
ANALYSIS OF METHODS AND TECHNICAL TOOLS
FOR TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
Rosen Vitanov, Plamen Balzhiev and Roumen Arnaudov
Faculty of Telecommunication, Technical University,8 Kl. Ohridski blvd., Sofia 1000, Bulgaria
rosenvitanov@mail.bg, baljiev@abv.bg, ra@tu-sofia.bg
Keywords: Road traffic and control, Counting vehicles, Measurement.
Abstract: In this article we analyse different methods for remote non-contact counting of moving objects at different
speeds: video, mechanical, optical, ultrasonic. The principles of their implementation, advantages and
disadvantages are described and the reliability of information processing methods is evaluated. A model of
road traffic measurement and analysis system is presented. It is specially emphasized on application of
different sensors in real-time data acquisition, management and analysis of traffic intensity.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, everyone is faced with road traffic
problems due to the ever growing urban population,
the formation of mega-cities, the inability of the road
infrastructure to take the ever increasing road traffic
stress and inefficiency of the existing traffic
management systems. To solve those problems it is
necessary to collect, analyse and systematize traffic
information - when and where traffic is densest,
what vehicles cross the road - cars, vans, trucks,
buses. Obtaining the data requires the use of
different methods and tools for identification and
counting of the moving vehicles.
Once the information is obtained it can be
organized and used to build intelligent systems for
traffic management and statistical databases. It will
be useful in various business areas such as logistics,
navigation, courier services in search of the most
efficient way of transportation to reduce fuel costs,
saving time and hence reduce air pollution.
Therefore, information needs to be frequently
updated and to be with the highest precision.
Collected information can be used for traffic
signalization systems, opening or closing highway
roadbeds. It can also be stored in databases and
analysed at later stages in case a decision have to be
taken if a road must be created, when a maintenance
should be carried out or how road infrastructure
must be changed.
This article aims to make comparisons between
various methods of traffic detection, highlighting
their strengths, weaknesses, areas of application,
efficiency, the most common errors in measurement
and finally make brief conclusions.
2 ROAD TRAFFIC DATA
COLLECTION SYSTEM
As defined by The National Electrical
Manufacturers Association [NEMA] it is "a system
for indicating the presence or passage of vehicles."
An information system responsible for collecting
data about road traffic in real time from one or many
junctions, highways, roads or streets requires sensors
to be deployed to count the passing cars. To obtain
more detailed information multiple sensors have to
be placed on a sufficiently large number of places.
Therefore, the designed systems should be cost-
effective, with great accuracy, not to be easily
broken, to require minimal (or not any at all)
changes on the existing road infrastructure, without
interference with the natural flow of vehicles, to be
easily moved from one place to another, to be easily
accessible.
All mentioned requirement demand
sophisticated, intelligent systems that can manage to
process and analyse all the acquired data from the
sensor network and detect certain events on the road.
On Figure 1 presents intelligent traffic monitoring
and analysis system. It includes several traffic
detection units which count and transmit data to the
data acquisition and analysis unit for processing. All
145
Vitanov R., Balzhiev P. and Arnaudov R.
ANALYSIS OF METHODS AND TECHNICAL TOOLS FOR TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS.
DOI: 10.5220/0004459601450148
In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design (BMSD 2011), pages 145-148
ISBN: 978-989-8425-68-3
Copyright
c
2011 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

data and result could be monitored and further
processed.
Figure 1: Road traffic data collection and analysis system.
3 ROAD TRAFFIC DATA
COLLECTION METHODS AND
SENSORS
Nowadays there is a great variety of efficient vehicle
detection methods. “In order to assess the present
and future traffic demands, for the development of
need-based infrastructure accurate information and
continuous monitoring of traffic is necessary”
(Ministry of Works and Transport of , Gaborone,
Botswana, 2004, Chapter 1.2)[MWTGB]. Traffic
count technologies can be in general divided by the
place, where sensors are situated - in-the-roadway
(intrusive) and over-the-roadway (non-intrusive).
3.1 Intrusive Methods
Intrusive methods rely on direct interaction between
the vehicle and the sensors along the road. The
implemented sensors are deployed can be divided in
three groups - embedded in the road pavement,
embedded in the sub-grade of the road, taped or
attached to the surface of the road. Typical
representatives of the in-the-road methods include
inductive-loop detectors, which are saw-cut into the
pavement; magnetometers, which may be placed
underneath a paved roadway or bridge structure; and
tape switches, which are mounted on the roadway
surface.
