainly
adopting early market strategy should also relatively
emphasize early adaption strategy in order to timely
alter wrong market expectations. Firms mainly using
early market strategy should also considering early
market strategy and mainstream strategy to capture
high potential first-mover advantages and avoid high
financial risks. Similarly, firms mainly with main-
stream strategy will consider early adoption strategy
and conservation strategy, and firms mainly with
conservation strategy will try mainstream strategy
under some situations.
Four control variables: industry, firm size, de-
partment, and job position were included in this re-
search. Industry was measured as a categorical vari-
able indicated by respondents as either from manu-
facturing or non-manufacturing sectors. Firm size
was measured by the number of employees.
De-
partment was measured as a categorical variable
indicated by respondents as either from IT-related or
non IT-related departments. Job position was meas-
ured by the hierarchical level of respondents from
employee (1) to department head (3).
EMPLOYEES' INNOVATION BEHAVIOR - The Role of External Information Awareness and Proactiveness of
Innovation Strategy
11
4.2 Data Collection
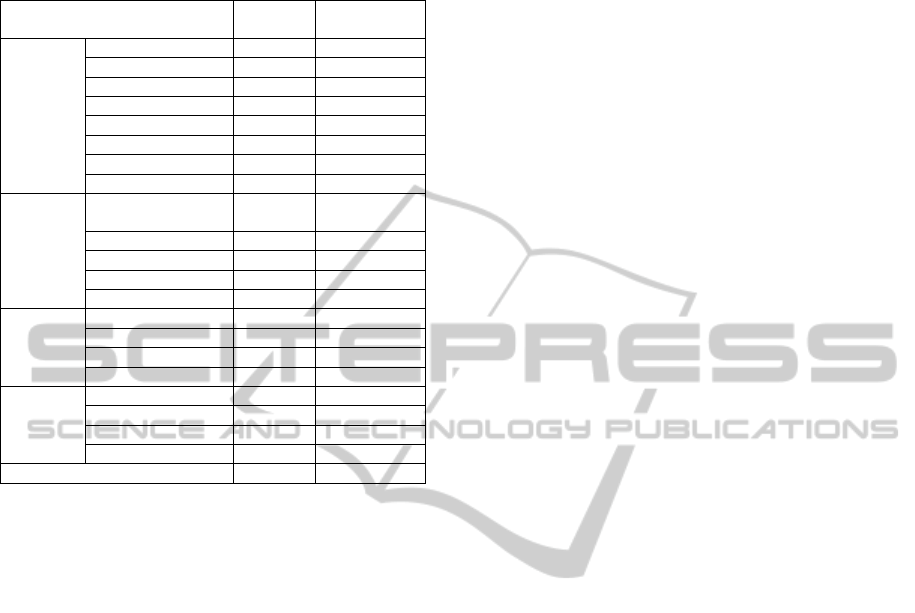
Table 1: Demographic Profile.
Characteristic Number of
Response
Percentage of
Respondent
Industry Manufacturing 70 55.1%
Finance 4 3.1%
Construction 12 9.4%
Service 8 6.3%
Advertisement 7 5.5%
Distribution 15 11.8%
Energy 4 3.1%
Transportation 7 5.5%
Department Corporate develop-
ment
95 74.8%
Business planning 3 2.4%
Cooperate IT-related 10 7.9%
Business IT-related 1 0.8%
Other 18 14.2%
Job Position Department head 19 15%
Section head 62 48.8%
Employee 41 32.3%
Other 5 3.9%
Number of
Employees
More than 1000 82 64.6%
501 - 1000 20 15.7%
101 - 500 20 15.7%
Less than 100 5 3.9%
Total 127 100%
A survey was conducted in Japan with the support of
the Japanese Innovation Management College in late
2010. The questionnaire was sent to 1,819 employ-
ees listed in the database of NTT DATA Corpora-
tion. We received 127 completed responses and the
response rate is 7 percent. The demographic profile
of the respondents is shown in Table 1. Most of re-
sponses are from large organizations with more than
1000 employees (64.6 percent). Most respondents
work in the manufacturing sector (70 percent).
Among the respondents, 74.8 percent are from the
corporate development department, 48.8 percent are
section heads, and 32.3 percent are non-managerial
staff.
5 DATA ANALYSIS
The Smart PLS (Partial Least Square) version 2.0
and the Bootstrap resampling method with 2000
resamples were used to test the research model by
structure equation modelling (SEM).
