
KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY FOR PERVASIVE AND
REAL-TIME INTELLIGENT DECISION SUPPORT
IN INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE
Filipe Portela
1
, Pedro Gago
2
, Manuel Filipe Santos
1
, Alvaro Silva
3
, Fernando Rua
3
,
José Machado
4
, António Abelha
4
and José Neves
4
1
Centro Algoritmi, Universidade do Minho, Guimarães, Portugal
2
Instituto Politécnico de Leiria, Leiria, Portugal
3
Unidade de Cuidados Intesnivos, Centro Hospitalar do Porto, Porto, Portugal
4
Departamento de Informática,Universidade do Minho, Azurem, Guimarães, Portugal
Keywords: Pervasive, Decision support process, Real-time, Clinical data, Data acquisition, Intensive care medicine.
Abstract: Pervasiveness, real-time and online processing are important requirements included in the researchers’
agenda for the development of future generation of Intelligent Decision Support Systems (IDSS). In
particular, knowledge discovery based IDSS operating in critical environments such of intensive care,
should be adapted to those new requests. This paper introduces the way how INTCare, an IDSS developed
in the intensive care unit of the Centro Hospitalar do Porto, will accommodate the new functionalities.
Solutions are proposed for the most important constraints, e.g., paper based data, missing values, values out-
of-range, data integration, data quality. The benefits and limitations of the approach are discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the future, the decision-making process and the
form how the people make decisions should take
into account new requirements like pervasiveness,
real-time and online processing. This paper explores
how these requirements can be integrated in the
critical health care arena in order to improve the
decision process. The work is part of a major
project: INTCare - an IDSS for intensive care units.
The Intensive Care Units (ICU) are considered
critical units where each decision needs to be correct
and performed very carefully. The existence of a
high number of data sources difficult, the data
dissemination and the decision making process by
the doctor. In the ICUs exist many electronic
platforms with patient information, systems which
collect vital signs and other systems that contains lab
results, medical proceedings, etc., however still exist
much information that were manually registered in
the paper format. This is a common problem on the
ICUs and is essentially associated to the nursing
records (Lyerla et al., 2010). The creation of
intelligent agents (De Turck et al., 2007);
(Wooldridge, 1999) allow, perform some automatic
tasks, continuously and in real-time. However the
process automation has some restrictions, due to
problems that arise during tasks execution like
incorrect values, null values, missing identification
and others. In order to resolve these problems we
develop a platform for monitoring the patient data
electronically with a total control of values by the
humans. The main goal of this paper is to present
architecture to ensure that all the clinical data that
normally is used in the decision-making process is
accessible electronically, enabling a pervasive and
real-time approach. Beyond this chapter, a
background will be presented on the ICU, the data
acquisition process and the major problems detected.
Chapter IV presents the platform developed in order
obtain the decision variables in real-time and make
them available in electronic and in online mode.
Chapter V is dedicated to the data quality, and
presents some forms of data processing to increase
the data quality. Chapter VI makes a brief
presentation of the intelligent agents that were used
in the KD process. Finally, the results related to the
data quality will be presented and discussed.
Conclusions and future work cease the paper.
241
Portela F., Gago P., Santos M., Silva A., Rua F., Machado J., Abelha A. and Neves J..
KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY FOR PERVASIVE AND REAL-TIME INTELLIGENT DECISION SUPPORT IN INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE.
DOI: 10.5220/0003677002410249
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2011), pages 241-249
ISBN: 978-989-8425-81-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Intensive Medicine Environment
Intensive Medicine (IM) is a critical area where
anything can fail, because the itensivists are dealing
with human lives in particularly and weakened
conditions. ICU uses IM to treat their patients and is
a critical environment because have some complex
health care situations (Bricon-Souf and Newman,
2007), the activities occurring in it are sometimes
adverse, dangerous and tiring the various organ
systems of the patient may be affected at the same
time (Apostolakos and Papadakos, 2001) and this is
a challenging for the that operate in this
environment.
2.2 INTCare
INTCare is an IDSS that was developed to Intensive
Medicine, with the main goal predicts the organ
failure and outcome (Gago et al., 2006); (Manuel
Filipe Santos et al., 2011) in real time (Portela et al.,
2010). The system is being concluded and is been
tested in the ICU of the Hospital Santo António
(HSA) in Porto. The INTCare system is divided into
four subsystems: data acquisition, knowledge
management, inference and interface (Portela et al.,
2010) and uses intelligent agents to, for example,
automate the collection, processing and
transformation of data, and update the predictive
models in real-time, without the human intervention.
2.2.1 System Features
The number of INTCare features has been increasing
according new problems or situation that we find
and with the objective to create a most complete
system possible. In order to complete the KDD
process, the system attends some requirements
(Manuel Filipe Santos and Portela, 2011): Online
Learning; Real-Time; Adaptability; Data mining
models; Decision models; Optimization; Intelligent
agents; Pervasive; Accuracy; Safety; Privacy; Secure
Access from Exterior; User Policy.
