
A COOPERATIVE MODEL FOR MULTI-CLASS PEER-TO-PEER
STREAMING NETWORKS
Pablo Romero, Mar
´
ıa Elisa Bertinat, Dar
´
ıo Padula, Pablo Rodr
´
ıguez-Bocca
and Franco Robledo Amoza
Laboratorio de Probabilidad y Estad
´
ıstica, Facultad de Ingenier
´
ıa, Universidad de la Rep
´
ublica, Montevideo, Uruguay
Keywords:
Peer-to-peer, Piece selection strategies, Bandwidth, Free-riding.
Abstract:
Peer-to-peer networks are strongly based on cooperation. The users, called peers, communicate basically in
a three-level based policy. In the first one, peers discover others interested in the same content, and is called
swarm selection strategy (or swarming). Then, peers must select the best ones to cooperate, what is called
peer selection strategy. Finally, peers cooperate sending pieces to each other, and the planning must attend the
piece selection strategy.
In this paper we propose an extension of a simple model based on cooperation for peer-to-peer video streaming
networks. We assume that the swarming classifies peers according to their bandwidth. In this model we meet
both the peer and the piece selection strategies, for simplified scenarios. The aim is to design network policies
in order to achieve the highest continuity of video reproduction when peers reach a stationary state. We show
that under full knowledge, the network can scale even under free-riding effects. At the same time, we provide
theoretical results that reveal Rarest First has a poor performance in comparison with other techniques. Finally,
we analyze the scalability in a worst-case scenario when a variable amount of special peers are included in the
network.
1 INTRODUCTION
An important amount of today’s Internet traffic is
due to live video streaming (Bertinat et al., 2009c).
For this reason, several peer-to-peer streaming net-
works were developed in the last years. The most
successful ones are PPlive(Liu et al., 2009; Huang
et al., 2008), TVUnetwork(TVUnetworks home page,
2007), SopCast(SopCast - Free P2P internet TV,
2007), with proprietary and unpublished mesh-based
protocols (Rodr
´
ıguez-Bocca, 2008). Mesh-based P2P
networks are virtual unstructured networks devel-
oped at the application layer, over the Internet in-
frastructure. Bittorrent is the best known mesh-based
P2P protocol, originally created for file sharing pur-
poses (Cohen, 2003). The users, called peers, offer
their resources (bandwidth in a streaming application)
to others, basically because they share common inter-
ests. They can connect and disconnect freely. This
makes P2P networks an attractive tool for them, but
increases P2P’s design challenges, because the re-
source availability depends on them.
In P2P, the cooperation is the key element in or-
der to assure a certain quality of experience to end-
users (Rodr
´
ıguez-Bocca, 2008). There are three main
steps in all mesh-based P2P protocols for cooperation.
First, when a peer enters the net it should discover
other peers sharing the same content, which is called
swarm selection strategy. Once a new peer knows
other peers in his swarm, he must select the best ones
to cooperate, what is called peer selection strategy.
Once a new peer handshakes other peers, it should de-
cide which pieces of the streaming content should be
asked first, called the piece selection strategy (Berti-
nat et al., 2009b).
The research literature related on Peer-to-Peer net-
works focused, from the beginnings, in system de-
sign and traffic measurements for file sharing (Ri-
peanu, 2001; Cohen, 2003). The new challenges
adopted for streaming purposes inspired the scien-
tific community to elaborate diverse mathematical
models to understand the behavior and scalability of
streaming systems, including Markov Chains, Fluid
Models, Branching Processes and Marginal Probabil-
ities (Zhou et al., 2007; Zhao et al., 2009) . In this
work we propose an extension of the simple model
for cooperation defined in (Zhou et al., 2007). There,
a pull process is considered, in which peers cooperate
with each other in order to recover a video stream-
ing content which is delivered by a server. The aim
274
Romero P., Elisa Bertinat M., Padula D., Rodríguez-Bocca P. and Robledo Amoza F..
A COOPERATIVE MODEL FOR MULTI-CLASS PEER-TO-PEER STREAMING NETWORKS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003744502740282
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES-2012), pages 274-282
ISBN: 978-989-8425-97-3
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

is to find an optimal permutation, that dictates the
order in which pieces must be downloaded in or-
der to achieve high continuity of video reproduction.
This model has been extensively analyzed in (Berti-
nat et al., 2009a; Bertinat et al., 2009b; Romero et al.,
2010; Rodr
´
ıguez, 2009; Zhao et al., 2009). Specifi-
cally, in (Zhao et al., 2009) the authors state properties
of the optimal permutation for highly populated sce-
narios of identical peers, and a server with bounded
uploading capacity.
This paper is structured as follows. Section 2 de-
tails the simple model for cooperation in peer-to-peer
streaming networks originally defined in (Zhou et al.,
2007). In Section 3 we summarize the main results of
combinatorial problems concerning the simple model
for cooperation. The contributions of this paper are
the introduction of an extension of this mathemat-
ical model considering different peer classes (free-
riders, normal peers, double-bandwidth peers and
super-peers), an analysis of this new model under dif-
ferent scenarios and discussion of this results. At the
same time we provide theoretical results that confirm
super-peers can highly outperform the Rarest First
strategy, which is widely used nowadays for file shar-
ing purposes. We will work between the performance
of the Rarest First and super-peer strategy, given that
the performance of super-peers is not achievable in
practice. This latter fact will be also proved.
