
A WEAKLY SUPERVISED APPROACH FOR LARGE-SCALE
RELATION EXTRACTION
Ludovic Jean-Louis, Romaric Besanc¸on, Olivier Ferret and Adrien Durand
CEA, LIST, Vision and Content Engineering Laboratory, Fontenay-aux-Roses, F-92265 France
Keywords:
Information extraction, Relation extraction.
Abstract:
Standard Information Extraction (IE) systems are designed for a specific domain and a limited number of re-
lations. Recent work has been undertaken to deal with large-scale IE systems. Such systems are characterized
by a large number of relations and no restriction on the domain, which makes difficult the definition of manual
resources or the use of supervised techniques. In this paper, we present a large-scale IE system based on a
weakly supervised method of pattern learning. This method uses pairs of entities known to be in relation to
automatically extract example sentences from which the patterns are learned. We present the results of this
system on the data from the KBP task of the TAC 2010 evaluation campaign.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the context of information extraction, the objective
of relation extraction is to find if two entities are se-
mantically linked and when it is possible, to deter-
mine the nature of this link. In the work we present
here, we are more specifically interested in extracting
relations between named entities for building large-
scale knowledge bases. Such building has been re-
cently achieved in the context of Semantic Web by
exploiting semi-structured data from open sources of
information. One of the most representative exam-
ples of this trend is the DBpedia project
1
(Bizer et al.,
2009), which built a large knowledge base from the
semi-structured part of Wikipedia. The next step in
this process is to supplement such knowledge bases
by exploiting texts, which are a larger but more diffi-
cult to deal with source of information, and more par-
ticularly, extracting automatically relations between
entities from them.
Work about relation extraction can be considered
according to the degree of supervision it requires. At
the lower level of supervision, which is also called
unsupervised extraction, the type of the relations to
extract is not fixed a priori, neither by examples nor
a model. Only constraints about the linked entities,
as their type, are set. The type of the extracted re-
lations is defined a posteriori, by gathering similar
relations. Such approach can be found in (Shinyama
1
http://dbpedia.org/About
and Sekine, 2006) or (Banko and Etzioni, 2008) for
instance. The opposite approach, called supervised
extraction, consists in fixing both the type of the tar-
get relations and the means for extracting them from
texts. It takes the form of either a handcrafted model,
typically defined as a set of rules, or a model built by
a machine learning algorithm from a set of contex-
tualized relation examples coming from a manually
annotated corpus. This second option is mostly repre-
sented by statistical machine learning models focus-
ing on taking into account various kinds of features
(lexical, syntactic, semantic ...) (Zhou et al., 2005),
for instance by finding kernel functions dealing with
complex structures such as those produced by syntac-
tic parsers (Zhou et al., 2007).
Between these two extrema, weakly supervised
approaches refer to cases where either examples or
a model are provided but are not sufficient for devel-
oping a fully operational relation extraction system.
As a consequence, this initial definition must be ex-
tended in an automatic way, generally by exploiting
an unannotated corpus. Work in this area shows two
main cases, that can be eventually combined, of un-
derspecification of this initial definition:
• underspecification due to the extent of the defini-
tion. Only a small set of relation examples or an
incomplete model are given;
• underspecification due to the nature of the def-
inition, which occurs when the examples or the
model have to be instantiated for being used.
94
Jean-Louis L., Besançon R., Ferret O. and Durand A..
A WEAKLY SUPERVISED APPROACH FOR LARGE-SCALE RELATION EXTRACTION.
DOI: 10.5220/0003661200940103
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval (KDIR-2011), pages 94-103
ISBN: 978-989-8425-79-9
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

The first case is classically tackled following the
methodology of (Hearst, 1992) by the means of a
bootstrapping mechanism: starting from a model of
the target relations made of a restricted set of ini-
tial examples or extraction rules, new examples are
acquired from a corpus and used for completing the
model. This two-step process is re-applied while the
model is not developed enough for covering any new
example. (Agichtein and Gravano, 2000) is a typical
application of such methodology in the case of rela-
tions between named entities.
The second case is represented by the recent no-
tion of Distant supervision, introduced explicitly by
(Mintz et al., 2009) but already present in previous
work about bootstrapping. Examples are given in this
approach with an underspecified form as they are lim-
ited to pairs of entities: they are given both without
context and without a linguistic form. The develop-
ment of such approach is favored by the availability of
large knowledge bases extracted from resources such
as Wikipedia.
In this article, we present a large-scale informa-
tion extraction method based on a weakly supervised
learning of relation extraction patterns. Moreover,
this learning starts from relation examples reduced to
pairs of named entities. These pairs are then mapped
onto a reference corpus for building the set of con-
textualized relation examples from which the extrac-
tion patterns are learned. This process comes under
what we have called above the Distant supervision ap-
proach. We also present the results of the evaluation
of our method in the framework defined by the KBP
(Knowledge Based Population) track of the TAC 2010
(Text Analysis Conference) evaluation.
2 OVERVIEW
We focus in this work on a large-scale extraction of
relations with the hypothesis that a specific knowl-
edge base (KB) already exists. This KB is partially
filled with relations that are automatically acquired
from semi-structured data. We limit our study to the
relations between named entities because we want to
rely on entities that are usually well recognized but
we do not focus our work on a specific domain where
the entity recognition could be guided by a known ter-
minology. The idea of “large-scale” extraction actu-
ally covers several aspects. The first one corresponds
to the large number of relation types that are consid-
ered, which implies that a rule-based approach based
on handcrafted rules is hardly possible. A second as-
pect is the existence of a large number of existing re-
lations (i.e. the association of two entity values with
a relation type). These relations give a good start-
ing point for machine learning techniques to learn a
model for these types of relations. Finally, a third as-
pect is the large size of the collection of documents in
which the new relations are searched, which implies
the use of information retrieval techniques to retrieve
good candidates on which a more sophisticated ex-
traction is then performed (we cannot apply patterns
for instance on all the sentences of such corpus).
