
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED SYSTEM TO SUPPORT LEGAL CASE
CONSTRUCTION
Stefania Castellani, Nikolaos Lagos, Nicolas Hairon, Antonietta Grasso,
David Martin and Frederique Segond
Xerox Research Centre Europe, 6, Chemin de Maupertuis, 38240, Meylan, France
Keywords: Legal case reasoning and building, Human computer interaction, Information extraction, Sensemaking,
corporate litigation processes, Semantics-based litigation.
Abstract: We have designed a system to support collaborative case reasoning and building in corporate litigation
cases, that is, processes of bringing and pursuing lawsuits. The design is based on our understanding of the
domain acquired through analysis of the literature, interviews of various parties involved in corporate
litigation processes, and studies of the commercial tools already available. In this paper we illustrate the
designed system and in particular the interaction modes that it supports that we believe address a number of
the requirements that emerged through our analysis. We also describe its main components and their
integration, including a knowledge model that represents the domain, and a natural language processing
component for extracting semantic information. A description of a prototype system is also provided.
1 INTRODUCTION
The work of corporate litigation lawyers is an
interesting and challenging field to study and design
for, both from an organizational and a technical
point of view: it is a highly complex process,
involving a variety of actors, who must manage and
analyse huge corpuses of information. The litigation
process involves two main parts: 1) e-discovery (see
the Electronic Discovery Reference Model (2011)) -
the analysis of immense document sets to isolate
only those documents relevant (i.e. responsive) to
the case and 2) case construction – the finding of
evidence and argument construction based on the
contents of the set of relevant documents so
determined. The case reasoning activity ultimately
produces the defense or attack line to be used to
settle or to go to court.
The primary goal of the searching and browsing
facilities offered in current litigation tools is to find
relevant documents, often using keyword/boolean
based search techniques. Although this has proved to
be relatively useful in the e-discovery phase, during
case construction the emphasis shifts from finding
documents to finding entities and actionable
information derived from these entities (Noel and
Azemard, 2008; Sheth et al., 2002; Lagos et al.,
2010). This kind of search is an important part of the
lawyers’ work and tools currently on the market
allow users to store information on relevant
characters and events. However, there is little in the
way of support to help users identify the relevant
information and once the information is identified
they must manually enter it in the tools database.
Moreover little support is provided for collaborative
work and information sharing among the members
of a legal team working on a case.
On the basis of these observations and more
specific requirements that we collected from
interviews with lawyers and technology service
providers, a review of litigation support tools
currently available on the market, and an
examination of the few available case studies
(Attfield et al., 2008; Attfield and Blandford, 2008
and 2009) we are developing a work environment
for lawyers. The system is meant to help lawyers
search for information from the document collection
associated with a legal case, build the case, reason
about lines of inquiry, and share findings with
colleagues working on the creation of an outline for
the case. In particular, the system is designed to
provide some forms of support for lawyers working
to identify characters, e.g., people or organizations
that have played a role in a case, events they have
participated in, etc. Also the system aims at offering
15
Castellani S., Lagos N., Hairon N., Grasso A., Martin D. and Segond F..
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED SYSTEM TO SUPPORT LEGAL CASE CONSTRUCTION.
DOI: 10.5220/0003629700150027
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development (KEOD-2011), pages 15-27
ISBN: 978-989-8425-80-5
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

to the members of a legal team a shared
representation of the legal case while being able to
work individually on specific lines of inquiry.
Previous work on some components of the
system has already been described in (Castellani et
al., 2010 and Lagos et al., 2010). In this paper we
illustrate the overall design of the system and a first
prototype for it based on semantic technologies that
implement parts of the design.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents an analysis of current practices in
litigation in relation to case building and reasoning.
Section 3 illustrates the design of the system,
including the overall architecture, its components,
and the interaction modes that it supports. Section 4
presents our work for prototyping the system.
Finally section 5 discusses related and future work.
2 ANALYSIS OF CURRENT
LITIGATION PRACTICES
The litigation process usually involves two groups of
lawyers: a key case team of senior lawyers (SLs)
that starts the process, talks to the clients and
generates the first documents, specifically letters of
complaints, review protocols and the “issues” or
main lines of inquiry. These are used by the
responsiveness reviewers/issue-coders team, formed
by junior lawyers (JLs) and paralegals (reaching up
to 600 members), often organized in sub-teams, who
read every single document from the usually very
large set of documents that are potentially relevant
to the case to determine the set of responsive
documents. In this phase they also typically assign
relevant documents to “issues”, which are subtopics
used later on to reason around and organize the case.
After responsiveness review the still large set of
remaining documents is further reviewed and
filtered so that only the most important and relevant
documents are seen by the key case team, which
develops the case.
The role of technology in the above process is
currently pretty limited, but is expanding in scope.
