
RELIABLE MODELLING AND OPTIMISATION CONTROL
OF REACTIVE POLYMER COMPOSITE MOULDING
PROCESSES USING BOOTSTRAP AGGREGATED
NEURAL NETWORK MODELS
Jie Zhang
1
and Nikos G. Pantelelis
2
1
School of Chemical Engineering and Advanced Materials, Newcastle University, NE1 7RU, Newcastle Upon Tyne, U.K.
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Technical University of Athens, Athens, Greece
Keywords: Neural networks, Polymer composite moulding, Bootstrap re-sampling, Modelling, Optimisation.
Abstract: This paper presents using bootstrap aggregated neural networks for the modelling and optimisation control
of reactive polymer composite moulding processes. Bootstrap aggregated neural networks combine multiple
neural networks developed from bootstrap re-sampling replications of the original training data in order to
enhance model prediction and generalisation capability. Neural network models for modelling the degree of
cure (through modelling the measured resistance) are developed from real industrial process operational
data. Both static and dynamic models are developed and the developed neural network models are validated
on unseen process operation data. The bootstrap aggregated neural network models give accurate and
reliable predictions than single neural networks. Optimal heating profile is obtained by solving an
optimisation problem using the dynamic neural network model. The model prediction confidence bound is
incorporated in the optimisation objective function in order to enhance the reliability of the calculated
optimal control profile. In addition to maximise the final degree of cure, model prediction confidence bound
is minimised. Application results on a simulated polymer composite moulding process demonstrate that the
proposed reliable optimisation control strategy is effective.
1 INTRODUCTION
Polymer composite materials have been increasingly
used in many areas, for example, aerospace,
automobile, and construction industries, due to their
various advantages. For example, polymer
composite is of much light weight and comparable
strength compared with steel. Automobiles using
polymer composite parts instead of steel parts will
significantly save fuel consumption due to the much
reduced weight. Polymer composite is corrosion
resistant compared to steel making them ideal
materials for many manufacturing industries. The
curing of thermoset based polymer composite
material is dominated by complex process dynamics
and trial and error procedure is the only practical
tool for process optimisation (Pantelelis, 2005).
Reactive polymer composite moulding processes
are typical batch processes. The degree of cure is an
important parameter in reactive polymer composite
moulding processes. Only when the product is
almost fully cured the mould can be opened. Thus,
modelling the degree of cure is very important in the
control and optimisation of reactive polymer
composite moulding processes. Development of
detailed mechanistic models for the degree of cure is
generally time consuming and effort demanding.
Data based empirical modelling can be a very useful
alternative in this case. Neural networks have been
shown to be capable of approximating any
continuous nonlinear functions (Cybenko, 1989) and
have been applied to nonlinear process modelling
(Bhat and McAvoy, 1990); (Bulsari, 1995); (Su et
al., 1992).
A problem of conventional neural network is the
lack of robustness and generalization capability due
to limitation in training data and/or training
methods. An effective approach to improve neural
network model generalization is by combining
multiple neural networks (Breiman, 1996); (Sridhar
et al., 1996); (Zhang et al., 1997).
The paper
presents a study on using bootstrap aggregated
236
Zhang J. and G. Pantelelis N..
RELIABLE MODELLING AND OPTIMISATION CONTROL OF REACTIVE POLYMER COMPOSITE MOULDING PROCESSES USING BOOTSTRAP
AGGREGATED NEURAL NETWORK MODELS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003682602360241
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications (NCTA-2011), pages 236-241
ISBN: 978-989-8425-84-3
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

neural networks for modelling the degree of cure
and optimisation of polymer composite moulding
processes.
The paper is organised as follows. Section 2
presents modelling of reactive polymer composite
moulding process using bootstrap aggregated neural
networks. Section 3 presents optimisation control of
reactive polymer composite moulding process based
the neural network model. Section 4 concludes the
paper.
