
SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS AS DATA CLASSIFIERS IN
MEDICAL APPLICATIONS
Jana Tuckova, Marek Bartu, Petr Zetocha and Pavel Grill
Czech Technical University, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department of Circuit Theory, Prague, Czech Republic
Keywords: Self-organizing maps, Classifier, Medical applications.
Abstract: Many researchers use mathematical-engineering methods in different domains of life, and medical research
is no exception. One area for application of such methods is to assist people with different forms of disabili-
ties. The methods described in the following text are oriented towards the analysis of disordered children’s
speech with the diagnosis of Specific Language Impairment (SLI), also named as Developmental Dyspha-
sia (DD), and the analysis of the expressive speech. Both methods make use of Kohonen Self-Organizing
Maps (KSOM) or Supervised Self-Organizing Maps (SSOM) for the analysis and the classification of featu-
res from utterances of healthy and ill children, or adult speakers for emotions analysis. The possibility of
cluster visualisation is used for monitoring of disorder trends and therapy success. These experiments also
demonstrate the ability of the KSOM or SSOM to classify emotions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many problems in technology, medicine, and the
natural and social sciences still remain unsolved, on
the grounds of the complexity of their solutions and
the considerable quantity of data that requires
processing. Seeking help through new information
technology is highly desirable; one such method is
through the development of artificial neural
networks (ANN). Success in the application of ANN
depends on the thorough knowledge of their
function, which cuts across a wide range of
academic disciplines – mathematics, numerous
technical fields, physiology, medicine, phonetics,
phonology, linguistics and social sciences. The
robustness of the solutions for real methods by
means of ANN is a great advantage.
One area where researchers are applying tested
mathematical engineering methods is that of helping
people with different forms of disabilities. The
nervous system and the brain are ranked among the
most crucial components of a living organism, with
particularly great influence on the quality of human
life. For this reason, biological neural networks have
become the inspiration for computer modelling of
their features and modelling of their function. Our
research in this area is focused on searching for the
relation between the clinical and the electrophysiolo-
gical symptoms of children with SLI. Our
experiments take as their starting point our long
research into speech signals. Bearing in mind that
speech is one of the most complex human activities,
we work towards an interaction of methods
grounded in the results from both engineers and
neurologists, in the hope that our method helps in
the therapy of SLI patients. Language impairment
can be caused by a number of brain disorders. Our
long-term effort, of which the present submission is
one part, will be to confirm the hypothesis that
KSOM can classify these different disorders.
Specific language impairment is one of the most
frequently occurring neurodevelopmental disorders,
affecting five percent of the paediatric population
(Dlouha at al., 2007). The condition is frequently
defined as an inability to acquire and learn normal
communication skills in proportion to age, even
though with the presence of adequate peripheral
hearing and intelligence, and the absence of a broad
sensorimotor deficit or congenital malformation of
the speech or vocal systems.
Developmental dysphasia, as a central disorder
of speech signal processing, affects not only all
speech modalities (phonetic-phonologic,
morphological-syntactic, lexical-semantic as well as
memory) but also other developmental aspects of the
child’s personality.
422
Tuckova J., Bartu M., Zetocha P. and Grill P..
SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS AS DATA CLASSIFIERS IN MEDICAL APPLICATIONS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003722604220429
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications (Special Session on Challenges in Neuroengineering-
2011), pages 422-429
ISBN: 978-989-8425-84-3
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

We can establish a relation between
developmental dysphasia (Hrncir and Komarek,
2004); (Pospisilova, 2005) and the assessment of the
degree of perception and impairment of the speech.
The partial problems are mentioned from the point
of view of logopaedics in (Love and Webb, 2001),
which represents an engineering-based approach to
the solution on the part of complex research.
Our method involves clustering the pattern
chara-cteristics visible through the allocation of the
vowels, or respectively through the changes in
allocation of the vowels pronounced by the patients.
