
MULTI-CLASS DATA CLASSIFICATION FOR IMBALANCED
DATA SET USING COMBINED SAMPLING APPROACHES
Wanthanee Prachuabsupakij and Nuanwan Soonthornphisaj
1
Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand
Keywords: Imbalanced dataset, Multi-class classification, Machine learning, Decision tree.
Abstract: Two important challenges in machine learning are the imbalanced class problem and multi-class
classification, because several real-world applications have imbalanced class distribution and involve the
classification of data into classes. The primary problem of classification in imbalanced data sets concerns
measure of performance. The performance of standard learning algorithm tends to be biased towards the
majority class and ignore the minority class. This paper presents a new approach (KSAMPLING), which is
a combination of k-means clustering and sampling methods. K-means algorithm is used for spitting the
dataset into two clusters. After that, we combine two types of sampling technique, over-sampling and under-
sampling, to re-balance the class distribution. We have conducted experiments on five highly imbalanced
datasets from the UCI. Decision trees are used to classify the class of data. The experimental results showed
that the prediction performance of KSAMPLING is better than the state-of-the-art methods in the AUC
results and F-measure are also improved.
1 INTRODUCTION
The multi-class classification problems based on
imbalanced training data set has received increasing
attention in many real applications domains, such as
bioinformatics, risk management, anomaly
detection, information retrieval, and text
classification. Class imbalance occurs when the
number of instances of one class (majority/negative
class) outnumbers the number of instances of other
classes (minority/positive class) in samples or
training datasets. The classification on imbalanced
data always causes problems because traditional
classification algorithms tend to misclassify the
minority class instances as majority, and lead to poor
classification accuracy for unseen samples from the
minority class. Many solutions are previously
proposed to solve the class imbalance problem
through either data (Chen et al., 2010); (Liu et al.,
2010) or algorithm levels (Benjamin & Nathalie,
2008). The data level approach aims to correct
problems with the distribution of a data set before it
will be classified, including over-sampling the
minority class, or under-sampling the majority class.
At the algorithm level, solutions try to adapt tra-
1
Corresponding author
ditional classification algorithms to bias towards the
small class, such as one-class learning, boosting
schemes, and cost sensitive learning.
In recent years, the machine leraning community
has focused on imbalanced problems related to two-
class classification. Multi-class problems are
reduced to two-class problem and then use two-class
learning for classification such as One-Against-One
(OAO) (Fernandez et al., 2010), One-Against-All
(OAA) (Chen et al., 2010).
In this paper, we propose a new classification
method, that integrate both over-sampling and
under-sampling techniques for improving the
classification of imbalanced datasets with more than
two classes, named k-means with Sampling
technique (KSAMPLING). K-means (Forgy, 1965)
is used to seperate all instances into two clusters. For
each cluster, we combine two types of sampling
methods for balancing the class distribution. For
over-sampling, we use SMOTE to preprocess data
by increasing the size of the training subset base on
over-sampling that has a significant imbalance
between their classes to construct two new training
dataset. Next, Random under-sampling is used for
removing the majority class to balance the class
distribution by randomly. Then, we apply a decision
trees learner (Quinlan, 1986) for class prediction
166
Prachuabsupakij W. and Soonthornphisaj N..
MULTI-CLASS DATA CLASSIFICATION FOR IMBALANCED DATA SET USING COMBINED SAMPLING APPROACHES.
DOI: 10.5220/0003635201580163
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval (KDIR-2011), pages 158-163
ISBN: 978-989-8425-79-9
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

within a cluster. Decision trees were chosen as the
approach for classification because it is the intuitive
understanding of model. Many other machine
learning models, such as neural networks, are
difficult to interpret. Finally, the prediction is
obtained by combining the results from both clusters
through majority vote. Furthermore, we select 5
multi-class datasets with varying levels of imbalance
data from the UCI machine learning repository
(Arthur Asuncion, 2007) and the performance
measurement is based on Probabilistic Area under
the ROC Curve (AUC) (Hand and Till, 2001) and
the F-measure. Experimental results show that our
approach achives high performance in learning from
imbalanced multi-class problems.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2
discusses about related work. Section 3 describes
our approach whereas Section 4 explains the
experiments carried out; and finally, Section 5
summarize the conclusion of our work.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Decision Trees
A decision tree is a supervised learning algorithm
proposed by Quinlan 1986. The tree is constructed
using only best attributes that are able to
differentiate the concepts of the target class. Each
node in the tree is an attribute selected from the
training set using gain ratio. The gain ratio measures
the different between the entropy of training set
before and after selecting attribute. The attribute
with the highest value of the gain ratio is selected to
be a node in the tree. Applying pruning method to a
tree is desirable because the tree that is a small size
to avoid unnecessary complexity, and to avoid over-
fitting of the dataset in future prediction.