2 MODELLING OF REACTIVE
POLYMER COMPOSITE
MOULDING PROCESS USING
NEURAL NETWORKS
2.1 Bootstrap aggregated Neural
Networks
Neural networks have been shown to be capable of
approximating any continuous nonlinear functions
(Cybenko, 1989) and have been applied to nonlinear
process modelling (Bhat and McAvoy, 1990);
(Bulsari, 1995); (Su et al., 1992). In most of the
reported applications, a single neural network is
used to model the concerned nonlinear process. A
limitation of single neural network models is that
they can lack generalisation when applied to unseen
data, i.e. the trained neural network gives good
performance on the training data but gives
unsatisfactory performance on unseen data which is
not used in the training process. Several techniques
have been reported in the literature for improving
neural network generalisation capability, such as
regularisation (Bishop, 1991), early stopping
(Bishop, 1995), Bayesian learning (MacKay, 1992),
training with both dynamic and static process data
(Zhang, 2001), and combining multiple networks
(Sridhar et al., 1996); (Wolpert, 1992); (Zhang et al.,
1997). In training with regularisation, the magnitude
of network weight is introduced as a penalty term in
the training objective function in order to avoid
unnecessarily large network weights which generally
lead to poor generalization performance. In training
with early stopping, neural network performance on
the testing data is checked during the training
process and the training process stops when the
neural network prediction errors on the testing data
start to increase. Among these techniques,
combining multiple networks is a very promising
approach to improving model predictions on unseen
data. The emphasis of this approach is on
generalisation accuracy on future predictions (i.e.
predictions on unseen data). When building neural
network models, it is quite possible that different
networks perform well in different regions of the
input space. By combining multiple neural networks,
prediction accuracy on the entire input space could
be improved. Bootstrap aggregated neural networks
have been successfully used for the inferential
estimation of polymer quality (Zhang et al., 1997),
prediction of final product quality (Zhang et al.,
1998), and estimation of reactive impurities and
reactor fouling (Zhang et al., 1999) in a batch
polymerisation process.
A diagram of bootstrap aggregated neural
networks is shown in Fig. 1, where several neural
network models are developed to model the same
relationship. Instead of selecting a “best” single
neural network model, these individual neural
networks are combined together to improve model
accuracy and robustness. The overall output of the
aggregated neural network is a weighted
combination of the individual neural network
outputs. This can be represented by the following
equation.
fX wf X
i i
i
n
() ()
1
(1)
where f(X) is the aggregated neural network
predictor, f
i
(X) is the ith neural network, w
i
is the
aggregating weight for combining the ith neural
network, n is the number of neural networks, and X
is a vector of neural network inputs. Proper
determination of the stacking weights is essential for
good modelling performance. A popular choice of
stacking weights is simple averaging, i.e. the stacked
neural network output is an average of the individual
network outputs. Since the individual neural
networks are highly correlated, appropriate stacking
weights could be obtained through principal
component regression (PCR) (Zhang et al., 1997).
Instead of using constant stacking weights, the
stacking weights can also dynamically change with
the model inputs (Ahmad and Zhang, 2005; 2006).
Another advantage of bootstrap aggregated
neural network is that model prediction confidence
bounds can be calculated from individual network
predictions (Zhang, 1999). The standard error of the
ith predicted value is estimated as
2/12
1
})];();([
1
1
{
i
n
b
b
ie
xyWxy
n
(2)
where y(x
i
; .) =
n
b
b
i
nWxy
1
/);(
and n is the
number of neural networks in an aggregated neural
RELIABLE MODELLING AND OPTIMISATION CONTROL OF REACTIVE POLYMER COMPOSITE MOULDING
PROCESSES USING BOOTSTRAP AGGREGATED NEURAL NETWORK MODELS
237

network. Assuming that the individual network
prediction errors are normally distributed, the 95%
prediction confidence bounds can be calculated as
y(x
i
; .) 1.96
e
. A narrower confidence bound, i.e.
smaller
e
, indicates that the associated model
prediction is more reliable.
X
Y
Figure 1: A bootstrap aggregated neural network.