This characteristic is the formant frequency of the
vowels shift. These formants are computed by a
modified Burg algorithm from the vaw signal of
monosyllabic and multi-syllabic words. Analysis of
layout and movement of the features in the map can
be one of the symptoms in identification of
neurological disease. Also, it is important to monitor
the ability to perceive and reproduce emotional
speech in neurological patients.
Much research around the world focuses on the
processing of emotional speech, a task of particular
difficulty. The language of emotion includes
thousands of words with myriad shades of feeling,
degrees of redundancy, and shared meaning. Bearing
in mind its high complexity, it may be impossible to
describe these characteristics analytically.
Nonetheless, neural network training can offer one
satisfactory solution. Briefly to characterise the
publications of international researchers concerning
emotional speech by ANN application, the specific
projects differ in the number and type of classified
emotions, acoustic characteristics, the type of
classifiers, and the degree of precision. Comparison
of the SVM (Support Vector Machine), RBF (Radial
Basis Function), kNN (k-Nearest Neighbours),
Naive Bayes and MLNN (two hidden layers with 15
neurons) in emotions analysis is described in (Xiao
at al., 2010). The success for the five classes was
81%. A description of the five emotional states
(pleasure, sadness, fear, anger, and neutral state) is
undertaken in (Mahmoud and Hassan, 2009). Here,
the algorithm is based on the relationship of a height
note versus the 12 half tones of the melodic scale.
The last-mentioned publication is closest to our
methods described in (Tuckova and Sramka, 2010).
A preference for self-organizing maps (SOM)
has been assumed from the nature of our problem.
For many real problems, the target values for all the
patterns of the database are unknown (as is true in
our case too). Nor do we know all the characteristics
of the patterns.
2 HYPOTHESIS
Kohonen's Self-Organizing Features Map (KSOM)
is a form of ANN that is trained by unsupervised
learning rules. It is an iterative process which
transforms multidimensional input data into decrea-
sing-dimensional space. This process is based on the
clustering method; cluster analysis methods search
for interdependences and joint properties in a set of
submitted patterns. T. Kohonen was inspired by the
self-organising procedure in a human brain, by its
adaptation and learning ability (more in Kohonen,
2001). At the basis of this method lies the fact that a
human brain creates a map with specific areas, the
areas that concentrate and treat different impulses.
The clusters are allocated on the map and
indicate the number of dominant properties in one
training epoch; clusters can point to movement in
the input data and “re-grade” any characterization
into different groups in the course of repetition.
2.1 Speech Analysis of the Patients
with SLI
Specific Language Impairment has a direct impact
on children’s speech ability. Utterances of SLI
children are different from the utterances of a
healthy child of the same age. Usually, these
differences are examined and classified by a speech
therapist. Our long-time aim is to develop software
capable of classifying temporal and frequency
differences in children’s speech. We have started
from the hypothesis that SLI involves a disorder of
movement of the vocal organs in articulation,
influencing the formant generation (Tuckova and
Komarek, 2009). The vowel mapping of patients is
different in comparison to the vowel mapping of
healthy children. The utterances are merged into a
set of patterns using KSOM (Kohonen, 2001).
The software enables the quick extraction of the
measure of distortion between patterns obtained
from the particular utterance and the selected set of
similar utterances. The software will help to observe
trends in the progress of the disorder and assist in
selecting an appropriate therapy, as well as
improving and making more objective the diagnosis
of the disease. The ability to distinguish emotions is
also one of the important aims in the therapeutic
process.
2.2 Emotions Analysis
It is possible to use prosody characteristics, such as
timbre, intensity and rhythm, which are part of the
SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS AS DATA CLASSIFIERS IN MEDICAL APPLICATIONS
423

melody. Important indicators for the emotional and
voluntary attitude of a speaker (Krcmova, 2008),
(Palkova, 1994) are expressive changes of melody
(i.e. change of a height of voice in a sentence).
The method presented here is based on the idea
of the musical interval (Tuckova and Sramka, 2010).
