
SOLVING THE RCPSP WITH AN EVOLUTIONARY
ALGORITHM BASED ON INSTANCE INFORMATION
José António Oliveira, Luís Dias and Guilherme Pereira
Centre ALGORITMI, University of Minho, Braga, Portugal
Keywords: Optimization, Project Management, Scheduling, RCPSP, Metaheuristics, Genetic Algorithm, Random Keys.
Abstract: The Resource Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (RCPSP) is NP-hard thus justifying the use meta-
heuristics for its solution. This paper presents an evolutionary algorithm developed for the RCPSP problem.
This evolutionary algorithm uses an alphabet based on random keys that makes easier its implementation
while solving combinatorial optimization problems. Random keys allow the use of conventional genetic
operators, what makes easier the adaptation of the evolutionary algorithm to new problems. To improve the
method's performance, this evolutionary algorithm uses an initial population that is generated considering
the information available for the instance. This paper studies the impact of using that information in the
initial population. The computational experiments presented compare two types of initial population - the
conventional one (generated randomly) and this new approach that considers the information of the
instance.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Resource Constrained Project Scheduling
Problem (RSPSP) is a classic project scheduling
problem, and belongs to the set of Combinatorial
Optimization (CO) problems that are very hard to
solve and therefore require heuristic procedures. The
use of exact methods to solve this type of CO
problems is limited to small size instances. The
RCPSP problem is a generalization of the
production-specific Job-Shop Scheduling Problem
(JSSP). According to (Zhang et al., 2007), the
Branch and Bound methods for JSSP do not solve
instances larger than 250 operations within a
reasonable time. As stated in (Liu et al., 2008), in
practical manufacturing environments, the scale of
job shop scheduling problems could be much larger
- in some big textile factories, the number of jobs
can be as much as 1,000.
Heuristic methods became very popular and have
gained success in solving scheduling problems. For
the last twenty years, a huge quantity of papers have
been published presenting several metaheuristic
methods. From Simulated Annealing to Particle
Swarm Optimization (Lian et al., 2006), there are
several variants of the same class of method. A very
popular method among researchers is the
Evolutionary Algorithms (EA).
Vaessens et al. (1996) presented the Genetic
Algorithms as the less effective metaheuristic to
solve the JSSP. A possibility to increase the
efficiency and the effectiveness on an algorithm is to
include in the algorithm specific knowledge of the
problem. Several works include some specific local
search for the JSSP that is based in the critical path
of a disjunctive graph. This work presents a strategy
to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of an
Evolutionary Algorithm to solve the RCPSP. Once
verified the difficulty to solve the RCPSP changes
from instance to instance, a procedure can be
implemented to get knowledge from the instance and
transfer it to the EA's initial population. The
developed EA is based in a previous one, developed
by us, to the JSSP (Oliveira et al., 2010) according
to the similarities between both problems. Above all
of this, the strategy to enhance the effectiveness was
tested in the JSSP by Oliveira et al. (2010) and in a
very particular case it improves the makespan in
about 8%.
The paper is organized as follows: an
introductory section defines the RCPSP problem and
its representation with the use of an AoN graph; a
central section describes the methodology and a
numerical example that supports the explanation of
the constructive algorithm; finally, some conclusions
and a discussion on future work are presented.
157
António Oliveira J., Dias L. and Pereira G..
SOLVING THE RCPSP WITH AN EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHM BASED ON INSTANCE INFORMATION.
DOI: 10.5220/0003759401570164
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES-2012), pages 157-164
ISBN: 978-989-8425-97-3
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 RCPSP
A project can be represented as a network of n
activities in a graph, where exist links between pairs
of activities, representing processing precedence
between them. The order to process the set of
activities must respect the precedence set. There are
two ways to represent a project: the activity-on-arc
(AoA) and the activity-on-node (AoN).
