
A WEARABLE GAIT ANALYSIS SYSTEM USING INERTIAL
SENSORS PART II
Evaluation in a Clinical Setting
A. Sant’Anna
1
, N. Wickstr
¨
om
1
H. Eklund
2
and R. Tranberg
3
1
Intelligent Systems Lab, Halmstad University, Halmstad, Sweden
2
Center for Person-Centered Care, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
3
Department of Orthopedics, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Keywords:
Gait Analysis, Inertial Sensors, Symmetry, Normality, Clinical Environment.
Abstract:
The gold standard for gait analysis, in-lab 3D motion capture, is not routinely used for clinical assessment due
to limitations in availability, cost and required training. Inexpensive alternatives to quantitative gait analysis
are needed to increase the its adoption. Inertial sensors such as accelerometers and gyroscopes are promising
tools for the development of wearable gait analysis (WGA) systems. The present study evaluates the use of
a WGA system on hip-arthroplasty patients in a real clinical setting. The system provides information about
gait symmetry and normality. Results show that the normality measurements are well correlated with various
quantitative and qualitative measures of recovery and health status.
1 INTRODUCTION
Gait analysis (GA) is a tool that can aid the assess-
ment of several physical and cognitive conditions.
Perhaps the most widely adopted use of GA is in
the treatment of cerebral palsy children (Chang et al.,
2010), (DeLuca et al., 1997). A few other areas
have also investigated GA as an aid to clinical assess-
ment, e.g. Parkinson’s disease (Salarian et al., 2004),
(Frenkel-Toledo et al., 2005), and stroke (Cruz and
Dhaher, 2008), (Silver et al., 2000). Despite many
positive results, GA is still not routinely used in the
clinical setting.
Several factors contribute to the low adoption of
GA as a clinical tool. The gold standard for GA is 3D
in-lab motion capture (MOCAP), which can consider-
ably improve clinical assessment, e.g. (Lofterød and
Terjesen, 2008), (Morais Filho et al., 2008). However,
the interpretation of results requires specific training
and experience, and its use as a routine procedure is
not widely accepted from an economical perspective
(Simon, 2004). In addition, a state-of-the-art MO-
CAP system is often not available in small practices
and underpreviledged areas. The alternative to MO-
CAP is observational gait analysis (OGA), which is
intrinsically subjective and sensitive to the observer’s
experience (Toro et al., 2003). Nonetheless, in 1999
Coutts (Coutts, 1999) argued that despite its limita-
tions, OGA would never be totally replaced as the de-
fault GA method in the clinical environment because
of ease of use.
Recently large efforts have been employed in de-
veloping low-cost, mobile GA systems that can com-
plement OGA with objective, reliable, quantitative
data. The success of such systems will hopefully in-
cur in a wide-spread adoption of quantitative GA as
a clinical tool. The design of these system may be
guided by a few practical requirements:
• Easy to use: It is important that the system require
no special training and very little extra effort from
the staff in order to ensure cost effectiveness. It is
also desirable that the system be used quickly and
independent of infrastructure/location.
• Unobtrusive: To spare patients, who may be in
pain or discomfort, the system must be small, light
weight, and comfortable to wear. In addition, the
system should not interfere with the patient’s nat-
ural movements. Cumbersome equipment may
make the patient feel self conscious, and act un-
naturally.
• Valid and reliable: The information acquired by
the system must be accurate, and representative
of clinical assessment.
• Easy to interpret: Kinematic information and
other specific gait parameters are mostly useful
5
Sant’Anna A., Wickström N., Eklund H. and Tranberg R..
A WEARABLE GAIT ANALYSIS SYSTEM USING INERTIAL SENSORS PART II - Evaluation in a Clinical Setting.
DOI: 10.5220/0003707700050014
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2012), pages 5-14
ISBN: 978-989-8425-89-8
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

for clinicians who have experience with gait anal-
ysis. To ensure wide-spread adoption, the system
must provide intuitive and easy to interpret infor-
mation.
The present study aims at developing a small
wearable system that fulfills the above requirements,
and can be successfully deployed in the clinical set-
ting. Part I of the study introduced a symbolic ap-
proach to the analysis of gait symmetry and normal-
ity using miniature accelerometers and gyroscopes.
The proposed method was then compared to symme-
try and normality measures extracted from 3D MO-
CAP kinematic data.
Part II now investigates the viability of using the
system to evaluate patients in a real clinical setting.
The data collection took place at the orthopedic ward
at Sahlgrenska Univeristy Hospital, M
¨
olndal, Swe-
den. Eleven unilateral hip-arthroplasty patients un-
derwent GA with the proposed system at discharge,
and once again approximately three months later.
Measures of symmetry and normality were derived
and evaluated against a timed 10-meter walk test and
a EQ-5D health questionnaire.
2 RELATED WORK
Due to limitations in availability, cost and training
required for 3D GA, this section only discusses GA
methods that can be performed inexpensively and in-
dependently of a MOCAP gait lab, namely observa-
tional gait analysis (OGA) and wearable sensor sys-
tems.
2.1 Observational Gait Analysis
Observational gait analysis (OGA) can be further di-
vided into: naked eye observation (NE-OGA), and
video-aided observation (VA-OGA). VA-OGA has a
clear advantage over NE-OGA in that it allows more
freedom to the observer, enabling pause, slow motion,
and other functions. In some cases, quantitative mea-
surements, such as joint angles (Embrey et al., 1990),
can be directly calculated from the image.
VA-OGA is often accompanied by a form or ques-
tionnaire that facilitates the extraction of relevant in-
formation from the video. These forms typically em-
ploy binary or gross estimates of variables, such as
Presence/Absence or Normal/Mild/Sever. Very fre-
quently, new questionnaires are developed for specific
studies or clinics, e.g. (Brunnekreef et al., 2005),
(Kawamura et al., 2007). Although various ques-
tionnaires evaluate similar features, they often differ
largely in rating scheme and variables of interest.