Technology is mainly used to retrieve and store the
document set for e-discovery, which may then be
searched using keyword search. Even if more
sophisticated technologies like conceptual searches
have been suggested by technology providers, they
have encountered resistance. Among the reasons for
this is the need to be able to explain in court just
how the documents have been filtered and why that
method is valid. This situation however is changing.
Technology that can semi-automatically categorize
the documents and collaboratively assist in e-
discovery is being developed and trialed (Privault et
al., 2010). Likewise, database-like tools
(CASEMAP, 2011) have appeared on the market to
assist the phase of case construction by letting the
teams to store relevant entities and construct an
outline of case defense or attack.
Another important aspect to note is that the
current largely manual legal work process implies a
strict and procedural division of labour where the
phases are distinct. There is little space for
collaboration, and each refinement step weeds away
documents following precise rules that provide
material for the next phase and further sensemaking
of the document set. We believe that these two
aspects are interconnected and that the introduction
of technology, while hopefully at first speeding up
the simpler steps, will further dissipate the barriers
between phases and enhance the phase of case
construction. Procedurally, this is preferable as case
building starts as soon as the legal case is issued but
current logistical constraints enforce an unfortunate
separation of discovery and case construction.
How do litigation lawyers search through the
documents to construct the case? Attfield’s study
(Attfield et al., 2008; Attfield and Blandford, 2008
and 2009) provides insight on the reasoning
surrounding manual case construction performed by
a legal team. First of all, given the size of the
dataset, and in order to appropriately distribute the
labour, investigators usually need to gradually
“decompose an investigation into meaningful and
tractable chunks of enquiry” (Attfield et al., 2008)
taking into account any relevant information found
during the investigation. This is important because
of the need to separate and keep track of the
“theories” eventually “eliminated when evidence
found was contradictory or unsupportive” (Attfield
et al., 2008). Additionally, a key point to understand
is that the information that constitutes evidence for a
fact can be contained across a set of documents. In
these cases the risk is that something is not seen as
relevant when first uncovered because the extra
contextual information which will flesh it out as
relevant has not (yet) been found and connected to it
(Attfield and Blandford, 2008). Thus as a potential
area of support it would be useful for the lawyers to
find, explore and manage the information within the
entire document set (i.e. across documents) and to
view low-level lines of enquiry in terms of a bigger
picture (Attfield et al., 2008; Castellani et al., 2010).
As reported in (Attfield and Blandford, 2009): “The
capability of iteratively selecting records and setting
KEOD 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
16

them aside, perhaps in addition to code filtering,
would provide greater flexibility for exploring and
discussing different possibilities.” And also,
“document references within event entries allowed
the chronologies to act as indexes supporting the re-
retrieval of raw evidence. [...] However, these links
were not automated. More efficient access would be
supported if the source documents could be accessed
directly for the summary representation.”
To complement these observations, we also
found evidence from interviews we conducted that
JLs have problems in managing consistency and
getting up to date with the case. The current
procedural practice is that they work under great
time pressure and are involved just in assigning
documents to issues rather than in creating “the
case”. However, if they had the support for this, they
could communicate new knowledge in a timely
fashion to the rest of the team (both JLs and SLs)
working on the case. Therefore, as also reported in
(Attfield et al., 2008) methods to discuss findings,
synchronise work and exchange information are
vital.
Another aspect emerging from the literature and
from analysis of the commercial databases for case
construction is that legal reasoning evolves through
manipulation of specific semantic entities. It is
especially important for lawyers to identify key
players and their relationships and to build
chronologies of events relevant for a case
(CASEMAP, 2011); (Attfield et al., 2008); (Lagos et
al. 2010). As reported in (Attfield et al., 2008;
Attfield and Blandford, 2009): lawyers can be
searching for documents by focusing on particular
time periods or on specific events, e.g. meetings, in
support of their conjectures; “each team created one
or more “issue
”
chronologies and, as these evolved
important content was selected and consolidated
into a single master chronology”; lawyers need to
record information on events, times, participants and
documents related.
On the basis of this analysis we have envisioned
a future scenario of collaborative work for litigation
and developed a design of a case building system,
supporting it, which is currently under
implementation. The next section illustrates the
design of the system.
3 THE CASE BUILDING SYSTEM
The Case Building System (CBS) that we are
developing aims at providing lawyers with tools to
help them individually and collaboratively keep a
record of their findings and lines of inquiry and seek
new information from a document collection. CBS
sits on top of a knowledge base containing case
documents, such as letters of complaint (issued at
the beginning of a litigation process) and responsive
documents (as they emerge from the e-discovery
phase). The knowledge base also contains
information elements, (people, events, locations,
etc.) automatically extracted by the system from
those documents. Key features include:
It is a unified system supporting case reasoning
and building from the early stages of litigation.