In the AoA mode, the set of nodes represents the
"events" (start/end processing) and the set of arcs
represents the "activities." In the AoN scheme, the
set of nodes represents the "activities" and the set of
arcs represents the precedence between the
"activities." In general, each activity requires the
simultaneous use of several resources
(Demeulemeester et al., 2003). In this paper, the
AoN scheme has been adopted since it allows a
direct correspondence with the disjunctive graph that
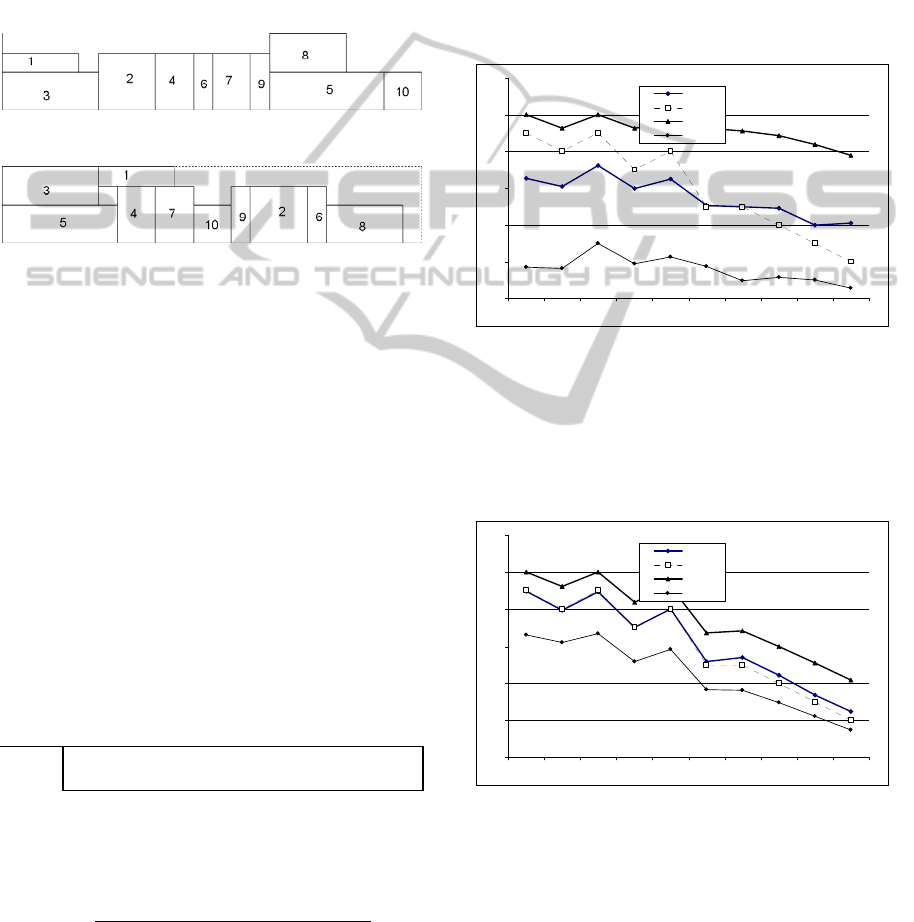
is usually used to represent the JSSP. Figure 1 shows
a project network with 10 activities, represented in a
AoN scheme (Ranjbar and Kianfar, 2009).
Figure 1: AoN project network.
For a given r renewable resources R1,..,Rr, a
constant amount of bk units of resource Rk is
available at any time. Activity j must be processed
for dj time units, where preemption is not allowed.
During this period of time, a constant amount of rjk
units of resource Rk is occupied. The objective is to
determine the starting times of Sj for the activities
j = 1,..,n in a way that:
i) at each time t, the total resource demanded is
less than or equal to the resource availability
for each resource type;
ii) the given precedence constraints are fulfilled;
iii) the makespan
max 1
max
n
jj
CC
=
=
, where
jjj
CSd=+
, is minimized.
Figure 1 shows also 2 dummy activities, node 0
and node 11 which represent the starting time of the
project (node 0) and the project conclusion time
(node 11). Their duration is null. Each node shows
the duration of the activity and the amount of
renewable resources. In this project instance it is
considered only one renewable resource. The set of
arcs represent the precedence set of the project.
Activity 6 can only be started after activities 1 and 2
are completed.
The RCPSP is a highly complex optimization
problem due to its combinatorial nature. This
problem belongs to the NP-hard class (Brucker et
al., 1998), and so an efficient algorithm for obtaining
exact solutions is unknown.
The research on the RCPSP has been extensive
along the years and it involves exact algorithms and
heuristic methodology. Generally, the exact methods
are based on branch and bound algorithm, where the
branch strategies are related to the choice of
activities in the disjunctive graph that represents the
project. Also, in this field of research, the continuous
development of new and better lower bounds for the
optimal solution is pointed out, what is a
fundamental auxiliary information for the heuristic
methods.
The state-of-the-art RCPSP performed by
Hartmann and Kolisch (2000) and updated later
(Kolisch and Hartmann, 2006) shows a bigger
number of publications on heuristics than on exact
methods. In this study, the authors explain that, in
the specialized bibliography, there are several
heuristic methodologies to deal with RCPSP. These
methods can be classified as “single pass” (over
activities set) or “multiple pass”, based in priority
dispatch rules to construct the solution, local
iterative improvement and meta-heuristics.