3.1.1 Pneumatic Sensors
Pneumatic sensors rely on a direct hit of a vehicle to
detect it. In most cases a “rubber tubes are placed
across the road lanes to detect vehicles from
pressure changes that are produced when a vehicles’
tires passes over the tube. The pulse created is
recorded and processed by a counter located on the
side of the road. The main drawback of this
technology is that it has limited lane coverage and its
efficiency is subject to weather, temperature and
traffic conditions. This system may also not be
efficient in measuring low speed flows (Leduc,
2008).
Another drawback is the great wear factor of the
tubes - the more vehicles cross the tubes the bigger
chance of micro punctures to appear. Constant
changes of seasons will make the rubber degrade
more rapidly than usual. Another drawback is the
tubes must be filled with temperature independent
gas, like Nitrogen, so the pressure inside them will
not rely on any environment changes. Also if two or
more cars hit the tube at the same time, sensor will
miscount. On the other hand they are very easily
deployed on the road. They need no other
preparations (like digging the road or mounting on
poles). Suitable for short-term counts of roads with
low traffic (suburb roads, etc.).
3.1.2 Optical Fiber Sensing
Optic fibers placed in plastic and/or rubber tubes
could be implemented as detection sensors. When a
vehicle passes over the fiber a fluctuation of the light
stream appears. A photo-receiver detects the changes
in the optical signal and converts them in electrical
impulses. Due to tenderness of the fiber core it can
be easily damaged by heavier or high-speed moving
vehicles. Therefore this method needs a thicker
housing for better protection of the optic fiber. Some
of the drawbacks due to weather conditions in
pneumatic sensors are missing – like weather and
temperature dependencies. For insurance, the fiber
optic cable can be put into pre-cut line in the road,
and then fixed with flexible gum. Figure 2 presents a
measured signal of external interference on the
optical fiber. As seen there is a noticeable change in
measured signal which could be utilized in traffic
measurement and analysis.
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0 102030405060708090100
Light Intensity
Nubmer of Samples
Figure 2: Fiber optic signal and movement detection.
BMSD 2011 - First International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
146
3.1.3 Piezoelectric Sensors
Piezoelectric sensors described by Vehicle Detector
Clearinghouse (2000)[VDC], are sensors that use
piezoelectric effect to detect passing vehicles.
Drawbacks of this method are that a certain part of
the pavement must be cut. In winters if a pile of
snow is on the road the sensor may miscount. Sensor
can brake if it is exposed to extreme stresses. They
are independent to weather and climate changes.
Also a miscount may occur when the road's surface
extrapolates due to extreme temperatures.
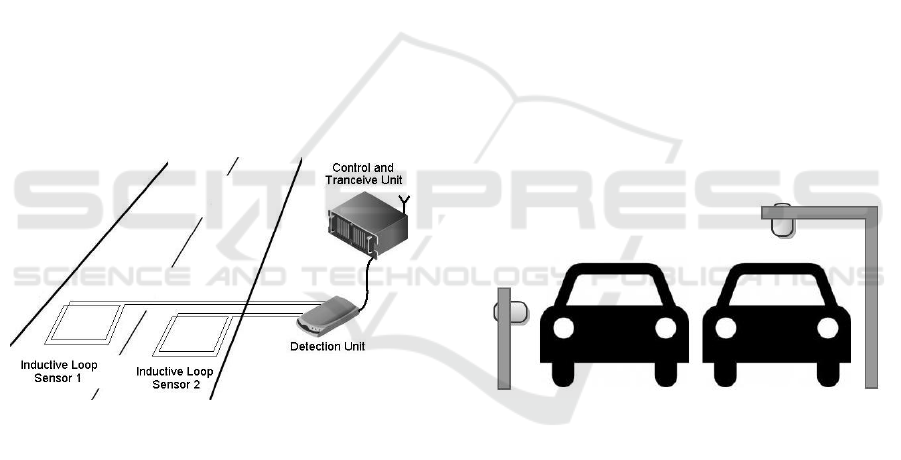
3.1.4 Inductive loop Sensors
Inductive-loops sensors (Figure 3) are wires that are
placed under the road surface in square-like shape.
They are connected to a detection unit which
collects traffic data. Then an electrical signal is fed
to the wires and electromagnetic field is created.
When a car passes over it the induction of the loop
changes and a vehicle is detected ([VDC,
2000],[MWTGB, 2004]). However this method is
expensive due to the fact that the inductive-loop
must be placed beneath the road surface.
Figure 3: Implementation of inductive loop sensors.