This approach, as presented in Figure 1, is com-
posed of two steps: a first step of pattern learning
from occurrences of known relations and a step of re-
lation extraction for the discovery of new relations.
The first step starts with known instances of rela-
tions R(E1,E2) to find occurrences of these relations
in texts for covering as many different ways of ex-
pressing them as possible; then we use these occur-
rences to learn a set of patterns associated with the
target type of relation. The second step starts with
incomplete relations R(E1,x), where the source entity
E1 is known and the target entity x has to be discov-
ered, and searches occurrences of relation R involv-
ing E1 in a collection of texts. The entity x is then
extracted using the patterns learned in the first step.
These two steps are described in more details in the
following sections.
2.1 Relation Pattern Learning
Our procedure for learning relation patterns relies on
the induction of lexical patterns from example sen-
tences containing occurrences of the target relations.
Its objective is to model the different ways a seman-
tic relation between two entities is linguistically ex-
pressed. For instance, the two sentence excerpts be-
low contain relation occurrences for the type of rela-
tion founded by with the entity pairs (Charles Revson,
Revlon Cosmetics) and (Mayer Lehman, Lehman
Brothers investment):
The glamourous cabaret chanteuse reportedly had
had a romantic liaison with <source>Charles
Revson</source>, the founder of <target>Revlon
Cosmetics</target> ... – Lehman was a great-
grandson of <source>Mayer Lehman</source>,
a founder of the <target>Lehman Brothers
investment</target> house ...
A lot of algorithms for building and generaliz-
ing lexical patterns were already proposed (Ravichan-
dran, 2005; Ruiz-Casado et al., 2007). Our approach
is similar to (Pantel et al., 2004) and follows more
directly the method of (Embarek and Ferret, 2008).
Starting with a pair of entities and two sentences con-
taining these entities and expressing the target rela-
tion, its principle is to find and to capture the ele-
A WEAKLY SUPERVISED APPROACH FOR LARGE-SCALE RELATION EXTRACTION
95

Knowledge base
rel(E1,E2)
Incomplete relations
rel(E1,?)
corpus
Retrieval of relation
occurrences
Pattern induction
Retrieval of candidate
sentences
Application of patterns
Relation extraction and
selection
Relation filtering
Learning of relation patterns Extraction of relations
Relation patterns
Expansion
corpus
Extracted relations
founded(Metawe,2005)
founded(HDNet,2001)
... network was HDNet, founded in 2001 by Dallas..
Metaweb, founded in 2005 is a spinoff company.
<E1>, founded in <E2>
country(Bernama,?)
Bernama
Malaysaian National news agency
… relations between Malaysia and Britain,
the state Bernama news agency …
News agency Bernama says Malaysian
prime minister will ...
… relations between Malaysia and Britain,
the state Bernama news agency …
Malaysia
Malaysia
Figure 1: Overview of the system.
ments that are shared by the two sentences in the sur-
rounding context of the two entities. More specifi-
cally, we identify these shared elements among three
levels of linguistic information about words: inflected
form, lemma and part-of-speech category. These lev-
els of information are produced by the OpenNLP
2
tools, also used for named entity recognition. Having
these three levels enables the building of more expres-
sive patterns that represent an interesting compromise
in terms of generalization between the specificity of
lexicalized elements and the more general nature of
part-of-speech categories.
The induction of a pattern from two occurrences
of relations relies more precisely on the three follow-
ing steps:
• computation of the minimal edit distance between
the two example sentences, that is to say, the min-
imal number of edit operation (insertion, deletion
and substitution) that are necessary to turn one
sentence into the other one. All the operations are
given here the same weight;
• optimal alignment between the two example sen-
tences from the matrix of distances between sub-
sequences resulting from the computation of the
edit distance. The classical algorithm for achiev-
ing such alignment is enhanced for enabling a
match of two words at one of the three available
levels of information when two words are tested
for a substitution;
• building of patterns by completing alignments
with two wildcard operators when it is necessary:
(*s*) stands for 0 or 1 instance of any word while
(*g*) represents exactly 1 instance of any word.
2
http://opennlp.sourceforge.net/index.html
Table 1 shows the result of the induction of a pat-
tern for the type of relation founded by from the two
sentence excerpts above.
Table 1: Example of pattern induction.
Charles Revson , the founder of
Revlon Cos-
metics
Mayer Lehman , a founder of the
Lehman
Brothers
investment
<source> , DET founder of (*s*)
<target>
This example illustrates our different levels of
generalization: for a word such as of, only the in-
flected form is taken. In the case of a word such
as founder, the inflected form is taken here but the
lemma level would be selected for an excerpt such
as X, the founders of ... At a higher level of gen-
eralization, the part-of-speech category DET (deter-
miner) covers a and the, which makes the resulting
pattern relevant for an excerpt such as ”Charles Ket-
tering, another founder of DELCO ...”. This exam-
ple also illustrates the use of wildcards as a substi-
tute for any word, that is to say the highest level of
generalization. As it is always possible to generalize
two sentences by a pattern only made of wildcards,
fixing an upper limit to the number of wildcards that
can used in the generalization process is necessary for
having patterns that are specific enough to the target
type of relation. Moreover, as our work is open do-
main and based on general named entities, we prefer
to induce a large number of specific patterns rather
than a small set of very general patterns to favor on
precision. This argument also accounts for our choice
of not generalizing patterns themselves by applying
to them the generalization process described above.
Thus, the maximal number of wildcards in a pattern
KDIR 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
96

is set to 1 in the evaluation of section 3.