Section 4 contains a generalization of the simple
model, and an analysis of different scenarios. More
specifically, Subsection 4.1 presents the Extended
Model (EM for short). In Subsection 4.2 we show
that super-peers achieve an upper bound in the per-
formance of every possible piece selection strategy
in the simple model. Super-peers play a prestigious
role in the new model here proposed. Subsection 4.3
shows that the EM is in fact an extension of the sim-
ple model, and consequently the computational com-
plexity of its resolution is higher than the complexity
of the simple model. Subsection 4.4 shows how to
deal with free-riders under the extended model. We
define a natural hypothesis of full knowledge in the
network, in which the network scales even under pres-
ence of free-riders. However, we show that the perfor-
mance dramatically decreases if peers (or the server)
cannot recognize the different classes of peers in the
network, unless super-peers are included in the net-
work. In fact, under full knowledge (when the server
and peers can recognize the different classes of peers),
the network always scales, meaning that the continu-
ity of the video reproduction will remain high inde-
pendently of the number of peers in the network. This
fact is proved in Subsection 4.5.
The most complex interaction is between normal
and double-bandwidth peers. We analyze this sce-
nario in Section 5. Specifically, the study is focused
on the scalability of the network when a variable
amount of superpeers is present. Finally, Section 6
contains the main conclusions of this work.
2 A SIMPLE MODEL FOR
COOPERATION
Consider a static network with M identical peers with
buffer size N, and one server that contains the original
video content. The server cuts the video into pieces
and shares them in order. In each time slot, it chooses
only one peer randomly to send one piece. That peer
places the piece in the first buffer position, and that
piece will advance one buffer position in each time
slot, until it reaches position N. Pieces from position
N are displayed at the screen of that user. It is as-
sumed that all peers are synchronized with time (i.e.
every peer plays the piece at position N, see Figure 1
for a graphical description).
Figure 1: Buffer model for each peer. Position 1 represents
the newest video piece in the network, and N the next piece
to be displayed.
All peers can also communicate with each other
in order to ask for pieces. In each time slot, every
peer chooses one of the M − 1 other peers at ran-
dom, and can get no more than one piece during that
time slot. The piece selection strategy works as fol-
lows: each peer chooses a permutation π of the set
B = {1,..., N − 1}. Each element of B represent one
position of the buffer size, without regarding the last
(position N), which is expected to be played on that
time slot. Suppose peer P
1
chooses peer P
2
. Then P
1
looks for position π
1
of its own buffer. If it has that
piece, it looks for π
2
and so on. Otherwise, it checks
if peer P
2
has that piece, and takes it. This process
is repeated until either P
1
gets one piece during that
time slot or it checks with no success every place of
its buffer. In the former (latter) case we say peer P
1
had a good (resp. bad) time slot.
In (Zhou et al., 2007), a symmetric strategy is con-
sidered, which means that every peer follows the same
piece selection strategy π. Let us call p
i
the proba-
bility that a peer has piece i ∈ {1, ...,N} under sta-
tionary state (this probability is the same for differ-
A COOPERATIVE MODEL FOR MULTI-CLASS PEER-TO-PEER STREAMING NETWORKS
275

ent peers because of the symmetry). It can be proved
that (Zhou et al., 2007):
(
p
1
=
1
M
p
i+1
= p
i
+ (1 − p
i
)p
i
s
i
,∀i ∈ B.
(1)
Clearly, the probability of a given peer to be chosen
by the server is one out of M, so p
1
=
1
M
. We know
that under steady state we have that p
i
(t) = p
i
, so the
probability vector does not depend on time. As a con-
sequence, the piece at position i + 1 can be obtained
in two different ways. The first one is by promotion
with time of piece at position i (with probability p
i
).
The second is because the peer did not have the piece
i (event with probability 1 − p
i
) but the requested peer
did (probability p
i
) and piece at position i was chosen
to be downloaded in the previous time slot (event with
probability s
i
). The strategic sequence s
i
represents
the probability of taking the piece at position i, given
that the requesting peer does not have that piece and
the requested does. Note that s
i
will depend on the
permutation, and under this model we identify piece
selection strategies with one permutation of the ele-
ments in the set B.
3 ANALYSIS OF THE SIMPLE
MODEL
The previous model was originally proposed in (Zhou
et al., 2007), and was extensively analyzed in (Berti-
nat et al., 2009a; Bertinat et al., 2009b; Romero et al.,
2010; Rodr
´
ıguez, 2009). Here, we summarize the
main results, and provide a new pessimistic one, that
assures the Rarest First strategy (a widely developed
technique used in BitTorrent (Cohen, 2003)) has a low
(linear) convergence rate to the perfect video quality,
when the buffer size tends to infinity. At the same
time, we will show that is impossible to achieve more
than a quadratic convergence rate. Consequently, we
will work between linear and quadratic convergence
to the perfect video quality (outperforming Rarest
First), whenever the buffer tends to be unlimited. We
will formalize these ideas next. We suppose a sym-
metric network in steady state:
Definition 3.1. The continuity of the video reproduc-
tion is measured by c = p
N
.
Definition 3.2. The buffering time is L =
∑
N
i=1
p
i
Definition 3.1 is clear: count the number of pieces
showed at the screen and divide it by the total number
of time slots. When the number of time slots tends to
infinity, we have the continuity of the video reproduc-
tion.
Definition 3.2 deserves an explanation. Suppose a
new peer P enters to that static network with an empty
buffer. In the next time slots, it will get many pieces
with high probability via requests. More precisely,
the expected number of time slots needed to reach the
steady state is the expected number of pieces of a peer,
or p
1
+ . .. + p
N
.