In the metaheuristics set, several approaches
have arisen, such as: evolution strategies, taboo
search, ant colony system, variable neighbourhood
search and simulated annealing. Some of those
metaheuristics include hybridization with local
search procedures and with single pass or multiple
pass. An example of hybridization is given by
Ranjbar and Kianfar (2009). They presented a
hybrid metaheuristic algorithm for solving the
RCPSP, which contains a scatter search skeleton and
uses a special solution combination method for
making children.
The process to construct a solution is a
fundamental component in the heuristic
methodology. With RCPSP in particular, this
component is called Schedule Generation Scheme
(SGS). For the RCPSP, two SGS models exist: the
serial model and the parallel model. It is possible to
find in the literature heuristic procedures that use
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
158

either one scheme or the other, but it is also possible
to find some methodologies that use both, or even a
combination of the two models.
Analyzing the computational results presented in
the literature performed with test instances with 30,
60 and 120 activities, it is possible to point out that
the better approximation methodology is the
population-based heuristic with representation of list
of activities and serial SGS. The parallel SGS seems
to be better when dealing with large instances.
It seems that further research for approach
methods will concentrate on the development of
algorithms which integrate the Forward–Backward
Improvement strategy (FBI), since four of the best
six heuristics already use this local search strategy.
The FBI strategy has two phases: the first phase
gives a feasible schedule using a priority dispatch
rule to sequence the activities in a bidirectional way;
the second phase tries to improve the resources
assignment performing successive bidirectional
passes without increasing the project duration
obtained in the first phase.
The performance of a heuristic can be improved
by integrating specific knowledge of the problem.
With the RCPSP, the integration of a constructive
algorithm in an Evolutionary Algorithm (EA)
constructs only active schedules. This strategy is
implemented similarly to that performed for the
particular case of the Job Shop Scheduling Problem.
3 EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHM
This work adopts a method based on Evolutionary
Algorithms. EA can be viewed as a metaheuristic
search techniques that imitates the principle of
evolution in nature i.e., EAs use a set of competing
potential solutions of the problem which evolve
according to rules of selection and transformation.
It is possible to briefly describe the functioning
of an EA in the following way. An EA proceeds in
iterations called generations. In each generation, a
set of solutions called population is generated.
Usually, the first population is generated randomly.
A new population is generated from a current
population using selection and transformation
operators. The members of a population are called
individuals. The fitness-function assigns a value
called fitness to each individual. Given an individual
and its fitness, a selection operator decides if an
individual from the current population is used as an
input of a transformation operator. A transformation
operator creates a new element of a new population
from an arbitrary number of elements of the current
population. It is expected that during the search
process, increasingly better solutions are found. To
achieve this goal, it is necessary that the
transformation operators focus attention on high
fitness. Very common transformation operators are
reproduction (copying an individual to the new
population unaltered), mutation (an individual is
changed in a random fashion) and crossover (where
parts of two individuals are combined).
The simplicity of an EA to model more complex
problems and its easy integration with other
optimization methods were factors that were
considered for its choice. One advantage of this EA
is the portability to other problems. The algorithm
proposed was conceived to solve the RCPSP, but the
method can be adapted to solve other variants or
extensions of the RCPSP, such as the RCMPSP. In
fact, the EA was already adapted to solve other type
of problems in the Project Planning field (Silva et
al., 2010). When implementing an appropriate
algorithm to construct solutions based on
chromosome, the EA can also solve other scheduling
algorithms like job shop (Oliveira et al., 2010).
Furthermore, random keys chromosome (Bean,
1994) also enables to apply the algorithm in other
type of problems once conventional genetic
operators, which are problem independent, could be
used.
As Gonçalves et al. (2005) state, the important
feature of random keys is that all offspring formed
by crossover are feasible solutions, when it is used
as a constructive procedure based on the available
operations to schedule and the priority is given by
the random key allele. Through the dynamics of the
genetic algorithm, the system learns the relationship
between random key vectors and solutions with
good objective function values.
A chromosome represents a solution to the
problem and is encoded as a vector of random keys
(random numbers). In this work, according to Cheng
et al. (1996), the problem representation is indeed a
mix from priority rule-based representation and
random keys representation. An excellent
classification of heuristics algorithms for the RCPSP
was provided by Kolisch and Hartmann (1999).
They discussed several methods and alternatives to
generate different type of solutions for the RCPSP
and, in particularly, they provided detailed
algorithms to generate active schedules. In the
meantime, in this EA the solutions are decoded /
constructed by an algorithm, that is based on Giffler
and Thompson’s algorithm (Giffler and Thompson,
1960) for the JSSP. While the Giffler and
Thompson’s algorithm can generate all the active
SOLVING THE RCPSP WITH AN EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHM BASED ON INSTANCE INFORMATION
159

plans for the JSSP, the adapted constructive
algorithm only generates a plan according to the
chromosome. Similar to the JSSP, the solutions of
RCPSP can be classified on three sets: Semi-active,
Active, and Non-delay schedules (Sprecher et al.,
1995).