2.2.2 System Requirements
In order to accomplish the features defined before,
the system has to have some important requirements
(Portela et al., 2010). These requirements were now
incorporated and are part of KDD process: 1) Fault
tolerance capacities; 2) Remove null and noisy data;
3) Ensure the patient identification; 4) Continuous
data acquisition; 5) Time restrictions for the data
acquisition and storage; 6) Digital data archive in
order to promote the dematerialization of paper
based processes; This paper will explain the
decisions and alterations performed.
2.3 Intelligent Agents
The intelligent agents used by INTCare and are
capable to performs autonomous actions, without the
human interaction, in order to meet its goals (Gago
et al., 2006). To implement this system, use of multi-
agent systems is fundamental, with this is possible
have various agents cooperates in order to manage a
variety of problems (Foster et al., 2005); (Machado,
2006). INTCare uses intelligent agents to perform
some actions that make the system work through
autonomous actions that perform some essential
tasks. These tasks support some system modules:
Data Acquisition, Management of Knowledge,
Inference and Interface. The flexibility and
effectiveness of such systems depend on the agents
and the interactions between them.
2.4 Pervasive Health Care
Pervasive HealthCare (PHC) appears with the
objective to resolve some problems in the Health
Care like the data quality and the data access.
Varshney (U. Varshney, 2007, 2009) defines PHC as
Health for all, anytime and anywhere by removing
restrictions such as location and time, increasing the
coverage and quality of health care. However the
problem is how we can do it? Is it viable in a critical
environment, like is Intensive Care? These questions
arises, for though the PHC have the potential to
reduce costs, improve service quality and facilitate
the treatment of the patients also faces many
technical hurdles and administrative (Upkar
Varshney, 2003) as resistance to change and
significant changes in systems and technologies.
The problem with this type of scenario is that the
information is not always available when it is
required that sometimes prevents the physician to
make the best decision for the patient, this happens
because there also a lot of information in paper.
Solution arises as the possibility of providing all
necessary information electronically and the
creations of decision models that help the doctor
make the best decision in real time.
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
242
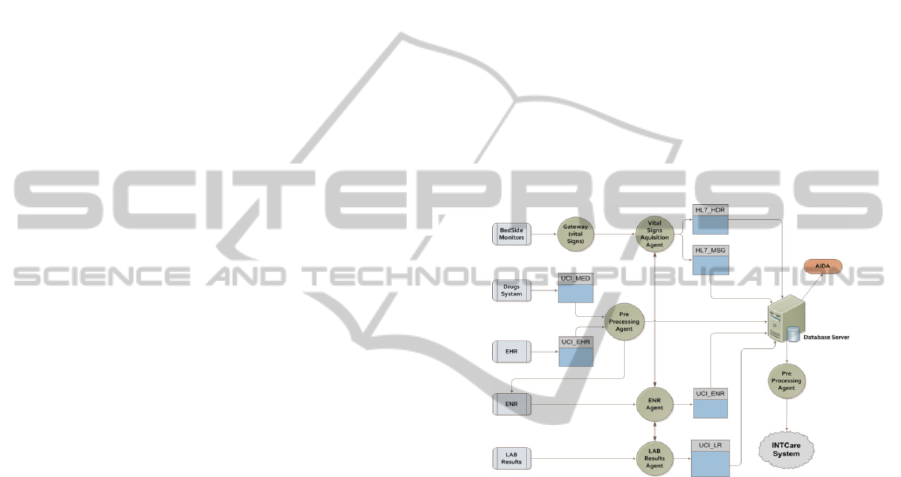
3 ICU – DATA ACQUISITION
Data acquisition is a central issue for a pervasive
intelligent decision support in order to enable a way
of work in real-time. A considerable number of
different data sources exist that should be integrated
in the ICU data acquisition process.
3.1 Data Sources
This processed has essentiality in five data sources:
Vital Signs: Contains all vital signs collected by the
sensors connected to the patient. This data are
collect by the bedside monitors, e.g. Blood Pressure,
SPO2, Respiratory and Frequency Rate, etc.
Electronic Health Record (EHR): Has all
information about the patient at admission e.g.
patient identification (PID), age, name, sex,
admission from, admission type, comorbidities, etc.
Drugs System: This system is responsible to control
the patient therapeutic plan. For each patient, it
contains a detailed plan with, the drugs prescription,
dosages, administration dates, etc.
Lab Results: Every day patients make lab analysis
the results will be collected and processed by a
laboratory. It contains all the values for each patient:
oximetry, clinical chemistry, and hematology.