Two VA-OGA forms have been more thoroughly
investigated and more widely adopted: the Visual
Gait Assessment Scale (VGAS) (Dickens and Smith,
2006), (Brown et al., 2008) and the Edinburgh Visual
Gait Score (EVGS) (Read et al., 2003), (Ong et al.,
2008). Both questionnaires target the assessment of
ambulatory children with cerebral palsy. Form and
questionnaires have also been used to aid NE-OGA.
The physician Rating Scale seems to be the most fre-
quently used, (Koman et al., 1993), (Maathuis et al.,
2005), (Wren et al., 2005), also targeted to children
with cerebral palsy.
OGA can be complemented by other more quan-
titative measurements, such as average gait speed, av-
erage step length and other gait parameters. These are
typically measured during walking tests, such as the
10-m walking test (Dean et al., 2001), (Kempen et al.,
2011), or the timed up and go test (TUG) (Kristensen
et al., 2007), (Nordin et al., 2008). The TUG is nor-
mally employed in studies where balance and risk of
fall are of interest, as it requires that the subject stand
up and sit down on a chair without help.
The 10-m walking test, on the other hand, is a
simple way of determining, average gait speed, stride
length and cadence. Average gait speed, for exam-
ple, has been identified as an indicator of: activity
of daily living function in geriatric patients (Potter
et al., 1995); high risk of health-related outcomes in
well-functioning older people (Cesari et al., 2005),
and leg strength in older people (Buchner et al.,
1996). Stride length is another interesting measure
that has been associated with, for example, metabolic
cost and impact during walking (Russell et al., 2010),
(Mercer et al., 2003).
2.2 Mobile GA Systems
Current sensor and hardware technologies have made
possible the creation of small wearable systems for
GA. A large number of authors have dedicated their
efforts to developing mobile, simpler alternatives to
3D in-lab GA. Such systems may be categorized
according to the information they produce: spatio-
temporal (ST) parameters, kinematics, or overall
characteristics of gait. These categories are not neces-
sarily mutually exclusive, but they represent different
levels of information complexity.
ST parameters, such as stride time and veloc-
ity, can only convey information about when and/or
where the foot hits the ground. One way to visualize
this is to imagine that ST parameters could be cal-
culated from a series of foot-prints over time. Sys-
tems that measure ST parameters are usually simpler
and more commonly used. Some of the earliest sys-
BIOSIGNALS 2012 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
6

tems employed foot-switches to determine initial and
terminal contact, e.g. (Hausdorff and Ladin, 1995).
More recently, studies have found accelerometer mea-
surements valid and reliable means of determining
walking speed, cadence, stride length and other ST
parameters, e.g. (Saremi et al., 2006), (Senden et al.,
2009), (Bautmans et al., 2011). Although ST infor-
mation can be very useful, it does not represent the
subject’s gait pattern as a whole. It is important to
know what happens between foot-prints.
The second category encompasses those systems
that are able to extract kinematic data such as trajec-
tories, and joint angles. Some of these systems pro-
vide only foot pitch and ground incline in addition to
ST information, e.g. (Sabatini et al., 2005), (Bam-
berg et al., 2008). Others provide measures of joint
angle progressions, segment rotations and accelera-
tions, e.g. (Dejnabadi et al., 2005), (Mayagoitia et al.,
2002b). These systems can provide an inexpensive
alternative to in-lab 3D GA. However, proper training
and experience are required for interpreting kinematic
information. In addition, these systems are too cum-
bersome to be used for extended periods of times.
The third category aims at extracting more gen-
eral characteristics of gait such as gait symmetry
(Gouwanda and Senanayake, 2011), gait regularity
(Moe-Nilssen and Helbostad, 2004), and balance (Al-
lum and Carpenter, 2005), (Mayagoitia et al., 2002a).
Although this information may be derived from ST
and/or kinematic data, systems can be made much
simpler if they directly measure general character-
istics. For example, (Moe-Nilssen and Helbostad,
2004) measures gait symmetry using only one ac-
celerometer placed on the lower back, whereas all
methods mentioned in the previous categories make
use of at least one sensor node on each lower limb.
General characteristics of gait are usually not enough
for determining the cause of the subject’s gait abnor-
mality. However, they are easy to interpret and can be
used to monitor the subject’s progress after treatment
has been established.
Although measures of symmetry have been
largely investigated, measures of gait normality are
lacking. In Part I of the present study a measure
of normality was introduced, derived from three sen-
sor nodes containing accelerometers and gyroscopes.
This measure was compared to measures of normal-
ity computed from 3D kinematic data. In Part II of
the study, the viability and usefulness of the proposed
normality index is investigated in a clinical setting.
3 METHOD
3.1 Data Collection
Eleven patients were included in the study. All pa-
tients had undergone unilateral hip-arthroplasty for
the first time and presented no other physical or cog-
nitive conditions. The group was composed of four
women and seven men, the mean age was 69±15
years, mean weight was 81±20 Kg, and mean height
was 172±9 cm.
The data collection was designed to be very quick
in consideration of the patients, most of whom were
in great discomfort. The patients were equipped with
three Shimmer
R
sensor nodes. One node was placed
on each outer shank, approximately three centimeters
above the lateral malleolus, the remaining node was
placed directly under the navel. Sensors were secured
on the skin with surgical tape. The sensor nodes were
synchronized with the help of beacon signals from a
host computer and the data was stored on-board in a
micro SD card.
The patients were then asked to walk by them-
selves along a 10-meter walkway at a comfortable
speed, twice. The walkway was marked with black
tape on the floor. The time and number of steps taken
to complete the walkway were recorded at each time.
This procedure took place on the day the patient
was discharged from the hospital, and a few months
later, when the patient came back for a follow-up eval-
uation. The average number of days spent at the ward
after surgery was 4±1 day. The time between base-
line and follow-up measurements was 108±15 days.
All patients employed a walking aid during baseline
measurements, six used two crutches and five used a
walker with wheels. During follow-up measurements
six patients used one crutch and five patients walked
without any aiding device.
Patients filled out an EQ-5D
TM
health question-
naire (Swedish version) approximately two weeks be-
fore surgery, and soon after their follow-up session.