5.1 Tests of Measurement Model
All scales show high internal consistency and reli-
ability. The Cronbach’s alpha estimates for attitude,
subjective norm, perceived behavioral control, em-
ployees’ innovation behavior and external informa-
tion awareness shown in Table 2 were all above the
recommend threshold of 0.70 (Hair et al., 2005). In
structural equation modelling (SEM), composite
reliability (CR) is also used to value the reliability of
constructs, and the suggested threshold of it is 0.70
(Chin et al., 1996). In Table 2, all CRs of constructs
are above 0.85. In addition, the loadings of each
item to constructs are also significant at p<0.001.
Convergent validity is assessed by average vari-
ance extracted (AVE) and factor analysis. In Table 2,
all AVEs are above the recommended acceptable
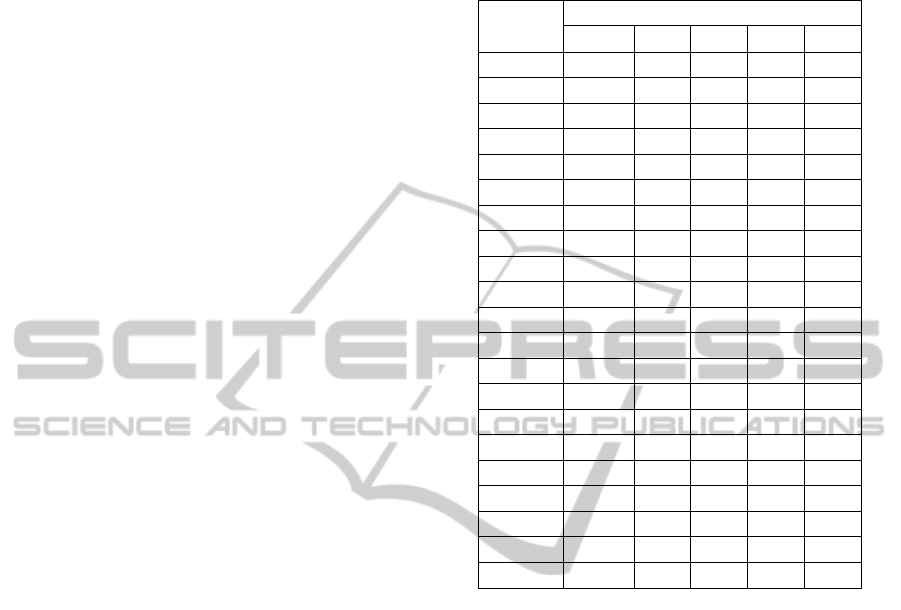
value of 0.50 (Chin et al., 1996). The exploratory
maximum-likelihood factor analysis with Equamax
rotation supports our proposed evaluation of con-
structs (see Appendix). Five corresponding factors
are extracted. Next, an acceptable individual reliabil-
ity of item is shown by the item loadings to their
related constructs being above 0.70. In our study, the
loadings of each item to constructs in the sample are
all above the recommended benchmark of 0.70
(Chin et al., 1996).
The discriminant validity demonstrates the dif-
ference of construct measures in the research model.
Results of comparing square root of AVEs and con-
structs correlation coefficients support the adequate
discriminant validity of our questionnaire. In con-
struct correlation part of Table 2, bold numbers in
the diagonal are the square roots of AVE, while off-
diagonal numbers are Kendall’s tau correlation coef-
ficients among constructs. Kendall’s tau correlation
coefficient is better measure of correlations of ordi-
nal variables, which can be interpreted as same as
Pearson correlation coefficient (Lee et al, 2010). In
Table 2, none of the constructs correlation coeffi-
cients is bigger than the corresponding square roots
of AVE, which means all constructs are more corre-
lated with their own measuring items than with any
other constructs.
A test of multicollinearity was also conducted.
The highest variance inflation factors (VIF) is 2.29,
which is well below the threshold value of 3.3, sug-
gesting that multicollinearity is unlikely to be a
problem for our data (Diamantopoulos and
Winklhofer, 2001).
5.2 Tests of Structural Model
Figure 2 shows the results of the structural model.
One tailed t-test is used to assess the hypotheses. We
found that H1a, H1b, and H1c are strongly sup-
ported at p<0.01. Employees who hold positive atti-
tude towards innovation (β=0.24), perceive pressure
from relevant social referents to carry out innovative
activities (β=0.30), and feel that they have necessary
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
12

resources or support for innovation (β=0.42), are
likely to engage in more innovation behaviors.
