
A RELATIONAL DISTANCE-BASED FRAMEWORK FOR
HIERARCHICAL IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
Laura Antanas, Martijn van Otterlo, Jos
´
e Oramas M., Tinne Tuytelaars and Luc De Raedt
Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Keywords:
Hierarchical image understanding, Relational instance-based learning, Structured representations.
Abstract:
Understanding images in terms of hierarchical and logical structures is crucial for many semantic tasks, in-
cluding image retrieval, scene understanding and robot vision. This paper combines compositional hierarchies,
qualitative spatial relations, relational instance-based learning and robust feature extraction in one framework.
For each layer in the hierarchy, substructures in the images are detected, classified and then employed one layer
up the hierarchy to obtain higher-level semantic structures, by making use of qualitative spatial relations. The
approach is applied to street view images. We employ a four-layer hierarchy in which subsequently corners,
windows and doors, and individual houses are detected.
1 INTRODUCTION
Interpreting visual scenes is a hard task. The field
of computer vision has developed many techniques
over the past decades for segmentation, classifica-
tion, recognition and retrieval of images, objects
and scenes, e.g., (Li et al., 2009; Sudderth et al.,
2008). Many of these techniques use a plethora of
local low-to medium-level features such as geomet-
ric primitives, patches, point clouds and invariant fea-
tures (Tuytelaars and Mikolajczyk, 2007). However,
for high-level tasks such features may not suffice. It
is more intuitive to understand and describe visual
scenes in terms of hierarchical structural or graph-
like representations, which express the natural com-
position of scenes into objects, parts of objects and
lower-level substructures (Pinz et al., 2009).
Man-made scenes exhibit considerable structure
that can be captured using qualitative spatial relations.
For example, a typical house consists of aligned ele-
ments such as: a roof, some windows, one or more
doors and possibly a chimney. A hierarchical aspect
is that windows and chimneys themselves are com-
posed of particular configurations of local features
(e.g., corners with a certain appearance arranged in
a rectangular-like way and ‘brick’-like patterns of a
certain shape, respectively). Our view on image rep-
resentation builds on very early ideas that hierarchi-
cal structure and relational constraints are key compo-
nents of an image understanding system (Hanson and
Riseman, 1978). Since then both (relational) machine
learning and low-to-medium-level vision as separate
research fields have progressed tremendously, and
currently novel, modern combinations can be con-
structed along these lines.
In this paper we start from the idea that visual
scenes are best described using high-level representa-
tional devices such as graphs and more generally us-
ing logical languages (De Raedt, 2008). The advan-
tage of these rich symbolic representations is that they
can, for example, make abstractions of exact locations
using spatial relations between scene components and
generalize over similar situations, independent of the
metric details. We describe a novel, model-free rela-
tional distance-based technique for hierarchical image
understanding. It considers the structural aspect of
a scene and is based on recent developments in rela-
tional learning. Instead of using a formal model of the
distribution of scenes (e.g., in the form of a grammar),
we start from a set of annotated examples of objects in
the scene. Yet, our framework preserves desired prop-
erties of grammars, that is, it employs structured input
features and outputs a structured explanation of the
image at each layer in the hierarchy. The base layer
relies on local feature descriptors. A subsequent layer
consists of objects and higher levels consist of con-
figurations of objects. Spatial logical representations
are used to generalize over configurations with differ-
ent number of components. We explicitly focus on
the recognition of known substructures in street view
images (i.e., windows, doors and houses), although,
our approach can be used for other domains as well.
Our main contribution is a new framework in
which spatial configurations and relational distance
functions are used throughout all levels of a hierarchy,
in a unified way, to recognize known objects. Many
Antanas L., van Otterlo M., Oramas J., Tuytelaars T. and De Raedt L. (2012).