The EQ-5D
TM
is a standardized instrument for use as
a measure of health outcome, developed by the Euro-
Qol Group (www.euroqol.org). The English version
of the questionnaire, validated for Ireland, is shown
in Figures 1 and 2. Each answer is given a value from
1 to 3, good health state results in low values.
This study was approved by the Regional Ethics
Board in Gothenburg, Sweden.
3.2 Observational Gait Analysis
The time, Tm, and number of steps, NumSteps, taken
to complete the 10-meter walk test were used to com-
A WEARABLE GAIT ANALYSIS SYSTEM USING INERTIAL SENSORS PART II - Evaluation in a Clinical Setting
7

By placing a tick in one box in each group below, please
indicate which statements best describe your own health
state today.
Mobility
I have no problems in walking about 1
I have some problems in walking about 2
I am confined to bed 3
Self-Care
I have no problems with self-care 1
I have some problems washing or dressing 2
I am unable to wash or dress myself 3
Usual Activities (e.g. work, study, house-
work, family or leisure activities)
I have no problems with performing my usual
activities
1
I have some problems with performing my
usual activities
2
I am unable to perform my usual activities 3
Pain/Discomfort
I have no pain or discomfort 1
I have moderate pain or discomfort 2
I have extreme pain or discomfort 3
Anxiety/Depression
I am not anxious or depressed 1
I am moderately anxious or depressed 2
I am extremely anxious or depressed 3
Figure 1: EQ-5D
TM
Part A: English version validated for
Ireland.
c
1990 EuroQol Group EQ-5D
TM
is a trademark
of the EuroQol Group.
pute average speed, Speed = 10/T m (m/s), and av-
erage step length, StepLeng = 10/NumSteps (m). In
addition, step length was normalized by the patient’s
height. These variables were used as reference for the
improvement of the patient, under the assumption that
average speed and step length should increase as the
patient recovers.
3.3 Inertial Sensor Gait Analysis
The method used to compute symmetry and normal-
ity from the sensor data is described in more detail in
Part I of this study. The sensor data is first symbol-
ized into equiprobable symbols. The periods between
consecutive similar symbols are calculated and repre-
sented as period histograms. Symmetry is calculated
from the gyroscope data of the shanks as the relative
error between the histograms derived from the right
and left sides. Similarly, Normality is derived from
the accelerometer data of the waist as the difference
between the subject’s histograms and histograms de-
rived from a reference set of healthy individuals. The
reference data set was obtained from healthy, con-
To help people say how good or bad a health
state is, we have drown a scale (rather like
a thermometer) on which the best state you
can imagine is marked 100 and the worst
state you can imagine is marked 0.
We would like you to indicate on this scale
how good or bad your own health is today,
in your opinion. Please do this by drawing a
line from the box below to whichever point
on the scale indicates how good or bad your
health state is today.
Figure 2: EQ-5D
TM
Part B: English version validated for
Ireland.
c
1990 EuroQol Group EQ-5D
TM
is a trademark
of the EuroQol Group.
siderably younger individuals, average age 34 ± 13
years, walking normally.
The histograms are normalized to stride time so
as to be independent of stride frequency. This nor-
malization by stride variables is common in kinematic
gait analysis and it ensures that results are not biased
by gait cadence, stride length or speed.
During the follow-up session, the gait of the pa-
tients may be considerably different from those of
the reference group. Nonetheless, it is expected that
patients’ gait patterns approach the reference group
more at follow-up than at baseline.
3.4 Data Analysis
The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was used
to evaluate the correlation between two variables. The
non-parametric Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to
compare two distributions, and a Kruskal-Wallis test
was used to compare more than two distributions. All
linear model approximations were calculated based
on least mean square errors.
The area under the receiver operating character-
istic curve (AUC) was used to evaluate the discrimi-
natory power of the normality index. The ROC curve
was constructed based on tests performed on the same
individuals. Therefore, any statistically significant
comparison between different AUC must take into ac-
count the correlated nature of the data. A nonpara-
BIOSIGNALS 2012 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
8
metric approach based on generalized U-statistics was
used to estimate the covariance matrix of the different
curves (DeLong et al., 1988).
All measurements included two trials, which were
used to assess the test-retest reliability of each index
using intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) type A-
1 as a measure of absolute agreement (McGraw and
Wong, 1996). All tests were bi-directional with con-
fidence level, α = 0.05. All data analysis was under-
taken in MATLAB (MathWorks, Natick, MA).
4 RESULTS
All but one participant answered the EQ-5D
TM
ques-
tionnaire on both occasions. The values of the an-
swers given to each category were added to a single
score for that category. Results from before the op-
eration and after the follow-up session are shown in
Figure 3. Lower scores correspond to more patients
in better health. The biggest changes were regarding
mobility, usual activities and pain/discomfort.
mobility self-care activities pain/disc. anxiety/depr.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
sum of questionnaire scores
before surgery
after follow-up
Figure 3: Questionnaire results from before the surgery and
after the follow-up sessions. Lower scores correspond to
more patients in better health.