It supports recording multiple lines of inquiry and
the discovery of new information.
It is strongly visual and interactive with several
views based on key semantic dimensions (time,
structure, etc.)
It provides collaboration support, e.g. awareness of
what colleagues have found, so that activities can be
synchronised and findings shared.
It is semi-automatic in its knowledge extraction
and suggestions to let lawyers benefit from the
power of content analysis whilst remaining in
control.
Figure 1 shows the design of the user interface of the
system. The user interacts with a visual environment
organized in 4 interactive working areas that capture
the current status of the lawyer’s work, that is,
current lines of thought and acquired and emerging
information captured and displayed according to
several dimensions.
DocumentVisualiser (1 in Figure 1) allows the user
to search for documents, in the whole collection or
only within documents already included in the case,
and navigate the contents of selected documents that
display extracted information elements, e.g. events.
The user can select information elements within
documents to be explored and potentially included in
the case by sending them to other views. In this way
document evidence can be associated to information
elements extracted in support of a line of inquiry.
CastOfObjects (3 in Figure 1) provides a
structured view of the information elements
currently selected and saved by the users as salient
information for the case, including characters,
events, and the facts that constitute the various lines
of inquiry. Characters represent the important
“actors” of the story, e.g. a person or an organization
that have played a role in the case. Events are events
that have happened, e.g. “John Doe met Jane Roe in
Zurich in March 2000” or situations, e.g. “M. Jones
is head of the human resources department”. Facts
are the units of case construction and collaboration
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED SYSTEM TO SUPPORT LEGAL CASE CONSTRUCTION
17

Figure 1: The Case Building System’s working area.
and can be constructed from a number of
information elements. This view allows the user to
search for further elements to be included or for
elements already considered as relevant, for example
by other members of the team working on the case,
to record additional selected elements, and to
manually enter new elements. Also, the user can see
elements that other members of the team have
inserted.
TimeLine (2 in Figure 1) shows a temporal
dimension of the case in the form of a chronological
visualisation of the events selected and saved by the
users as relevant to the case. Events with fuzzy dates
can be displayed with a special visual cue to
differentiate them from the ones with precise dates.
Users can select events to be inserted in the
TimeLine either by selecting them from documents
or by manually entering them. It will be visible if
events have been manually added or extracted from
documents. Events stored in the CastOfObjects will
also be displayed. Moreover users will be able to
express connections among the events. Also, the
user should be able to see the elements that other
members of the team have inserted.
CaseSpace (4 in Figure 1) is an exploratory space
where the lawyers can build and visualize networks
of case elements. A network can be expanded
starting by one of its nodes and searching for
extracted connected elements or by manually adding
new elements and connections. The displayed
elements will have features that will represent
diverse information including the “importance” of
the element in the case and the degree of connection
with other nodes which could be a combination of
scores given by the system according to some
properties and the score given by the users. The
networks can be saved as clusters of evidence for a
chunk of inquiry and shared with the other members
of the legal team working on the case. Otherwise if
the lawyer estimates that they do not support
evidence for a chunk of inquiry they can be
discarded.
This collaborative visual environment provides
the user with tools to visualise and navigate
documents and information, store important
information that has then to be made persistent, and
“play” with lines of inquiry. It should also provide
the lawyers with a view of the current status of the
team’s work, and then a somewhat shared
representation of the legal case that they can
navigate and progressively enrich. According to our
scenario of work, the lawyers of the team will work
individually with the CBS conducting their
investigations while the system supports the
synchronization of their work and the collaborative
construction of the global case. Figure 2 shows a
simplified representation of the information flow in
the system during this work.
KEOD 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
18
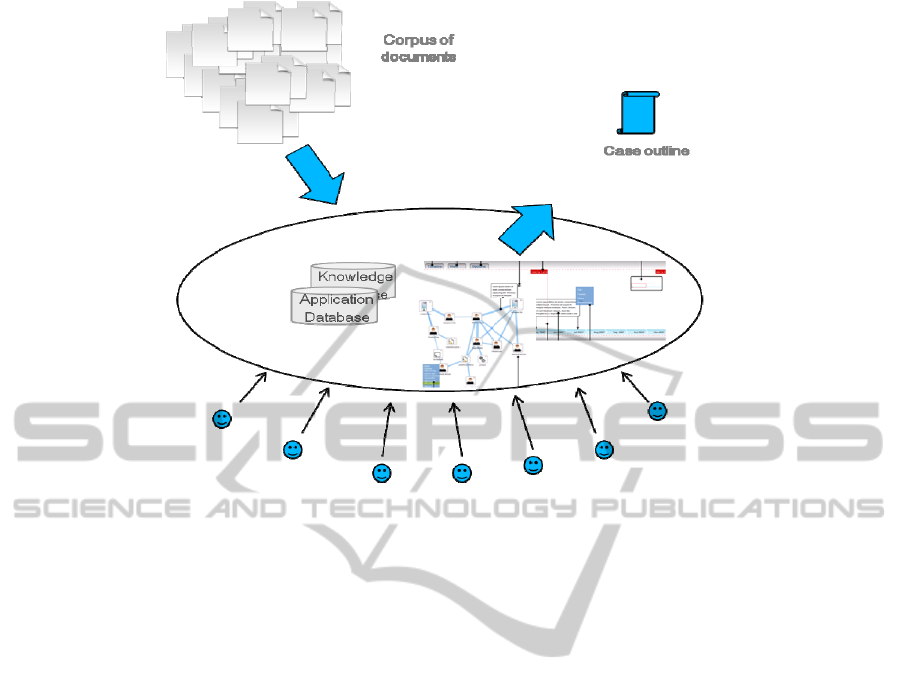
Figure 2: A simplified representation of the information flow in the system.