2.2 The Class Imbalance Problem
The class imbalance problem has recently attracted
considerable attention in the machine learning
research. To solve this problem, two ways have been
proposed: data and algorithm levels. In this section,
we provide a focused review of the data level
approach.
The objective of over-sampling method is to
increase more instances from minority class either
duplicates or interpolates minority instances.
Duplicating the instances will lead to over-fitting
problem. In 2002, Chawla et al proposed an
algorithm called SMOTE algorithm (Chawla et al.,
2002). It over-samples the minority class using
interpolation method. The algorithm starts with
searching for the k-nearest neighbours of every
minority instance and generates synthetic minority
data by calculating linear interpolations between a
minority class instance and a randomly selected
neighbour. Some of the important works include the
adaptive over-sampling algorithm (Chen et al.,
2010), memetic algorithm (MA) (Fernadez-Navarro
et al., 2011).
Under-sampling method balances the class
distribution by removing instances from the majority
class. The most popular under-sampling approach is
random under-sampling. Random under-sampling
(RUS) employed resampling technique. The
instances of the majority class are randomly
eliminated until the ratio between the minority and
majority class is at the desired level.
The
disadvantage of random under-sampling is that it
discards data that may contain useful information.
Note that RUS was proposed in (Yen and Lee,
2009) and (Seiffert et al., 2010).
2.3 Solutions for the
Multi-classification
Problems with multi-class classifications can be
solved by decomposing the multi-class classification
into several binary classifications that can be solved
by the two-class learner. Several methods have been
proposed for decomposition such as
One-Against-
One (Hastie and Tibshirani, 1998) and One-Against-
All (Anand et al., 1995).
OAO is a simple approach that reduces a multi-
class problem into k binary problems. Each learner is
trained to separate a class i from the remaining
classes. Another approach of decomposition
strategies is OAA. In this approach, given k classes,
each class is compared with each other class.
Therefore,
2
1)k(k
binary classifiers are generated.
The classifier is trained to discriminate between
these two classes only. Finally, it combines the
results with the majority vote.
For multi-class imbalanced problems, there are
some methods that combine both OAO and SMOTE
approaches. One of these methods is introduced by
Fernandez et al. (Fernandez et al., 2010). It applies
an over-sampling step before the pair-wise learning
process. The quality of this method can be tested
using the linguistic fuzzy rule based classification
system and fuzzy hybrid genetics-based machine
learning algorithm.
Another approach uses a dynamic over-sampling
MULTI-CLASS DATA CLASSIFICATION FOR IMBALANCED DATA SET USING COMBINED SAMPLING
APPROACHES
167

method that incorporated into a memetic algorithm
to optimizes radial basis functions neural networks
called dynamic smote radial basis function (DSRBF)
(Fernadez-Navarro et al., 2011).
3 METHODOLOGY
In this section, we present our method that can
enhance the prediction of both minority and majority
classes. Figure 1 illustrates the basic idea of
KSAMPLING and its details are shown in Table 1.