As advantages of this strategy, we have pointed
the minor dimension of solution space, which
includes the optimum solution and the fact that it
does not produce impossible or disinteresting
solutions from the optimization point of view. On
the other hand, since the dimensions between the
representation space and the solution space are very
different, this option can represent a problem
because different chromosomes can represent the
same solution.
Using the adapted Giffler and Thompson’s
algorithm to construct a solution based on the
priority values of each activity, a Serial Schedule
Generation Scheme is adopted. It has been shown by
Kolisch (1996) that a serial scheme yields better
results when a large number of schedules is
computed for one project instance. Attending
Hartmann (1998), the parallel scheme might exclude
all optimal solutions from the search space, while
the search space of the serial scheme always
contains an optimal schedule.
The constructive algorithm has n stages and in
each stage an activity is scheduled. To assist the
algorithm’s presentation, consider the following
notation existing in stage t:
t
P - the partial schedule of the
(
)
1t −
scheduled
activities;
t
S - the set of activities schedulable at stage t , i.e.
all the activities that must precede those in
t
S
are in
t
P ;
t
Q - the set of activities queued at stage t , i.e. all
the activities that are not in
t
S nor in
t
P ;
k
σ
- the earliest time that activity
k
a in
t
S could be
started;
k
φ
- the earliest time that activity
k
a in
t
S could be
finished, that is
kkk
p
φ
σ
=+
;
M
∗
- the set of resources used by
k
a in
t
S which
has
{
}
min
kk
aS k
φ
φ
∗
∈
=
;
t
S
∗
- the conflict set formed by
k
a in
t
S which use
at least one resource of
M
∗
and
j
σ
φ
∗
< ;
j
a
∗
- the selected activity to be scheduled at stage t .
Table 1 presents the constructive algorithm that
is used to build a solution.
In Step 3, instead of using a priority dispatching
rule, the information given by the chromosome is
used. If the maximum allele value is equal for two or
more operations, one is chosen randomly.
Table 1: A constructive algorithm.
3.1 First Generation
In the RCPSP it is possible to calculate for each
activity the remaining time for completion of the
project. In the project network this time is referred to
as “tail”. This value represents the longest path from
the activity to node n+1. It is easy to admit that the
activities with large tail must be sequenced first
because they could define the makespan. Indeed,
there exists the dispatching rule that is used in
practice JSSP which sequences operations in first
place that belongs to the job with Most Work
Remaining (MWR).
Consider the following example presented in
Figure 1, with ten activities. In this instance there is
only one constrained renewable resource with 4
available units. Table 2 presents this instance. The
activities are numbered sequentially and represented
by index j. The duration of each activity is given in
the row “duration”.
Table 2: The instance data.
Activity 12345678910
duration 4352612432
resources 1323233212
tail 9897855432
Step 1
Let
1t
=
with
1
P
being null.
1
S
will be the
set of all activities with no predecessors.
Step 2
Find
{
}
min
kt
aS k
φ
φ
∗
∈
=
and identify
M
∗
.
Form
t
S
∗
.
Step 3
Select activity
j
a
∗
in
t
S
∗
, with the greatest
allele value.
Step 4
Move to next stage by
(1)
adding
j
a
∗
to
t
P
, so creating
1t
P
+
;
(2) removing
j
a
∗
from the list of
predecessors of activities in
t
Q
deleting
j
a
∗
from
t
S
and creating
1t
S
+
by adding to
t
S
the activities
that
j
a
∗
as the only predecessor;
(3)
deleting
j
a
∗
from
t
S
and creating
1t
S
+
by adding to
t
S
the activities
with no predecessors;
(4)
incrementing
t
by 1.
Step 5
If there are any activities left
unscheduled
(
)
tN<
, go to Step 2.
Otherwise, stop.
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
160
The tail row shows the remaining time to
complete the project including the processing of the
activity. For instance, the tail of activity 3 is 9 and is
equal to the duration of activities 3, 8 and, 11, and
that is respectively 5, 4, and 0 (Figure 1). It
correspond to the longest path from node 3 to node
11.
Applying the MWR rule to this instance the
schedule is given in Figure 2. For this small
example, the optimal solution is presented in Figure
3.
Figure 2: Gantt chart of MWR solution.
Figure 3: Gantt chart of optimal solution.