In speech, we can find a parameter which
corresponds to the tone relationship, and for speech
emotions it may have important perceptual values
even in changes of the frequency range appearing in
speech intonation. Compound tone is not only the
tone of all music instruments: it is also a tone of
speech, and its spectrum is a set of integral multiples
of the fundamental frequency, known as the
harmonic row. The amplitude of the exciting tone is
the fifth relationship by the series of the harmonic
row, which is coded by the frequency differences of
successively proceeding harmonic tones. The
relationship of any two tones to their fundament is
perceived independently of the tones being sounded
at the same time (interfluence over colour of speech,
interrelations between fundamental frequency and
speech formants or between speech formants
respectively) or gradually (influence over intonation
behaviour of fundamental frequency). Musical
scales are nothing other than banks of tones all
bound together by specifically given conditions
whose sequence has a common relationship to tone
F1. We talk about tonality, which has a strong
emotive context: e.g. minor scales are perceived as
sad and major scales as happy. Recalling this fact,
the mutual relationships of tones can code emotions
even in speech. Musical interval is the frequency
difference between a specific n-tone and reference
tone.
3 METHODS
Our team has created specific speech databases. For
the first method described, it is a speech database of
children with SLI, and a comparative database of
healthy children. For this purpose, only utterances of
healthy children without even any minor speech
disorders are used. The same methodology is used,
but with a different database from patients utterances
that will be recorded. For the second described
method, emotional speech is pronounced by
professional actors in the pilot study.
3.1 Speech Analysis of the Patients
with SLI
All the utterances in our database (Zetocha, 2007)
were divided into two parts: the first (major) part to
train KSOM and the second (minor) part is reserved
for comparison to the features extracted from utte-
rances of children suffering from SLI (DD). This
separation is to avoid the problem of adaptation to
specific speakers. The utterances are divided in the
ratio of approximately two to one. Separated maps
are trained for different types of utterances (e.g.
vowels, monosyllables, etc.). The utterances are
stored in the wave files. Standard methods – MFCC,
PLP and LPC – are utilized to encode speech before
the processing by KSOMs. There are separate
networks for each type of coefficient, thus implying
three different maps (one for each type of
coefficient) for each group of utterances. PLP and
MFCC were made for speech recognition tasks and
therefore have a tendency to generalize, whereas
LPC coefficients could describe particular vocal
tracts with regard to specific features of the speaker.
LPC coefficients have proven to offer very good
results with utterances of very young children and
also children with speech disorders. Our original
intention was to compare the results obtained by
each type of coefficients and choose the best-suited
one. After several experiments, we decided to keep
all three speech parametrizations being evaluated at
one time, but taken separately.
KSOMs are utilized to find identical
characteristic features in utterances. Features in the
signal spatially or temporally adjacent are
represented by patterns. By training the nets, the
characteristic set of patterns for a given set of
utterances is found. If the maps are trained with
healthy children’s utterances, the patterns represent
the distribution of the feature in their speech.
Moreover, this distribution will differ from the
distribution obtained from the utterances of SLI
children. The differences could be enumerated in
proportion to the progress of treatment being
described: in cases of effective therapy, the
differences tend to decrease.
The maps and the unified distance matrix (U-
matrix) form a representation of the KSOM that
visualizes clusters and the distance between the
neurons and their neighbours. The KSOM neurons
are represented by hexagonal cells (in our
experiment). The distance between the adjacent
neurons is calculated and displayed in different
colours. Light colours (from yellow to red) between
neurons correspond to a large distance and thus
represent a difference between the values in the
input space. Dark colours (blue) between the
neurons mean that the vectors are close to each other
in the input space. Dark areas represent clusters and
NCTA 2011 - International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
424

light areas represent cluster boundaries. A new SOM
variant has been put into use for vowel
classification, namely the supervised self-organizing
map (SSOM), which combines aspects of the vector
quantization method with the topology-preserving
ordering of the quantization vectors. The algorithm
of the SSOM represents a very effective method of
classification.