The algorithm starts with k-means algorithm in order
to split the training set into 2 classes. Then the class
distribution in each cluster was rebalanced by
sampling approach. KSAMPLING consists of two
steps:
The first step is a re-clustering process using
k-mean algorithm. The instances are divided into
certain number of clusters (assume k clusters) fixed
a priori. KSAMPLING divides all instances into two
clusters by setting k to be 2. In order to measure the
distance between two instances, we use the
Euclidean distance. Considering the instances for
each cluster, let Ny
i
denotes the number of data
instances of class y
i
in training data set. Let C
1
and
C
2
denote the first cluster and the second cluster
respectively. If Ny
i
in C
1
is greater than Ny
i
in C
2
then all instances of class y
i
in both clusters are
assigned to C
1
. On the other hand, if Ny
i
in C
2
is
greater than Ny
i
in C
1
then all instances of class y
i
in both clusters are assigned to C
2
.
After the re-clustering process, we get two set of
new samples, E
1
and E
2
. These samples are
rebalanced by increasing a number of instances (a
distribution of 75-25%), using over-sampling
technique. Imbalance ratio (IR) (Fernandez et al.,
2010); (Orriols-Puig and Bernadó-Mansilla, 2009) is
used as a criteria during the process. The imbalanced
ratio is defined as the fraction between the number
of instances of the majority and minority class. If the
value of imbalanced ratio obtained from E
1
is higher
than 3 the over-sampling method is applied for E
1
.
Therefore we get T
11
. The imbalanced ratio of T
11
is
examined. In case that its value is higher than 1.5 (a
distribution of 60-40 %), T
12
is obtained by doing
over-sampling on T
11
.
For the last training set (T
13
), we use random
under-sampling technique to reduce d instances of
the majority class in
T
12
, where d is the different
between the number of instances in the minority
classes
T
12
and T
11
. Next, T
11
, T
12
, and T
13
are
learned using decision trees algorithm (j48). Finally
we get a set of hypotheses ( h
11,
h
12
, and h
13
). Note
that, we get totally six hypotheses from two clusters.
(All processes are applied for E
2
, as well).
The prediction is done using majority vote