In (Zhou et al., 2007), the performance of classical
strategies are studied, named Rarest First, the Greedy
strategy, and a Mixture of them. The name Rarest
First is inspired by BitTorrent (Cohen, 2003). This
piece selection policy tries to achieve uniform distri-
bution, copying the rarest pieces in the network. In
this way, it assures that rarest pieces are easier to find
via requests. Under this model, observe that the vec-
tor (p
i
)
1≤i≤N
is monotonous increasing. Then, Rarest
First takes the identity permutation π
i
= i, ∀i ∈ B
(ask for the first piece in the buffer, then the second
and so on until either downloading a piece or com-
pleting a bad time slot). The strategic sequence in
Rarest First is:
s
i
= (1 −1/M)
i−1
∏
j=1
[p
j
+ (1 − p
j
)
2
] (2)
Expression 2 has a simple interpretation. In order to
download the piece at position i ∈ B, the peer must fail
in all previous positions j = 1,... , i − 1 and must not
be chosen by the server (with probability 1−1/M). A
fail at position j occurs when the peer already has a
piece at position j (with probability p
j
) or it does not
have that piece but neither the requested peer (event
with probability (1 − p
i
)
2
). A direct induction for
i ∈ {1,... ,N} shows that s
i
= 1 − p
i
holds for Rarest
First (Zhou et al., 2007).
On the other hand, the greedy notion of the problem is
to ask first for the nearest piece to be played (i.e. the
piece at position N − 1, because that one at position
N is being played). Then, the Greedy strategy con-
siders the permutation π
i
= N − i,∀i ∈ B. Its strategic
sequence is:
s
i
= (1 −1/M)
N−1
∏
j=i+1
[p
j
+ (1 − p
j
)
2
] (3)
The interpretation is analogous to that of Rarest First,
but reading the buffer in the opposite way. A mixture
of both strategies can be obtained reading the buffer in
the increasing way (using Rarest First) until a certain
buffer position m : 1 < m < N, and then completing
the buffer using Greedy from position N − 1 down-to
m + 1. The “Mixture” strategies are defined depend-
ing on m.
There are piece selection strategies that outperform
classical strategies, as well as the Mixture strategy.
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
276

In fact, in (Bertinat et al., 2009a) a subfamily of per-
mutation strategies was defined with polynomial size.
That subfamily contains the classical strategies, as
well as their mixtures, and has a polynomial cardinal-
ity in terms of the buffer size. An exhaustive search
in this family permits to achieve higher continuities,
keeping at the same time reduced buffering times. A
more sophisticated design of piece selection strategies
can be found in (Romero et al., 2010). There, a sin-
gle objective function was defined, which captures the
continuity and latency:
Theorem 3.3. If π is an arbitrary permutation of B
and X
π
is the random variable that counts the number
of steps in a good time slot, then its expected value is:
E(X
π
) =
M
M − 1
N−1
∑
i=1
π
i
(p
i+1
− p
i
) (4)
Note that in Rarest First we get E(X
π
) ∝ N p
N
−
L. The convex combination of continuity and la-
tency takes a natural form in this combinatorial prob-
lem (maximize E(X
π
) choosing the best permutation
π). We translated this problem in a second oppor-
tunity into a suitable Asymmetric Traveling Sales-
man Problem (ATSP). Finally, an Ant Colony-based
search (Dorigo and Stutzle, 2004) permits to find
cheap tours (or equivalently permutations) and this
permutations had a direct interpretation in the simple
model, outperforming again classical selection strate-
gies. We refer the reader to (Romero et al., 2010) for
an overview.
In the next section, we will enrich the simple
model by considering different classes of peers, ac-
cording to a swarm selection policy based on band-
width. The analysis is primarily focused on extreme
scenarios, attending the interaction of four classes of
peers: free-riders (Class 0 with zero upload band-
width), normal peers with unit bandwidth (Class 1),
double-peers with double bandwidth (Class 2) and
super-peers with unlimited bandwidth (Class 3). All
peers have unlimited downloading capacities (so, the
limitation is in the uploading bandwidth). The main
issue is to plan the network in order to maximize the
continuity of reproduction, in a more realistic model.
4 A GENERALIZATION OF THE
SIMPLE MODEL
4.1 Definition of the Extended Model
Suppose a static network that has M peers of Class X,
M
0
peers of Class Y and a server that has the original
video content (where X,Y ∈ {0,1,2,3}). The server
cuts the video into small pieces, and shares them in
turns. In each time slot, the server chooses one peer at
random from Class X with probability α, or one peer
at random from Class Y with probability 1 − α, and
sends one piece to that peer. As in the simple model,
peers can cooperate. More precisely, one peer from
Class X either chooses with probability β another peer
at random from its own class or a peer from Class Y at
random with probability 1 − β. Symmetrically, peers
from Class Y can request other peers from their own
class (chosen at random) with probability β
0
, or from
Class X (with probability 1 − β
0
). Every peer tries to
download the highest number of pieces during each
time slot, and that number will depend on the upload-
ing bandwidth of the contacted class. For example,
if a peer requests a double-peer (with double band-
width), it will be able to download two pieces during
the same time slot. The process of the request is iden-
tical to that of the simple model, but it may continue
after one piece is obtained.
Definition 4.1. A free-rider is a peer that has infi-
nite downloading bandwidth, but no uploading band-
width. When a peer requests a free rider, it will get no
piece on that time slot.
In other words, it is a selfish peer, that asks for
pieces but does not share them.
Definition 4.2. A normal peer has infinite download-
ing bandwidth and unit uploading bandwidth. When
a peer requests a normal peer, the time slot works as
in the simple model.
Definition 4.3. A double-bandwidth peer has infinite
downloading bandwidth and double uploading band-
width. When a peer requests a double-bandwidth
peer, it can get zero, one or two pieces.