A lawyer can start working by importing in CBS
a document containing some of the parameters of the
case (e.g. letter of compliant) or the set of
documents that should be processed (e.g. responsive
documents collection) or both. Each user can ask the
system to list specific kinds of information elements
extracted from the collection of documents, e.g.
people or select some of them from the
DocumentVisualizer or the CastOfObjects, to be
inserted in the CaseSpace, for exploring a line of
thought.
Inserting information elements in the
CastOfObjects or the TimeLine records them as
relevant and makes them accessible to other team
members. Users can also continue their exploratory
work by launching searches by expanding the nodes
in the network currently displayed in the CaseSpace.
Searches on people, events, documents, etc. can
be specified by a lawyer as
WHO/WHAT/WHEN/WHERE (WHs) questions
guided by the system on the basis of the information
contained in the documents and leveraging
information on past searches made by other lawyers
(Castellani et al., 2010). More precisely, the user can
specify WHs questions by combining building
blocks that correspond to entities and their
relationships related to the contents of the
documents. The user starts to build a question by
choosing the type of answer he would like to get by
selecting one of the building blocks among “WHO”,
“WHAT”, “WHERE”, and “WHEN”.
Then the system guides the user at each step of
the question construction using a combination of
structure, semantic and content-based mechanisms.
These mechanisms allows the system to show to the
user the list of blocks that (s)he could use, that is,
that would allow the definition of a request for
information both syntactically valid and leading to
some answers in the current corpus. The user can
then select within this list the extension (s)he wants
for the WH question. Figure 3 shows an example of
question formulation (in order to search for “Who
has worked for Comp1 in 2002?”) according to the
designed interaction (for a more detailed description
of the designed interaction see (Castellani et al.,
2010).
The CaseSpace is an exploratory space for
building and visualizing networks of elements,
extracted from the documents and/or built by the
lawyers using their knowledge of the case. Selected
networks can be saved and shared with other
lawyers e.g. as a support to a line of inquiry or
evidence of a fact.
The Timeline allows lawyers to capture and
visualize the sequence of events selected during their
work and annotate causal connections among them.
Filters allow them to visualize their own
chronologies or to see also the ones that other
colleagues have reconstructed.
In order to support the interaction described so
far we have designed the architecture of the CBS as
shown in Figure 4. The Knowledge Model (KM) is
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED SYSTEM TO SUPPORT LEGAL CASE CONSTRUCTION
19

Figure 3: Example of question formulation by building blocks composition.
used to represent the elements of information useful
for the lawyers during the envisioned scenario of
work described above. To automate (up to a certain
degree) the process of finding information in a large
corpus of documents a Natural Language Processing
(NLP) system is used. The NLP system extracts the
entities and relations defined in the KM. The
extracted information is inserted into a Knowledge
Base (KB) structured based on the KM. This would
allow us to check for inconsistencies and even
potentially infer new information, for instance based
on transitive relations. New information added by
the users through new annotations in the
CastOfObjects or the TimeLine is stored in a
different base, the Application Base (AB). The AB
holds the data added by users of the system and has
a similar schema to the KB with the addition of user
metadata (e.g. timestamps). Links are kept between
the extracted information and the corresponding
document, so that when a character, that is an entity
such as a person or an organisation, or an event is
selected, the corresponding text in the document is
available through the DocumentVisualiser.
Each component of the system is further
described in the following sections.
3.1 The Knowledge Model
In order to describe the data to be extracted for
supporting case building activities we have defined a
Knowledge Model with three different layers (Lagos
et al., 2010). Figure 5 shows a fragment of the KM’
hierarchy.
The System layer supports the integration with
the indexing tools focusing on low-level features
(such as text zones). For example the class Mention
is used as the container of attributes that record the
offset of the word that evokes extracted information.