among six hypotheses. Given a test example, if the
final prediction obtained from the majority vote
among three hypotheses of E
1
is equal to R
2
then the
classification is depend on the majority vote of
hypotheses of E
2
. Otherwise, the prediction will rely
on the majority vote of three hypotheses of E
1
.
Table 1: KSAMPLING algorithm.
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Datasets and Setup
The proposed methodologies are applied to five
datasets from the UCI Machine Learning Repository
(Arthur Asuncion, 2007).
KDIR 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
168
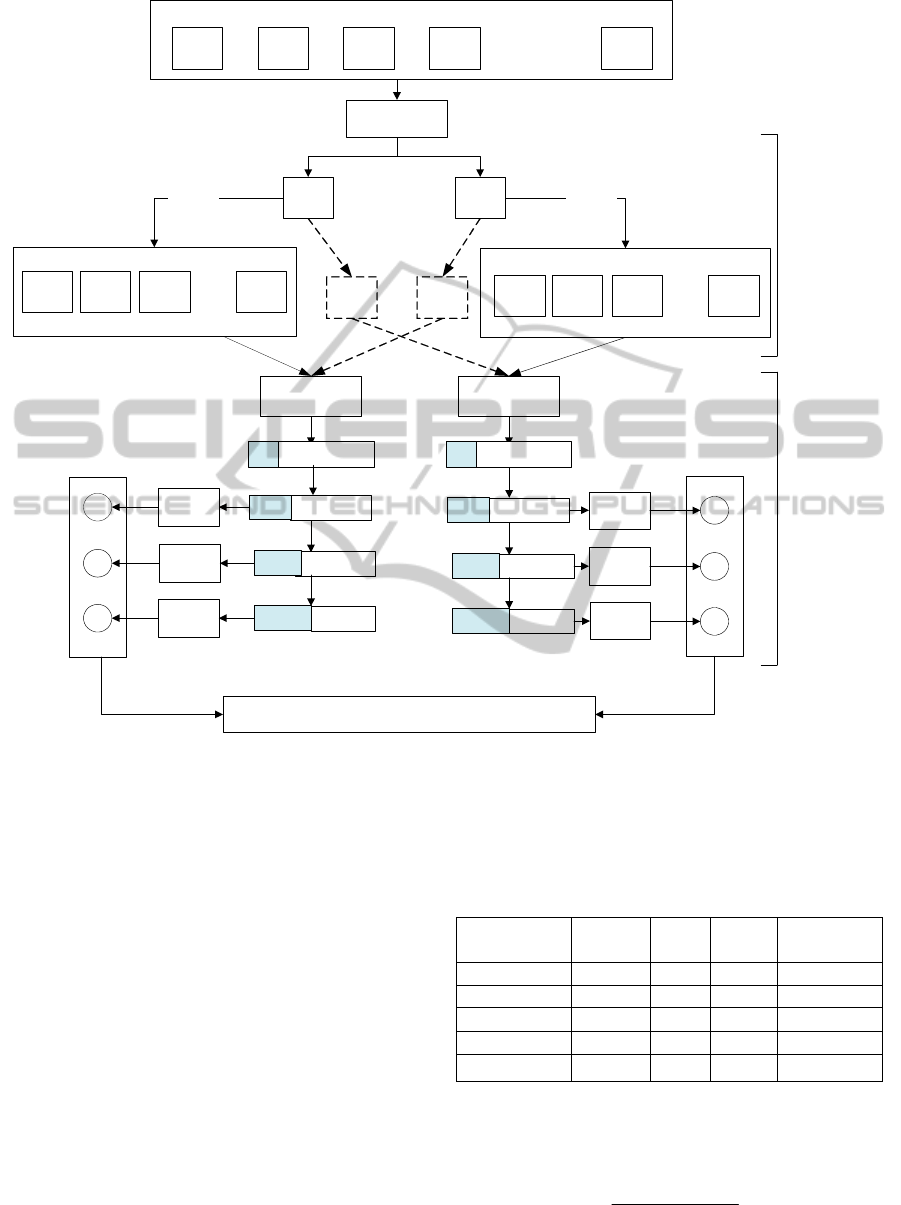
Figure 1: The KSAMPLING algorithm.
These are Abalone, Glass, Yeast, Pageblocks,
and Car. These datasets are varying in the number of
classes and class distributions to ensure a thorough
assessment of performance. Yeast and Glass are
datasets that have highest imbalance ratio. Abalone
is a dataset that has maximum the number of classes.
Table 2 summarize the characteristics of the datasets
used in our approach.
The KSAMPLING technique is compared to
different algorithms: decision tree, SMOTE, One-
Against-All (OAA), One-Against-One (OAO), OAA
with SMOTE, and OAO with SMOTE. In all state-
of-the art approaches, j48 is used as the classifier.
We have implemented KSAMPLING within the
WEKA 3.6.0 framework (Witten et al., 2005), A
decision tree (J48) was used as a baseline classifier.
The experimental design was conducted using 10-
fold cross validation. Euclidean distance was used to
compute distance between instances and cluster in
the k-means algorithm. The evaluation measures
used in our experiments are the area under the ROC
curve (AUC)
(Huang and Ling, 2005) and F-
measure that base on the confusion matrix.
Table 2: Summary of the datasets characteristics.
Datasets
#
Feature
#
Class
#
Data
Imbalanced
ratio
Glass 9 6 214 0.04 : 0.96
Yeast 8 10 1483 0.04 : 0.96
Car 6 4 1728 0.05 : 0.95
Abalone 7 28 731 0.06 : 0.94
PageBlocks 10 5 5473 0.10 : 0.90
The AUC measures the misclassification rate of
one class and the accuracy of the other. The AUC is
defined as
2
FP -TP+1
= AUC
raterate
(1)
Y1
1
Y1
2
Y1
3
Y1
n
……..
Y
1
Y
2
Y
3
Y
4
Y
m
……..
k-means (k=2)
C
1
C
2
R
1
R
2
Relabel
Relabel
Y2
1
Y2
2
Y2
3
Y2
n
……..