Symmetry results for baseline and follow-up mea-
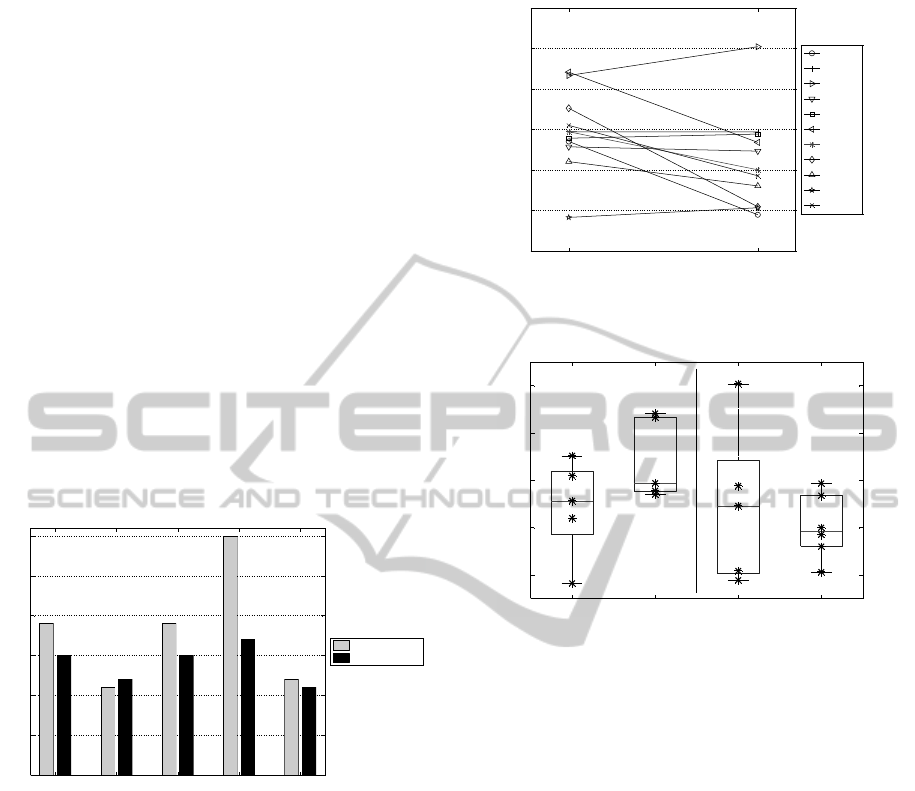
surements are shown in Figure 4 for each subject.
Measurements were averaged over both trials of each
session. The symmetry index ranges from 0 to
100, a low symmetry index indicates good symmetry
whereas a high value indicates asymmetry. Accord-
ing to the proposed index, gait symmetry improved at
follow-up for approximately half the subjects. The
asymmetry at follow-up may be caused by the use
of one crutch. The symmetry index according walk-
ing aid is shown in Figure 5. There is a clear dif-
ference between the symmetry of patients using two
crutches at baseline and patients walking with no aid
at follow-up. However, none of the distributions were
significantly different.
baseline follow-up
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
symmetry - shank sensors
subj1
subj2
subj3
subj4
subj5
subj6
subj7
subj8
subj9
subj10
subj11
Figure 4: Symmetry results at baseline and follow-up. The
two distributions are not statistically significantly different.
walker crutches one crutch none
30
40
50
60
70
symmetry - shank sensors
baseline - follow-up
Figure 5: Symmetry results according to walking aid. Be-
sides the data points, the plot presents box-plot representa-
tions of the distributions. The whiskers represent the small-
est and largest observations, the edges of the box correspond
to the lower and upper quartiles, the horizontal line indi-
cates the median. The distributions are not statistically sig-
nificantly different.
Normality results are shown in Figure 6, measure-
ments for each patient were averaged over both tri-
als of each session. Similarly, the normality index
ranges between 0 and 100, and a low value indicates
good normality. In this case, the follow-up measure-
ments were better than baseline measurements for all
patients. A Wilcoxon test indicated that baseline and
follow-up groups were statistically significantly dif-
ferent, p<0.0001. Figure 7 illustrates the distribution
of the normality index according to walking aid. As
expected, the normality index for those patients walk-
ing without aid was, on average, better than the others.
A Kruskal-Wallis test indicated that the free walking
group was statistically different from the walker and
crutches groups, and that the one crutch group was
statistically different from the walker group.
In order to calculate the correlation between nor-
mality and walking aid, each category was repre-
sented by a number. In the order shown in Figure 7,
walker was represented by 1 and no-aid was repre-
A WEARABLE GAIT ANALYSIS SYSTEM USING INERTIAL SENSORS PART II - Evaluation in a Clinical Setting
9
baseline follow-up
90
95
100
normality - waist sensor
subj1
subj2
subj3
subj4
subj5
subj6
subj7
subj8
subj9
subj10
subj11
Figure 6: Normality results at baseline and at follow-up.
The two distributions are statistically different according to
a Wilcoxon rank sum test, p<0.0001.
walker crutches one crutch none
85
90
95
100
normality - waist sensor
baseline - follow-up
Figure 7: Normality results according to walking aid. A
Kruskal-Wallis test indicates that the distribution of no
walking aid is significantly different from distributions of
two crutches and walker. The one crutch distribution is sig-
nificantly different from the walker distribution. Normality
is well correlated with walking aid, according to a Spear-
man’s rank correlation coefficient of r=-0.78, p<0.0001.
sented by 4. The resulting Spearman’s rank correla-
tion coefficient was r=-0.78, p<0.0001.
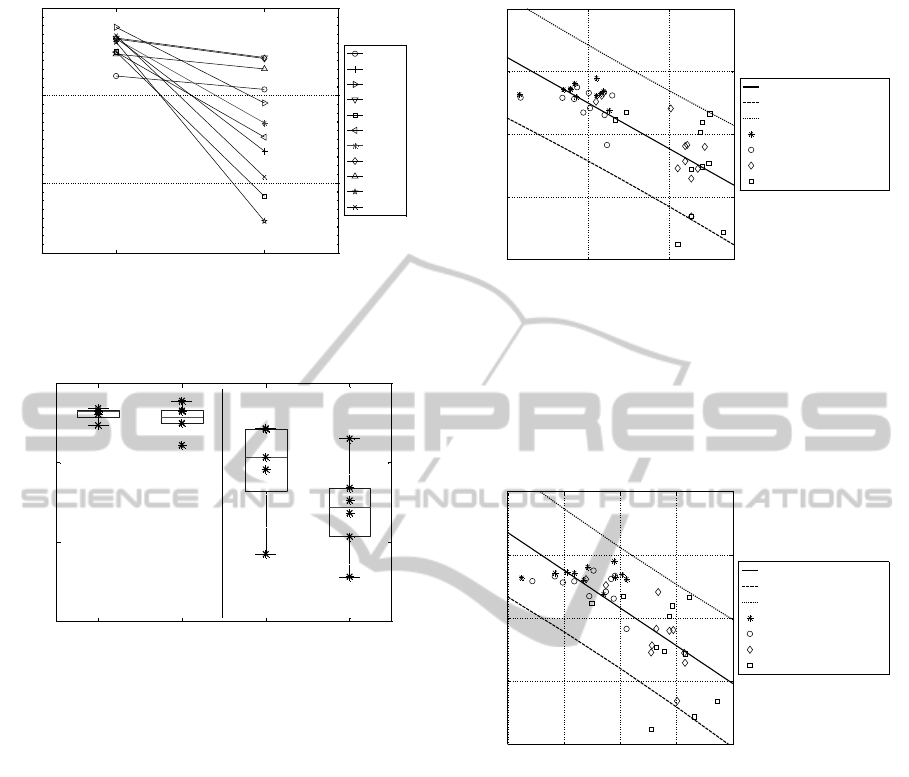
The normality index also correlates well with both
average speed, r=-0.79 p<0.0001, and normalized av-
erage step length, r=-0.76 p<0.0001. Normality val-
ues for each individual trial are shown against aver-
age speed values in Figure 8, and against normal-
ized step length in Figure 9. On both plots the lin-
ear model approximation is shown as a solid line, and
the 95% confidence interval (CI) for predicted obser-
vations is shown as dotted lines. The mean average
speed at baseline, 0.46±0.16 m/s, was significantly
different from the speed at follow-up, 1.06±0.22 m/s,
p<0.0001.