In the context of distant supervision in which our
work takes place, example sentences are not directly
available but result from the mapping onto a corpus
of relations given as pairs of entities (for instance, the
pair (Ray Charles, Albany) for the type of relation
city of birth). More concretely in our case, they are
obtained by querying a search engine with pairs of
entities corresponding to relations of the target type
and by restricting its results to sentences that actually
contain a pair of entities. The nature of these restric-
tions has of course a direct impact on the quantity and
the precision of final patterns: the more severe they
are, the less example sentences we get but the better
the induced patterns are. (Agirre et al., 2009) adds for
instance the constraint that the two entities of a rela-
tion pair must not be separated in a sentence by more
than ten words.
Another important issue concerning the induction
of patterns is its computational cost. This process is
performed by considering each pair of example sen-
tences, which can have a too high computational cost
when the number of example sentences is significant:
for 10,000 examples, around 50 millions of distinct
pairs of sentences have to be compared (n(n − 1)/2
exactly). The most straightforward way to solve this
problem is to reduce drastically the number of exam-
ple sentences before the induction of patterns. How-
ever, such solution implies having a smaller coverage
of the different linguistic expressions of a type of re-
lation if this reduction is performed blindly. Our so-
lution to this problem exploits the fact that two sen-
tences sharing a small number of words will not lead
to an interesting pattern. The distance we use for in-
ducing patterns – the edit distance – was chosen be-
cause of its ability to take into account the order of
words but of course, it first depends on the number of
words the two compared sentences share. As a con-
sequence, the a priori filtering of example sentence
pairs can be based on the computation of a similarity
measure between sentences that only exploits a bag
of words representation of them, as the cosine mea-
sure, and the application of a minimal threshold to
these similarity values for discarding pairs that are
not likely to lead to an interesting pattern. The co-
sine measure can be computed efficiently, either ap-
proximately, by using methods such as Local Sensi-
tive Hashing (Gionis et al., 1999), or without any ap-
proximation but the necessity to fix an a priori min-
imal similarity threshold, which corresponds to our
case. We chose more precisely the All Pairs Similarity
Search (APSS) algorithm proposed in (Bayardo et al.,
2007) which computes the cosine measure only for
the pairs of objects – example sentences in our case –
whose similarity is higher or equal to a fixed thresh-
old. This algorithm relies on the incremental index-
ing of the objects whose similarity has to be evaluated
and implements a set of optimizations of this indexing
process based on both data gathered a priori about the
features of these objects and their sorting according to
these features.
More precisely, we have two levels of filtering
based on APSS. Learning patterns from a large num-
ber of example sentences often leads to several oc-
currences of the same pattern, either because an ex-
ample sentence is found in several documents or be-
cause there are several occurrences of the same lin-
guistic expression of a type of relation with differ-
ent entity values (Obama’s height is 1.87m; Sarkozy’s
height is 1.65m). As a consequence, we first apply
a high similarity threshold for identifying and dis-
carding identical sentences; second, a lower thresh-
old aims at checking that sentences are similar enough
for inducing a meaningful pattern. In order to reduce
further the number of comparisons between example
sentences, the similarity values resulting from APSS
are exploited for clustering these sentences by rely-
ing on the Markov Clustering algorithm (van Don-
gen, 2000). Finally, patterns are induced only from
sentences that are part of the same cluster.
2.2 Relation Extraction
The extraction of new relations is done from the ex-
isting types of relations and given entities: we are
searching to add knowledge to an existing knowledge
base by adding missing attributes to entities already
in the KB. The first step of relation extraction is the
selection of candidate sentences that are likely to con-
tain the expression of a relation. It starts from a query
containing one entity associated with its type and the
type of the target entity. The retrieval of the candi-
date sentences is performed, as in the pattern learn-
ing step, using a search engine in which the target
corpus has been indexed. In our experiments, we
used Lucene
3
, with an indexing process taking into
account the specific needs of our task: documents
were segmented into excerpts of three sentences us-
ing a sliding window and the resulting segments were
indexed by their plain words and their named enti-
ties with their type. Moreover, we also performed a
kind of query expansion focusing on the source en-
tity. Indeed, the source entity sometimes appears in
the target base of documents under a slightly differ-
ent form than in the query: for instance, Bill Clin-
ton is often used instead of William Jefferson Blythe
3
http://lucene.apache.org
A WEAKLY SUPERVISED APPROACH FOR LARGE-SCALE RELATION EXTRACTION
97

III Clinton, which is the normalized form of the en-
tity in the KB. The expansion is based on an expan-
sion database automatically built from Wikipedia
4
:
each entity is expanded by all the formulations ex-
tracted from the redirection pages of Wikipedia for
this entity. This expansion database contains alterna-
tive forms for 2.4 million entities and, starting from
an entity such as Barack Obama, makes it possible to
retrieve documents referring to {B. Hussein Obama,
Barack H. Obama Junior, Barack Obama Jr, Barack
Hussein Obama Jr., etc.}.
As we only deal with intra-sentential relations, the
retrieval of document excerpts is followed by the ver-
ification that the source entity co-occurs with a pos-
sible target entity in a sentence. The detection of the
target entity is based on the presence of compatible
named entities but also on reference lists of values for
types, as in the relation per:title, that do not corre-
spond to named entities. We then apply the patterns
learned in the first step to all candidate sentences. The
target entities extracted by these patterns are gathered
and sorted. We only keep the most frequent entities:
our hypothesis is that the more relevant the target en-
tities are the more often they appear in documents
together with the source entity. For relations with a
unique target entity (e.g. date of birth), we choose
the most frequent entity. For relations with several
possible target values (e.g. places of residence), an
arbitrary number of three values is taken since we
do not have knowledge (either prior knowledge or
learned from documents) about the correct number of
values. Finally, a filter is applied to the target enti-
ties to check the compatibility of their value with con-
straints relative to the type of information we search.
These constraints are defined by lists of values or reg-
ular expression. For instance, we check that the coun-
try of birth of a person is part of a list of known coun-
tries as the named entity type for the target entity –
location – is not specific enough to guarantee the va-
lidity of the found information.