For example, if one peer follows the Rarest First
strategy and requests a double-bandwidth peer, then
the request works as in the simple model. However,
if a download occurs, the peer goes on asking for the
next pieces, until downloading another one or reach-
ing position N − 1 of its buffer. An analogous request
occurs when the piece selection strategy is identified
with an arbitrary permutation.
Definition 4.4. A super-peer has both infinite down-
loading and uploading bandwidth. When a peer re-
quests a super-peer, it will take all pieces in only one
time slot.
The optimization problem is specified next. The
two classes X and Y , the number of peers M and M
0
and the buffer size N are given. We want to plan the
network by choosing the parameters α, β and β
0
as
well as the permutation strategy π, in order to maxi-
mize the average continuity of reproduction in the net-
work. More specifically, the Extended Model (from
A COOPERATIVE MODEL FOR MULTI-CLASS PEER-TO-PEER STREAMING NETWORKS
277

now on the EM) is captured with the next optimiza-
tion problem:
max f (π,M,N,α,β) =
M p
N
+ M
0
p
0
N
M + M
0
(5)
s.t.
p
1
=
α
M
p
0
1
=
1−α
M
0
p
i+1
= p
i
+ (1 − p
i
)[βp
i
s
(X,X,π)
i
+ (1 − β)p
0
i
s
(X,Y,π)
i
]
p
0
i+1
= p
0
i
+ (1 − p
0
i
)[β
0
p
0
i
s
(Y,Y,π)
i
+ (1 − β
0
)p
i
s
(Y,X ,π)
i
]
α,β,β
0
∈ [0,1]
where s
(X,Y,π)
i
is the probability that a peer from class
X is using the permutation strategy π (which is a per-
mutation of the set {1,.. .,N − 1}) and requesting a
peer from class Y takes piece at position i. These ex-
pression will be analyzed for each possible scenario.
The objective is to maximize the average quality of
experience of all peers in the network (identifying
quality with continuity of reproduction). If we re-
call that the server sends with probability α one peer
from Class X at random, then obviously p
1
= α/M
and p
0
1
= (1 − α)/M
0
hold. The next equations are
correct under steady state, and take into account the
fact that the requested peer can be from their own
class or the foreign class. We shall fix the parame-
ters β and β
0
according to random peer selection (i.e.
β = M/(M + M
0
) and β
0
= M
0
/(M + M
0
)). In fact,
we will show that under a full knowledge assump-
tion, the network can work in optimal conditions and
the combinatorial problem is reduced to the simple
model, which has been extensively analyzed in pre-
vious works (Bertinat et al., 2009a; Bertinat et al.,
2009b; Romero et al., 2010; Rodr
´
ıguez, 2009). The
intuition here is that if the server as well as the peers
can discover which peers have the highest bandwidth,
then the server will send pieces to them, and all peers
will direct requests to this powerful peers (which play
the role of intermediate nodes of a tree-like structure).
There are exactly 4
2
−C
4
2
= 10 different interac-
tion of pairs of the four classes (we are considering
only once the cases of interaction between classes X
and Y , when X 6= Y ). Moreover, the cases of self-
interaction can be reduced to the simple model. More
precisely, the self-interaction between free-riders is
strictly inadmissible, and does not deserve our atten-
tion. The interaction between normal peers behaves
exactly as in the simple model, and between double-
bandwidth peers translates proportionally to the case
of the simple model (in fact, cut the time slot into two
half). There is something to say for the case of self-
interaction between super-peers. As a consequence,
we will focus on 7 scenarios: the six different pairs of
classes, and the simple model with infinite bandwidth.
4.2 The Best Strategy for the Simple
Model
Certainly, the best piece selection strategy for the sim-
ple model occurs when all peers in the network have
infinite bandwidth, and they can download all pieces
in only one time slot. In fact, in steady state the strate-
gic sequence for this case is s
i
= 1. This means that if
one peer does not have a piece and the requested does,
the peer always downloads that piece. Naturally, the
sequence p
i
is the highest possible, because:
p
i+1
= p
i
+ (1 − p
i
)p
i
≥ p
i
+ (1 − p
i
)p
i
s
i
, (6)
whenever s
i
≤ 1, which is obvious (s
i
is a probability
for every i ∈ B). Hence, the probability p
N
is never ex-
actly 1 (as a trivial induction can show), but the high-
est possible. By technological reasons, it is natural
to ask what happens in the case of unlimited storage
(when the buffer size N tends to infinity).
Theorem 4.5. Under the simple model, the super-
peers tend to experiment perfect continuity when the
buffer tends to infinity:
lim
N→∞
p
N
= 1. (7)
Moreover, the convergence order is quadratic.
Proof. Super-peers are characterized by s
i
= 1. Sub-
stituting in (1) we have that:
p
1
=
1
M
p
i+1
= p
i
(2 − p
i
),i ∈ B
Taking i = N − 1 we have that p
N
= p
N−1
(2 − p
N−1
).
The sequence (p
i
)
1≤i≤N
is monotonous increasing
and bounded by 1; hence it has a limit a. Taking N
tending to infinity:
a = a(2 − a) (8)
So a = 0 or a = 1. But p
1
= 1/M > 0 and (p
i
)
1≤i≤N
is monotonous increasing. Consequently a = 1, and
lim
N→∞
p
N
= 1. (9)
Finally, its convergence order can be found easily:
lim
N→∞
1 − p
N
(1 − p
N−1
)
2
=
lim
N→∞
1 − p
N−1
(2 − p
N−1
)
(1 − p
N−1
)
2
= 1.
Hence, its convergence order is 2, and the result holds.