A RELATIONAL DISTANCE-BASED FRAMEWORK FOR HIERARCHICAL IMAGE UNDERSTANDING.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods, pages 206-218
DOI: 10.5220/0003779702060218
Copyright
c
SciTePress

computer vision algorithms use probabilistic classi-
fiers, distance functions and kernels for object detec-
tion. Yet, these techniques are less well equipped for
detecting higher-level concepts that consist of qualita-
tive spatial configurations of objects, for which rela-
tional generalization techniques (De Raedt, 2008) are
required. Thus far, most work in computer vision has
focused on fixed compositional structures (Felzen-
szwalb et al., 2010) or constellation models (Fergus
et al., 2007). We further show how recent results in re-
lational distance metrics (De Raedt and Ramon, 2009)
can be utilized as a generalization technique to help
recognize higher-level structures in an image. We as-
sume manually labeled examples of object categories
we want to recognize throughout all layers in the hier-
archy (i.e., houses, windows and doors). Each house
is annotated with the locations and shapes of its con-
stituent windows and doors. We represent an object as
a set of parts and a set of qualitative spatial relations
defined on them (hence; a relational attribute graph).
Each image substructure is spatially embedded in a
2D plane, and parts are related to each other with re-
spect to this space. A strong point of our framework is
that distance functions at each level of the hierarchy,
either in terms of low-level features or high-level rela-
tional spatial composites, can easily be replaced by al-
ternatives. In addition to a novel framework combin-
ing robust visual features and relational generalization
techniques, we introduce a new annotated dataset de-
rived from Google StreetView Images.
2 RELATED WORK
Several papers have applied computer vision tech-
niques to house facades domain. In (Hartz and Neu-
mann, 2007; Hartz, 2009) structure models of mean-
ingful facade concepts are learned from examples.
In (Zhao et al., 2010) the authors tackle the house
delineation problem by generating vertical separating
lines on the facade and using a dissimilarity measure
between these features. Finally (M
¨
uller et al., 2007;
Koutsourakis et al., 2009) assume to have the struc-
ture of a building facade and then estimate the param-
eters of the model. Different from these, our work
uses distances between logical interpretations to de-
tect known structures in an instance-based fashion.
In other domains, i.e., document analysis,
distance-based techniques have been used in a re-
lational setting (Esposito et al., 1992), yet they do
not address the intrinsically noisy nature of vision-
based interpretation of images of houses. In fact, most
papers that do address such problems use a model-
based approach and perform interpretation through
image grammars (Hartz and Neumann, 2007; Lippow
et al., 2008; Felzenszwalb et al., 2010). These have
been well-studied in the literature (Zhu and Mumford,
2006), but need considerably more bias (or learning
procedures) to supply (or learn) the grammar rules.
This in contrast to our model-free approach, which
is based on comparison to annotated examples. The
use of rich logical formalisms in non-grammar ap-
proaches by the state-of-the-art in computer vision is
limited (Szeliski, 2010). Closely related are graph
matching and graph kernel-based techniques for im-
age understanding (Caetano et al., 2009; Harchaoui
and Bach, 2007). However, different from these, our
framework builds on recent general results on dis-
tance metrics for logical interpretations (De Raedt and
Ramon, 2009). In this sense, we approach a cur-
rent interest in using relational learning techniques for
complex vision tasks (Petrou, 2008). Other relevant
work includes approaches based on relational object
models (Bar-Hillel and Weinshall, 2008) or proba-
bilistic relational learning (Dubba et al., 2010).
3 HIERARCHICAL IMAGE
UNDERSTANDING
In our hierarchical framework an image Z is described
at several layers 0,...,k in the hierarchy, with 0 the
base layer and k the top layer (Figure 1). At each
layer, the description consists of a set of classified re-
gions of interest (or parts) C
i
as well as the spatial re-
lationships among them. The classes denote the con-
cepts the parts belong to. The task then consists of
using the description of an image at level i to obtain
and classify the parts C
i+1
at the next higher level i+1
in the hierarchy. We call this the delineation task. We
assume that annotated images at all layers are avail-
able as training data.
(2) object
layer
(1) primitive
layer
(0) pixel
layer
(k) scene
layer
(3) higher-level
concepts
layer
...
Figure 1: A typical hierarchy with k + 1 layers. A layer
i is a set of classified entities (empty circles) arranged in
spatial configurations. Each configuration generates a clas-
sified entity at the next higher-level i + 1 in the hierarchy.