3 EVALUATION
We present in this section our system’ results on the
data of the Slot Filling task of the TAC-KBP 2010
(TAC-KBP, 2010) evaluation. Our experiments have
been carried out for English. The Slot Filling task
matches the scope of our work as defined in section 2:
the task aims at extracting from a large corpus the tar-
get entity of a relation, given that its source entity is
4
More precisely, we used the Wikipedia dump pro-
vided by the university of New York http://nlp.cs.nyu.edu/
wikipedia-data.
part of a knowledge base that contains a large collec-
tion of examples of the target relation type. In this
context, 42 relation types are considered, 16 relations
for entity type ORGANIZATION (ORG) and 26 rela-
tions for entity type PERSON (PER). The list of these
relation types is presented in Table 2. Note that all the
experiments were conducted in parallel for all relation
types on a 24 nodes (4 processors/node) cluster.
3.1 Evaluation Framework
The evaluation material from the TAC-KBP track is
made of the following data:
• a 1.8 million documents text corpus (1,780,980
exactly) divided into 0.04% of transcripts (broad-
cast conversations, broadcast news, conversa-
tional telephone speech), 72.24% of newswire
data and 27.72% Web pages;
• a knowledge base (KB) built from an October
2008 Wikipedia snapshot: each page containing
an infobox was assigned a unique identifier to-
gether with an entity type among types person, or-
ganization, geopolitical entity and unknown, de-
pending on the fields in the infobox. Typically,
pages from infobox Infobox Actor were associ-
ated with type person. Finally, 818,741 entries
were selected to populate the KB, each entry be-
ing associated with a set of properties (the fields
from the infobox) and a description text. As a
consequence, relations in the KB are represented
as tuples (identifier, infobox type, name, prop-
erty, value), e.g., (E0000437; Infobox Actor; Ju-
lia Roberts; PER; birthplace; Atlanta);
• a mapping of Wikipedia properties to the
relation types of the evaluation. For in-
stance, Infobox Actor:birthplace is mapped to
per:city of birth. This mapping is a way of tak-
ing into account the heterogeneous nature of the
labels of Wikipedia properties;
• a list of 100 source entities for which target en-
tities have to be extracted for all the target rela-
tion types. Among those entities, 15 are already
present in the KB while 85 are new. Moreover, we
only focus in this study on the relations of a source
entity for which a target entity was actually found
in the corpus
5
, that is to say, a total of 2,069 rela-
tions. Their distribution according to their type is
presented in column Nb Ref. of Table 2.
5
The list of target entities that are present in the corpus
was built by the KBP organizers from the results of all par-
ticipants.
KDIR 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
98
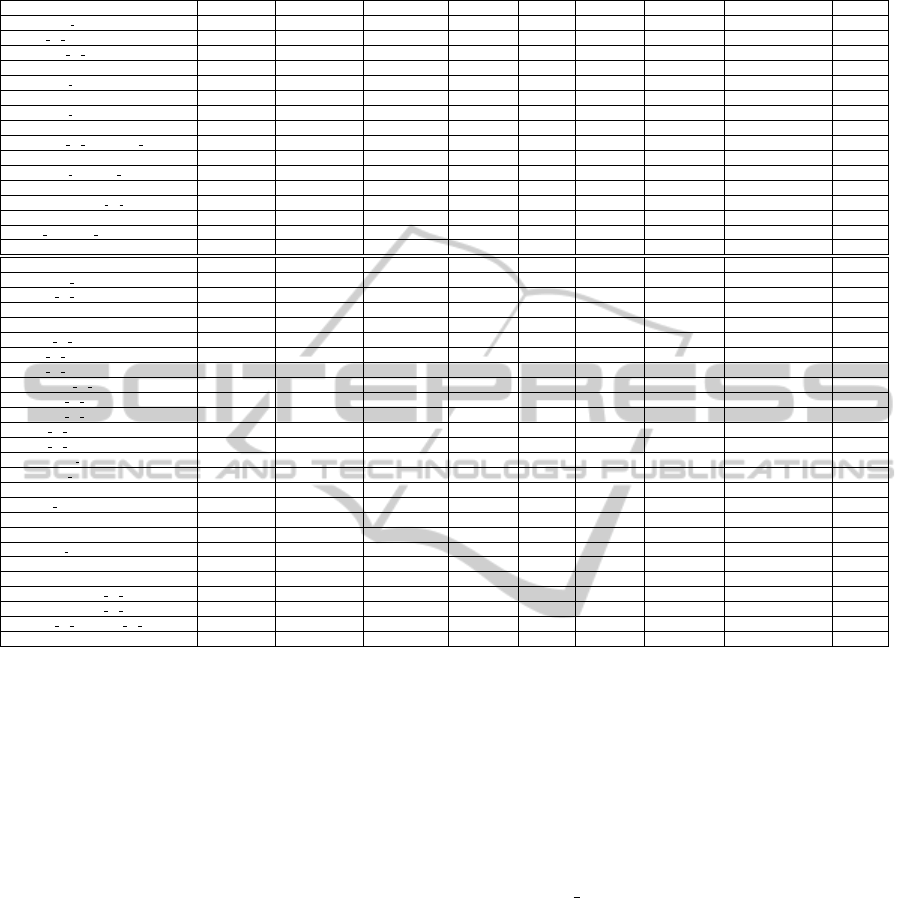
Table 2: Results for the different steps, by relation type.