2.2 Modelling the Degree of Cure in an
Industrial Polymer Composite
Moulding Process
Neural network models were developed using
industrial data from an EU research project –
iREMO (intelligent reactive polymer composite
moulding). The process is for the manufacturing of
car parts
.
In the real reactive polymer composite moulding
processes studied in this project, the curing process
is monitored using OptiMould which measures
resistance. The data set contains 6 runs at different
moulding temperatures. Data from 4 runs were used
to build neural network models and data from the
other 2 runs were used as unseen validation data.
The original data were sampled and stored at
unequal sampling times due to the limitation in the
sensor. For the purpose of neural network modelling,
especially dynamic modelling, the data were re-
sampled at equal sampling time. A sampling time of
30s were used.
Two types of neural network models were
developed: a static model and a dynamic model. The
static model is of the following form:
),()( TtftR
(3)
where R(t) is the resistance at time t (min), T is the
moulding temperature (
o
C), and f() is a nonlinear
function represented by a neural network.
A bootstrap aggregated neural network
containing 30 single hidden layer neural networks
each with 12 hidden neurons was developed. The
networks were trained with Levenberg-Marquardt
algorithm (Marquardt, 1963) with regularisation and
early stopping. Figure 2 shows the predicted
resistance on the 2 unseen validation runs. In Figure
2, the actual measure resistances are shown as the
solid lines whereas the neural network predictions
are shown as dashed lines. The dotted lines are the
95% prediction confidence bounds. It can be seen
that the neural network predictions are very
accurate. Furthermore, the prediction confidence
bounds are quite narrow, especially towards the end
of the curing cycle where the model predictions are
of more importance. This indicates that the bootstrap
aggregated neural network gives accurate and
reliable predictions. Thus it can be applied to the
real industrial process with confidence.
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
10
8
Tim e (s )
Resist ance (MOhm)
-:actual; --:NN model prediction; ..:95% confidence
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
10
8
Tim e (s )
Resistance (MOhm)
-:actual; --:NN model prediction; ..:95% confidence
Figure 2: Static neural network model predicted resistance
and the 95% prediction confidence bounds on the 2 unseen
runs.
The dynamic model is of the following form:
y(t) = f[y(t-1), y(t-2), u(t-1)] (4)
where y is the resistance, u is the applied
temperature, t is discrete time, f() is a nonlinear
function represented by the neural network.
A bootstrap aggregated neural network
containing 30 single hidden layer neural networks
with 8 hidden neurons was developed. The networks
were trained with Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm
with regularisation and early stopping. Figure 3
shows the predicted resistance on the 2 unseen
validation runs. In Figure 3, the actual measure
resistances are shown as the solid lines, one-step-
ahead predictions are shown as dashed lines, and
multi-step-ahead predictions are shown as the dash-
dotted lines. It can be seen that the neural network
one-step-ahead predictions are very accurate. The
multi-step-ahead predictions are also very accurate,
though not as accurate as the one-step-ahead
predictions. In contrast to the static model,
predictions in the dynamic model can be updated
using the online measured resistance. The static
model, on the other hand, does not require measured
NCTA 2011 - International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
238

resistance as model input. When the measured
resistance is affected by air bubble or carbon fibre,
the dynamic model would not give good predictions
and the static model can be used. Thus the two types
of models can used in a complimentary way.
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
10
8
Time (s )
Resist ance (MOhm)
-:actural; --:NN model 1-step-ahead predic tion; -.:mult i-s tep ahead predict ion
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
10
0
10
2
10
4
10
6
10
8
Time (s )
Resist ance (MOhm)
-:actural; --:NN model 1-step-ahead predic tion; -.:mult i-s tep ahead predict ion
Figure 3: Dynamic neural network model predicted
resistance on the 2 unseen runs.
3 RELIABLE OPTIMISING
CONTROL
Using a neural network dynamic model, the optimal
control profile (e.g. heating profile) is calculated off-
line by solving the following optimisation problem.