3.2 Emotions Analysis
The sentences in the pilot study were read by
professional actors, two female and one male.
Speech recording was performed in a recording
studio with professional equipment (format “wav“,
sampling frequency 44 kHz, 24bit). Utterances were
recorded for four types of emotions: anger, boredom,
pleasure and sadness.
The changes in the melody of the sentence are
defined as its intonation, a quality also related to the
meaning of the sentence, and its emotional timbre.
Recorded emotional speech was subjectively
evaluated by four persons. The final database
contained 720 patterns (360 patterns for one-word
sentences and 360 patterns for multiword sentences).
One-word sentences are important for analysis of
disordered children’s speech. The ability to
formulate emotions is unbalanced among children
with a massive disorder, leaving them able to
perceive and formulate only isolated words. The
ability to distinguish emotions is one of the
important aims in the therapeutic process.
The success of prosody control is clearly depen-
dent on the labelling of the natural speech signal in
the database. Labelling (determination of boundaries
between speech units) and phonetic transcription of
sentences from the speech corpus is performed in the
phase of pre-processing.
As we mention in paragraph 2.2, the musical
intervals (for example the quint – the ratio of the
fifth tone divided by the first tone, with a numerical
value of 1.498) were used for emotion
characterization. The reference frequency, i.e. the
fundamental frequency in our case, is given by the
choices in each utterance feature, for which we use
the autocorrelation function. The frequency ratios
are compared with the music intervals and the input
vector for KSOM training is computed.
3.3 Software
One of the goals of our research is to create a
software pack with a user-friendly interface for
medical doctors or other medical staff. Its base is
formed with SOM Toolbox, developed in the
Laboratory of Information and Computer Science
(CIS) of the Helsinki University of Technology and
is built using the MATLAB script language. The
SOM Toolbox contains functions for creation,
visualization and analysis of the Self-Organizing
Maps, and is available free of charge under the
General Public License from (Vesanto at al., 2000).
For the project, new special M-files, which should
be a part of the supporting program package, were
created (Tuckova at al., 2009). The batch algorithm
was chosen because it ignores the order of vectors in
the training set and the results are therefore more
stable.
The software compares between patterns
retrieved from healthy children’s utterances and the
utterances of children with the disorder. The
comparison is per-formed on two sets: the first is the
set of patterns obtained from utterances of healthy
children menti-oned above. The second is the set of
patterns from dysphatic child utterances. The
processing is the same for both input sets: after
parametrization, they are classified utilizing
previously trained maps, which is performed
separately for each parametriza-tion and for each
group of utterances. The resulting vectors are then
compared on the basis of the occu-rrence of specific
features in each input set. Additi-onally, the software
allows for comparison of the utterance of one
dysphatic child to the utterances of a specific group
of children (based on age, gender, similar disease,
etc.). The same software was inde-pendently used
for emotion classification.