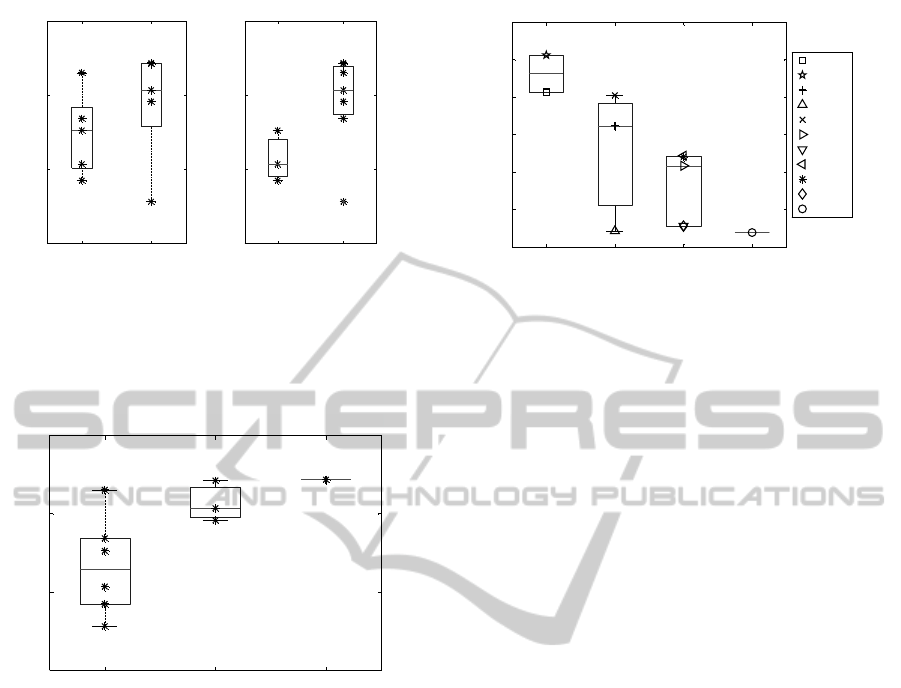
Normality results were also compared to the EQ-
5D
TM
answers that varied the most between be-
fore the surgery and after follow-up, namely mo-
bility (Figure 10), usual activities (Figure 11), and
pain/discomfort (Figure 10). In all cases, there is a
0 0.5 1
85
90
95
100
105
average speed (m/s) - reference data
normality index - waist sensor
fitted curve
lower bound 95% CI
upper bound 95% CI
baseline trial1
baseline trial2
follow-up trial1
follow-up trial2
Figure 8: Normality compared to average speed. Variables
are well correlated, Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient
r=-0.79, p<0.0001. The solid line indicates the linear model
approximation a+bx, where a=95.5 with confidence inter-
val (CI) [94.9, 96.3]; and b=-2.6 with CI [-3.3, -1.9]. The
dashed and dotted lines indicate the 95% CI of predicted
observations.
10 20 30 40 50
85
90
95
100
105
normalized step length (% of hight)
normality index - waist sensor
fitted curve
lower bound 95% CI
upper bound 95% CI
baseline trial1
baseline trial2
follow-up trial1
follow-up trial2
Figure 9: Normality compared to average step length. Vari-
ables are well correlated, Spearman’s rank correlation co-
efficient r=-0.76, p<0.0001. The solid line indicates the
linear model approximation a+bx, where a=95.5 with con-
fidence interval (CI) [94.9, 96.3]; and b=-2.5 with CI [-3.2,
-1.8]. The dashed and dotted lines indicate the 95% CI of
predicted observations.
tendency for better health to be accompanied by bet-
ter normality index. This correlation is particularly
strong between normality and usual activities scores,
Spearman’s r=0.75, p=0.0127. There was no correla-
tion between the health scale in Part B of the ques-
tionnaire and normality.
Improvement in normality was calculated as the
difference between baseline and follow-up values.
Figure 12 shows how improvement in normality cor-
relates with number of days spent at the ward af-
ter surgery. Although a Wilcoxon test indicated that
there was no statistically significant difference be-
BIOSIGNALS 2012 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
10
ans 1 ans 2
85
90
95
100
normality - waist sensor
A) EQ-5D mobility
ans 1 ans 2
85
90
95
100
normality - waist sensor
B) EQ-5D pain/discomfort
Figure 10: Normality compared to EQ-5D
TM
answers re-
garding (A) mobility and (B) pain/discomfort. Mobility an-
swers - ans 1: I have no problems in walking about; ans 2: I
have some problems in walking about. Pain/discomfort an-
swers - ans 1: I have no pain or discomfort; ans 2: I have
moderate pain or discomfort.
ans 1 ans 2 ans 3
85
90
95
100
normality - waist sensor
EQ-5D usual activities
Figure 11: Normality compared to EQ-5D
TM
answers re-
garding usual activities. Ans 1: I have no problems with
performing my usual activities; ans 2: I have some problems
with performing my usual activities; ans 3: I am unable to
perform my usual activities. Variables are well correlated,
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient r=0.75, p=0.0127.
tween groups, the Spearman’s rank correlation coef-
ficient was r=-0.75, p=0.0081. There was no correla-
tion between improvement in normality and days be-
tween baseline and follow-up sessions.