)()]([min
321
,,
1
feffd
tuu
twtwtwJ
fN
s.t. product quality and operation constraints
where
d
is the desired degree of cure, t
f
is the batch
time, σ
e
is the standard error of neural network
predictions, w
1
, w
2
and w
3
are weighting factors, and
u
1
,…, u
N
form the control profile. Earlier studies by
Zhang (2004) and Mukherjee and Zhang (2008)
show that penalising wide model prediction
confidence bounds (i.e. large σ
e
) leads to reliable
optimal control policies.
The optimisation control strategy is tested on
simulation using the mechanistic model given in
(Pantelelis, 2005). The basic kinetic model is a
combination of autocatalytic and nth order reaction
terms with Arrhenius dependence of the rate
constants:
76
5
)1(
)273(
exp
)1(
)273(
exp
2
4
1
3
PP
P
aa
TR
P
P
a
TR
P
P
dt
da
(5)
where P
1
and P
2
are the activation energies, P
3
and
P
4
are the rates constants, and P
5
to P
7
are the
reaction orders. Two improved models incorporating
glass transition temperature and a diffusion term are
given in (Pantelelis, 2005). The improved model is
used in this study and the model parameters can be
found in (Pantelelis, 2005). From simulation, 7
batches were simulated and the sampling time is 4
minutes.
A dynamic neural network model was developed
using 3 batches (batches 3, 5, 7) and the developed
models are validated on 4 unseen validation batches
(batches 1, 2, 4, 6). The developed model is a
bootstrap aggregated neural network containing 30
neural networks. Each network is a single hidden
layer feed forward neural network with 5 hidden
neurons. The network was trained with Levenberg-
Marquardt algorithm with regularisation and early
stopping. Table 1 shows the mean squared errors
(MSE) from one-step-ahead predictions and multi-
step ahead predictions on the 4 unseen validation
batches. It can be seen from Table 1 that the model
predictions are very accurate.
Table 1: MSE of model predictions on validation data.
batch 1-step-ahead predictions Long range predictions
1 0.0316×10
-3
0.2853×10
-3
2 0.0422×10
-3
0.2235×10
-3
4 0.1126×10
-3
0.1968×10
-3
6 0.0253×10
-3
0.2047×10
-3
In this study, the desired degree of cure is set to 1
and the constraints on the applied temperature are
20
o
C T 160
o
C and 0
o
C ΔT 70
o
C. The batch
time is divided into several intervals each of 4
minutes and several possible batch times (in multiple
of 4) were considered. Several batch ending times
were considered and it is found that a batch time of
20 minutes is the shortest possible batch time. Two
types of control profiles were considered: piecewise
linear profile where the applied temperature linearly
increases within each interval and piecewise
constant profile where the applied temperature is
kept constant within each interval. The optimisation
problem is solved using sequential quadratic
programming (SQP) implemented in the MATLAB
Optimisation Toolbox. The SQP optimisation
method mimics Newton’s method for constrained
optimisation in that at each major iteration an
approximation is made of the Hessian matrix of the
Lagrangian function using a quasi-Newton updating
method. This is then used to generate a quadratic
programming sub-problem which is solved and the
solution is used to form a search direction for a line
search procedure. The weighting parameter w
3
is
selected as 0.1 in both cases.