Part of this layer is also a class that represents the
source of the information and serves the system in
three different ways: record information provenance;
point to the source in case manual verification of the
results is required by the lawyers; and enable
document searching according to document
metadata.
The Domain layer represents general concepts
that we believe are useful to be considered in legal
case building and reasoning activities. For instance,
people and organisations are typical examples of
characters that may have a role in a legal case.
Special attention is given to the representation
and analysis of events, as they serve as the core
ingredient for supporting WHs questions. For
instance, the role of the characters in a case is
determined, among other factors, by the events in
which they participate. Naturally that is a two way
relation. The events that a key character participates
in may be important for the case and the participants
of a key event may be key characters. One of the
core requirements is therefore identifying the other
factors, in addition to the participants, that make an
event important. These include:
The topic of an event, if any;
The role of a character in the event;
The relative time of an event in the chronology of
the case;
The location where the event took place.
Events are extracted from the collection of
documents associated to a legal case. They may des
cribe situations, e.g., meetings, actions, e.g.,
studying, or even statuses, e.g., belong to. The
events identified will depend on the domain that the
legal case covers. Additionally, we have identified a
KEOD 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
20

InteractionLayer
KnowledgeBase
KnowledgeModel
ApplicationBase
Corpus
NaturalLanguageProcessing
System
Extraction
Component
Integration
Component
Figure 4: The architecture of the Case Building System.
Entity
Event Meet
Person
Location
TemporalConcept
Mention
System
Layer
Domain
Layer
Application
Layer
Agent
Interval
Instant
Organisation
ChemicalSubstance
TOP
InformationResource
Document
User
Figure 5: Top concepts in the knowledge model’s hierarchy.
number of classes of relations among people and
organisations that we believe to be of interest to
lawyers, during case construction, independently
from the litigation domain. Those classes correspond
to events or event abstractions and include:
Role-based events, such as “is employed by”;
Interaction-based events, such as “meets”, which
corresponds to the act of an entity (i.e. person or
organisation) interacting with another entity;
Reference events, such as “says”, which
correspond to the act of an entity referring to another
entity through a written or spoken message;
Cognitive events, such as “knows”, which indica-
tes knowledge of a topic or entity. For example the
writing of an email indicates the authors’ knowledge
of the contents.
The Application Layer deals with the entities
that need to be extracted in relation to specific issues
of the litigation case. For example, chemical
substances should be extracted for pharmaceutical
cases.
3.2 The Natural Language Processing
System
In order to extract and organize this kind of
information our system has to combine event and
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED SYSTEM TO SUPPORT LEGAL CASE CONSTRUCTION
21

named entity extraction. Extracted information has
to be aligned to the KM described in section 3.1 and
include named entities such as persons and
organizations, events, and temporal expressions (to
enable the creation of a timeline), while inter-
sentence information should also be integrated (i.e.
using coreference). The various components of the
NLP subsystem have been described in more detail
in (Lagos et al., 2010).
3.3 The Knowledge and Application
Databases
The information extracted from the NLP system is
stored in a Knowledge Base (KB) that includes
references to the initial information source
(document ids). This allows the creation of links
between the information that is presented to the
system’s users and the documents from which this
information has been extracted, so that the user can
verify the information in its context. The
information extracted actually is a graph with links
between entities and objects that describe those
entities. Let’s consider as an example the very
simple phrase “John Doe met Jane Roe in Zurich in
March 2000”. A fragment of the generated graph
that is stored in the KB is presented in Figure 6. The
event is used to connect the two named entities
(“John Doe” and “Jane Roe”) with the spatio-
temporal attributes of their interaction (“Zurich” and
“March 2000”). This has immediate implications on
the development of a timeline of events where
different case participants can be positioned.
The Application Database (AD) holds
information that is inserted in the system with a
different means than the NLP system. This may
include metadata (such as timestamps) but also and
very importantly user created information. Suppose
for example that the user has the ability to include
another entity as the participant to an event, add
information to an incomplete event representation,
or even identify two events describing the same real
world situation, then that information is stored in the
AD and after validation it is propagated to the KB.
4 PROTOTYPE
IMPLEMENTATION
We have designed and implemented a prototype of
the CBS with the aim of providing the user with
search and visualization facilities based on the
interaction modes previously described. These
facilities include a first version of the
DocumentVisualiser, of the CaseSpace and of the
building blocks based search mechanism.
The prototype follows a client-server architecture
integrating four subsystems (Figure 7).
The NLP subsystem extracts semantic
information from the document corpus according to
the given set of ontologies. To this end, it takes as
input the documents (plain text files) and ontologies
(OWL files).
The XIP Parser (Ait-Mokhtar et al., 2002) has
been used for this task, as described in (Lagos et al.,
2010). The NLP system outputs a collection of RDF
files containing the semantic information extracted
from the documents.