Electronic Nursing Record (ENR): Allow to have
all information about the patient admitted in the ICU
in electronic format e.g. fluid balance, medical
scores, therapeutics plans, events, etc.
3.2 Data Acquisition Process
The Data acquisition process has been modified in
last two years. In the start (2009) more than 80% of
data were register in paper or were not accessible
electronically, of these, only 30% were stored offline
(manually) in database.
Now in 2011 we can have all data in electronic
format, and these, can be registered, validated or
consulted in real-time and automatic or manual
form. After we collect the data, the processing and
transformation process begin; largely of this tasks
will perform automatic by the intelligent agents.
Like we can see in Figure 1 are four, the data
sources that contain information to the knowledge
process, this data will be acquired and processed
according each agent task. Finally this process is
responsible for the processing and transformation
data to the INTCare system according the variables
required to the data mining. The main objective of
autonomous acquisition process is processing the
patient data in the moment that were collected and
validate it according the values defined in ICU.
This operation will increase the data quality
stored in the database, allow the calculation of
critical events and prepares the data to create the
best decision models.
3.3 Data Acquisition Problems
The number of problems associated to automatic
data acquisition process is high, complex and can
compromise all decision making process. These
problems can have different natures, like, humans,
techniques, informatics, environments, etc.
The most common problems are: sensors
disconnected, data collected without PID, missing
values and values with noise and system failures. In
order to mitigate this problems, were defined the
requirements that need to be addicted to the system.
Figure 1: ICU Data Acquisition architecture.
4 NURSING RECORDS - ENR
After made a questionnaire we concluded that
normally the decision is based in the vital-signs
results, the registers presented in the Paper Nursing
Record (PNR). Normally, proceedings, therapeutics,
and events are also used in the decision models;
however some of these data was not available in
real-time. Moreover different platforms and formats
should be considered. The decision process is not
made instantly, this limitation stems from problems
like the data access time, different platforms with the
necessary data and the format how the data are
stored, i.e., the data aren't clear (pdf format, difficult
to analyse the entire hospital stay, dubious values).
Paper based registers, and the acquisition of
wrong values is the main problems of the ICU and is
the biggest obstacle for the creation of prevision and
decision models. Based on the information collected
and on a selection of the most important variables
KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY FOR PERVASIVE AND REAL-TIME INTELLIGENT DECISION SUPPORT IN
INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE
243

for the decision making process, a platform was
created to allow the automatic data monitoring. PNR
has been substituted by the ENR. ENR is a touch-
screen system interoperating with all the information
systems used in the ICU. Contains patients’ data and
allows for a higher number of functionalities to
record, store and validate the values collected in the
environment, in an online and real-time way.
4.1 Systems Interoperability
ENR encompasses a lot of data provided from other
systems: EHR, Medical Systems, BM and Lab
Results. This facilitates the nurses and doctor work,
because now they know where is the information
that they need to care the patient. With this option
there are no longer islands of information, passing
all the clinical and patient data to be accessible in
the same space.
4.2 Main Features
Besides the integration some other features are
available with the introduction of ENR in the ICU.
In order to enable the KDD process, the ENR
contains a set of features to streamline the process:
Collect information about patient process;
Get correct vital signs values, therapeutic and
drugs plans, Lab Results and medical request;
Allow manual fluid balance registers, manual
medical and nursing recording and validation of
values and record of adverse events;
Automatic calculation of medical scores;
Store all validated data in database.
4.2.1 Patient Clinical Data Logbook
An important benefit in the use of this platform is
the mode the clinical data are collected and
presented for each day. The ENR is based on a grid
divided in 24 hours, presenting for each hour the
values of the selected variables, e.g., vital signs,
drugs and schedules events. All monitoring data that
are scheduled to some variables appear in the ENR
automatically. The data will be collected and
inserted by the agents. this data can be also stored
manually by the nurses, near the patient, in the
moment that the things happen. The nurse chooses
the event that happened, from a set of predefined
events, in that moment and this automatically appear
in another table with the description and the time of
the event. For the decision process, the medical staff
can consult the patient historical registers, only
choosing the date before. The base of the grid is the
same, changing only the values and variables
collected in the chosen day.
Figure 2: Knowledge Discovery Process in ICU.
4.2.2 Lab Results (LR)
The Lab Results are not under the nurse’s control in
the ICU, because they are ordered by the doctors and
executed by the labs. The clinical results appear in
the ENR according to the laboratory work. This
platform has a singular form to present the lab
results in a grid. With this solution is possible to
compare all the results by patient grouped by the
clinical exam class and date. This facilitates the
decision process because it makes possible the
analyses of the results evolution by patient and by
variable during all stay.