RELIABLE MODELLING AND OPTIMISATION CONTROL OF REACTIVE POLYMER COMPOSITE MOULDING
PROCESSES USING BOOTSTRAP AGGREGATED NEURAL NETWORK MODELS
239
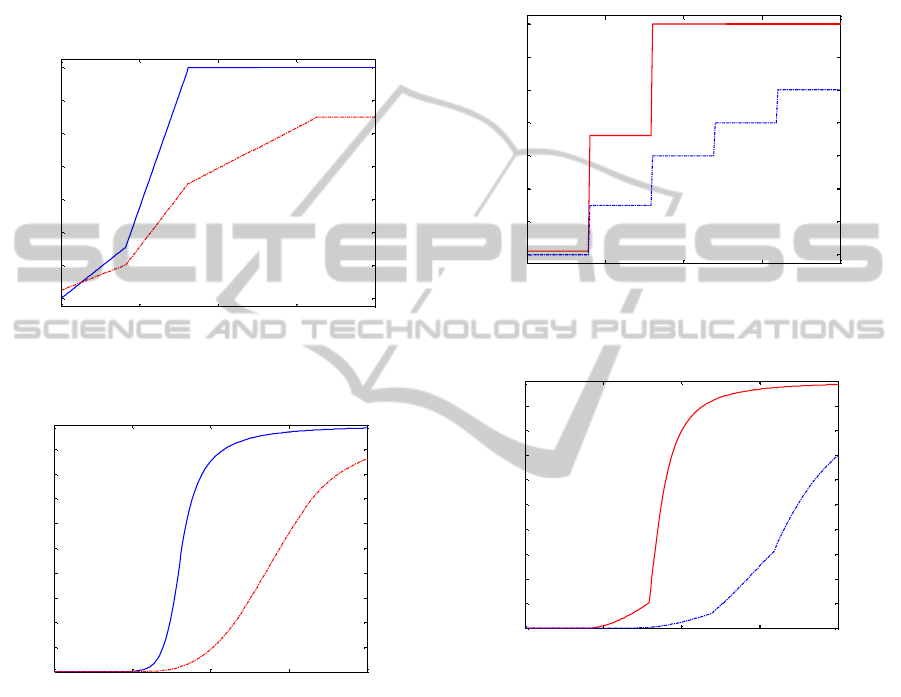
Figure 4 shows the initial and optimised
temperature profiles for the piecewise linear control
profile and Figure 5 shows the corresponding degree
of cure profiles. It can be seen from Figure 5 that the
final degree of cure under the initial temperature
profile is less than 0.9. Through optimisation based
on the neural network model, the final degree of
cure under the optimised temperature profile is
0.9866, which is very close to one.
0 5 10 15 20
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
Time (min)
Temperature (
o
C)
-:after optimisation; -.:before optimisation
Figure 4: Temperature before (-.) and after (-) optimisation
for the piecewise linear control profiles.
0 5 10 15 20
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Time (min)
Degree of cure
-:after optimisation; -.:before optimisation
Figure 5: Degree of cure before (-.) and after (-)
optimisation for the piecewise linear control profiles.
Figure 6 shows the initial and optimised
temperature profiles for the piecewise constant
control profile and Figure 7 shows the corresponding
degree of cure profiles. It can be seen from Figure 7
that the final degree of cure under the initial
temperature profile is less than 0.7. Through
optimisation based on the neural network model, the
final degree of cure under the optimised temperature
profile is 0.9876, which is very close to one. The
neural network predicted final degree of cure under
this optimal curing temperature profile is 0.9722,
which is very close to the actual value.
The results obtained demonstrate that the neural
network models developed from polymer composite
moulding process operation data can accurately
represent the process and can be effectively used in
finding the optimal temperature profile. The final
degree of cure can be significantly improved through
optimisation using the neural network models.
0 5 10 15 20
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
Time (min)
Temperature (
o
C)
-:after optimisation; -.:before optimisation
Figure 6: Temperature before (-.) and after (-) optimisation
for the piecewise constant control profiles.
0 5 10 15 20
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Time (min)
Degree of cure
-:after optimisation; -.:before optimisation
Figure 7: Degree of cure before (-.) and after (-)
optimisation for the piecewise constant control profiles.
4 CONCLUSIONS
A reliable modelling and optimisation control
strategy for reactive polymer composite moulding
process based on bootstrap aggregated neural
networks is presented in this paper. Application
results on both simulated and real industrial data
demonstrate that the developed neural network
models can accurately predict the degree of cure
(through predicting the measured resistance). In
addition, model prediction confidence bounds are
obtained from bootstrap aggregated neural networks.
By incorporating the model prediction confidence
NCTA 2011 - International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
240

bounds into the optimisation objective function and
penalising wide model prediction confidence
bounds, reliable optimisation control policy is
obtained. Application to a simulated reactive
polymer composite moulding process demonstrates
that the proposed reliable optimisation control
technique is very effective.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research is supported by the EU through the
project iREMO – intelligent reactive polymer
composite moulding (grant No. NMP2-SL-2009-
228662).