Relation type Target type Doc. Rec (%) Rel. Rec (%) Nb Learn. Nb Test Nb Induc. Nb Patterns Pattern Cov. (%) Nb Ref.
org:alternate names ORG 89.17 33.33 20,013 10,006 214 6,007 66.10 120
org:city of headquarters LOC + list 90.12 59.26 6,847 3,423 4,553 2,010,749 65.52 81
org:country of headquarters LOC + list 91.04 55.22 18,401 9,200 2,110 185,158 69.56 67
org:dissolved DATE 100 25 532 266 87 775 0 4
org:founded by ORG/PER 95.45 31.82 1,954 977 197 4,385 77.87 28
org:founded DATE 92.86 53.57 13,688 6,844 127 22,482 77.34 22
org:member of ORG 100 100 7,951 3,976 102 103 70 2
org:members ORG 77.78 11.11 531 265 183 552 86 9
org:number of employees members regexp + list 90.48 23.81 7,173 3,586 216 3,109 100 21
org:parents ORG 96.67 43.33 22,361 11,181 3,013 485,947 69.04 30
org:political religious affiliation ORG 78.57 64.29 3,427 1,713 406 3,250 55.36 14
org:shareholders ORG/PER 66.67 33.33 3 2 0 0 0 3
org:stateorprovince of headquarters LOC + list 92.65 63.24 9,672 4,836 1,422 148,610 69.93 68
org:subsidiaries ORG 82.69 28.85 5,588 2,794 498 3,764 56.48 52
org:top members employees PER 91.48 37.22 40,929 20,464 108 1,010 70.57 223
org:website regexp 78.26 30.43 30,813 15,407 32 28 0 23
per:age regexp + list 85.32 32.11 157 79 3 1 0 109
per:alternate names PER 61.63 11.63 18,115 9,057 68 2,818 82.58 86
per:cause of death list 100 0 1 1 0 0 0 2
per:charges list 61.54 0 184 92 0 0 0 13
per:children PER 72 16 2,010 1,005 147 238 0 25
per:cities of residence LOC + list 77.59 34.48 3,631 1,815 722 14,297 77.88 58
per:city of birth LOC + list 69.23 15.38 4,745 2,373 2,252 62,455 63.34 13
per:city of death LOC + list 100 100 1,631 816 505 2,860 70.27 1
per:countries of residence LOC + list 73.53 20.59 8,098 4,049 2,181 205,344 80.08 34
per:country of birth LOC + list 82.35 5.88 11,085 5,542 11,192 9,145,385 65.02 17
per:country of death LOC + list 2,873 1,436 1,068 22,374 62.89 0
per:date of birth DATE 90 20 11,689 5,845 30 22 0 20
per:date of death DATE 100 0 4,692 2,346 54 63 33.33 1
per:employee of ORG 84.21 29.32 24,762 12,381 2,435 704,833 71.13 133
per:member of ORG 82.42 36.26 27,523 13,761 3,901 740,999 57.25 91
per:origin list 81.58 42.11 37,626 18,813 2,710 276,653 74.41 76
per:other family PER 86.67 33.33 4 2 0 0 0 30
per:parents PER 78.13 9.38 1,314 657 37 604 77.78 64
per:religion list 85.71 57.14 1,468 734 515 1,575 80 7
per:schools attended ORG + list 87.50 37.50 2,246 1,123 67 170 4.17 16
per:siblings PER 78.26 20.29 4 2 0 0 0 69
per:spouse PER 80 35.56 5,385 2,693 3,094 314,329 80 45
per:stateorprovince of birth LOC + list 80 50 7,047 3,523 2,097 60,782 75.42 10
per:stateorprovince of death LOC + list 100 100 1,616 808 278 911 66.67 1
per:states or provinces of residence LOC + list 84.21 50 4,980 2,490 1,166 115,418 77.90 38
per:title list 84.55 52.77 31,574 15,787 8,797 1,573,512 49.07 343
Target type: method for the final identification of the target entity. Doc. Rec.: recall of sentence retrieval in terms of reference documents. Rel. Rec.: recall of
candidate sentences in terms of reference documents. Nb Learn.: number of relations used for pattern learning. Nb Test: number of relations used for evaluating
patterns. Nb Induc.: number of sentences containing relation occurrences used for pattern induction. Nb Patterns: number of patterns induced from occurrences
of relations. Patterns Cov.: coverage of induced patterns. Nb Ref.: number of reference relations.
3.2 Evaluation of Pattern Learning
Patterns are used to confirm/deny the existence of a
relation among two entities. As a consequence, it is
important to ensure that the induced patterns have a
high enough coverage to take into account as many
variants as possible among the occurrences of rela-
tions. To assess the quality of these patterns, we di-
vided the relations from the KB into a training set (2/3
of the relations) and a test set (1/3 of the relations) and
we measured the coverage of the patterns by comput-
ing the percentage of relation occurrences of the test
set that were found by applying the patterns learned
from the relation occurrences of the training set. We
used for this evaluation the previously described TAC-
KBP 2010 corpus. It should be noted that using this
corpus to evaluate the extraction of relations does not
invalidate its use for patterns learning since the rela-
tions are different for both tasks.
We provide in Table 2 the number of relations in
the training and test sets in columns Nb Learn. and Nb
Test respectively. The number of sentences that con-
tain occurrences of relations used for pattern general-
ization is shown in the column Nb Induc. The number
of patterns generated from these candidate sentences
is shown in the column Nb Patterns of the same table.
For instance, if we consider the relation type
org:alternate names, only 214 candidate sentences
demonstrating an evidence of the relation are selected
from the 20,013 relations of the training set. These
214 sentences are then used to generate 6,007 pat-
terns with a coverage of 66.10% (i.e. we find 66.10%
of the sentences containing occurrences of the 10,006
test relations). The large gap between the 20,013 rela-
tions and the 214 sentences is due to two main factors:
• a constraint applied during the selection of the
candidate sentences: we only keep the sentences
in which the named entities are fully recognized,
whereas named entities can be partially (or im-
properly) recognized by linguistic processing;
• the nature of documents in the corpus: 72% of
A WEAKLY SUPERVISED APPROACH FOR LARGE-SCALE RELATION EXTRACTION
99

documents are news articles published between
January 2008 and August 2009, which explains
the lack of documents, if any, regarding some per-
sons or organizations existing in the KB.