Among the predictors, perceived behavioral control
to innovation has stronger influence on innovation
behavior than the other two factors. None of the con-
trol variables are significant to influence employees’
innovation behaviors. All these factors explained
70% of the variance in employees’ innovation be-
havior.
Furthermore, the influence from external infor-
mation awareness and proactiveness of innovation
strategy to three antecedents: attitude, subjective
norm and perceived behavioral control are all sig-
nificant at p<0.01 (See Figure 2). External informa-
tion awareness and proactiveness of innovation
strategy explain about 30% in employees’ attitude,
subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control.
Hence, H2 (a, b, and c) and H3 (a, b, and c) are also
supported by the data. In firms, which tend to do
proactive innovation as an innovation leader and
focus on external information capturing and sharing
within organizations, employees develop higher
psychological stimulus to do innovation than in the
other. In addition, the coefficient from proactiveness
of innovation strategy to external information
awareness (β=0.23) is also significant at p<0.01
(H4). So firms with proactive innovation strategies
are likely to process high awareness of information
about the external environment.
In addition, to test the mediating role of attitude,
subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control,
we calculated the Sobel mediation test statistic (see
Table 3). Results indicate that they are all significant
at p<0.05. This suggests that psychological factors:
attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral
control, mediate the effects of external information
awareness and proactiveness of innovation strategy
on employees’ innovation behavior.
Table 3: Sobel Test Statistic.
Independent
Variable
Mediator
Attitude
Subjective
Norm
Perceived
Behavioral
Control
External
Information
Awareness
2.08* 2.53** 2.53**
Proactiveness
of Innovation
Strategy
2.74** 3.88*** 3.74***
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, **p<0.001
Table 2: Psychometric Properties of Constructs and Construct Correlations.
Construct
Cronbach’s
Alpha
AVE CR
Construct Correlation
IB ATT SN BC EIA
Employees’ Innovation Behavior (IB) .89 .75 .92
.87
Attitude towards Innovation (A) .92 .81 .94 .54
.90
Subjective Norm about Innovation (SN) .80 .63 .87 .48 .44
.79
Perceived Behavioral Control to Innovation (PBC) .83 .66 .88 .54 .57 .41
.81
External Information Awareness (EIA) .84 .62 .89 .36 .25 .26 .24
.79
Proactiveness of Innovation Strategy (PIS)* - - - .37 .38 .39 .40 .19
* The Cronbach’s alpha, AVE, and CR of PIS is not computed as it is measured with a Guttman scale
Figure 2: Results of Structural Model.
Attitude towards Inno-
vation
(R
2
=0.28)
Perceived behavioral
control to Innovation
(R
2
=0.30)
Subjective Norm about
Innovation
(R
2
=0.30)
Employee’s Innovation
Behavior
(R
2
=0.70)
External Information
Awareness
(R
2
=0.053)
H1b: 0.30
(4.53) ***
H1c: 0.42
(4.94) ***
H2a: 0.26
(3.36) ***
H2b: 0.24
(2.91) **
H2c: 0.26
(3.16) ***
H1a: 0.24
(2.69) **
Proactiveness of
Innovation Strategy
H3a: 0.41
(5.49) ***
H3b: 0.43
(6.29) ***
H3c: 0.43
(5.27) ***
Control Variables:
Industry, 0.17 (3.06) **
Firm Size, -0.07 (1.11)
Department, 0.04 (0.82)
Job Position, -0.01 (0.15)
H4: 0.23
(2.86) **
a. t-value in parentheses
b. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001
EMPLOYEES' INNOVATION BEHAVIOR - The Role of External Information Awareness and Proactiveness of
Innovation Strategy
13

6 DISCUSSION
6.1 Implications for Research
The results from SEM support all our hypotheses
and help us to answer our two research questions.
Attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavior
control are three primary social psychological fac-
tors influencing employees’ innovation behavior.
External information awareness and proactiveness of
innovation strategy, as two important organizational
characteristics, is positive related to employees’ in-
novation behavior through improving three mediat-
ing social psychological factors.