REFERENCES
Ahmad, Z. and J. Zhang, (2005). “Bayesian selective
combination of multiple neural networks for
improving long range predictions in nonlinear process
modelling”, Neural Computing & Applications, 14,
78-87.
Ahmad, Z. and J. Zhang, (2006). “Combination of
multiple neural networks using data fusion techniques
for enhanced nonlinear process modeling”, Computers
& Chemical Engineering, 30, 295-308.
Bhat, N. V. and T. J. McAvoy, (1990). “Use of neural nets
for dynamical modelling and control of chemical
process systems”, Computers & Chemical
Engineering, 14, 573-583.
Bishop, C., (1991). “Improving the generalisation
properties of radial basis function neural networks”,
Neural Computation, 13, 579-588.
Bishop, C., (1995). Neural Networks for Pattern
Recognition. Oxford University Press: Oxford.
Breiman, L., (1996). “Bagging predictor”, Machine
Learning, 24, 123-140.
Bulsari, A. B., (Ed), (1995). Computer-Aided Chemical
Engineering, Vol.6, Neural Networks for Chemical
Engineers, Elsevier: Amsterdam.
Cybenko, G., (1989). “Approximation by superposition of
a sigmoidal function”, Math. Control Signal Systems,
2, 303-314.
MacKay, D. J. C., (1992). “Bayesian interpolation”,
Neural Computation, 4, 415-447.
Marquardt, D., (1963). “An algorithm for least squares
estimation of nonlinear parameters”, SIAM J. Appl.
Math., 11, 431-441.
Mukherjee, A. and J. Zhang, (2008). “A reliable multi-
objective control strategy for batch processes based on
bootstrap aggregated neural network models”, Journal
of Process Control, 18, 720-734.
Pantelelis, N. G., (2005). “Towards the dynamic
optimisation for the cure control of thermoset-matrix
composite materials”, Composites Science and
Technology, 65, 1254–1263.
Sridhar, D. V., R. C. Seagrave, and E. B. Bartlett, (1996).
“Process modelling using stacked neural networks”,
AIChE Journal, 42, 2529-2539.
Su, H. T., T. J. McAvoy, and P. Werbos (1992). “Long-
term prediction of chemical process using recurrent
neural networks: a parallel training approach”, Ind.
Eng. Chem. Res., 31, 1338-1352.
Tian, Y., J. Zhang, and A. J. Morris, (2001). “Modeling
and optimal control of a batch polymerization reactor
using a hybrid stacked recurrent neural network
model”, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 40, 4525-4535.
Wolpert, D. H., (1992). “Stacked generalization”, Neural
Networks, 5, 241-259.
Zhang, J., A. J. Morris, E. B. Martin, and C. Kiparissides,
(1997). “Inferential estimation of polymer quality
using stacked neural networks”, Computers &
Chemical Engineering, 21, s1025-s1030.
Zhang, J., A. J. Morris, E. B. Martin, and C. Kiparissides,
(1998). “Prediction of polymer quality in batch
polymerisation reactors using robust neural networks”,
Chemical Engineering Journal, 69, 135-143.
Zhang, J., A. J. Morris, E. B. Martin, and C. Kiparissides,
(1999). “Estimation of impurity and fouling in batch
polymerisation reactors through the application of
neural networks”, Computers & Chemical
Engineering, 23(3), 301-314.
Zhang, J., (1999). “Developing robust non-linear models
through bootstrap aggregated neural networks”,
Neurocomputing, 25, 93-113.
Zhang, J., (2001). “Developing robust neural network
models by using both dynamic and static process
operating data”, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 40, 234-241.
RELIABLE MODELLING AND OPTIMISATION CONTROL OF REACTIVE POLYMER COMPOSITE MOULDING
PROCESSES USING BOOTSTRAP AGGREGATED NEURAL NETWORK MODELS
241