4.2.3 ICU Scores
In the ICU is used a set of scores, especially pain
scores, Glasgow (Jones, 1979), SOFA (Vincent et
al., 1998) and SAPS (Le Gall et al., 1993) to predict
some clinical problem or know the real situation of
the patient. The introduction of ENR associated with
the electronic acquisition and registering of all data,
allow for the automatic scores calculation.
A mechanism of calculation was developed in
the ENR for each target score. Every time a new
value arrives to the variables included in the score,
the ENR Agent verifies which the worst value of the
day is and according to the range of each target
score it assigns a punctuation to be calculated in the
final. The final result only will be calculated when
all variables of the score were obtained. If some
variable wasn't collected automatically, the nurses
can introduce the result manually. The calculation of
scores will be explained in the next chapter.
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
244

5 ICU – DATA QUALITY
The quality of data is very important for a good
decision-making process. The data quality interferes
directly in the success of to the knowledge discovery
process that occurs in the ICU. This process starts
with the data stored in database collected from the
Vital Signs, EHR, Drugs System, Lab Results and
Events. All information collected will be stored in
database. Dependent of the variables collected and
the targets defined, the data will be validated and
prepared according the processing and
transformation rules.
The data resulting of this process is the real data
collected in ICU about the patient. This data will be
available through ENR and is prepared to be used by
DM techniques ( Santos and Portela, 2011); (Villas
Boas et al., 2010) and create knowledge to the
INTCare System. This process is represented in the
Figure 2. The ENR collects the data that was
automatic acquired, stored in database, processed
and transformed. The resulting data from the
processing tasks will be the real data and are these
that will be showed by ENR. The ENR also is a data
sources and also is subject to this process of quality.
5.1 Data Processing Process
All data collected will be processed by the agents
that execute the tasks and rules defined for each
variable / source. The data processing process is part
of a set of INTCare requirements:
a) Fault Tolerance Capacities and Continuous
Data Acquisition Process. For each value collected,
system working or record expected, the agent will
process the information received in database and if
anything not in agreement with the expected, a
message will be sent. Depending the type of fail,
exist some predefined solution tasks: If the failure
was in gateway, the agent send a message to the
gateway and it will restart instantly, if the failure
was in the LR or in drugs system a force refresh of
the system will be done, finally if something fail in
ENR system, the last record stored in database will
be loaded.
b) Processing to Remove Null and Noisy Data.
This process will be constantly running and has two
types of operations. The first type consist in a
constant looking for null records, if the line stored in
database contains null values, this will be delete.
The second type is responsible for autonomous
validation of the data collected automatic and in real
time from bedside monitors (BM) according the
range values defined to ICU, i.e. if the vital signs
values collected were correct and were possible in
the ICU environment the agent will validate the
results and store the data in a table with the real data.
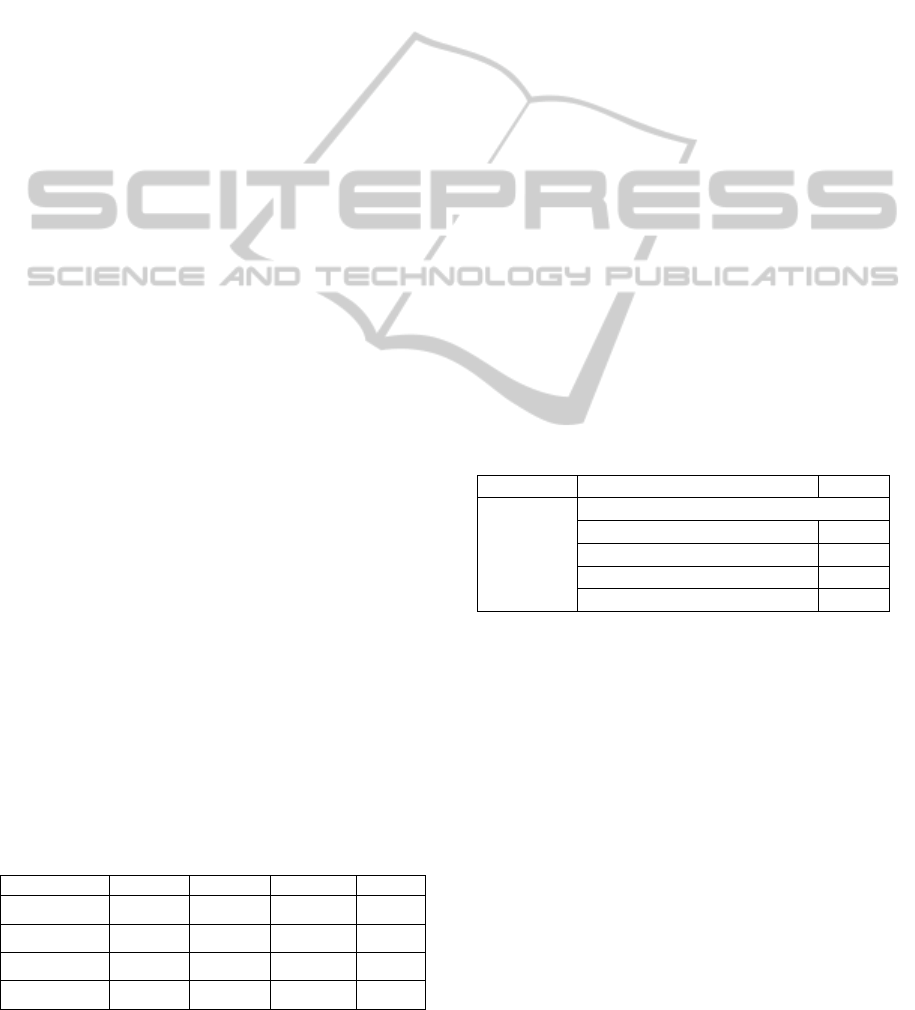
Table 1 shows the minimum and maximum values
attributed to the vital signs variables that will be
used to Data Mining. The objective is eliminating
the data that has noise, or incorrect values. An
example of noise values is the temperature, because
when the sensor is disconnected from the patient the
temperature collected is from the environment (~24º
to 27º) and not from the patient (~35º to 42º). The
final validation will be always done hourly by the
nursing staff through the ENR functionalities. With
this option if a value is out of range but is true, the
nurse can rectify that and make that value real,
registering this in the database.