Detailed results regarding the pattern coverage for
each relation type are presented in column Patterns
Cov. of Table 2. As far as efficiency is concerned, the
computation time for pattern generalization concern-
ing for instance the relation type per:country of birth
(11,192 sample sentences to compare) drops from
690mn and 5s without filtering to 30s with filtering
6
,
which illustrates the benefit of this operation in terms
of computation time.
3.3 Evaluation of Relation Extraction
The relation extraction process is composed of sev-
eral steps, each of them influencing the overall result.
Consequently, we performed separate evaluations for
the retrieval of the candidate sentences and the core
relation extraction process.
3.3.1 Retrieval of Candidate Sentences
A prerequisite for extracting relevant relations is en-
suring that the search engine returns enough relevant
documents so that we can identify the target entities.
We measured the coverage based on the document
search result, i.e. the percentage of documents re-
trieved by the index that are in the reference. We tried
several strategies by testing different values for pa-
rameters such as the number of retrieved documents
or whether to use query expansion or not. From this
evaluation, the best configuration is to query the index
using the source entities and their expansions together
with considering the top 1,000 returned documents:
this configuration allows retrieving 84.24% of refer-
ence documents. Detailed results by relation type are
provided in the column Doc. Rec. of Table 2.
The candidate sentences for a given relation type
are selected based on previously retrieved documents
by ensuring that each sentence contains both the
source entity and the entity type of the target en-
tity. The quality and the number of candidate sen-
tences are largely affected by the named entity recog-
nition process. Since we do not have a reference for
named entities in the corpus, we cannot evaluate the
loss caused by entity recognition errors. However, we
evaluated the proportion of reference documents in
which we found candidate sentences. This informa-
tion allows to set an upper bound for the percentage
of relations that could be extracted if the following
6
The version with filtering being parallelized, the time
given is a sum of the time recorded for each processor.
steps performed ideally. We obtained a total cover-
age of 37.55% of sentences belonging to documents
of the reference. The breakdown by relation type is
presented in the column Rel. Rec. of Table 2.
3.3.2 Relation Extraction
To evaluate the extracted relations, we used the met-
rics and the tools provided for the TAC-KBP cam-
paign
7
. The judgment about the correctness of a re-
lation is only based on the entity string with no re-
striction to the documents of the reference
8
. Table 3
summarizes our results regarding this evaluation –
grouped for all relation types – and demonstrates the
impact of the filtering of target entities in terms of re-
call (R), precision (P) and f1-measure (F1). Note that
the filtering process ensures that target entities match
some regular expressions and/or belong to a list of
closed values. Column Target type in Table 2 presents
the type of filtering applied for each relation type.
On one hand, results in Table 3 show that the filter-
ing of target entities improves the performance of the
system (average +2.74% f1-measure). On the other
hand, they validate the assumption that patterns in-
duced using the APSS are as relevant as those induced
by considering every pair of relation examples (in this
case, there is an improvement of +1.72% f1-measure
on average).
Table 3: Impact of target entities filtering.
Before filtering After filtering
R. (%) P. (%) F1. (%) R. (%) P. (%) F1. (%)
All relation
pairs
16.28 11.20 13.26 18.07 13.66 15.56
APSS
16.90 12.76 14.54 18.67 16.87 17.72
Table 4 presents results from various systems on
two similar corpus, KBP 2009 and KBP 2010 corpus,
the latter adding to the first one Web documents and
transcripts, a priori more difficult to process. These
figures cover only the relations that are actually in the
corpus. Hence, they integrate a constraint that the Slot
Filling participants had to deal with and that is not
taken into account in our system since it was devel-
oped outside the campaign, namely to decide whether
the relation exists in the corpus. In this table, columns
2009 and 2010 denote the scores of the top three and
last three systems for KBP 2009 and KBP 2010. (Ji
et al., 2010) have shown that out of 492 reference re-
lations, 60.4% were within the same sentence while
the remaining 39.6% were cross-sentence: such re-
lations are handled by using coreference resolution
7
http://nlp.cs.qc.cuny.edu/kbp/2010/scoring.html
8
In fact, the reference is not complete as it was built
using only TAC-KBP participants’ outputs.
KDIR 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
100

or by applying inference mechanisms. Therefore, we
have distinguished in the column 2010 (a) of Table 4
the scores of systems that are more directly compa-
rable to ours because they only deal with relation ex-
traction within the same sentence.
The top system of KBP 2010 (Chada et al., 2010)
clearly outperforms others: +36.63% compared to the
second and +4.68% compared to a human annotator.
This performance is based both on the use of a manu-
ally annotated corpus – 3 million documents (not in
the KBP corpus) – and the use of mechanisms for
cross-sentence relation extraction: pronominal coref-
erence resolution, metonymy between entities, reso-
lution of semantic dependencies between words and
entities, etc. Using an additional corpus seems to be a
crucial factor compared to the other top systems while
these ones differentiate themselves from the median
results by taking into account cross-sentence rela-
tions. The worst results, especially for 2010, mainly
come from systems under development.
Regarding our system, Table 4 situates our re-
sults in the average of those obtained by KBP 2010
participants and in the top three systems based on
within sentence relation extraction approaches. In the
latter case, the most efficient approach (29.15% f1-
measure) (Byrne and Dunnion, 2010) uses a set of
manually constructed rules that achieves a precision
score (66.55%) equivalent to the best score of the
campaign (66.80%) and a recall score (18.67%) lying
in the average score (15.33%). This strong imbalance
between precision and recall is rather symptomatic of
manual approaches.
Table 4: Results on TAC-KBP data (f1-measure).