The normality index can also be evaluated based
on its discriminatory values. That is, the ability to
differentiate baseline measurements from follow-up
measurements. The AUC was 0.94, confidence in-
terval (CI) (0.87, 1.00), p<0.0001. The test-retest
reliability was also high, r=0.81, CI (0.60, 0.92),
p<0.0001.
5 DISCUSSION
The average speeds at baseline and follow-up are in
agreement with measurements reported in (Kennedy
2 days 3 days 4 days 6 days
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
Improvement in normality
days at the ward after surgery
subj5
subj10
subj2
subj9
subj11
subj3
subj4
subj6
subj7
subj8
subj1
Figure 12: Improvement in normality compared to days
spent at ward after surgery. Improvement in normality is
the difference between normality values at baseline and at
follow-up. Although the distributions are not statistically
different, variables are well correlated, Spearman’s rank
correlation coefficient r=-0.75, p=0.0081.
et al., 2005), 0.46 m/s less than 16 days after hip re-
placement surgery and 1.17 m/s more than 20 days
after surgery. Average gait speed of approximately
1 m/s three months after surgery were also reported
in (Aminian et al., 1999). According to (Macni-
col et al., 1980) the greatest improvements in gait
speed are observed within the first three months post-
op. The follow-up measurement can, therefore, be
considered representative of patient’s improvement in
gait speed. In addition, (Palombaro et al., 2006) deter-
mined that changes in speed superior to 0.10 m/s are
clinically meaningful after hip fracture treatment. The
changes in speed observed from baseline to follow-
up, 0.60±0.29, are therefore also clinically meaning-
ful.
Measures of gait normality correlate well with
both gait speed, Figure 8 and step length, Figure 9.
Given that speed and step length are measures related
to patient recovery, there is a good chance the normal-
ity index is also a good indicator of recovery. Unfor-
tunately, no other quantitative gait parameters were
available in the data set to demonstrate that the nor-
mality index correlates to recovery when the data is
corrected for speed. However, in Part I of this study
symmetry and normality measures are shown to cor-
relate to joint-angle curves normalized to stride time,
not containing any velocity information. The normal-
ity index is also normalized to stride time and as such
is independent of walking cadence. It is expected that
the normality index would differentiate between nor-
mal and abnormal patterns at the same speed. Further
investigations are needed to support this assumption.
Another factor supporting the usefulness of the
normality index is its correlation with the type of
walking aid used during the test, Figure 7. The test-
retest reliability and discriminatory power of the in-
A WEARABLE GAIT ANALYSIS SYSTEM USING INERTIAL SENSORS PART II - Evaluation in a Clinical Setting
11

dex were also satisfactory. Overall, the proposed in-
dex can possibly be developed into a reliable and clin-
ically relevant measure of gait normality.
Another interesting result was the correlation be-
tween improvement of normality and number of days
spent at the ward, Figure 12. Whereas there was no
correlation between improvement in normality and
number of days between baseline and follow-up. This
possibly suggests that the rate of recovery at the ward
is indicative of the total rate of recovery, which is little
affected by the recovery time at home. This assump-
tion should be further investigated.
Normality results and the answers to the EQ-5D
TM
questionnaire showed some positive trends. Greater
discomfort and difficulties in performing usual activ-
ities seem to be accompanied with worse normality,
Figure 10. Besides the self-assessment questionnaire,
the use of walking aids was also considered an indi-
cation of how well the patient’s health status was, i.e.
patients who did not need any walking aid were, on
average, in better condition than those who used one
crutch. Another indicator of recovery was the num-
ber of days the patient spent at ward, assuming that
patients who recovered better or more quickly were
discharged sooner. The normality index seems to be
in agreement with all the above mentioned qualitative
health status assessments.
Symmetry results are difficult to judge due to the
variety of walking aids used. The large variety of
symmetry at follow-up, Figure 4, was mostly influ-
enced by the patients using one crutch only. This
could be explained by the fact that some patients
were more dependent on the crutch and consequently
leaned more to one side. Whereas some patients
barely used the crutch for support.
Due to their recent surgery, patients were very un-
comfortable during the baseline measurements. It was
important to keep the data collection as simple and
quick as possible. No more than five minutes had to
be spared by the patient to complete the entire pro-
cedure, and they were all willing to participate in the
study. Briefness is also important for the staff respon-
sible for the procedure so that the addition of GA is
not an extra burden. The placement of the sensors was
also quick and easy. However, in the future, the waist
sensor should be placed on the lower back so as not
to be affected by subjects’ different shapes and sizes.
Another issue with the present study is that the
number of participants was very small. Any statistical
inference on the results is greatly affected by the sam-
ple size. However, results are promising and suggest
that a larger study will likely produce positive results.
At the ward where the data was collected, gait
analysis is not normally used, and most records are
based on rough qualitative descriptions. This lack
of quantitative measures makes the assessment of pa-
tient improvement a difficult and very subjective task.
The introduction of a simple 10-meter walk test can
already provide quantitative measures of speed and
stride length. The addition of a wearable GA system,
however, can quickly increase the amount of quanti-
tative data to include more complex measures of sym-
metry and normality.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The present study investigated the viability of using a
wearable gait analysis (GA) system to assess patients
in a real clinical environment. The proposed system
served as a tool to facilitate the extraction of certain
gait characteristics, namely symmetry and normality.