As employees own limited ability to process all
kinds of stimuli around them, they use affective and
cognitive representations of related information to
handle the complexity (Fagerberg, 2005). Although
prior studies have examined employees’ innovation
behavior (De Jong and Den Hartog, 2007, Scott,
1994), and highlighted “intrinsic motivation” as a
critical antecedent (Amabile, 1997; Scott and Bruce,
1994), there are few empirical studies on the psycho-
logical analysis of employees’ innovation. In this
research, we applied the theory of planned behavior
as a basic structure to better understand how to en-
courage employees to innovate by providing empiri-
cal evidence of mediating effects of three psycho-
logical antecedents.
The first contribution of this study is to examine
the power of TPB model in explaining the innova-
tion behavior of employees. While prior research
only focuses on the influence of some psychological
factors, TPB provides a strong theoretical structure
to this study to understand the effects of psychologi-
cal factors to employees’ innovation behavior.
Through comparing path coefficients of the three
psychological antecedents, our results show that
perceived behavioral control to innovation has the
strongest influence on employees’ innovation among
the three antecedents. This supports findings in prior
research (Scott and Bruce, 1994). Therefore, future
studies may examine ways to improve perceived
behavioral control.
The second contribution of this paper is examin-
ing the effects of two organizational factors: external
information awareness and proactiveness of innova-
tion strategy on employees’ innovation behavior. In
empirical studies of TPB, only the individual psy-
chological factors are considered and the potential
influences of other factors, especially organizational
factors, have been neglected. But in practical man-
agement, those organizational factors are likely to be
more controllable by managers than individual fac-
tors. Hence, this study addresses a limitation of prior
research. TPB also suggests that organizational fac-
tors may influence the way that employees perceive
things or actions, and, as a result, affect behavior
(Ajzen, 2005). Similarly, we have shown that the
effects of external information awareness and proac-
tiveness of innovation strategy are mediated through
attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioral
control. Understanding this mediating relationship is
important because it empirically demonstrates of the
underlying mechanism through which organizational
factors influence employees’ behavior. Our results
also suggest that external information awareness and
proactiveness of innovation strategy are important
triggers for employees’ innovation. This may also
help to explain the importance of external informa-
tion, and the positive relationship between proactive
innovation strategies with firm performance, when
employees’ innovation behavior becomes an impor-
tant strategic resource to gain and maintain competi-
tive advantage.
Third, this study is among the first to collect data
from Japanese companies. Based on its unique con-
tinuous innovation strategy, Japan owns a big mar-
ket share in some industries like automobiles and
electronics (Fagerberg, 2005). Recent studies on
employees’ innovation behavior focusing on the
effect of factors such as job design and leadership
have mainly been conducted in the United States
(Scott and Bruce, 1994, 1998), Netherlands (De
Jong and Den Hartog, 2007; Pieterse et al, 2010) and
Spain (Martin et al, 2007). However, Japan is gener-
ally considered to be culturally different from these
countries in terms of social collectivism, privilege
preference, seniority-based social status, tolerance of
hierarchy and risk aversion (Hofstede, 2004). It is
therefore interesting to examine whether their find-
ings apply to Japan. This study suggests that the
fundings of studies in other countries is possible to
apply to Japan, but the careful reconsideration based
on Japanese culture is also needed.
6.2 Implications for Practice
Our results show that attitude, subjective norm, and
perceived behavioral control are important to predict
employees’ innovation behavior. Among them, per-
ceived behavioral control has stronger effect on em-
ployees’ innovation behavior than the others. Thus,
in order to effectively encourage employees’ innova-
tion behavior, managers may play supporting role
rather than deciding and persuading role to increase
employees’ perceived controllability and self-
efficacy for innovative behavior. Some ways include
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
14

providing innovation freedom, innovation opportuni-
ties, innovation-related resources, and training to
employees.
This research focuses on two important organiza-
tional factors: external information awareness and
proactiveness of innovation strategy. Our results
suggest managers to improve external information
awareness of their companies, for its positive influ-
ence to employees’ attitude, subjective norm, and
perceived behavioral control. Hence, organizations
should establish strong relationships with external
innovation partners, and share the captured informa-
tion and knowledge within organizations. Existing
knowledge management technology may be helpful
for its capability to capture information from exter-
nal environment and share them within organiza-
tions.
The potential influence of proactiveness of inno-
vation strategy may also be important in practice.
Therefore, organizations should firstly emphasize to
be an innovation leader rather than an innovation
follower, and change to be research-oriented. Then
they also should generate and access a wide range of
new ideas and bravely invest in the quick implemen-
tation of them to capture new opportunities. Al-
though there is a high risk in proactive innovation
strategy, its benefits to increase employees’ innova-
tion behavior also need to be taken into account. As
recent research considers human resources and busi-
ness processes to be unique resources to gain com-
petitive advantages, an innovation leader will be
difficult to be copied and surpassed by an innovation
follower.