In our case, the base layer consists of the image
itself, while the parts are pixels. In the primitive layer
the parts are local patterns, e.g., a corner. The object
layer is then built from spatial configurations of such
local patterns, forming regions of interest belonging
to concepts such as door and window. These are then
used at the next level to find higher-level regions of
interest representing houses. We stop at the scene
layer which groups houses into streets. Each layer
consists of parts and the classes they belong to, and it
is formed by making use of spatial configurations of
parts from the previous lower-level layer. This hier-
archical image understanding framework propagates
the detected parts in a bottom up manner through each
layer. Information flow is similar at all levels; first,
the parts C
i−1
of the previous layer are detected, then
current-level parts are generated using configurations
of C
i−1
and finally the best ones C
i
are kept to be fur-
ther employed at the next layer.
4 REPRESENTATION AND
FUNCTION OF ONE LAYER
Let us describe in more detail how to represent an
image Z at one layer in the hierarchy. We assume
knowledge about the identity of the layer and access
to automatically detected and extracted regions of in-
terest in the image at this layer, together with their
descriptors. Based on these assumptions we define
a language consisting of visual entities, spatial rela-
tions between visual entities, composite entities and
membership relations between a visual entity and a
composite entity. The language can differ from one
layer to another, depending on the characteristics of
the parts (or entities) at each layer.
A visual entity (vent(id,attr1,. ..)) represents
an entity of the image at the current layer i, e.g., a
corner or a window with id as its unique object iden-
tifier. Attributes of a visual entity are its position,
i.e., the coordinates of the visual entity bounding box,
and a class or concept label. Spatial relations im-
pose a structure on visual entities (e.g. spatial neigh-
borhood) and are defined using a logical background
theory (a set of Prolog rules as in relational learn-
ing). As one example consider the spatial relation
cRight(id
1
,id
2
,dist) (close aligned horizontally
to the right) with an attribute for the Euclidean dis-
tance dist between two visual entities id
1
and id
2
. A
composite entity (cent(ic,attr1, ...)) is a candidate
visual entity at the next level i + 1; it consists of a set
of visual entities at level i and the relations that hold
among them; thus it implicitly groups a set of visual
entities into a composite entity, using the part-of re-
lation. Thus, composite and visual entities are linked
through membership relations partof(id,ic). All
visual entities, composite entities, spatial and mem-
bership relations for image Z at one layer are denoted
V
Z
, C
Z
, S
Z
and M
Z
, respectively. We define a visual
interpretation I
Z
of an image Z as their union. For any
composite entity c we denote V
c
as the set of visual
entities grouped by c, S
c
as the set of spatial relations
representing the projection of S
Z
on V
c
and M
c
as the
set of membership relationships between the elements
of V
c
and c itself. We further denote I
c
as the subset
of I
Z
that contains the visual entities V
c
, their spatial
relations S
c
grouped by c, corresponding membership
relations M
c
and c itself. V S
c
finally consists of V
c
and S
c
in I
c
, while V S
Z
is determined by V
Z
and S
Z
in
I
Z
. An example of a visual interpretation at the house
layer for Figure 2(a) is given in Figure 2(c). Some
elements of C
Z
capture the inherent structure of the
concept house; the rest belong to the category none.
It is convenient to visualize interpretations as
graphs in which the entities correspond to vertices and
the relations to directed (labeled) edges. A compos-
ite entity then denotes the subgraph V S
c
. The task is
to construct the set of relevant composite entities C
such that the visual entities for level i + 1 can be ob-
tained. This is a combinatorial problem as potentially
all subgraphs in V S
Z
are candidates. The generation
of meaningful new entities is also a novel task in the
relational learning context. It can be seen as a dual to
predicate invention (Muggleton and Buntine, 1988).
There the goal is to determine new and useful pred-
icates. Here the task is to invent new entities. In a
probabilistic context, it is related to existence uncer-
tainty, a term coined in the literature on probabilistic
relational models (Getoor et al., 2000).
Our goal is to recognize known visual structures
in a new image. We approach it in two main steps:
classification and selection. In the classification step,
for each of the candidate visual entities in C, we need
to determine the concept they belong to (if any). This
can be cast into a concept-learning problem. For each
target class (such as house, window and door) we have
examples in our training set. Consider, for instance,
the concept of a house. In Figure 2(b) the compos-
ite entity ic
1
forms a positive example, while ic
2
is a
negative example. For each composite entity c that
forms a positive example of a concept, we use the vi-
sual interpretation V S
c
as prototype. Such a prototype
is shown as a graph in Figure 4 on the left, where it is
matched with a part of another image interpretation.