4 EXPERIMENTS
In the experiments describing disordered speech
analysis, we analyzed the vowel mapping. Our
method involves clustering the pattern characte-
ristics visible by the allocation of the vowels
respectively by changes in allocation of the vowels
pronounced by the patients. To avoid such a mal-
adaptation, we built up a database consisting of utte-
rances of 72 healthy children (44 female and 28
male) between the ages of 4 and 10. The number is
not final, as we are still working on the extension of
the database. The database is not limited solely to
the purpose of the described method: it is also
intended for use by the students in advanced signal
processing courses. Figures 1and 2 display the re-
sults of the classification. Each figure shows the
trained KSOM for vowels, with each colour repre-
senting one vowels ( red colour for “a”, orange
SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS AS DATA CLASSIFIERS IN MEDICAL APPLICATIONS
425
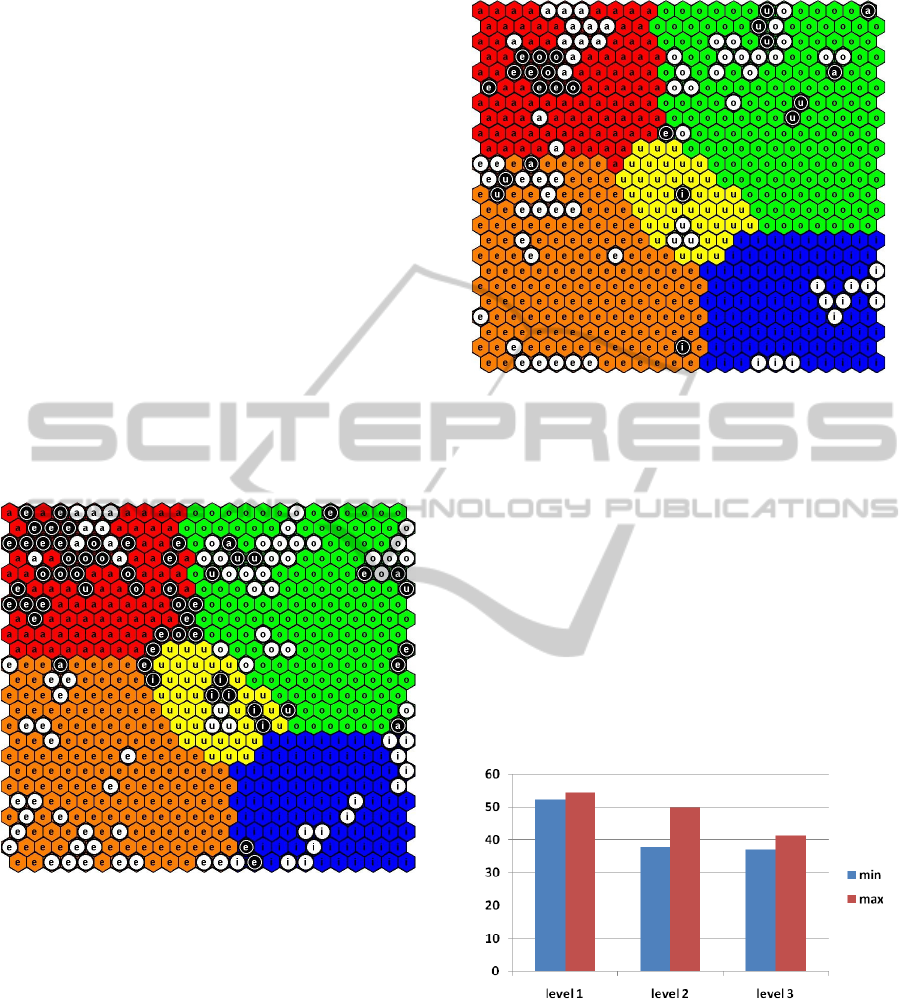
colour for “e”, blue colour for “i”, green colour for
“o” and yellow colour for “u”). The training set
consists of the utterances of all healthy children in
the database. Utterances from a child with SLI are
then classified and shown within the map. White
units indicate the successful classifications from the
map trained by the speech data of healthy children,
black units represent classification errors (wrong
vowel indications are written in units). Their number
and location in the map change after each recording,
depending on the change of the state of health of the
patients. Likewise, the ability for good pronuncia-
tion depends on age. The aim of medical therapy is
to achieve a minimum of wrong classifications. Data
analysis is, however, aggravated by the following
fact: afflicted children are not able to pronounce
certain vowels (the monitored children have
displayed problems with the pronunciation of ”e”,
”i”, and at certain times with ”u”). The obtained
results are confirmed by psychological evaluation of
patients and by the results of the EEG.
Figure 1: Map for vowel classification of the children with
SLI – the first record.
The same children were examined in the course
of three or four-month periods, when they
underwent logopaedic therapy. After each period,
the same utterances are recorded and analyzed. The
classification result is given in figure 2. As could be
observed, the number of misclassified features is
significantly lower, which shows improvement, and
this finding is confirmed by the results of medical
examinations.
As described above, these results could also be
quantified, which allows us to perform statistical
evaluations and calculate the accuracy of the results.