The system was easy to use and did not require more
than five minutes to complete the entire test proce-
dure. It was small, light weight, and did not interfere
with the patient’s movements. In addition, the infor-
mation provided by the system correlated well with
the level of recovery and health status of the patients
in a very intuitive way. The proposed system, there-
fore, fulfills the practical requirements that are essen-
tial to the successful implementation of wearable GA
systems as clinical tools.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was partially funded by the Promobilia
Foundation. The authors would like to thank Lars-
Eric Olsson, PhD, for including the present study
in his project, funded by the Institute of Health and
Care Sciences, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of
Gothenburg, Sweden.
REFERENCES
Allum, J. H. J. and Carpenter, M. G. (2005). A speedy so-
lution for balance and gait analysis: angular velocity
measured at the centre of body mass. Current Opinion
in Neurology, 18(1):15–21.
Aminian, K., Rezakhanlou, K., De Andres, E., Fritsch, C.,
Leyvraz, P. F., and Robert, P. (1999). Temporal feature
estimation during walking using miniature accelerom-
eters: an analysis of gait improvement after hip arthro-
plasty. Medical and Biological Engineering and Com-
puting, 37:686–691.
Bamberg, S., Benbasat, A., Scarborough, D., Krebs, D.,
and Paradiso, J. (2008). Gait analysis using a shoe-
integrated wireless sensor system. IEEE Transactions
BIOSIGNALS 2012 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
12

on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 12(4):413
–423.
Bautmans, I., Jansen, B., Keymolen, B. V., and Mets,
T. (2011). Reliability and clinical correlates of 3d-
accelerometry based gait analysis outcomes according
to age and fall-risk. Gait & Posture, 33(3):366 – 372.
Brown, C., Hillman, S., Richardson, A., Herman, J., and
Robb, J. (2008). Reliability and validity of the visual
gait assessment scale for children with hemiplegic
cerebral palsy when used by experienced and inexpe-
rienced observers. Gait & Posture, 27(4):648–652.
Brunnekreef, J., van Uden, C., van Moorsel, S., and
Kooloos, J. (2005). Reliability of videotaped obser-
vational gait analysis in patients with orthopedic im-
pairments. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 6(1):17.
Buchner, D. M., Larson, E. B., Wagner, E. H., Koepsell,
T. D., and De Lateur, B. J. (1996). Evidence for a
non-linear relationship between leg strength and gait
speed. Age and Ageing, 25(5):386–391.
Cesari, M., Kritchevsky, S. B., Penninx, B. W. H. J., Nick-
las, B. J., Simonsick, E. M., Newman, A. B., Tylavsky,
F. A., Brach, J. S., Satterfield, S., Bauer, D. C.,
Visser, M., Rubin, S. M., Harris, T. B., and Pahor, M.
(2005). Prognostic value of usual gait speed in well-
functioning older people - results from the health, ag-
ing and body composition study. Journal of the Amer-
ican Geriatrics Society, 53(10):1675–1680.
Chang, F. M., Rhodes, J. T., Flynn, K. M., and Carollo,
J. J. (2010). The role of gait analysis in treating gait
abnormalities in cerebral palsy. Orthopedic Clinics of
North America, 41(4):489 – 506.
Coutts, F. (1999). Gait analysis in the therapeutic environ-
ment. Manual Therapy, 4(1):2 – 10.
Cruz, T. H. and Dhaher, Y. Y. (2008). Evidence of abnormal
lower-limb torque coupling after stroke: An isomet-
ric study supplemental materials and methods. Stroke,
39(1):139–147.
Dean, C. M., Richards, C. L., and Malouin, F. (2001).
Walking speed over 10 metres overestimates loco-
motor capacity after stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation,
15(4):415–421.
Dejnabadi, H., Jolles, B., and Aminian, K. (2005). A new
approach to accurate measurement of uniaxial joint
angles based on a combination of accelerometers and
gyroscopes. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engi-
neering, 52(8):1478 –1484.
DeLong, E. R., DeLong, D. M., and Clarke-Pearson, D. L.
(1988). Comparing the areas under two or more corre-
lated receiver operating characteristic curves: A non-
parametric approach. Biometrics, 44(3):837–845.
DeLuca, P. A., Davis, R. B.,
˜
Ounpuu, S., Rose, S., and
Sirkin, R. (1997). Alterations in surgical decision
making in patients with cerebral palsy based on three-
dimensional gait analysis. Journal of Pediatric Or-
thopaedics, 17(5):608–614.
Dickens, W. E. and Smith, M. F. (2006). Validation of a
visual gait assessment scale for children with hemi-
plegic cerebral palsy. Gait & Posture, 23(1):78–82.
Embrey, D. G., Yates, L., and Mott, D. H. (1990). Effects of
neuro-developmental treatment and orthoses on knee
flexion during gait: A single-subject design. Physical
Therapy, 70(10):626–637.
Frenkel-Toledo, S., Giladi, N., Peretz, C., Herman, T., Gru-
endlinger, L., and Hausdorff, J. (2005). Effect of gait
speed on gait rhythmicity in Parkinson’s disease: vari-
ability of stride time and swing time respond differ-
ently. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilita-
tion, 2(1):23.
Gouwanda, D. and Senanayake, A. S. M. N. (2011).
Identifying gait asymmetry using gyroscopes-a cross-
correlation and normalized symmetry index approach.
Journal of Biomechanics, 44(5):972 – 978.
Hausdorff, J. and Ladin, Z. amd Wei, J. (1995). Footswitch
system for measurement of the temporal parameters
of gait. Journal of Biomechanics, 28(3):347–351.
Kawamura, C. M., Filho, M. C. M., Barreto, M. M., Asa, S.
K. P., Juliano, Y., and Novo, N. F. (2007). Comparison
between visual and three-dimensional gait analysis in
patients with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. Gait &
Posture, 25(1):18–24.
Kempen, J., de Groot, V., Knol, D., Polman, C., Lankhorst,
G., and Beckerman, H. (2011). Community walking
can be assessed using a 10 metre timed walk test. Mul-
tiple Sclerosis Journal.
Kennedy, D., Stratford, P., Wessel, J., Gollish, J., and Pen-
ney, D. (2005). Assessing stability and change of four
performance measures: a longitudinal study evaluat-
ing outcome following total hip and knee arthroplasty.