Table 1: ICU Vital Signs Range.
Vital Sign Min Max
Blood Pressure (BP) 0 300
SPO2 40 100
Temperature (Temp) 30 45
Respiratory Rate (RR) 0 40
Heart Rate (HR) 0 250
c) Ensure the Patient Identification in Records.
Put the patient id in the monitors, is a manual
process, and because of that is a process that are in
constant fails. The objective is tried to turn this
process autonomous, without any type of human
intervention. The first solution founded was put a
RFID tag in the patient that will identify them in the
system, but this was an expensive solution and slow
to implement. In order to resolve this problem a
more fast possible we decide create a task that
verify, in the EHR, the patients admitted to ICU and
have a null date of discharge then, it sees the number
of the patient bed that came in the HL7 message sent
by gateway and compares with the values present in
the patient admission EHR table. After find a match,
the pre-processing agent will substitute the in the
message the null PID by the patient id present in the
EHR. This make it an autonomous process, which
runs every moments that arrives a new message to
the table, it is a before insert operation.
d) Time Restrictions for the Data Acquisition
and Storage. With the objective that data processing
will be done with the most recent data acquired, a set
of auto operations is scheduled, tasks like the auto
save, auto refresh, auto validation of data, etc. If any
operation can't be executed and if the agents don’t
receive any type of data to process and the
responsible agent will send an alert message
identifying the problem and possible solutions. Each
KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY FOR PERVASIVE AND REAL-TIME INTELLIGENT DECISION SUPPORT IN
INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE
245
individual agent (vital signs acquisition, pre-
processing agent, ENR, and Lab Results) is
responsible for the operation of their tasks group.
e) Digital Data Archive in Order to Promote the
Dematerialization of Paper based Processes. The
solution founded to this requirement involves a set
of agents, tasks and electronic process that can be
executed automatic and controlled by the humans.
The objective of this requirement is processing all
Fluid balance, nursing records, medical scores,
according the panel tables defined in ICU with this
we hope ensure the actuality of tables, ensure that
the data will be processed to data mining models i.e.,
all manual register types will be transformed in
online and electronic records that can be done in real
time by the humans in the moment that the situation
happens or value need to be collected. This
requirement was the base of development of the
entire ENR, intelligent agents, interoperability
between systems and other types of operations.
5.2 Data Transformation Process
To the development of prevision models in real-time
using Data Mining (DM) techniques and basing that
in the offline results obtained in the past (Gago et
al., 2007); (Á. Silva et al., 2008) is necessary
implement a set of automatic operations that
facilitate the calculation of critical events and
medical scores.
a) Critical Events. A critical event happened when
a patient have values out of normal range for a
determinate time. Table 2 is the base to the
calculation of critical Events function and presents
three types for the calculation of critical events. The
calculation of critical events is a consequent task of
the processing to remove null and noisy data. For
this, this operations only will be used for the values
pre-validated by the system, i.e., the calculation is
done with base in the maximum range defined for
ICU, the normal range and the time for an event be
critical (A. Silva et al., 2006).
First is verified if the value is normal or critical,
next, will calculated the time of the event and stored
in the critical events table, an event identification.
Table 2: ICU Critical Events Range.