In the chosen random key representation, a
chromosome is a vector of N genes that are real
numbers between 0 and 1. The representation has
one gene for each activity. Table 3 presents two
chromosomes for a RCPSP of ten activities. The
second chromosome (chrms2) was generated
randomly, while the first chromosome (chrms1)
represents the information that is obtained dividing
in the example above the tail value per maximum
tail value plus one (9+1 in the example). Applying
the constructive algorithm and considering the
chromosome chrms1, the solution of Figure 2 is
obtained. Attending to this property we implement a
procedure to generate the first population that
includes some knowledge about the instance in the
form of the tail of each activity.
Table 3: Chromosomes for a RCPSP10.
Activity
1
2
345
6
7
8
910
chrms1
0.90 0.80 0.90 0.70 0.80 0.50 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20
chrms2
0,30 0.30 0.70 0.80 0.30 0.40 0.20 0.70 0.10 0.20
To generate L individuals in a population the
following expression at (1) is used to generate the
allele value for each gene j:
(
)
;
max( )
jj
j
j
randbetween tail tail i GAP
allele
tail i GAP
+×
=
+×
(1)
3.2 Considerations About GAP
The GAP value allows obtaining at the end of
population a quite random chromosome. The higher
the GAP, the more random is the population. Lower
GAP gives a population close to the MWR dispatch
rule.
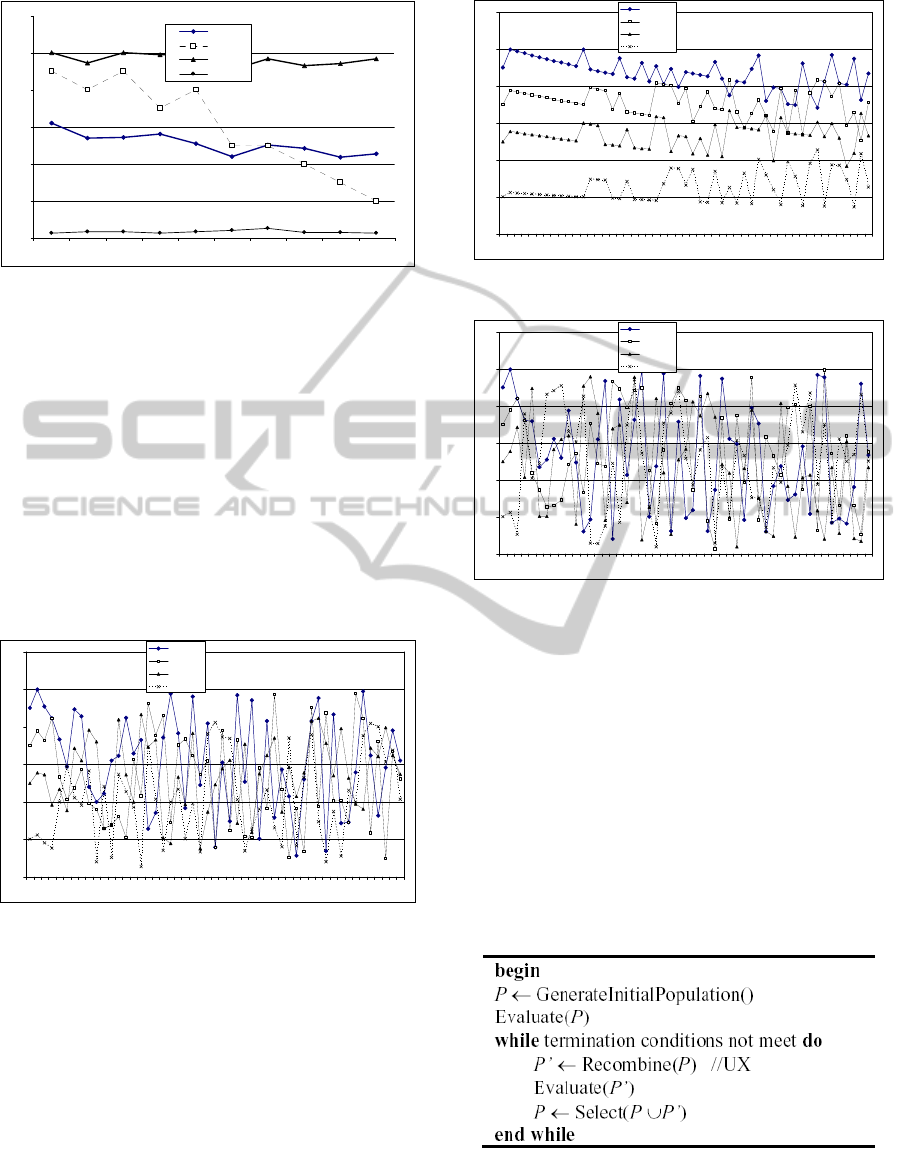
For a population of 50 individuals, the graphic
presented in Figure 4 presents some statistics of the
allele values for each gene (10 activities / genes).