Consist of Consist of
New samples (E
1
) New samples (E
2
)
min maj
Oversampling if IR > 3
Traning1
(T
11
)
h
1
Decision trees
hypotheses
Final classfication
H* : based on majority vote
maj
min
maj
min
Oversampling if IR > 1.5
Traning2
(T
12
)
maj
min
Random Undersampling
Traning3
(T
13
)
h
2
h
3
min maj
Traning4
(T
21
)
maj
min
maj
min
Traning5
(T
22
)
maj
min
Traning6
(T
23
)
h
4
Decision trees
hypotheses
h
5
h
6
Multi-class training set
Reclustering
Process
Data
Rebalancing
Process
MULTI-CLASS DATA CLASSIFICATION FOR IMBALANCED DATA SET USING COMBINED SAMPLING
APPROACHES
169

Table 3: F-measure comparisons among KSAMPLING and other methods.
Datasets/
Methods
J48 OAO OAA SMOTE
OAO with
SMOTE
OAA with
SMOTE
KSAMPLING
Abalone 0.209 0.218 0.094 0.625 0.646 0.580
0.777
Glass 0.801 0.718 0.734
0.853
0.833 0.851 0.839
Yeast 0.552 0.573 0.570 0.724 0.730 0.728
0.833
Pageblocks 0.969 0.972 0.968 0.982 0.983 0.982
0.999
Car 0.924 0.941 0.921 0.970 0.979 0.983
0.984
Table 4: AUC comparisons among KSAMPLING and other methods.
Datasets/
Methods
J48 OAO OAA SMOTE
OAO with
SMOTE
OAA with
SMOTE
KSAMPLING
Abalone 0.559 0.569 0.509 0.806
0.818
0.787 0.790
Glass 0.766 0.807 0.820 0.912 0.898 0.910
0.917
Yeast 0.707 0.723 0.716 0.843 0.844 0.841
0.900
Pageblocks 0.920 0.925 0.918 0.988 0.989 0.988
1.000
Car 0.936 0.946 0.926 0.981 0.986 0.989
0.990
Where
TP
rate
is the proportion of instances which
were classified as class x, among all instances which
truly have class x, and FP
rate
the proportion of
examples which were classified as class x, but
belong to a different class, among all instances
which are not of class x.
However, the AUC have
been used to enhance
the quality of binary classifier. In multi-class
problems, the results are shown in terms of
probabilistic AUC (Hand and Till, 2001). In this
approach, the AUC for each class is calculated,
taking one class as positive and the other as
negative. Then, the equation for total AUC is as
follows:
))AUC(c)AUC(c(
2
1
AUC
2i1i
Cc
i
Cc
itotal
(2)
Where AUC(c
i
) is calculated by considering the
instances of c
i
as positive and the instances of other
classes as negatives, and C
1
and C
2
are the number
of classes in the cluster1 and cluster2 respectively.
4.2 Results
The performance measured in term of F-measure in
all data sets are shown in Table 3. The results show
that KSAMPLING outperformed other algorithms in
four datasets. Consider the Abalone dataset, there
are maximum the number of classes, the
performance of baseline algorithms on this dataset
(J48, OAO, OAA) obtain 0.209, 0.218, and 0.094
respectively, whereas using sampling approach
(SMOTE) can enhance the performance on Abalone
dataset (0.625). However, our method has got better
performance (0.777) than baseline and baseline with
sampling algorithms. On Glass dataset, our method
is a bit below than SMOTE and OAA with SMOTE
because Glass is a small dataset. On Pageblocks
dataset, the F-measure of KSAMPLING is equal to
0.999. This digit is actually equal to 1, this result
show that KSAMPLING provided the best model for
the class prediction.
From Table 4, we found that KSAMPLING can
provide better AUC results on most of the data sets
compared to other algorithms. Except for Abalone
dataset, we see that OAO with SMOTE seems to
provide better AUC rate on most datasets. In
PageBlocks dataset, the AUC of KSAMPLING is
equal to 1, this means that KSAMPLING provided
the best model for the class prediction.
For all experimental results, KSAMPLING
obtains high performance in term of F-measure and
AUC for each class when decision tree is applied as
a baseline classifiers.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we presented the KSAMPLING
approach, which improve the classification accuracy
based on multi-class imbalance problem; using k-
means algorithm to separate all instances into two
clusters and combining sampling methods, over-
sampling and under-sampling, for re-balance the
class distribution. SMOTE algorithm is used for
over-sampling instances in each cluster when IR
between the corresponding classes is higher than a
threshold. Random under-sampling is applied on the
majority class in order to further decrease the
imbalance ratio.