BP O2 HR Urine
NormalRange 90−180≥90% 60−120≥30
CriticalEv.a≥1h≥1h≥1h≥2h
CriticalEv.b≥1hin2h≥1hin2h≥1hin2h –
CriticalEv.c <60 <80 <30V>180 ≤10
After received a row in the database, the agent
will read the variable id, and will compare the result
collected with the values present in Table 2 for that
variable. If the value is out of normal range the row
will be update and the type of result will be defined
with critical (1) if the values is out of normal range
and are worse than values defined for the critical
event c, the row will be assigned to a critical event,
will be update with number 2 and will be copied to
table ICU_CEVENTS. The function 3 shows how
the data collected will be tagged according the
critical state (0,1,2). To calculate the other two types
of critical events will be used the sum functions to
calculate the time that a value was out of normal
range.
b) Medical Scores. There exist three types of
scores that is used in ICU: MEWS (Gardner-Thorpe,
Love, Wrightson, Walsh, & Keeling, 2006), SAPS
(Le Gall, et al., 1993), SOFA (Vincent, et al., 1998).
For each score a set of transformations operation
will be done. The operations are similar for all
scores. The SOFA scores is used in DM models and
will presented that transformation. The value is
allocated according to the score punctuation table.
Using the number of points associated, the final
score will be calculated and the result will be
inserted in the scores table. The results obtained are
collected automatically.
Table 3: SOFA Table (respiratory organ).
System VariabletotheCalculation Score
Respiratory
System
PaO
2
/FiO
2
(mmHg)
<400 1
<300 2
<200andmechanicallyventilated 3
<100andmechanicallyventilated 4
6 ICU – AGENTS
In an ICU data can be acquired from a different
number of sources. In our architecture we propose
several data acquisition agents with clear boundaries
and responsibilities. Moreover, given the paramount
importance of data quality for data mining a data
quality agent responsible for detecting errors in the
data was devised. Indeed, data acquisition in the
ICU is error prone as, for instance, sensors may be
displaced as patients move. The agents included in
the data acquisition module are:
A Gateway agent (a
gat
)
connected to the bedside
monitors. Operating in real-time, this agent captures
the vital signs data from the bedside monitors (BM).
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
246
Vital Signs Acquisition agent is in charge of
receiving and parsing the HL7 messages sent by the
Gateway. Other than that real time parsing this agent
also stores the information in the database tables.
In order to allow a straightforward data entry by
the nurses, the ENR Agent (a
enr
) was created
(Portela, Vilas-Boas, Santos, & Fernando, 2010).
This agent is able to save the data automatically or
as a response to a request from the nurse. With this
agent we are able to capture the clinical data from
the medical and nursing staff. The data recorded by
this agent includes the fluid balance, patient
proceedings, and other scores.
Working in close connection with the ENR
agent, the LR agent (a
lr
) is responsible for capturing
the clinical data from the lab results. Every five
minutes this agent checks if there are new lab results
available. Whenever there are new lab results
available the LR agent gets them and stores the
information in the database before sending the
relevant information to the ENR agent. If we are to
use the collected data for decision support we must
make as sure as possible that it contains no errors. In
INTCARE architecture this is a task of the Pre-
Processing (a
pp
) agent.
In an ICU setting it is easy to see sensors that
aren’t correctly placed. This happens mostly due to
patient movement, even if incorrectly placed most
sensors continue to collect data. Naturally this
means that some pre-processing is necessary in order
to avoid that such incorrect values reach the records.
Whenever this happens for a short period the pre-
processing agent replaces the incorrect values with
the average of the values collected prior and after the
error. If the error condition lasts for a long time the
agent replaces the values with zeros, indicating that
no valid values were collected. Finally, this agent
creates a valid medical record for the patient. It does
this by combining all the available values and
ensuring that those values make sense.
7 RESULTS
Until 2009 the doctors based their decisions on
information essentially in paper format or on data
that were accessible only in specific systems or
places. Nowadays, all of this information is available
in electronic format and can be accessed online and
in real-time, in a pervasive approach.