6.3 Limitations and Future Research
The findings in this study should be interpreted in
view of its limitations. First, most of the respondents
are from the manufacturing sector. More studies of
other sectors are needed to assess the proposed
model. Second, this study focuses on Japanese com-
panies, so there may be some geographical or cul-
tural specificities and the findings may not general-
ize to other settings. It may be interesting to assess
the proposed model in other countries, especially
those with different culture compared to Japan, like
China, Finland and Australia. Third, only perceptive
measures have been used in our research. Self-
reports may contain some presentational biases
(Gaes et al, 1978). Hence, future research may con-
sider using objective measurement of employees’
innovation behavior. Fourth, there may be other or-
ganizational and environmental factors influencing
employees’ innovation behavior. Examples include
organizational factors like organizational structure,
risk-taking tendency, job and business process orien-
tation, and environmental factors such as environ-
mental dynamism. Future research may consider
studying the effects of these factors to better under-
stand the phenomenon.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The TPB-based psychological analysis of employ-
ees’ innovation behavior deepens our understanding
of employees’ innovation behavior by considering
the effects of two organizational characteristics: ex-
ternal information awareness and proactiveness of
innovation strategy. In this knowledge-intensive
economy, in order to effectively encourage employ-
ees’ innovation, managers need to ensure that neces-
sary organizational resources are available to sup-
port employees. As efficient flow of information and
knowledge within organizations is critical for firms,
our findings about the importance of external infor-
mation awareness suggest that it is an important
characteristic of a innovative organization. At the
same time, managers should consider the benefits of
proactive innovation strategy on employees’ innova-
tion because it creates the necessary condition for
encouraging employees’ innovative behavior.
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I. 1991. The theory of planned behavior. Organiza-
tional Behavior and Human Decision Process, 50(2),
170-211.
Ajzen, I. 2005. Attitudes, Personality, and Behavior,
Maidenhead, England: Open University Press.
Amabile, T. M. 1997. Motivating creativity in organiza-
tions: on doing what you love and love what you do.
California Management Review, 40(1), 39-58.
Amo, B. W. 2006. Employee innovation behavior in
health care: the influence from management and col-
leagues. International Nursing Review, 53(3), 231-
237.
Arogon-Correa, J. A., and Sharma, S. 2003. A contingent
resource-based view of proactive corporate environ-
mental strategy. The Academy of Management Review,
28(1), 71-88.
Bock, G. W., Zmud, R. W., and Kim, Y. G. 2005. Behav-
ioral intention formation in knowledge sharing: exam-
ining the roles of extrinsic motivators, social-
psychological forces, and organizational climate. MIS
Quarterly, 29(1), 87-111.
Chin, W. W., Marcolin, B. L., and Newsted, P. R. 1996. A
partial least squares latent variable modeling approach
for measuring interaction effects: results from a monte
EMPLOYEES' INNOVATION BEHAVIOR - The Role of External Information Awareness and Proactiveness of
Innovation Strategy
15

carlo simulation study and voice mail emo-
tion/adoption study, in Proceedings of the 17th Inter-
national Conference on Information Systems, DeGross,
J. I., Jarvenpaa, S., and Srinivasan, A. (Eds.), 21-41.
Chesbrough, H. W. 2003. Open Innovation: The New Im-
perative for Creating and Profiting from Technology.
Harvard Business School, Boston.
Cohen, W. M., and Levinthal, D. A. 1990. Absorptive
capability: a new perspective on learning and innova-
tion. Administrative Science Quarterly, 35(1), 128-152.
Cooper, R. G., and Kleinschmidt, E. J. 1995. Benchmark-
ing the firm’s critical success factors in new product
development. Journal of Product Innovation Man-
agement, 12(5), 374-391.
De Jong, J. P. J., and Den Hartog, D. N. 2007. How lead-
ers influence employees' innovation behavior. Euro-
pean Journal of Innovation Management,10(1), 41-64.
Diamantopoulos, A., and Winklhofer, H. M. 2001. Index
construction with formative indicators: an alternative
to scale development. Journal of Marketing Research,
38 (2), 269-277.
Dorenbosch, L., van Engen, M. L., and Verhagen, M.