Observe also that super-peers achieve the smallest
buffering times, because if one super-peer enters the
network in steady state, then in one time slot reaches
the state of another super-peer.
It is interesting to compare this performance with re-
spect to the one obtained following Rarest First:
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
278

Theorem 4.6. The Rarest First strategy tends to have
perfect continuity when the buffer size tends to infin-
ity, but its convergence order is linear.
Proof. In Rarest First s
i
= 1 − p
i
holds for all i ∈ B.
As a consequence:
(
p
1
=
1
M
p
i+1
= p
i
+ (1 − p
i
)
2
p
i
Again, the limit of the sequence (p
i
)
1≤i≤N
exists
when N tends to infinity (it is a bounded increas-
ing real sequence). The limit a must comply that
a = a + (1 − a)
2
a. Then a = 0 or a = 1. The null
limit is discarded because the sequence (p
i
)
1≤i≤N
is
monotonous increasing and p
1
> 0. Hence, a = 1.
Finally, the convergence order is linear, given that:
lim
N→∞
1 − p
N
1 − p
N−1
=
lim
N→∞
1 − p
N−1
− p
N−1
(1 − p
N−1
)
2
1 − p
N−1
= 1.
As a consequence, the piece selection strategies
will always work with convergence order p such that
1 < p < 2 when the buffer increases. In fact, we know
there are better strategies than Rarest First, and that
there is no strategy better than the one of super-peers
(download the whole buffer of the requested peer).
4.3 The EM under Full-Knowledge
From now on, we study the EM (Extended Model)
when different classes interact (i.e. X 6= Y ).
Definition 4.7. We say that the network in the EM
has full knowledge, when the server can recognize
the different classes of peers in the network, and peers
can deduce the best class-request (if it is better to ask
one peer from its own class or the foreign class).
Definition 4.8. A peer-class has higher level than
other when it has higher uploading bandwidth.
Definition 4.9. We say that the server is fair when
each peer in the network has the same probability of
getting a piece from it.
Definition 4.10. We say that the network is balanced
when the peer selection strategy is at random.
Theorem 4.11. The EM is computationally more
complex than the Simple Model.
Proof. We will prove that the EM is trivially re-
duced to the simple model under full knowledge and
fairness. Without loss of generality, suppose X has
higher class than Y . Then clearly a peer has more
chances to download piece at position i requesting
peers from class X rather than from class Y , and
s
(X,X,π)
i
≥ s
(X,Y,π)
i
. Given that peer can recognize the
highest class, then they will always choose peers from
class X to ask for pieces, so β = 1 and β
0
= 0. By
symmetry, observe that s
(Y,X ,π)
i
= s
(X,X,π)
i
. Denote this
number with s
π
i
for brevity. Substituting in the EM we
have that:
p
1
=
α
M
p
0
1
=
1 − α
M
0
p
i+1
= p
i
+ (1 − p
i
)[p
i
s
π
i
]
p
0
i+1
= p
0
i
+ (1 − p
0
i
)[p
i
s
π
i
]
α ∈ [0,1]
Assuming fairness, the server will send pieces
with probability α = M/(M +M
0
). As a consequence,
p
1
= p
0
1
= 1/(M + M
0
). Hence, both recursive ex-
pressions are the same, and the sequences p
i
and p
0
i
coincide. Moreover, the problem was reduced to:
(
p
1
=
α
M
p
i+1
= p
i
+ (1 − p
i
)p
i
s
π
i
(10)
being π a permutation, which is exactly the simple
model with M + M
0
peers.
So far, we know that the peers with higher class
perform better under the simple model, and super-
peers achieve the best performance, with unit strategic
sequence (s
i
= 1).
4.4 Dealing with Free-riders
As we said before, the self-interaction of free-riders is
not admissible (it is evident that without cooperation
the network does not work). The reader can check
that if all peers are free-riders then p
i
= p
1
= β/M <
1/M,∀i, and this performance is not acceptable since
the network normally works with hundreds or thou-
sands of peers. Similar results are obtained for the
second class: p
0
i
= (1 −β)/M
0
is constant.
The interaction between free-riders and other
classes has a special treatment. Particularly, suppose
that X = 0 (free-rider class) and Y 6= 0. Under full
knowledge, the server will always choose to send
pieces to peers from class Y , so α = 0. Moreover,
free-riders will choose to complete requests consider-
ing peers from Class Y , which will prefer to do self-
requests, so β = 0 and β
0
= 1. Substituting in the EM:
A COOPERATIVE MODEL FOR MULTI-CLASS PEER-TO-PEER STREAMING NETWORKS
279

p
1
= 0
p
0
1
=
1
M
0
p
i+1
= p
i
+ (1 − p
i
)p
0
i
s
(X,Y,π)
i
p
0
i+1
= p
0
i
+ (1 − p
0
i
)p
0
i
s
(Y,Y,π)
i
As a consequence, the quality of all non-free-riders
in the network is equivalent to that of the simple
model. Note that p
1
= 0 but p
2
> 0. For example, if
the Rarest First strategy is applied, then the sequence
{p
i
}
1≤i≤N
converges to 1 as N tends to infinity, and
behaves exactly the same as {p
0
i
}
1≤i≤N
but with a
shift. In this way, the free-riders follow the perfor-
mance of the other class, and the network scales.