Non intrusive methods are methods where traffic
counting sensors do not interact directly with the
passing vehicles. They need less preparation time,
efforts and
3.2 Non-intrusive Methods
Non intrusive methods are methods where traffic
counting sensors do not interact directly with the
passing vehicles. They need less preparation time,
efforts and investments. Most of them are located
above the road lanes, others like video image
processing cameras, can be placed next to the road,
which leads to minimum or to none deployment
time, money and work. „Examples of over-roadway
sensors are video image processors that utilize
cameras mounted on tall poles adjacent to the
roadway or traffic signal mast arms over the
roadway; microwave radar, ultrasonic, and passive
infrared sensors mounted in a similar manner; and
laser radar sensors mounted on structures that span
the lanes to be monitored“ [USDT,2006].
3.2.1 Manual Counting
Manual counting is quite common method for
counting traffic. Not too expensive, does not need
any preparations. Data is recorded on a paper or in a
computer by one or two specially trained
professionals (Klein, Mils, Gibson 2006). However
it’s not suitable for long-term data collection or
highways with intense traffic. Some counting error
may occur due to “human error” factor.
3.2.2 Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors can be also divided in two groups
active and passive. Passive are not very accurate on
high-intense traffic areas. That's why they are not
widely-accepted. On the other hand active sensors
count at greater precision. They emit their own
sound wave which reflects form vehicle’s surface
and is received by a sensor.
Figure 4: Sideway and over-road ultrasonic sensor
implementation and detection.
Using some signal-processing algorithms speed
and direction could be measured and vehicle
classification could be estimated. They are weather-
independent, cannot be easily tricked and can be
used on high-traffic roads and highways. Also they
can determine with incresed accuracy vehicle types
even detect trailers [VDC, 2006].
3.2.3 Video Image processing
Video image processing is a method where instead
of sensors a video camera is used to detect traffic
and vehicles. Images from the camera are sent by
wire (or wirelessly) to a remote station where
images are stored and processed. There are many
ANALYSIS OF METHODS AND TECHNICAL TOOLS FOR TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
147

algorithms for detecting vehicles on the road – like
signal processing, artificial neuron networks, bitmap
processing etc. After a vehicle is detected another
algorithm is started to detect its speed, direction, and
even dimensions.
This method can provide us with different kind
of information. As this is still a developing
methodology there are some miscounts and system
can be easily fooled. It depends on the weather
conditions for example in foggy or too snowy
conditions nothing will be detected. Front protecting
glass of camera has to be cleaned frequently
otherwise the camera will not be able to detect
anything [VDC, 2007],[MWTGB, 2006], (Klein,
Mils, Gibson 2006).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Intrusive methods for vehicle counting purposes
need preparation steps, such as cutting big parts of
the road surface, deploying sensors, reconstruction
of the cut slots after sensors were deployed. This
with no doubts leads to more expenses,
inconvenience to drivers since the road has to be
closed for a certain period of time (depending on the
size of the project). Sensors can be easily broken due
to constant interaction with the passing vehicles or
due to cavities in the pavement, which will uncover
the sensors. They are suitable for small roads, where
traffic is not quite intensive and closing the road will
not lead to major inconvenience for drivers. The
accuracy and the reliability in some of them depend
on weather conditions and sometimes they may give
wrong information.
On the other hand non-intrusive methods are
more easily-installable to the existing infrastructure.
Their positioning is easier than intrusive sensors,
because there is no need of any road modifications.
Some of them are vulnerable to weather conditions,
but measure with greater accuracy. Further more
there is no need traffic to be stopped during their
installation. If a short-term measurement is needed
without road interventions, pneumatic method or
optical sensors are most appropriate.
REFERENCES
Leduc, G., 2008. Road Traffic Data: Collection Methods
and Applications. JRC 47967, European Commission,
Joint Research Centre, Institute for Prospective
Technological Studies.
2004. Traffic Data Collection and Analysis, Ministry of
Works and Transport, Roads Department, Gaborone,
Botswana.
Klein L. A., Mills M. K., Gibson, D. R. P., 2006. Traffic
Detector Handbook: Third Edition, Vol.1- FHWA-IP-
90-002, US Department of Transportation publishing
company.
Gibson, D., Milton K. Mills, Klein L. A., 2007. A New
Look at Sensors, Vehicle Detector Clearinghouse
publishing company.
Hoshide, G. Evaluation of Recreation Traffic Counters,
United States Forest Service.
Luz Elena Y. Mimbela. A Summary of Vehicle Detection
and Surveillance Technologies.
Luz Elena Y. Mimbela, 2000. A Summary of Vehicle
Detection and Surveillance Technologies use in
Intelligent Transportation Systems book, Vehicle
Detector Clearinghouse.
2006. Freeway Management and Operations Handbook
book, US Department of Transportation.
Hoshide, G. Evaluation of Recreation Traffic Counters,
United states forest service.
2004. Traffic Data Collection and Analysis, Ministry of
Works and Transport, Roads Department, Gaborone,
Botswana.
BMSD 2011 - First International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
148