The average value, maximum value, minimum value
and also the tail value of each operation is presented.
0,00
0,20
0,40
0,60
0,80
1,00
1,20
12345678910
average
tail
max
min
Figure 4: Statistics of allele’s values.
Figures 5 and 6 show the GAP effect in the
statistics of the allele values for the 10 activities.
Figure 5 shows the statistics when a small GAP is
used. The values are very close to the tail of each
operation.
0,00
0,20
0,40
0,60
0,80
1,00
1,20
12345678910
average
tail
max
min
Figure 5: Statistics of allele’s values with small GAP.
Figure 6 shows the statistics for a high GAP. The
range of variation for the alleles is very similar for
all genes, so the population is “more random”.
SOLVING THE RCPSP WITH AN EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHM BASED ON INSTANCE INFORMATION
161
0,00
0,20
0,40
0,60
0,80
1,00
1,20
12345678910
average
tail
max
min
Figure 6: Statistics of allele’s values with high GAP.
Figure 7 presents the alleles’ values of four genes
when using a GAP=2. These genes belong to the
activities having different tails values which are
respectively 9, 7, 5, and 2. It is possible to verify that
for the first chromosomes the alleles’ values
translate the priority give by the tail of each
operation. It is also possible to verify that the last
individuals have quite random alleles. It is possible
to see that in some individuals the activity 10
(Gene10) and activity 6 (Gene6) have a priority
greater than the activity 1 (Gene1). This situation
allows a first sequence of these activities before
activity 1, which is the activity with the greatest tail.
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
1,2
1 3 5 7 9 111315171921232527293133353739414345474951
Gene1
Gene4
Gene6
Gene10
Figure 7: The allele generation.
Figures 8 and 9 show the effect of GAP on the
allele generation for the same genes. Figure 8 shows
the alleles values when used as small GAP. The
values are very close to the tail of each operation.
Figure 9 shows the statistics for a high GAP. The
range of variation for the alleles is very similar for
all genes, so these allow “any” sequence to schedule
these four activities.
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
1,2
1 3 5 7 9 111315171921232527293133353739414345474951
Gene1
Gene4
Gene6
Gene10
Figure 8: The allele generation with small GAP.
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
1,2
1 3 5 7 9 111315171921232527293133353739414345474951
Gene1
Gene4
Gene6
Gene10
Figure 9: The allele generation with high GAP.
3.3 The Algorithm Structure
The genetic algorithm has a very simple structure
and can be represented in Table 4. It begins with
population generation and her evaluation. Attending
to the fitness of the chromosomes the individuals are
selected to be parents. The crossover is applied and
it generates a new temporary population that also is
evaluated. Comparing the fitness of the new
elements and of their progenitors the former
population is updated.
Table 4: Genetic algorithm.
The Uniform Crossover (UX) is used this work.
This genetic operator uses a new sequence of
random numbers and swaps both progenitors' alleles
if the random key is greater than a prefixed value.
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
162
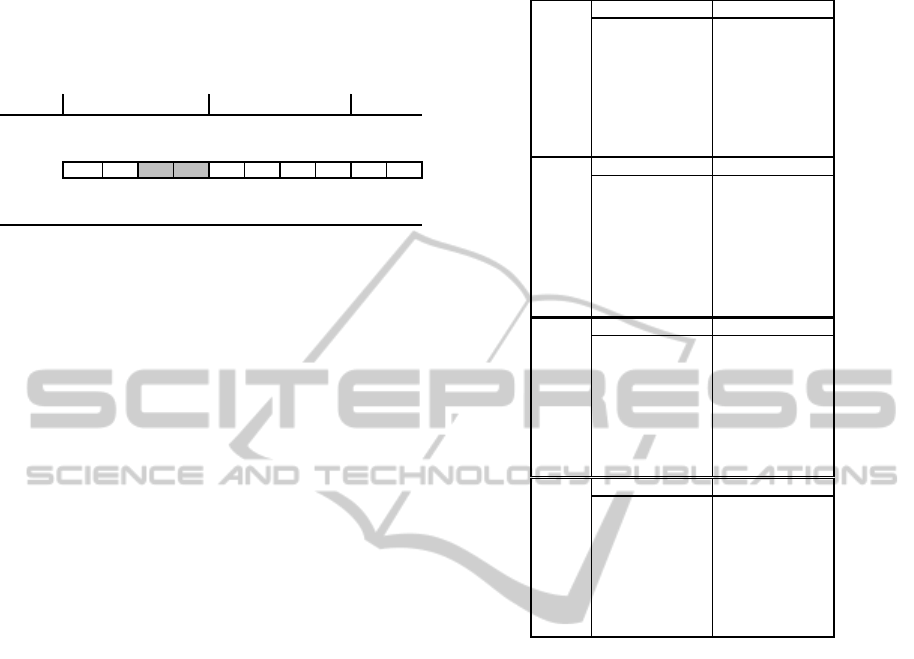
Table 5 illustrates the UX's application on two
parents (prnt1, prnt2), and swaps alleles if the
random key is greater or equal than 0.75.