The previous discussion shows that with full
knowledge, the planning of the network reduces to
choose a piece selection strategy, or a permutation
π, as in the case of the simple model (which has
been extensively analyzed already). However, if the
server cannot identify classes, it will tune α 6= 0,
and the performance of the network dramatically
decreases, because pieces given to free-riders will be
missing for all but only one peer. Hence, the network
scales if and only if α = 0. This results outstand
the importance of the recognition of free-riders,
under this new extension of the simple model. The
full-knowledge hypothesis is strictly necessary in this
case. This is an evidence of the empirical complexity
of designing a scalable streaming network: normally
the broadcaster does not have full knowledge, and
neither peers do.
4.5 The Network with Super-peers
Naturally, when one of the classes working in the net-
work are super-peers, the cooperation is easier. With
full knowledge of the network (i.e. the server as well
as peers can recognize classes of different peers), the
server will always send pieces to super-peers, and the
other class will be pleased to complete full requests
to them, making the network scalable. The quality of
experience of every peer in the network follows, un-
der these circumstances, the one of super-peers (as if
there were no other class) in the simple model. As a
consequence, all peers will have (discarding the small
initial shift) the next probabilities:
(
p
1
= 1/M
p
i+1
= p
i
(2 − p
i
),∀i ∈ B,
(11)
being M the number of super-peers in the network and
p
N
the continuity of video reproduction of each peer.
When free-riders or super-peers are present inside the
network, the analysis of the EM is trivial (because the
strategic sequence is reduced to 0 or 1 respectively).
In the next section we analyze the most complex in-
teraction.
5 INTERACTION BETWEEN
NORMAL AND
DOUBLE-BANDWIDTH PEERS
5.1 Presentation of the Problem
This case is clearly the most complex to analyze. In-
tuitively, the server should send pieces to the double-
bandwidth peers, and the request always directed to
them. Under full knowledge this will happen, and
normal-peers will tend to follow the quality of double-
bandwidth peers.
Let us focus on a more realistic scenario. Choose X
as normal peers and Y double-bandwidth peers. Now,
we will find an expression for the sequences s
(X,Y,π)
i
and s
(Y,Y,π)
i
(the other two cases are self-requests, and
expressed as in the simple model). For brevity, s
i
de-
notes the probability that normal-peers have to take
the first piece from a double-bandwidth peer. If k is
such that π
k+1
= i then:
s
i
= (1 −α/M)
k
∏
j=1
[1 − (1 − p
π
j
)p
0
π
j
] (12)
Expression (15) deserves an explanation. One peer
from class X will download the first piece at posi-
tion i from class Y following the permutation strat-
egy π whenever it fails in all previous positions (and
success at position i) and is not chosen by the server
(with probability p
1
= 1 − α/M). Hence, a fail at all
positions π
j
, j = 1,..., k −1 such that π
k
= i must oc-
cur. Moreover, a fail at position π
j
occurs when it
is not the case that the requesting peer does not have
that piece (with probability 1− p
π
j
) and the requested
peer does (event with probability p
0
π
j
). Then, a fail at
position π
j
has probability 1 − (1 − p
π
j
)p
0
π
j
.
Now, we are ready to express the sequence s
(X,Y,π)
i
:
s
(X,Y,π)
i
= s
i
+ s
i
k−1
∑
j=1
(1 − p
π
j
)p
0
π
j
1 − (1 − p
π
j
)p
0
π
j
(13)
When asking a double-bandwidth peer, we can down-
load piece at position i in the first chance (the first
term) or we downloaded a previous position π
j
, j =
1,... ,k − 1 with success. The factor
(1 − p
π
j
)p
0
π
j
/[1 − (1 − p
π
j
)p
0
π
j
],
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
280
represents a replace of a success instead of a fail at
position π
j
in the expression s
i
.
In a similar way, the strategic sequence s
(Y,Y,π)
i
is:
s
(Y,Y,π)
i
= s
∗
i
+ s
∗
i
k−1
∑
j=1
(1 − p
0
π
j
)p
0
π
j
1 − (1 − p
0
π
j
)p
0
π
j
, (14)
where
s
∗
i
= (1 −(1 − α)/M)
k−1:π
k
=i
∏
j=1
[1 − (1 − p
0
π
j
)p
0
π
j
].
(15)
The EM can be obtained for this interaction by sub-
stitution.
5.2 Empirical Results
We will concentrate on a worst case scenario, by tak-
ing the Rarest First strategy (i.e. π
i
= i), and ana-
lyzing the scalability of the network under different
mass of double-bandwidth peers, with no knowledge
of the network, which imples that the peer selection is
balanced: β = M/(M + M
0
) and β
0
= M
0
/(M + M
0
).
Consider the common-network values M +M
0
= 1000
and N = 40. Table 1 presents the objective function
f (α,M) = (M p
N
+ M
0
p
0
N
)/(M + M
0
) when the mass
of double-bandwidth peers is variable accordingly
with M
0
∈ {350,250,150,100,0} double-bandwidth
peers and correspondingly M = 1000 − M
0
normal
peers. Table 2 contains the function p
N
− p
0
N
taking
the same set for M and probability α.
Table 1: Expected continuity f (α,M) for a balanced net-
work with different number of double-bandwidth peers.
α 350 250 150 100 0
0.0 1.0000 0.9998 0.9979 0.9941 0.9666
0.1 1.0000 0.9998 0.9979 0.9940 0.9665
0.2 1.0000 0.9998 0.9978 0.9939 0.9663
0.3 1.0000 0.9998 0.9978 0.9938 0.9661
0.4 1.0000 0.9998 0.9977 0.9937 0.9658
0.5 1.0000 0.9998 0.9977 0.9936 0.9655
0.6 1.0000 0.9998 0.9976 0.9934 0.9651
0.7 1.0000 0.9997 0.9975 0.9932 0.9646
0.8 1.0000 0.9997 0.9974 0.9929 0.9638
0.9 1.0000 0.9997 0.9972 0.9925 0.9625
1.0 1.0000 0.9997 0.9970 0.9918 impossible
It can be appreciated from Table 1 that the net-
work always scales, although the server cannot recog-
nize peers and tunes incorrectly the parameter α. Cer-
tainly, the performance is the best when α = 0 (that
is, to choose always double-bandwidth peers to send
pieces). It can be noticed that the average continuity is
higher than 96% in all instances, so the video quality
is high. It is interesting to analyze if the video qual-
ity of normal peers is similar to double-peers or not.