The Knowledge Base Management subsystem
manages the RDF files produced by the NLP system
by storing them in a Knowledge Base (KB). Based
on the assumption that a relational database (RDB),
being a mature storage solution, would offer
robustness, a RDB has been selected as the backend
of the system. We could have chosen another storage
target as well (e.g. native RDF store). A number of
frameworks exist to enable this operation. Among
them, we have used Jena (JENA, 2011), a Java
library framework for developing semantic web
applications based on W3C recommendations for
RDF and OWL. Jena also supports SPARQL, the
RDF query language, enabling us to pose queries on
the KB. Jena API calls are encapsulated in the Query
API. The Query API is a server-side service that:
receives objects from the Client Application and
translates them into SPARQL queries. For example
the question “Who did John Doe meet in Zurich?”
would generate the following SPARQL code:
SELECT DISTINCT ?characterNameForm
WHERE {
?eventURI rdf:type ns1:Meet .
?eventURI ns1:hasParticipant
?characterURI .
?eventURI ns1:hasParticipant
?character2URI .
?eventURI ns1:hasLocation
?locationURI .
?locationURI ns2:hasMention
?locationMention .
?locationMention ns2:hasForm
?locationForm .
FILTER regex(str(?locationForm),
"Zurich", "i")
FILTER(?characterURI != ?character2URI)
?characterURI rdf:type
ns2:Person .
?character2URI rdf:type
ns2:Person
KEOD 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
22

Figure 6: Example of extracted information from documents.
?characterURI ns2:hasPersonName
?characterName .
?characterName ns2:hasNameForm
?characterNameForm .
?character2URI ns2:hasPersonName
?character2Name .
?character2Name ns2:hasNameForm
?character2NameForm .
FILTER regex(str(?character2NameForm),
"John Doe", "i")}
translates query results from Jena into Java objects
following an object data model designed to reflect
the ontological structure.
sends resulting Java objects to the Client
Application that follows the same object data model.
Note that a server-side library called BlazeDS
(BLAZEDS, 2011) is handling the binary
(de/)serialization of objects through the network
between the server (in Java) and the client (in
ActionScript) applications.
The Application Base Management subsystem
stores search results selected by the user. The
process includes a service that receives objects from
the Client Application and persists them in the
Application Database using a relational-object
mapping framework. Every time the Client
Application is initialized, the previously saved
objects are retrieved from the Application Database
and loaded in the CastOfObjects, which is
synchronized with the CaseSpace. As a
consequence, the system provides to its users the
same working environment from one session to
another.
The Client Application mainly offers a first
version of the DocumentVisualiser, of the
CastOfObjects, and of the building blocks based
search mechanism, which have been described in
section 3. In particular it supports a visual
mechanism for the formulation of questions for
searching information stored in the KB as a
composition of building blocks, with some of the
forms of guidance defined by the design. Figure 8
shows the initial configuration of the GUI for the
building blocks based formulation of questions. In
the upper part, coloured blocks mapping the KM
entities available for question composition are
displayed to the user as enabled blocks. It is possible
to drag and drop the enabled blocks in the question
area located below. A disabled block means that it
cannot be selected (Castellani et al., 2010).
Selecting one of the results of a search, e.g. the
name of a person, the user can see the document
corresponding to that result in the
DocumentVisualiser, with the relevant entity
highlighted. The user can save relevant results by
dragging and dropping them into the CastOfObjects.
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED SYSTEM TO SUPPORT LEGAL CASE CONSTRUCTION
23

Figure 7: The architecture of the prototyped system.
Figure 8: Building Blocks GUI for semantic query formulation.
KEOD 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
24

5 DISCUSSION
A number of commercial tools and research
prototypes already exist in the domain of litigation
support or search. However, no one seems to fit with
all the requirements we have identified in support of
case construction in litigation cases. Nevertheless,
we have identified a few interesting aspects from a
few of them.
The Polestar system (Pioch and Everett, 2006)
provides built-in support for collecting textual facts
from source documents and structured
argumentation, plus awareness mechanisms which
are based on activity on documents, but not on their
contents. Entity Workspace (Bier et al., 2006) allows
the organisation of extracted information in entity
groups. However, there is no timeline and only a
limited support for collaboration. Systems like
Sandbox/TRIST (Wright et al., 2006) and JigSaw
(Stasko et al., 2008) have interesting visualisation
capabilities, along the lines of CBS, but CBS is a
more unified system with more collaboration
support.
An interesting and quite widely used commercial
database to support case analysis is the already
mentioned CASEMAP (2011) and we have taken
into account features provided by this tool in
defining the requirements for our CBS, especially
around the semantic structure of the information
stored in the system (characters, etc.). On the other
hand CASEMAP’s system for creating entries is
completely manual whereas a semi-automatic
definition is supported in CBS, with the system also
suggesting probable relevant information.