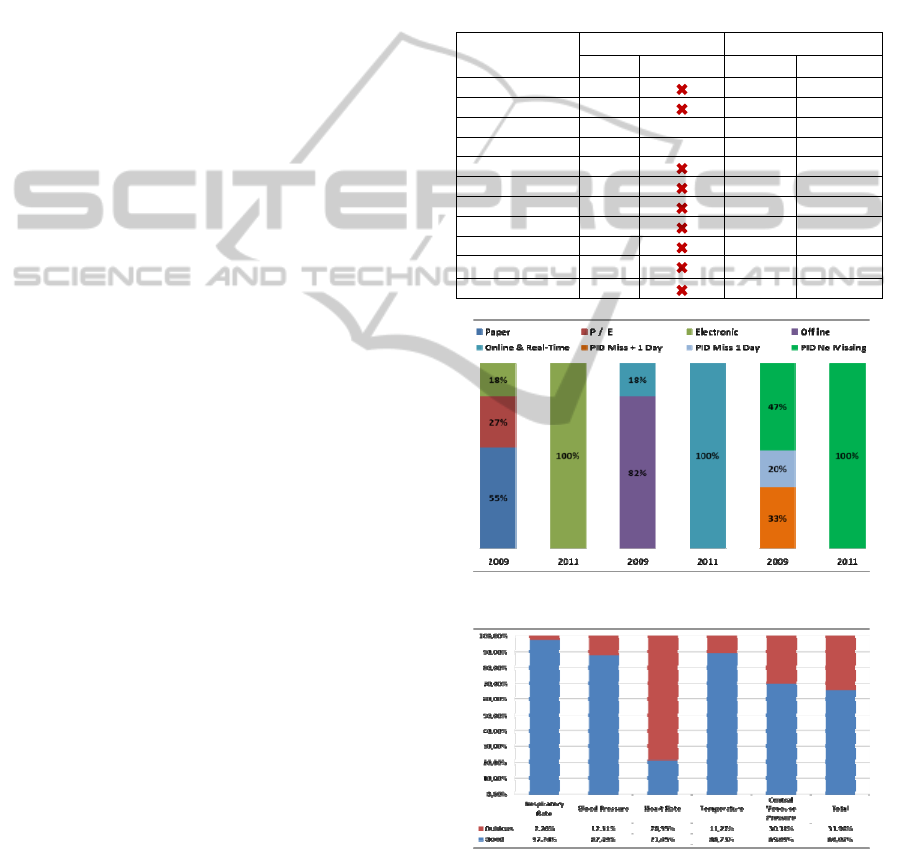
Table 4 shows the evolution of data sources and
the data access verified between 2009 and 2011. The
data source can be Paper (P), Electronic (E) or both
(P/E), i.e. some information are in paper and others
are in digital format. The chart 1 presents a
visualization of the percentage of data in each of
formats for those two years. Like we can verify in
2011, 100% of the data are electronic, acquired in
real-time and available online. This chart also
presents the percentage of processes without patient
ID (PID), that represents a decrease from 53 % in
2009 to 0 % in 2011, i.e., now all messages received
and data collected has PID.
Table 4: ICU Data Sources Format.
DataSources
Variables
2009 2011
Source Online Source Online
NursingRecord P E
√
VitalSigns P
E
√
DrugSystem
P
/
E
√
E
√
PatientEHR
E
√
E
√
Fluidbalance P
E
√
Procedures P/E
E
√
LabResults P
E
√
PatientEvents P / E
E
√
Ventilations P
E
√
PatientScores P
E
√
ICUScores P
E
√
Chart 1: Data access Formats (%).
Chart 2: Data Quality (%).
The modifications introduced in the ICU
information systems and the implementation of data
processing tasks, the level of the data quality
increased significantly. Analyzing the example in
chart 2, we achieved benefits in the all variables
KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY FOR PERVASIVE AND REAL-TIME INTELLIGENT DECISION SUPPORT IN
INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE
247

presented, especially in the heart rate where more
than 75% were worst values, i.e., values that were
collected and were out of normal range predefined in
the ICU. The overall benefit is about 34% which
represents the volume of data collected ignored after
the pre-processing.
8 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presented an approach to the KDD
procedure in order to enable a pervasive, online and
real-time processing of data in ICU. Such approach
brought improvements in the information
availability and consequently a more proactive
attitude by the doctors is facilitated. The doctors are
supported in their decisions anytime and anywhere.
In particular, data quality problems were completely
solved, e.g., monitored null values, values out of the
range and wrong patient ID. Finally, the quality of
decision making process has been significantly
increased. All the data (100%) used in the decision
process and in data mining models are reliable, i.e.
the values are in the range defined by ICU and the
doctors don't deal with dubious values. In the future
we will study the impact in the validity of data
mining models adding the data (decision variables)
obtained from this process, i.e. the therapeutics and
procedures. In order to control the failures, a
tolerance plan also will be created.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank FCT (Foundation of
Science and Technology, Portugal) for the financial
support through the contract PTDC/EIA/72819/
2006. The work of Filipe Portela was supported by
the grant SFRH/BD/70156/2010 from FCT.
REFERENCES
Abelha, A., Machado, J., Santos, M., Allegro, S., Rua, F.,
Paiva, M., et al. Agency for Integration, Diffusion and
Archive of Medical Information.
Apostolakos, M. J., & Papadakos, P. J. (2001). The
Intensive Care Manual: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Bricon-Souf, N., & Newman, C. R. (2007). Context
awareness in health care: A review.
[10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2006.01.003]. International
Journal of Medical Informatics, 76(1), 2-12.
De Turck, F., Decruyenaere, J., Thysebaert, P., Van
Hoecke, S., Volckaert, B., Danneels, C., et al. (2007).