Figure 2: Map for vowel classification of the same
children with SLI – 6 months later.
The other problem which we address through
KSOM is the specification of the SLI level. We
evaluated 22 healthy children (for KSOM training)
and 22 patients. Our goal was distribution of the
patients into 3 classes according to SLI level (level
1-mild, level 2-medium, level 3-severe SLI) – figure
3. We located the success rate (SR) of the vowel
classification in a map with a grid size of 24x24.
Input data were created by the vectors with 8
autoregressive coefficients. The speech therapists
specified 3 groups of patients, which were marked as
group 1 for mild SLI, group 2 for medium SLI and
group 3 for severe SLI.
Figure 3: Success rate for SLI levels. The blue colour
represents the minimal value, the violet colour represents
maximal value of SR.
The blue or violet colours represent the minimal
resp. maximal value of SR. Levels of SLI are
represented on the x-axis as levels 1, 2, and 3 from
the left. Table 1 summarizes minimal, maximal and
average values of SR for 3 categories of SLI. The
classification success for all 22 patients is shown in
Figure 3. We can deduce that through the use of
NCTA 2011 - International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
426
KSOM on the base of vowels classification, it is
possible to distribute the patients into several classes
(in our case 3). The average values of SR were 53%,
44% and 39%, for healthy children 87% (rounded).
The coefficient of correlation between SR and SLI
relevance levels was -0.7755.
Table 1: SLI levels: level 1 for mild, level 2 for medium,
level 3 for severe SLI.
level min [%] max[%] average[%]
1 52.2407 54.4056 53.3237
2 37.6723 49.8029 44.0436
3 36.9919 41.3514 38.7180
In the experiments describing emotion
classification, we prepared the input vector for
SSOM training with 29 patterns, which were created
from 20 values containing the ratios relating to the
musical intervals and 9 values describing the
acoustic qualities of the utterance feature (arithmetic
average of absolute value, standard deviation,
maximum and minimum in the time domain, the
fundamental frequency F
0
and formant frequency F
1
,
F
2
, F
3
, F
4
in the frequency domain). The size of the
map was 15x15, while quantization (QE) and
topographic (TE) errors of the map were also
computed. The TE figure predicts the conservation
of data topology between input and output space,
while QE reflects the accuracy of the mapping
(related to the number of the input matrix elements
and the size of the map). The success of the SOM
training depends on the size of the maps and on the
number of training samples. Table 2 shows TE and
QE for one-word (I) and multi-word (II) sentences.
Table 2: The success of emotion classification by SSOM
for input data based on musical intervals and for input data
supplemented with acoustic features.
Error I II
TE
20
/ TE
29
0.014 / 0.011 0.017 / 0.006
QE
20
/ QE
29
0.274 / 0.431 0.275 / 0.439
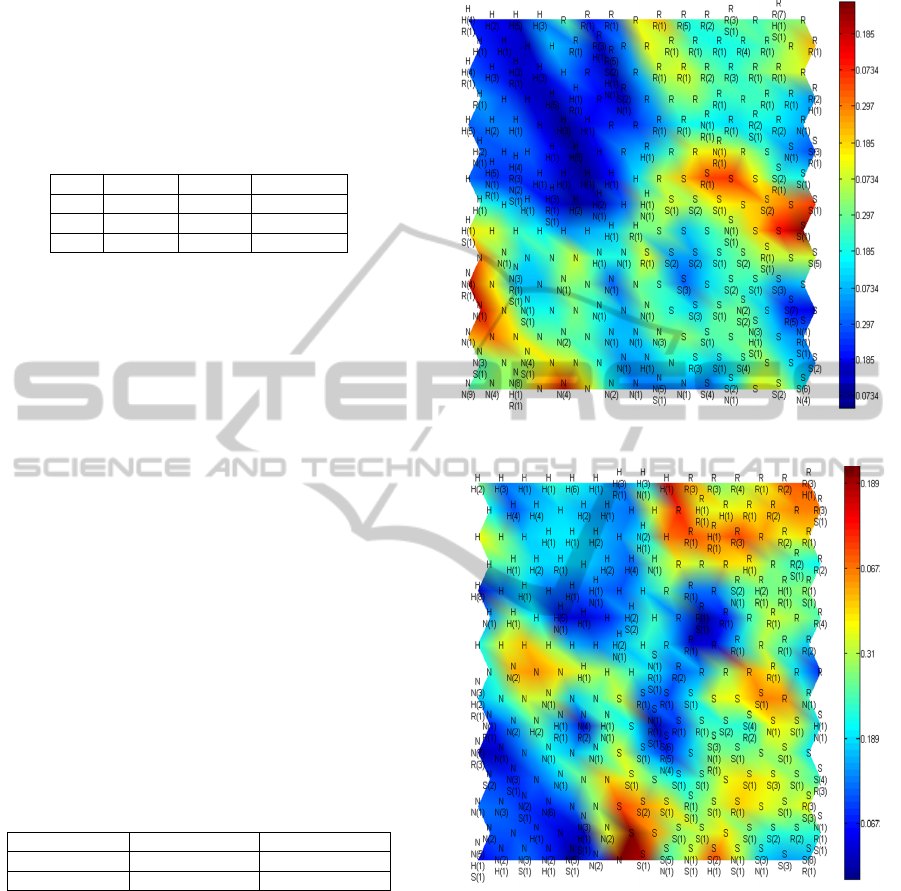
The U-matrix in Figures 4-5 represents the
emotion classes for one-word and multi-word
sentences (for 29 input parameters). The KSOM
neurons are represented by hexagonal cells (in our
experiment) marked by ’H’ for anger, ’N’ for
tedium, ’R’ for pleasure and ’S’ for sadness. Each