Table 2 contains the difference of continuity p
N
− p
0
N
.
Table 2: Difference in continuity p
N
− p
0
N
between double-
bandwidth peers and normal peers, with different number
of normal peers.
α 350 250 150 100 0
0.0 0.0002 0.0013 0.0067 0.0117 0.0006
0.1 0.0001 0.0010 0.0055 0.0094 0.0005
0.2 0.0001 0.0008 0.0041 0.0071 0.0004
0.3 0.0001 0.0005 0.0028 0.0048 0.0002
0.4 0.0000 0.0003 0.0014 0.0024 0.0001
0.5 0 0 0 0 0
0.6 -0.0000 -0.0003 -0.0015 -0.0025 -0.0001
0.7 -0.0001 -0.0006 -0.0030 -0.0051 -0.0003
0.8 -0.0001 -0.0009 -0.0047 -0.0077 -0.0004
0.9 -0.0002 -0.0013 -0.0065 -0.0106 -0.0006
1.0 -0.0002 -0.0017 -0.0086 -0.0140 impossible
It is obvious that when the parameter α increases, the
quality of normal peers is increased as well. More-
over, in the case α = 0.5 both classes of peers exper-
iment the same video quality, and there is a symme-
try in the instances α = i/10 and α = (10 − i)/10.
It is evident that peers can follow double-bandwidth
peers, and peers have better continuity than super-
peer when α > 0.5. This empirical analysis shows
that the network scales when peers and double-peers
interact, even under pessimistic scenarios. A further
experiment with the balanced case of α = 0.5 shows
the scalability property of this network when the stor-
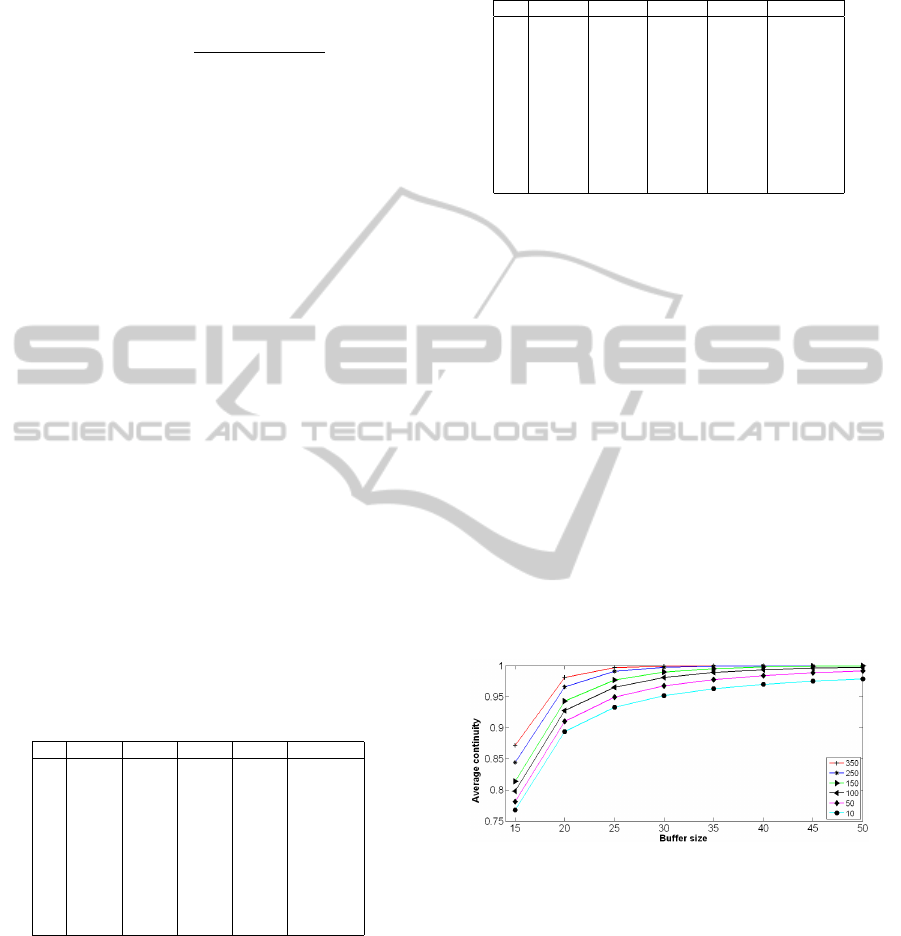
age size increases. Figure 2 reveals the average con-
tinuity of normal (and double-bandwidth) peers as a
function of the buffer size N, considering again dif-
ferent amounts of double-bandwidth peers. It can be
appreciated that the average continuity is higher than
90% when the storage capacity is higher than 25, even
when the number of double-bandwidth peers is small.
Figure 2: Evolution of the average continuity of peers as a
function of the buffer storage capacity N.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper proposes an extension of a simple model
for cooperation in peer-to-peer streaming networks.