Table 5: The UX crossover.
i
1
2
3
45
6
7
8
910
prnt1
0.89 0.48 0.24 0.03 0.41 0.11 0.24 0.12 0.33 0.30
prnt2
0.83 0.41 0.40 0.04 0.29 0.35 0.38 0.01 0.42 0.32
randkey
0.64 0.72 0.75 0.83 0.26 0.56 0.28 0.31 0.09 0.11
dscndt1
0.89 0.48 0.40 0.04 0.41 0.11 0.24 0.12 0.33 0.30
dscndt2
0.83 0.41 0.24 0.03 0.29 0.35 0.38 0.01 0.42 0.32
The genes 3 and 4 are changed and it originates
two descendants (dscndt1, dscndt2). Descendant 1 is
similar to parent 1, because it has about 75% of
genes of this parent.
4 EXPERIMENTS
The Genetic Algorithm was coded in C++ and the
computer used was a PC Pentium IV 3GHz
processor with 1024 Mbytes of RAM., with Linux
operative system.
The problem data set was taken from PSPLIB
datasets (Kolisch and Sprecher, 1997). The dataset
consists of four test sets J30, J60, J90 and J120 that
contain problem instances of 30, 60, 90 and 120
activities, respectively, and have been constructed
by the instance generator ProGen. In this
preliminary study we present results for 4 instances
with 30 activities: J301_1, J301_2, J301_3 and
J301_4. The optimal value for these instances are
respectively 43, 47, 47 and 62.
Table 6 resumes the computational experiments.
For each instance were made five runs considering
the tail information on the initial population, and
also were made five runs with an initial population
generated randomly. In each run the algorithm
performs 5000 iterations.
Table 6 shows the average value and the best
value of five runs. Each column shows the values in
different iterations of the algorithm. In the
computation experiments it was only used a value
for the GAP.
Globally in all experiments the use of tails’
information of the instance produces in average
1.8% better results. This advantage is more evident
in the initial iterations, so for some instances it was
obtained solutions about 5.5% better. In terms of
best solution the use of tails' information is relevant
on the initial iterations. In some instances the use of
tails information produces a solution about 3.6%
better than using a random initial population.
Table 6: Computational experiments.
Iteration Average Best Average Best
1 76.2 73 76.2 75
50 61.8 60 58.4 58
100 60.8 59 58.4 58
500 57.0 55 54.0 54
1000 56.0 54 54.0 54
2000 55.0 53 53.0 53
5000 53.4 53 53.0 53
J301_1_Random J301_1_tails
Iteration Average Best Average Best
1 89.2 84 90.4 90
50 84.2 84 82.6 81
100 84.0 84 82.6 81
500 80.8 80 78.4 78
1000 80.4 80 78.4 78
2000 78.8 77 78.4 78
5000 78.4 77 78.4 78
J301_2_Random J301_2_tails
Iteration Average Best Average Best
1 93.0 91 89.6 89
50 81.6 81 80.6 79
100 81.0 81 79.8 79
500 78.6 77 79.0 78
1000 76.6 75 76.0 76
2000 76.4 75 76.0 76
5000 75.4 75 76.0 76
J301_3_Random J301_3_tails
Iteration Average Best Average Best
1 152.6 146 149.6 147
50 148.0 146 144.4 143
100 145.4 142 144.4 143
500 140.2 138 136.0 136
1000 139.6 138 136.0 136
2000 139.0 138 136.0 136
5000 137.4 136 136.0 136
J301_4_tailsJ301_4_Random
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents a new method for generating the
initial population for an evolutionary algorithm that
solves the Resource Constrained Project Scheduling
Problem (RCPSP). This proposed method, through
known information for each instance, establishes
different priorities to the activities based on the
remaining processing time to finish the project, thus
generating an initial population. The algorithm uses
a representation based on random keys.