2005. On-the-job innovation: the impact of job design
and human resource management through production
ownership. Creativity and Innovation Management,
14(2), 129-141.
Fagerberg, J., Mowery, D. C., and Nelson, R. R. 2005. The
Oxford Handbook of Innovation. 1
st
Edition. Oxford
University, New York.
Forrester, R. H. 2000. Capturing learning and applying
knowledge: an investigation of the use of innovation
teams in Japanese and American automotive firms.
Journal of Business Research, 47(1), 35-45.
Frishammar, J., and Horte, S. A. 2005. Managing external
information in manufacturing firms: the impact on in-
novation performance. The Journal of Product Innova-
tion Management, 22(3), 251-266.
Freel, M. 2000. External linkages and product innovation
in small manufacturing firms. Entrepreneurship & Re-
gional Development, 12(3), 245-266.
Fishbein, M., and Ajzen, I. 1981. On construct validity: a
critique of miniard and cohen’s paper. Journal of Ex-
perimental Social Psychology, 17(3), 340-350.
Goodman, M. B. 1989. Executive summary: high visibility,
high risk, high reward. 1989 Professional Communi-
cation Conference, 18-20, 245-248.
Hair, J. F., Black, B., Babin, B., and Anderson, A. E. 2005.
Multivariate Data Analysis, 6
th
edition, Prentice-Hall:
Englewood Cliffs, N.
Hofstede, G., and Hofstede, G.J. 2004. Cultures and Or-
ganizations: Software of the Mind. McGraw-Hill
U.S.A., New York.
Jassen, O. 2004. How fairness perceptions make innova-
tive behavior more or less stressful. Journal of Organ-
izational Behavior, 25(2), 201-215.
Jimmieson, N. L., Peach, M., and White, K. M. 2008.
Utilizing the theory of planned behavior to inform
change management: an investigation of employee in-
tentions to support organizational change. Journal of
Applied Behavioral Science, 44(2), 237-262.
Kaufmann, A., and Todtling, F. 2002. How effective is
innovation support for SMEs? An analysis of the re-
gion of Upper Austria. Technovation, 2 (3), 147-159.
King, N., and Anderson, N. 2002. Managing Innovation
and Change: a Critical Guide for Organizations.
Thomson, London.
Knight, G. 2000. Entrepreneurship and marketing strategy:
the SME under globalization. Journal of International
Marketing, 8(2), 12-32.
Krueger Jr., N. 1998. Encouraging the identification of
environmental opportunities. Journal of Organiza-
tional Change Management, 11(2), 174-183.
Krueger Jr., N. 2007. The cognitive infrastructure of op-
portunity emergence. Entrepreneurship, part II, 185-
206.
Laursen, K., and Salter, A. 2006. Open for innovation: the
role of openness in explaining innovation performance
in among U.K. manufacturing firms. Strategic Man-
agement Journal, 27, 131-150.
Lee, L., and Wong, P. K., 2006. Individual attitudes, or-
ganizational reward system and patenting performance
of R&D scientists and engineers. M. P. R. Archive, ed.,
595, 44.
Lee, R., Klobas, J., Tezinde, T., and Murphy, J. 2010. The
underlying social identities of a nation's brand. Inter-
national Marketing Review, 27(4), 450-465.
Lieberman, M., and Montgomery, D. 1988. First mover
advantages. Strategic Management Journal, 9(1), 41-
58.
Lin, H. F, and Lee G. G. 2004. Perceptions of senior man-
agers towards knowledge-sharing behavior. Manage-
ment decision, 42(1), 108-125.
Lumpkin, G. T., and Dess, G. G. 1996. Clarifying the
entrepreneurial orientation construct and linking it to
performance. Academy of Management Review, 21(1),
135-172.
Martin, P., Salanova, M., and Peiro, J.M. 2007. Job de-
mands, job resources and individual innovation at
work: going beyond Karasek’s model. Psicothema,
12(4), 621-626.
Mendelson, H. 2000. Organizational architecture and suc-
cess in the information technology industry. Manage-
ment Science, 46(4), 513-529.
Morris, M. G., Venkatesh, V., and Ackerman, P. L. 2005.
Gender and age differences in employee decision
about new technology: an extension to the theory of
planned behavior. IEEE Transactions on Engineering
Management, 52 (1), 69-84.
Ong, C. H., Wan, D., and Chng, S.H. 2003. Factors affect-
ing individual innovation: an examination within a
Japanese subsidiary in Singapore. Technovation,
23(7), 617-631.