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 6(1):3.
Koman, L., Mooney, J., Smith, B., Goodman, A., and Mul-
vaney, T. (1993). Management of cerebral palsy with
botulinum-A toxin: preliminary investigation. Jour-
nal of pediatric orthopedics, 13(4):489–95.
Kristensen, M. T., Foss, N. B., and Kehlet, H. (2007).
Timed “up & go” test as a predictor of falls within
6 months after hip fracture surgery. Physical Therapy,
87(1):24–30.
Lofterød, B. and Terjesen, T. (2008). Results of treatment
when orthopaedic surgeons follow gait-analysis rec-
ommendations in children with cp. Developmental
Medicine & Child Neurology, 50(7):503–509.
Maathuis, K. G. B., van der Schans, C. P., van Iperen, A.,
Rietman, H. S., and Geertzen, J. H. B. (2005). Gait
in children with cerebral palsy: Observer reliability of
physician rating scale and edinburgh visual gait anal-
ysis interval testing scale. Journal of Pediatric Or-
thopaedics, 25(3).
Macnicol, M., McHardy, R., and Chalmers, J. (1980). Ex-
ercise testing before and after hip arthroplasty. Jour-
nal of Bone and Joint Surgery - British Volume, 62-
B(3):326–331.
Mayagoitia, R., L
¨
otters, J., Veltink, P., and Hermens, H.
(2002a). Standing balance evaluation using a triaxial
accelerometer. Gait & Posture, 16(1):55–59.
Mayagoitia, R., Nene, A. V., and Veltink, P. H. (2002b).
Accelerometer and rate gyroscope measurement of
kinematics: an inexpensive alternative to optical mo-
tion analysis systems. Journal of Biomechanics,
35(4):537–542.
McGraw, K. O. and Wong, S. P. (1996). Forming inferences
A WEARABLE GAIT ANALYSIS SYSTEM USING INERTIAL SENSORS PART II - Evaluation in a Clinical Setting
13

about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psycho-
logical Methods, 1:30–46.
Mercer, J. A., Devita, P., Derrick, T. R., and Bates,
B. T. (2003). Individual effects of stride length
and frequency on shock attenuation during running.
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 35(2):307–
313.
Moe-Nilssen, R. and Helbostad, J. L. (2004). Estimation
of gait cycle characteristics by trunk accelerometry.
Journal of Biomechanics, 37(1):121 – 126.
Morais Filho, M. C., Yoshida, R., Carvalho, W. S., Stein,
H. E., and Novo, N. F. (2008). Are the recommenda-
tions from three-dimensional gait analysis associated
with better postoperative outcomes in patients with
cerebral palsy? Gait & Posture, 28(2):316–322.
Nordin, E., Lindelf, N., Rosendahl, E., Jensen, J., and
Lundin-Olsson, L. (2008). Prognostic validity of the
timed up-and-go test, a modified get-up-and-go test,
staff’s global judgement and fall history in evaluating
fall risk in residential care facilities. Age and Ageing,
37(4):442–448.
Ong, A., Hillman, S., and Robb, J. (2008). Reliability and
validity of the edinburgh visual gait score for cerebral
palsy when used by inexperienced observers. Gait &
Posture, 28(2):323–326.
Palombaro, K. M., Craik, R. L., Mangione, K. K., and Tom-
linson, J. D. (2006). Determining meaningful changes
in gait speed after hip fracture. Physical Therapy,
86(6):809–816.
Potter, J. M., Evans, A. L., and Duncan, G. (1995). Gait
speed and activities of daily living function in geriatric
patients. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabil-
itation, 76(11):997 – 999.
Read, H. S., Hazlewood, M. E., Hillman, S. J., Prescott,
R. J., and Robb, J. E. (2003). Edinburgh visual gait
score for use in cerebral palsy. Journal of Pediatric
Orthopaedics, 23(3):296–301.
Russell, E., Braun, B., and Hamill, J. (2010). Does stride
length influence metabolic cost and biomechanical
risk factors for knee osteoarthritis in obese women?
Clinical Biomechanics, 25(5):438–443.
Sabatini, A. M., Martelloni, C., S., S., and F., C. (2005). As-
sessment of walking features from foot inertial sens-
ing. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,
52(3):486–494.
Salarian, A., Russmann, H., Vingerhoets, F., Dehollain, C.,
Blanc, Y., Burkhard, P., and Aminian, K. (2004). Gait
assessment in Parkinson’s disease: Toward an ambula-
tory system for long-term monitoring. IEEE Transac-
tions on Biomedical Engineering, 51(8):1434 –1443.
Saremi, K., Marehbian, J., Yan, X., Regnaux, J.-P.,
Elashoff, R., Bussel, B., and Dobkin, B. H. (2006).
Reliability and validity of bilateral thigh and foot ac-
celerometry measures of walking in healthy and hemi-
paretic subjects. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Re-
pair, 20(2):297–305.
Senden, R., Grimm, B., Heyligers, I., Savelberg, H., and
Meijer, K. (2009). Acceleration-based gait test for
healthy subjects: Reliability and reference data. Gait
& Posture, 30(2):192 – 196.
Silver, K., Macko, R., Forrester, L., Goldberg, A., and
Smith, G. (2000). Effects of aerobic treadmill train-
ing on gait velocity, cadence, and gait symmetry in
chronic hemiparetic stroke: A preliminary report.
Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair, 14(1):65–71.
Simon, S. R. (2004). Quantification of human motion: gait
analysis - benefits and limitations to its application to
clinical problems. Journal of Biomechanics, 37:1869–
1880.
Toro, B., Nester, C., and Farren, P. (2003). A review of ob-
servational gait assessment in clinical practice. Phys-
iotherapy Theory and Practice, 19(3):137–149.
Wren, T. A. L., Rethlefsen, S. A., Healy, B. S., Do, K. P.,
Dennis, S. W., and Kay, R. M. (2005). Reliability and
validity of visual assessments of gait using a modi-
fied physician rating scale for crouch and foot contact.
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, 25(5):646–650.
BIOSIGNALS 2012 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
14