The work described above is related to the
provision of a complete work environment for
lawyers to help them in the process of legal
construction. While in the past the use of NLP in this
domain was very limited, a more recent line of work
combines NLP with reasoning procedures and
representation models of a legal case, in order to
find relevant case precedents (i.e. judgements related
to previous cases). The central idea is that a case can
be represented as a set of facts (or factors) that
correspond to an abstraction level, appropriate for
comparison based on legal norms and outcomes.
In initial works (Ashley and Rissland, 1988);
(Ashley and Aleven, 1997); (Branting, 1989) factor
assignment was done manually under the direction
of experts. However, the high cost of development
and maintenance pushed research towards the use of
NLP techniques.
Bruninghaus and Ashley (2006) present a
framework called SMILE that utilises machine
learning to assign automatically factors to different
text passages based on a tagged collection. Although
the results are promising, the tests have been
performed on a small collection of documents
because a similar larger annotated collection does
not exist. A hierarchy or set of factors is developed
manually.
Weber-Lee et al. (1997) used a rule-based system
for NLP to define the rhetorical structure of the texts
and identify the parts in which the illocutionary
expressions are present. They identify four main
substructures, identification (i.e. surface features
such as date, city, reporter and petition type),
abstract (i.e. applicant and result), body (court
decision and its foundations), closing (votes, date,
place and names of participating attorneys).
According to the different substructure, different
rules are fired in the reasoning process.
As in our work, Maxwell et al. (2009) move
from factors and illocutionary expressions to the
extraction of semantic events for legal case retrieval,
where an event refers to any eventuality (event,
state, and attribute) existing in the legal text. They
report that although their results are promising, a
larger evaluation of event-based extraction
techniques as an enabler of understanding legal
relevance should be carried out for reaching definite
conclusions.
All these works have focused on case precedents
and their retrieval. We rather argue that object
retrieval can help in case construction activities, a
quite different process.
While there were some very good reasons to
select RDF and OWL related technologies to
construct our architecture, such as model flexibility,
explicit representation of semantics, out-of-the-box
reasoners (for OWL or RDFS) and proliferation of
freely available background knowledge (i.e. Linked
Data), we have also found out that the combination
we have selected is not highly scalable. This is a
major issue in litigation where millions of pages are
included in each case, which may mean hundreds of
millions of entities and billions of triples. Possible
approaches we are researching include: optimizing
the query construction process (e.g. rather than using
regular expressions within SPARQL FILTERs
research the combination of free text search and
RDF search), researching different store
implementations (for example a native RDF store
may have performed much better for SPARQL
querying thanks to customised indexes), or
developing native formats and schemas to the
expense of interoperability and out-of-the box reuse
of deductive reasoners.
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED SYSTEM TO SUPPORT LEGAL CASE CONSTRUCTION
25

Another point we would like to address relates to
the synchronization among different components of
the system. For example, currently the schema of the
AB is not automatically updated according to the
KM while the number of building blocks in the
search interface doesn’t automatically reflect
changes to the KM. Furthermore, while users can
select and save search results in the AB we do not
exploit user generated information in a more
elaborate way (e.g. for incomplete information).
One of the main strengths of the approach we
propose is related to the assumption that entities
from different documents will create an
interconnected graph that will enable the discovery
of implicit information. However, we have found
that merely annotating individual mentions of
characters and events may enable a certain amount
of new functionality, but there is more to be gained
by recognizing that the same characters and events
are mentioned multiple times in a single document
and across multiple documents, and synthesizing
richer representations that combine information from
multiple sources. We have implemented simple
coreference resolution mechanisms for mentions of
persons, but this is only a start. The mechanisms
could be enhanced to integrate encyclopedic
knowledge from external sources (e.g. knowing that
a referring expression “he” can’t be coreferent with
a name if the person with that name is known to be
female), and need to be extended to other types of
entities and to events. Reusing and integrating
existing ontologies is also under investigation.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have presented the overall design of
the Case Building System that we are developing
and the first prototype that we built for the system.
This is ongoing work and testing the design of the
system and complete its implementation will require
time.
However, we believe that we have produced a
novel and technically achievable design idea that is
interesting to share with the Knowledge Engineering
and Semantic Technologies community. We think
that we have a good basis to evaluate, refine and
evolve our concept with actual lawyers in realistic
and then actual situations of use.
REFERENCES
Ait-Mokhtar, S., Chanod, J. P., Roux, C., 2002. Robust-
ness Beyond Shallowness: Incremental Deep Parsing.
J. Nat. Lang. Eng. 8, 2-3, 121-144.
Ashley, K.D. and Rissland, E.L., 1988. A Case-Based
Approach to Modeling Legal Expertise. IEEE
Intelligent Systems, 3 (3) 70-77.