TAC KBP systems
2009 2010 2010 (a)
Nb. submissions (N)
/ participants
N=16 / 8 N=31 / 15 N=18
Human annotator
58.99% 61.10% 61.10%
1
st
score
34.35% 65.78% 29.15%
2
nd
score
25.05% 29.15% 14.22%
3
th
score
18% 28.29% 14.13%
(N-2)
th
score
5.90% 0.55% 0.55%
(N-1)
th
score
2.60% 0.19% 0.19%
N
th
score
1.75% 0.08% 0.08%
Our system
– 17.72% 17.72%
Mean
13.43% 17.49% 9.71%
Median
13.93% 14.13% 12.27%
4 RELATED WORK
Large scale relation extraction, within the meaning
defined in section 2, is a recent issue. Nevertheless,
by means of evaluations such as TAC-KBP, it has been
the subject of several works suggesting different ap-
proaches.
Concerning specifically the extraction of relations,
three main trends appear: using statistical learning
(Agirre et al., 2009; Chen et al., 2010b), using lexi-
cal pattern generalization (Li et al., 2009; McNamee
et al., 2009) and finally, tuning already existing sys-
tems for relation detection (Bikel et al., 2009). Com-
pared to the 2009 edition, rule-based approaches,
such as (Byrne and Dunnion, 2010), were introduced
in KBP 2010 as well as approaches based on Distant
supervision and classifiers (Surdeanu et al., 2010).
Our approach relies on lexical pattern generalization
and assumes, as in (Mintz et al., 2009), that the mere
presence of a pair of entities in a sentence is infor-
mative enough to indicate the effective presence of
a relation between these entities. In fact, this is not
always the case and thus we believe it is important
to filter the examples used for patterns generalization
beforehand as suggested by (Riedel et al., 2010).
Like our system, most systems developed for KBP
2009 do not exploit the dependencies among relation
types: for instance, there is an implicit link between
the age and the birth date of a person. However, in
(Chen et al., 2010a), the authors show that the results
obtained in (Li et al., 2009) (31.96% f1-measure) can
be improved (they get 34.81% f1-measure) by inte-
grating dependencies between relations using infer-
ence rules based on a first order logic extension. In
our work, we try to avoid integrating knowledge that
is too dependent on the relation types in order to have
a more generic approach, easily adaptable to other do-
mains. Finally, (Chada et al., 2010) showed in KBP
2010 a very significant increase in terms of perfor-
mance by integrating mechanisms for extracting rela-
tions beyond the sentence space: given the percentage
of relations that occur between sentences, such mech-
anisms seem necessary and we plan to integrate them
in our future work.
From a different angle, (Li et al., 2009) distin-
guished itself in KBP 2009 by using a two-step rela-
tion extraction process: the first aimed at finding po-
tential target entities within the documents of the eval-
uation corpus by using patterns of relations; the sec-
ond aimed at finding additional potential target enti-
ties that had been missed by the first step, by applying
the relation patterns on a recent Wikipedia snapshot.
The potential target entities retrieved by the process
were retained only if they can be found in a docu-
ment from the corpus. Additional entity acquisition
significantly increases their scores (they gain +9% f1-
measure compared to (Bikel et al., 2009)) but this
process implies using an external corpus that can be
viewed as closely related to the KB. In addition, re-
A WEAKLY SUPERVISED APPROACH FOR LARGE-SCALE RELATION EXTRACTION
101

sults on KBP 2010 have shown that the overall perfor-
mance could be improved without such complemen-
tary resource and that the effect of such process on
final results were lower compared to KBP 2009 (we
even observe a negative impact).
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
PERSPECTIVES
In this article, we present an information extraction
system designed for the large-scale extraction of at-
tribute relations between named entities. The “large-
scale” qualification is meant for both the integration
of a large number of types of relations and the search
of these relations in a large corpus. This system is
based on a weakly supervised approach in which the
examples are limited to pairs of entities in relation.
The extraction of relations is performed by the ap-
plication of lexico-syntactic patterns that are learned
from occurrences of relations automatically selected
from the entity pairs of the examples and used to rep-
resent the relation types. We evaluate our approach
using the evaluation framework from the Slot Fill-
ing task of the KBP evaluation campaign, concentrat-
ing on the problem of relation extraction itself (we
did not consider the case where the relation is not
present in the target corpus). The results obtained in
this context are comparable to the results obtained by
the participants of 2010 campaign, which we consider
promising for our system, since it is designed to be
generic and is not tuned to deal with the specificities
of the types of relations used in this campaign. We
also show that specific techniques used to deal with
the large-scale aspect of the task, such as the filter-
ing of the examples with the APSS technique, do not
decrease the performance and can even contribute to
improve it.
We are currently working on the improvement of
our system, trying to keep the idea of a generic sys-
tem with respect to the type of relation considered. In
particular, we focus on the pattern learning step: we
are considering both the use of a more important num-
ber of examples to learn the pattens and the improve-
ment of the quality of the examples. These two points
are connected because, usually, in order to get more
examples, we need to relax a constraint on the selec-
tion of the examples, which will generally increase
the number of false examples. To avoid this draw-
back, we will explore the use of a relation filtering
module which is capable of determining if a sentence
contains a relation between two entities or not with-
out any consideration on the nature of the relation (as
in (Banko and Etzioni, 2008)).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partly supported by the FP7 Virtuoso
project.
REFERENCES
Agichtein, E. and Gravano, L. (2000). Snowball: Extracting
Relations from Large Plain-Text Collections. In 5
th
ACM International Conference on Digital Libraries,
pages 85–94, San Antonio, Texas, USA.
Agirre, E., Chang, A., Jurafsky, D., Manning, C.,
Spitkovsky, V., and Yeh, E. (2009). Stanford-UBC at
TAC-KBP. In Second Text Analysis Conference (TAC
2009), Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA.