Results are then compared with the conventional
random generation and some promising conclusions
arise. In fact the experimental computation shows
better results when the information of the instance is
used, especially on initial iterations.
Definitely this could be a very simple way to
increase effectiveness of the algorithm. Furthermore
the use of instance information could also be
parameterized, obtaining levels of convergence of
the algorithm depending on available CPU time.
Since the random keys representation has no
Lemarkin property, it is our intention to apply the
SOLVING THE RCPSP WITH AN EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHM BASED ON INSTANCE INFORMATION
163

same strategy on initial population generation in
other types of representation for the RCPSP, namely
the permutation code.
Further work would also consist on applying this
method to other problems. The Resource
Constrained Multi-Project Scheduling Problem
(RCMPSP), as a generalization of the RCPSP,
would be the next candidate for evaluating the
advantages of the approach presented above.
REFERENCES
Bean, J. C., 1994. Genetics and random keys for
sequencing and optimization. ORSA Journal on
Computing, 6, 154–160.
Brucker, P., Knust, S., Schoo, A., Thiele, O., 1998. A
branch and bound algorithm for the resource-
constrained project scheduling problem. European
Journal of Operational Research, 107, 272-288.
Cheng, R., Gen, M., Tsujimura, Y., 1996. A tutorial
survey of job-shop scheduling problems using genetic
algorithms part I: Representation. Computers &
Industrial Engineering, 34 (4), 983–997.
Demeulemeester, E., Vanhocke, M., Herroelen, W., 2003.
RanGen: A Random Network Generator for Activity-
on-the-node Networks. Journal of Scheduling, 6, 17-
38.
Giffler, B., Thompson, G. L., 1960. Algorithms for
solving production scheduling problems. Operations
Research, 8, 487-503.
Gonçalves, J. F., Mendes, J. J., Resende, M. G. C., 2005.
A hybrid genetic algorithm for the job shop scheduling
problem. European Journal of Operational Research,
167, 77–95.
Hartmann, S., Kolisch, R., 2000. Experimental evaluation
of state-of-the-art heuristics for the resource-
constrained project scheduling problem. European
Journal of Operational Research, 127, 2, 394-407.
Kolisch, R., 1996. Serial and parallel resource-constrained
project scheduling methods revisited: Theory and
computation. European Journal of Operational
Research, 90, 320–333.
Kolisch, R., Hartmann S., 1999. Heuristic algorithms for
solving the resource-constrained project scheduling
problem - Classification and computational analysis,
in Weglarz, J. (Eds.): Project Scheduling – Recent
Models, Algorithms and Applications, Kluwer,
Boston, p. 147 - 178.
Kolisch, R., Hartmann, S., 2006. Experimental
investigation of heuristics for resource-constrained
project scheduling: An update. European Journal of
Operational Research, 174, 1, 23-37.
Kolisch, R., Sprecher, A., 1997. PSPLIB - A project
scheduling library. European Journal of Operational
Research, 96, 205-216.
Lian, Z., Gu, X., Jiao, B., 2006. A similar particle swarm
optimization algorithm for job-shop scheduling to
minimize makespan. Applied Mathematics and
Computation, 183, 1008–1017.
Liu, M., Hao, J., Wu, C., 2008. A prediction based
iterative decomposition algorithm for scheduling
large-scale job shops, Mathematical and Computer
Modelling, 47, 411–421.
Oliveira, J. A., Dias, L., Pereira, G., 2010. Solving the Job
Shop Problem with a random keys genetic algorithm
with instance parameters. Proceedings of 2nd
International Conference on Engineering
Optimization – EngOpt 2010, Lisbon – Portugal.
Ranjbar, M., Kianfar, F., 2009. A Hybrid Scatter Search
for the RCPSP. Transaction E: Industrial
Engineering, 16, 11-18.
Silva, H., Oliveira, J. A., Tereso, A., 2010. Um Algoritmo
Genético para Programação de Projectos em Redes de
Actividades com Complementaridade de Recursos.
Revista Ibérica de Sistemas y Tecnologías de la
Información,. 6, 59-72.
Sprecher, A., Kolisch, R., Drexl A., 1995. Semi-active,
active, and non-delay schedules for the resource-
constrained project scheduling problem, European
Journal of Operational Research, 80, 94-102.
Vaessens, R., Aarts, E., Lenstra, J. K., 1996. Job Shop
Scheduling by local search. INFORMS Journal on
Computing, 8, 302-317.
Zhang, C., Li, P., Guan, Z., Rao, Y., 2007. A tabu search
algorithm with a new neighborhood structure for the
job shop scheduling problem. Computers &
Operations Research, 53, 313-320.
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
164