Ashley, K. D. and Aleven, V., 1997. Reasoning
symbolically about partially matched cases. In Proc. of
the 15th Int. Joint Conf. on Artificial Intelligence –
Vol. 1. M. E. Pollack, Ed. Morgan Kaufmann
Publishers, San Francisco, CA, 335-341.
Attfield, S. and Blandford, A., 2008. E-discovery viewed
as integrated human-computer sensemaking: The
challenge of ‘frames’. In Proc: 2nd Int. DESI
Workshop.
Attfield, S., Blandford, A., and De Gabrielle, S., 2008.
Investigations within investigations: a recursive
framework for scalable sensemaking support. In: Proc.
of CHI’08 Workshop on Sensemaking.
Attfield, S. and Blandford, A., 2009. Looking for Fraud in
Digital Footprints: Sensemaking with Chronologies in
a Large Corporate Investigation. Working paper, UCL
Interaction Centre: London, UK.
Bier, E. A., Ishak, E. W., and Chi, E., 2006. Entity
Workspace: an evidence file that aids memory,
inference, and reading. In Proc. of ISI’06. Springer,
466-472.
BLAZEDS, 2011, available at http://opensource.adobe.
com/wiki/display/blazeds/BlazeDS, last accessed in
July 2009.
Branting, L. K., 1989. Representing and reusing
explanations of legal precedents. In Proc. of the 2nd
Int. Conf. on Artificial intelligence and Law (ICAIL).
ACM, NY, 103-110 (1989).
Brüninghaus, S. and Ashley, K. D., 2006. Progress in
textual case-based reasoning: predicting the outcome
of legal cases from text. In Proc. of the 21st National
Conference on Artificial intelligence, Vol, 2. A. Cohn,
Ed., AAAI Press, 1577-1580.
CASEMAP, 2011, LexisNexis, articles available at
http://www.casesoft.com/training/articles.asp, last
accessed in February 2011.
Castellani, S., Grasso, A., Benedetti, V., Lagos, N., and
Hairon, N., 2010. A semantics-based approach to
guide formulation of questions for documentary
recontruction activities. Accepted and presented at the
4th Int. Conf. on Advances in Semantic Processing.
Electronic Discovery Reference Model, http://edrm.net,
last accessed 29 April 2011.
JENA, 2011, available at http://jena.sourceforge.net/, last
accessed in July 2009.
Lagos, N., Segond, F., Castellani, S. and O’Neill, J., 2010.
Event extraction for legal case building and reasoning,
In Proc: of Int. Conf. on Intelligent Information
Processing (IIP’10), 92-101.
Maxwell, K. T., Oberlander, J., and Lavrenko, V., 2009.
Evaluation of semantic events for legal case retrieval.
In Proc. of the WSDM '09 Workshop on Exploiting
Semantic Annotations in information Retrieval.
(ESAIR). ACM, New York, NY, 39-41.
KEOD 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
26

Noel, L. and Azemard, G., 2008. From Semantic Web
Data to Inform-Action: a Means to an End. In: ACM
Computer Human Interaction.
Pioch, N. J. and Everett, J. O., 2006. POLESTAR –
Collaborative Knowledge Management and
Sensemaking Tools for Intelligence Analysts. In Proc.
of CIKM’06, ACM, 513-521.
Privault, C., O'Neill, J., Renders, J.-M., and Ciriza, V.,
2010. A new tangible user interface for machine
learning document review. Special Issue on "E-
Discovery", Guest Ed(s) K. D. Ashley, J. R. Baron and
J. G. Conrad, Artificial Intelligence and Law, 18, 4,
Sheth, A., Arpinar, B., Kashyap, V., 2002. Relationships
at the Heart of Semantic Web: Modeling, Discovering,
and Exploiting Complex Semantic Relationships,
Technical Report, LSDIS Lab, Computer Science,
Univ. of Georgia, Athens GA.
Stasko, J., Gorg, C., and Liu, Z., 2008. Jigsaw: supporting
investigative analysis through interactive
visualisation. In Information Visualisation 7, 118-132.
Weber-Lee, R., Barcia, R. M., Costa, M. C., Filho, I. W.,
Hoeschl, H. C., Bueno, T. C., Martins, A., and
Pacheco, R. C., 1997. A Large Case-Based Reasoner
for Legal Cases. In Proc. of the 2nd Int. Conf. on
Case-Based Reasoning Research and Development. D.
B. Leake and E. Plaza, Eds. LNCS, vol. 1266.
Springer-Verlag, London, 190-199.
Wright, W., Schroh, D., Proulx, P., Skaburskis, A., and
Cort, B., 2006. The Sandbox for Analysis - Concepts
and Methods. In Proc. of CHI'06, ACM 2006.
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED SYSTEM TO SUPPORT LEGAL CASE CONSTRUCTION
27