Banko, M. and Etzioni, O. (2008). The Tradeoffs Between
Open and Traditional Relation Extraction. In ACL-08:
HLT, pages 28–36, Columbus, Ohio.
Bayardo, R., Ma, Y., and Srikant, R. (2007). Scaling Up All
Pairs Similarity Search. In 16
th
International Confer-
ence on World Wide Web (WWW’07), pages 131–140,
Banff, Alberta, Canada.
Bikel, D., Castelli, V., Radu, F., and jung Han, D. (2009).
Entity Linking and Slot Filling through Statistical Pro-
cessing and Inference Rules. In Second Text Analysis
Conference (TAC 2009), Gaithersburg, USA.
Bizer, C., Lehmann, J., Kobilarov, G., Auer, S., Becker, C.,
Cyganiak, R., and Hellmann, S. (2009). DBpedia - A
crystallization point for the Web of Data. Journal of
Web Semantics, 7:154–165.
Byrne, L. and Dunnion, J. (2010). UCD IIRG at TAC 2010
KBP Slot Filling Task. In Third Text Analysis Confer-
ence (TAC 2010), Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA.
Chada, D., Aranha, C., and Monte, C. (2010). An Anal-
ysis of The Cortex Method at TAC 2010 KBP Slot-
Filling. In Third Text Analysis Conference (TAC
2010), Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA.
Chen, Z., Tamang, S., Lee, A., Li, X., Passantino, M., and
Ji, H. (2010a). Top-down and Bottom-up: A Com-
bined Approach to Slot Filling. In 6
th
Asia Infor-
mation Retrieval Symposium on Information Retrieval
Technology, pages 300–309, Taipei, Taiwan.
Chen, Z., Tamang, S., Lee, A., Li, X., Snover, M., Pas-
santino, M., Lin, W.-P., and Ji, H. (2010b). CUNY-
BLENDER TAC-KBP2010 Slot Filling System De-
scription. In Text Analysis Conference (TAC 2010),
Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA.
Embarek, M. and Ferret, O. (2008). Learning patterns
for building resources about semantic relations in the
medical domain. In 6
th
Conference on Language Re-
sources and Evaluation (LREC’08), Marrakech, Mo-
rocco.
Gionis, A., Indyk, P., and Motwani, R. (1999). Simi-
larity Search in High Dimensions via Hashing. In
25
th
International Conference on Very Large Data
Bases (VLDB’99), pages 518–529, Edinburgh, Scot-
land, UK.
KDIR 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
102

Hearst, M. (1992). Automatic Acquisition of Hyponyms
from Large Text Corpora. In 14
th
International Con-
ference on Computational linguistics (COLING’92),
pages 539–545, Nantes, France.
Ji, H., Grishman, R., and Trang Dang, H. (2010).
Overview of the TAC 2010 Knowledge Base Popu-
lation Track. In Third Text Analysis Conference (TAC
2010), Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA.
Li, F., Zheng, Z., Bu, F., Tang, Y., Zhu, X., and Huang,
M. (2009). THU QUANTA at TAC 2009 KBP and
RTE Track. In Second Text Analysis Conference (TAC
2009), Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA.
McNamee, P., Dredze, M., Gerber, A., Garera, N., Finin,
T., Mayfield, J., Piatko, C., Rao, D., Yarowsky, D.,
and Dreyer, M. (2009). HLTCOE Approaches to
Knowledge Base Population at TAC 2009. In Second
Text Analysis Conference (TAC 2009), Gaithersburg,
Maryland, USA.
Mintz, M., Bills, S., Snow, R., and Jurafsky, D. (2009). Dis-
tant supervision for relation extraction without labeled
data. In ACL-IJCNLP’09, pages 1003–1011, Suntec,
Singapore.
Pantel, P., Ravichandran, D., and Hovy, E. (2004). To-
wards Terascale Knowledge Acquisition. In 20
th
In-
ternational Conference on Computational Linguistics
(COLING’04), pages 771–777, Geneva, Switzerland.
Ravichandran, D. (2005). Terascale Knowledge Acquisi-
tion. PhD thesis, University of Southern California,
Los Angeles, CA, USA.
Riedel, S., Yao, L., and McCallum, A. (2010). Modeling
Relations and Their Mentions without Labeled Text.
In Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in
Databases, LNCS, pages 148–163.
Ruiz-Casado, M., Alfonseca, E., and Castells, P. (2007).
Automatising the Learning of Lexical Patterns: an
Application to the Enrichment of WordNet by Extract-
ing Semantic Relationships from Wikipedia. Data
Knowledge Engineering, 61:484–499.
Shinyama, Y. and Sekine, S. (2006). Preemptive Informa-
tion Extraction using Unrestricted Relation Discovery.
In HLT-NAACL 2006, pages 304–311, New York City,
USA.
Surdeanu, M., McClosky, D., Tibshirani, J., Bauer, J.,
Chang, A., Spitkovsky, V., and Manning, C. (2010).
A Simple Distant Supervision Approach for the TAC-
KBP Slot Filling Task. In Text Analysis Conference
(TAC 2010), Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA.
TAC-KBP (2010). Preliminary Task Description for
Knowledge-Base Population at TAC 2010.
van Dongen, S. (2000). Graph Clustering by Flow Simula-
tion. PhD thesis, University of Utrecht.
Zhou, G., Su, J., Zhang, J., and Zhang, M. (2005). Ex-
ploring Various Knowledge in Relation Extraction. In
ACL 2005, pages 427–434, Ann Arbor, USA.
Zhou, G., Zhang, M., Ji, D., and Zhu, Q. (2007).
Tree Kernel-Based Relation Extraction with Context-
Sensitive Structured Parse Tree Information. In
EMNLP - CoNLL’07, pages 728–736, Prague, Czech
Republic.
A WEAKLY SUPERVISED APPROACH FOR LARGE-SCALE RELATION EXTRACTION
103