The results on benchmark datasets
confirm that our method perform very well for
multi-class imbalance datasets. However, the
KDIR 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
170

KSAMPLING still has some drawbacks, the
accuracy rates can be dropped if the training set size
is small.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is supported by Faculty of Science,
Kasetsart University and National Science and
Technology Development Agency under Ministry of
Science and Technology of Thailand.
REFERENCES
Anand, R., Mehrotra, K., Mohan, C. K., & Ranka, S.
(1995). Efficient classification for multiclass problems
using modular neural networks. IEEE Transactions on
Neural Networks, 6(1), 117-124.
Arthur Asuncion , D. N. (2007). UCI machine learning
repository from http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets.
html
Benjamin, W., & Nathalie, J. (2008). Boosting Support
Vector Machines for Imbalanced Data Sets. In A. An,
S. Matwin, Z. Ras & D. Slezak (Eds.), Foundations of
Intelligent Systems (Vol. 4994, pp. 38-47): Springer
Berlin / Heidelberg.
Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., &
Kegelmeyer, W. P. (2002). SMOTE: synthetic
minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Int. Res.,
16(1), 321-357.
Chen, S., He, H., & A., G. E. (2010). RAMOBoost:
Ranked Minority Oversampling in Boosting. IEEE
Transactions on Neural Networks, 21(10), 1624-1642.
Fernadez-Navarro, F., Hervas-Martinez, C., & Gutierrez,
P. A. (2011). A dynamic over-sampling procedure
based on sensitivity for multi-class problems. Pattern
Recogn., 44(8), 1821-1833.
Fernandez, A., Jesus, M. J. D., & Herrera, F. (2010).
Multi-class imbalanced data-sets with linguistic fuzzy
rule based classification systems based on pairwise
learning. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the
Computational intelligence for knowledge-based
systems design, and 13th International Conference on
Information Processing and Management of
Uncertainty.
Forgy, E. (1965). Cluster analysis of multivariate data:
efficiency versus interpretability of classifications.
Biometrics, 21, 768-780.
Hand, D. J., & Till, R. J. (2001). A Simple Generalisation
of the Area Under the ROC Curve for Multiple Class
Classification Problems. Mach. Learn., 45(2), 171-
186.
Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (1998). Classification by
Pairwise Coupling. 26(2), 451-471.
Huang, J., & Ling, C. X. (2005). Using AUC and
Accuracy in Evaluating Learning Algorithms. IEEE
Trans. on Knowl. and Data Eng., 17(3), 299-310.
Liu, Y., Yu, X., Huang, J. X., & An, A. (2010).
Combining integrated sampling with SVM ensembles
for learning from imbalanced datasets. [doi: DOI:
10.1016/j.ipm.2010.11.007]. Information Processing
& Management, In Press, Corrected Proof.
Orriols-Puig, A., & Bernadó-Mansilla, E. (2009).
Evolutionary rule-based systems for imbalanced data
sets. Soft Computing - A Fusion of Foundations,
Methodologies and Applications, 13(3), 213-225.
Quinlan, J. R. (1986). Induction of Decision Trees.
Machine Learning, 1(1), 81-106.
Seiffert, C., Khoshgoftaar, T. M., Van Hulse, J., &
Napolitano, A. (2010). RUSBoost: A Hybrid
Approach to Alleviating Class Imbalance. Systems,
Man and Cybernetics, Part A: Systems and Humans,
IEEE Transactions on, 40(1), 185-197.
Witten, I. H., Frank, E., & Hall, M. A. (2005). Data
Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and
Techniques (Third Edition ed.). San Francisco:
Morgan Kaufmann.
Yen, S.-J., & Lee, Y.-S. (2009). Cluster-based under-
sampling approaches for imbalanced data
distributions. Expert Syst. Appl., 36(3), 5718-5727.
MULTI-CLASS DATA CLASSIFICATION FOR IMBALANCED DATA SET USING COMBINED SAMPLING
APPROACHES
171