This model assumes a swarming policy based on up-
loading bandwidth, classifying peers as free-riders,
normal, double-bandwidth and super-peers with infi-
nite bandwidth. A primitive analysis demonstrates the
strength of the full knowledge hypothesis in the net-
A COOPERATIVE MODEL FOR MULTI-CLASS PEER-TO-PEER STREAMING NETWORKS
281

work. In fact, the scalability of the network is guaran-
teed whenever the server as well as peers can recog-
nize different classes. When free-riders interact with
other classes, peers will always experiment cuts in the
video content, unless the server sends pieces to non-
free-riders. On the other hand, when super-peers take
part of it, the network scales.
The performance of the Rarest First strategy was con-
trasted with the one of super-peers. Particularly, the
convergence to the perfect probability is faster for
super-peers. Moreover, there is no real strategy that
can achieve quadratic convergence to the perfect con-
tinuity, even with high buffer size. Finally, the most
complex scenario considered the interaction between
normal and double-bandwidth peers, and was ana-
lyzed via simulations. Although there exist many
piece selection strategies with higher performance
than Rarest First, the results show that the network
scales using the latter strategy. This is an encourag-
ing result, which motivates to apply different piece
selection strategies. We have extensively analyzed
the simple model, and we are currently approaching
the general EM via metaheuristics. As a future work,
we point to apply the results in a real peer-to-peer
platform named GoalBit, an open source real plat-
form that widely offers live video-streaming to end
users(Bertinat et al., 2009c). It is worth to mention
that we do not know a global model for peer-to-peer
streaming networks that integrates swarming, peer se-
lection and piece selection strategies. It sounds ambi-
tious, and the model here proposed takes into account
peers as well as piece selection strategies, in a coop-
erative simplified environment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are pleased to thank the reviewers for
their constructive comments, and Lic. Fernanda
Fern
´
andez for her corrections. This work was par-
tially supported by project “Sistema eficiente de dis-
tribuci
´
on de video y TV en tiempo real”, for the na-
tional telephony operator ANTEL.
REFERENCES
Bertinat, M. E., Vera, D. D., Padula, D., Robledo, F.,
Rodr
´
ıguez-Bocca, P., and Romero, P. (2009a). Sys-
tematic procedure for improving continuity and la-
tency on a p2p streaming protocol. In Proceedings
of the 1th IEEE Latin-American Conference on Com-
munications (LatinCom’09), Washington, DC, USA.
IEEE Computer Society.
Bertinat, M. E., Vera, D. D., Padula, D., Robledo, F.,
Rodr
´
ıguez-Bocca, P., Romero, P., and Rubino, G.
(2009b). A cop for cooperation in a p2p stream-
ing protocol. In Proceedings of the IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Ultra Modern Telecommuni-
cations (ICUMT’09), Washington, DC, USA. IEEE
Computer Society.
Bertinat, M. E., Vera, D. D., Padula, D., Robledo, F.,
Rodr
´
ıguez-Bocca, P., Romero, P., and Rubino, G.
(2009c). Goalbit: The first free and open source peer-
to-peer streaming network. In Proceedings of the 5th
international IFIP/ACM Latin American conference
on Networking (LANC’09), pages 83–93, New York,
USA. ACM.
Cohen, B. (2003). Incentives build robustness in bittorrent.
www.bramcohen.com, 1:1–5.
Dorigo, M. and Stutzle, T. (2004). Ant Colony Optimiza-
tion. MIT Press.
Huang, Y., Fu, T. Z., Chiu, D.-M., Lui, J. C., and Huang,
C. (2008). Challenges, design and analysis of a large-
scale P2P-VoD system. In ACM SIGCOMM 2008 con-
ference on Data communication, Linkoping, Swede.
Liu, Y., Guo, L., Li, F., and Chen, S. (2009). A Case Study
of Traffic Locality in Internet P2P Live Streaming
Systems. In International Conference on Distributed
Computing Systems, ICDCS 2009, pages 423–432.
Ripeanu, M. (2001). Peer-to-peer architecture case study:
Gnutella network. In First International Conference
on Peer-to-Peer Computing, pages 99–100, Linkop-
ing, Sweden.
Rodr
´
ıguez, P. R. (2009). Optimizaci
´
on de la Estrategia de
Selecci
´
on de Piezas de Video en Redes P2P. Univer-
sidad de la Rep
´
ublica, Facultad de Ingenier
´
ıa, Insti-
tuto de Investigaci
´
on : LPE - IMERL. Montevideo,
Uruguay.
Rodr
´
ıguez-Bocca, P. (2008). Quality-centric design of Peer-
to-Peer systems for live-video broadcasting. PhD the-
sis, INRIA/IRISA, Universit
´
e de Rennes I, Rennes,
France.
Romero, P., Robledo, F., Rodr
´
ıguez-Bocca, P., Padula, D.,
and Bertinat, M. E. (2010). A cooperative network
game efficiently solved via an ant colony optimization
approach. In Proceedings of the Seventh International
Conference of Swarm Intelligence (ANTS’10), Lon-
don, UK. Springer, Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence.
SopCast - Free P2P internet TV (2007). http://
www.sopcast.org.
TVUnetworks home page (2007). http://tvunetworks.com/.
Zhao, B., Lui, J., and Chiu, D.-M. (2009). Exploring the
optimal chunk selection policy for data-driven P2P
streaming systems. In IEEE Ninth International Con-
ference on Peer-to-Peer Computing, pages 271–280,
Hong Kong, China.
Zhou, Y., Chiu, D. M., and Lui, J. (2007). A Simple Model
for Analyzing P2P Streaming Protocols. In Proceed-
ing of the IEEE International Conference on Network
Protocols (ICNP’07), pages 226–235, Beijing, China.
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
282