Design of a flexible platform for execution of medical
decision support agents in the intensive care unit.
Computers in Biology and Medicine, 37(1), 97-112.
Foster, D., McGregor, C., & El-Masri, S. (2005, 2005). A
survey of agent-based intelligent decision support
systems to support clinical management and research.
Gago, P., Santos, M. F., Silva, Á., Cortez, P., Neves, J., &
Gomes, L. (2006). INTCare: a knowledge discovery
based intelligent decision support system for intensive
care medicine. Journal of Decision Systems.
Gago, P., Silva, A., & Santos, M. F. (2007, Dec 03-07).
Adaptive decision support for intensive care. Paper
presented at the 13th Portuguese Conference on
Artificial Intelligence, Guimaraes, PORTUGAL.
Gardner-Thorpe, J., Love, N., Wrightson, J., Walsh, S., &
Keeling, N. (2006). The value of Modified Early
Warning Score (MEWS) in surgical in-patients: a
prospective observational study. Annals of The Royal
College of Surgeons of England, 88(6), 571.
Jennings, N. R. (2000). On agent-based software
engineering. Artificial Intelligence, 117(2), 277-296.
Jones, C. (1979). Glasgow coma scale. AJN The American
Journal of Nursing, 79(9), 1551.
Le Gall, J. R., Lemeshow, S., & Saulnier, F. (1993). A
new Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) based
on a European/North American multicenter study.
JAMA, 270(24), 2957-2963.
Lyerla, F., LeRouge, C., Cooke, D. A., Turpin, D., &
Wilson, L. (2010). A Nursing Clinical Decision Support
System And Potential Predictors Of Head-Of-Bed
Position For Patients Receiving Mechanical Ventilation.
American Journal of Critical Care, 19(1), 39-47.
Machado, J. A., António. Santos, Manuel, Neves, José.
(2006). Multi-agent based Problem Solving in Medical
Decision Support Systems. In R. C. a. F. L. Vale Z.
(Ed.), Decision Support, Knowledge and Decision
Technologies. Porto: IPP, ISEP.
Portela, F., Santos, M., Vilas-Boas, M., Rua, F., Silva, Á.,
& Neves, J. (2010). Real-time Intelligent decision
support in intensive medicine. Paper presented at the
KMIS 2010- International Conference on Knowledge
Management and Information Sharing.
Portela, F., Vilas-Boas, M., Santos, M. F., & Fernando, R.
(2010). Improvements in data quality for decision
support in Intensive Care. Paper presented at the eHealth
2010 - 3rd International ICST Conference on Electronic
Healthcare for the 21st century.
Santos, M. F., & Portela, F. (2011). Enabling Ubiquitous
Data Mining in Intensive Care - Features selection and
data pre-processing. Paper presented at the 13th ICEIS.
Santos, M. F., Portela, F., Vilas-Boas, M., Machado, J.,
Abelha, A., & Neves, J. (2011). INTCARE - Multi-agent
approach for real-time Intelligent Decision Support in
Intensive Medicine. Paper presented at the 3rd
International Conference on Agents and Artificial
Intelligence (ICAART).
Silva, A., Cortez, P., Santos, M. F., Gornesc, L., & Neves,
J. (2006). Mortality assessment in intensive care units
KMIS 2011 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
248

via adverse events using artificial neural networks.
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 36(3), 223-234.
Silva, Á., Cortez, P., Santos, M. F., Gomes, L., & Neves,
J. (2008). Rating organ failure via adverse events using
data mining in the intensive care unit. Artificial
Intelligence in Medicine, 43(3), 179-193.
Varshney, U. (2003). Pervasive Healthcare. Computer,
36(12), 138-140.
Varshney, U. (2007). Pervasive healthcare and wireless
health monitoring. Mobile Networks and Applications,
12(2), 113-127.
Varshney, U. (2009). Pervasive Healthcare Computing:
EMR/EHR, Wireless and Health Monitoring: Springer-
Verlag New York Inc.
Villas Boas, M., Gago, P., Portela, F., Rua, F., Silva, Á., &
Santos, M. F. (2010). Distributed and real time Data
Mining in the Intensive Care Unit. ECAI 2010.
Vincent, J., Mendonça, A., Cantraine, F., Moreno, R.,
Takala, J., Suter, P., et al. (1998). Use of the SOFA
score to assess the incidence of organ
dysfunction/failure in intensive care units : Results of a
multicenter, prospective study. Critical care medicine,
26, 1793-1800.
Wooldridge, M. (1999). Intelligent agents Multiagent
systems: a modern approach to distributed artificial
intelligence (pp. 27-77): MIT Press.
KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY FOR PERVASIVE AND REAL-TIME INTELLIGENT DECISION SUPPORT IN
INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE
249