cell is also marked by a character for class, by real
classified the font and number registered patterns.
The most separated clusters (largest distance) are
also most different in colour coding - dark blue
(down) and dark red (up). It relates to emotions as
Anger or Pleasure - dark blur and Sadness - dark red.
Tediousness is marked by light blue, close in the
scale to yellow used for Sadness.
Figure 4: U-matrix for one-word sentences.
Figure 5: U-matrix for multi-word sentences.
The results depend also on the precise
identification of the emotions by listeners at process
of the database creation. Both passive emotions are
negative, unpleasant for listeners. The pair of active
emotions, by contrast, gives a better feeling to the
listeners.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Our research involves an original method for the
SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS AS DATA CLASSIFIERS IN MEDICAL APPLICATIONS
427

intensity of speech defect monitoring in child
patients with developmental dysphasia. We draw
upon a body of knowledge consisting of phonetics,
acoustics and ANN applications. The KSOMs were
chosen for solving part of the project. New variants
of the SSOM were tested theoretically and
experimentally after the first experiments with the
Kohonen SOM.
We will concentrate on deeper analysis of child
speech, mainly devoting attention to longer speech
units (syllables, multi-syllabic words) and the
inability to formulate multi-syllabic words (three
and four syllables) or phoneme overlap faults, which
are other symptoms of developmental dysphasia.
The processing of speech signals is complicated by
the effect of the real environment (non-professional
speakers, high noise in the environment if the speech
was recorded in ordinary rooms). The second
problem that we have to address is the fact that we
are analyzing children’s speech. Often, its own
specific development is not complete for a particular
age group, or the quality of the utterances is strongly
influenced by emotion, the latter factor being one of
the reasons why we start with emotional speech
research. Also, we have at our disposal only a small
amount of speech data, especially for patients, even
though a permanent database is kept of child
speakers. The size of the database of healthy child
speech is also limited by the possibilities of data
recording in preschool and primary school
institutions, especially with respect to the concern
over parent permissions. We assume that it would be
necessary to open a sizable screening project during
preventive medical checkups of small children. The
self-organizing maps are favourable for persons
without an engineering background, primarily for
the ability to visualize higher-dimensional data
samples in a low-dimensional display. In the initial
phase of our research project we have been
concentrated on the verification of KSOM ability to
classify SLI patients into three classes. This
classification has been based on their speech
analysis. The pilot study confirms our premises (see
Figures 1, 2 and 3). In the future, we aim to focus on
the search for correlation between disordered speech
analysis and the localization of the brain failure, in
order to achieve a SLI diagnosis jointly with
neurologists.