Pizam, A. 1972. Psychological characteristics of innova-
tors. European Journal of Marketing 6(3), 203–210.
Pieterse, A. N., Knippenberg, D. V., Schippers, M., and
Stam, D. 2010. Transformational and transactional
leadership and innovative behavior: the moderating
role of psychological empowerment. Journal of Or-
ganization Behavior, 31(4), 609-623.
Price, J. L., and Mueller, C. W. 1986. Handbook of Or
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
16
ganizational Measurement. Pittman, Marshfield, MA.
Robinson, J. P., and Shaver, P. R. 1973. Measures of So-
cial Psychological Attitudes, the Institute for Social
Research. The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor,
MI.
Saleh, S. D., and Wang, C. K. 1993. The management of
innovation: strategy, structure, and organizational cul-
ture. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management,
40(1), 14-21.
Sender, S. W. 2007. Systematic agreement: A theory of
organizational alignment. Human Resource Develop-
ment Quarterly, 8(1), 23-40.
Scott, S. G., and Bruce, R. A. 1994. Determinants of inno-
vation behavior: a path model of individual innovation
in the workplace. The Academy of Management Jour-
nal, 37(3), 580-607.
Scott, S. G., and Bruce, R. A. 1998. Following the leader
in R&D: the joint effect of subordinate problem-
solving style and leader-member relations on innova-
tive behavior. IEEE Transactions on Engineering
Management, 45(1), 3-10.
Slater, S. F., and Mohr, J. J. 2006. Successful development
and commercialisation of technological innovation: in-
sights based on innovation type. The Journal of Prod-
uct Innovation Management, 23(1), 26-33.
Souitaris, V. 2001. External communication determinants
of innovation in the context of a newly industrialized
country: a comparison of objective and perceptual re-
sults from Greece. Technovation, 21(1), 25-34.
Souder, W.E. 1987. Managing New Product Innovation.
Health, Lexington, MA.
Tambe, P. B., Hitt, L. M., and Brynjolfsson, E. 2009. The
extroverted firm: how external information practices
affect productivity. 2008 International Conference on
Information Systems.
Turgoose, C., Thacker, C., Adams, M., Carmichael, C.,
Gray, M., Hall, L., and Todd, C. 2000. Innovation in
Manufacturing SMEs in South Yorkshire. Innovation
Advisory Service, Sheffield.
Unsworth, K.L., and Parker, S. 2003. Proactivity and in-
novation: promoting a new workforce for the new
workplace. The New Workplace: A Guide to the Hu-
man Impact of Modern Working Practices, John Wiley
& Sons, Chichester, 175-196.
Von Hippel, E. 1988. The Sources of Innovation. New
York: Oxford University Press.
Wiethoff, C. 2004. Motivation to learn and diversity train-
ing: application of the theory of planned behavior.
Human Resource Development Quarterly, 15(3), 263-
278.
Williams, S. D. 2004. Personality, attitude, and leader
influences on divergent thinking and creativity in or-
ganizations. European Journal of Innovation Man-
agement, 7(3), 187-204.
APPENDIX
Factor Analysis.
Construct
Items
Components
IB ATT SN PBC EIA
IB1
.54
.39 .25 .45 .19
IB2
.52
.22 .37 .34 .27
IB3
.65
.24 .26 .26 .23
IB4
.68
.21 .16 .39 .11
ATT1 .32
.65
.17 .42 .17
ATT2 .16
.79
.25 .23 .08
ATT3 .26
.71
.27 .30 .11
ATT4 .23
.79
.31 .21 .08
SN1 .05 .14
.82
.24 .16
SN2 .26 .26
.77
.16 .03
SN3 .49 .21
.40
.13 .08
SN4 .40 .21
.39
.01 .17
PBC1 .34 .39 .34
.48
.07
PBC2 .41 .29 .16
.46
.14
PBC3 .07 .20 .23
.82
.12
PBC4 .31 .24 .15
.61
.08
EIA1 .04 .10 .13 .10
.68
EIA2 .13 .09 .04 .07
.89
EIA3 .20 .06 .19 .02
.82
EIA4 .10 .01 .09 .10
.62
EIA5 .15 .22 .07 .25
.46
EMPLOYEES' INNOVATION BEHAVIOR - The Role of External Information Awareness and Proactiveness of
Innovation Strategy
17