One of the long-time goals of our research is to
create a soft-ware pack with a user-friendly interface
for doctors or other medical staff.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by grant GACR No.
102/09/0989 and by the research program Trans-
disciplinary Research in Biomedical Engineering
No. II. MSM 6840770012 of the Czech University
in Prague.
REFERENCES
Dlouha, O., Novak, A., Vokral, J., 2007. Central Auditory
Processing Disorder (CAPD) in Children with Specific
Language Impairment (SLI). In International Journal
of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, Vol. 71, Issue 6,
pp.903-907.
Hrncir, Z., Komarek, V., 2004. Analyses of EEG recor-
dings. In Neural Network World, Int. Journal on Non-
Standard Computing and Artificial Intelligence, vol.
14, no. 1, pp. 21–25.
Kohonen, T., 2001. Self-Organizing Maps. Springer–
Verlag, 3rd edition.
Krcmova, M., 2008. Phonetics and phonology [online].
Brno : Masarykova univerzita, [cit. 2010-04-04], (in
Czech) http://is.muni.cz/elportal/?id=766384. ISSN
1802-128X.
Love, R. J., Webb, W. G., 2001. Neurology for the
Speech-Language Pathologist. Elsevier Inc., New
York, USA. ISBN-13: 973-0-7506-7252-8.
Mahmoud, A. M., Hassan, W. H., 2009. Determinism in
speech pitch relation to emotion. In Proceedings of
the 2nd international Conference on interaction
Sciences: information Technology, Culture and
Human, Seoul, Korea, Nov. 24–26, vol. 403, ACM,
New York, NY, pp. 32–37.
Palkova, Z., 1994. Phonetic and phonologic of the Czech.
Karolinum, Prague (in Czech).
Pospisilova, L., 2005. Diagnostics questions of develop-
mental dysphasia. In Vox pediatrie, journal of general
practitioner for children and young, vol. 5, no. 1, pp.
25–27, (inCzech).
Tuckova, J., Komarek, V., 2009. Effectiveness of speech
analysis by self-organizing maps in children with
developmental language disorders. In Neuroendocri-
nology Letters, vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 939–948.
Tuckova, J., Bartu, M., Zetocha, P., 2009. Artificial neural
network applications in signal processing (in Czech).
Teaching text, Česká technika-nakladatelství ČVUT,
Praha, ISBN 978-80-01-04400-1.
Tuckova, J., Sramka, M. 2010. Emotional Speech
Analysis using Artificial Neural Networks. In Proc.
Int. Multiconf. on Computer Science and Information
Technology (IMCSIT2010), Wisla, Poland, ISBN
NCTA 2011 - International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
428

978-83-60810-22-4.
Vesanto, J., Himberg,J., Alhoniemi, E., Parhankangas J.,
2000. SOM Toolbox for Matlab 5, Helsinki University
of Technology, ISBN 951-22-4951-0. Homepage of
SOM Toolbox: www.cis.hut.fi/projects/somtoolbox
Xiao, Z., Dellandrea, E., Dou, W. W., Chen, L., 2010.
Multi-stage classification of emotional speech
motivated by a dimensional emotion model. In
Multimedia Tools and Applications Journal, Springer
Netherlands, vol. 46, Nu 1/January, pp. 119–145,
ISSN 1380-7501.
Zetocha, P., 2008. Design and realization of children
speech diabase. In Ministry of Education grant FRVS,
No.2453/2008 (in Czech)
SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS AS DATA CLASSIFIERS IN MEDICAL APPLICATIONS
429