Its corresponding visual interpretation is presented in
Figure 3. The composite entity classification task is
solved using an instance based learning approach. We
use a distance measure to find the best matches of can-

(a) An image Z.
id
6
window
window
id
1
house
ic
1
none
ic
2
house
ic
3
cRight
window
id
2
window
id
8
cent
door
id
3
window
id
4
door
id
7
window
id
5
vent
cAbove
(b) Graphical representation of image Z. Each visual entity corresponds
to a detected door/window (black circles in white bounding boxes de-
scribing spatial locations l
i
) and each composite entity is a possible house
defined by a subgroup of these objects (white circles). The spatial and
membership relations are marked by the continuous and interrupted lines,
respectively.
I
Z
= {vent(id
1
,l
1
,win),vent(id
2
,l
2
,win),
vent(id
3
,l
3
,door), vent(id
4
,l
4
,win),
vent(id
5
,l
5
,win),vent(id
6
,l
6
,win),
vent(id
7
,l
7
,door), vent(id
8
,l
8
,win),
cRight(id
1
,id
2
,d
1
),cAbove(id
2
,id
3
,d
2
),
cRight(id
3
,id
4
,d
3
),cRight(id
4
,id
5
,d
4
),... ,
cent(ic
1
,l
9
,house),cent(ic
2
,l
10
,none),
cent(ic
3
,l
11
,house),partOf(id1,ic
1
),partOf(id
2
,ic
1
),
partOf(id
2
,ic
2
),partOf(id
5
,ic
2
),... }.
(c) Corresponding visual interpretation I
Z
at the house layer for image
Z. Visual entities are denoted with vent while composite entities with
cent. Spatial relations are cRight (close to the right) and cAbove (close
above). The membership relation is denoted partOf.
Figure 2: Image representation at one layer.
didate composite entities with prototypes.
The entity classification step classifies each entity
in C in a local manner, that is, this step only takes
into account the entity to be classified and the set of
prototypes, but no context. This may give unintuitive
results at the global level. For instance, it could be
that two entities with a significant overlap are both
classified as houses. Therefore, we also perform a se-
lection step in which contextual constraints are taken
into account. Using global optimization we find the
best subset C
∗
of the classified entities in C. From C
∗
we then derive detections.
V S
c
= {cent(ic
1
,house),
vent(id1,l1,win),vent(id2,l2,door),vent(id3, l3, win),
vent(id4,l4,win),vent(id6,l6,win),cRight(id1,id2,d1),
cAbove(id2,id3,d2),cRight(id3,id4,d3),
cAbove(id2,id4,d4),cRight(id6,id3,d5),
cAbove(id1,id6,d6),partOf(id
1
,ic
1
),partOf(id
2
,ic
1
),
partOf(id
3
,ic
1
),partOf(id
4
,ic
1
),partOf(id
6
,ic
1
)}.
Figure 3: An example of an instance in the house facade do-
main at the house layer. The target attribute is the category
of the composite entity, i.e., house in this case.
5 LAYER-WISE SEMANTIC
SEGMENTATION
Next, we explain how composite generation, classi-
fication and selection functions work and fit together
to obtain the delineation at one layer in the hierar-
chy. Intuitively, given an image Z we detect known
structures by trying to best embed prototypes in Z. To
this end, we first generate composite entities, we then
classify and select them, and finally we obtain class
detections (Algorithm 1).
I Composite Entity Generation (GENERATE) . We
generate the set of relevant composite entities C for an
image Z using a language bias, common in relational
learning. As the number of all composite entities C
Z
is exponentially large in the size of V
Z
, we impose an
upper bound on the number of composite entities con-
sidered. The bound, calculated image-wise, is propor-
tional to the size of V
Z
, but not larger than a heuristi-
cally chosen maximum value. Each composite entity
maps a local configuration of visual entities, induced
by the close relation, which is thresholded on the
image characteristics. To each of these subgraphs a
composite entity c is created and connected to all its
visual entities using membership relations. The spa-
tial relations are evaluated for pairs of visual entities,
thereby forming locally connected subgraphs. The re-
sult is the subset C of candidate composite entities.
The candidate generation is done recursively for
every image. It starts with a less strict threshold on the
close relation and it decreases the threshold at each
iteration until the constraint on the upper bound of the
size of C is met. To find the best delineation in case
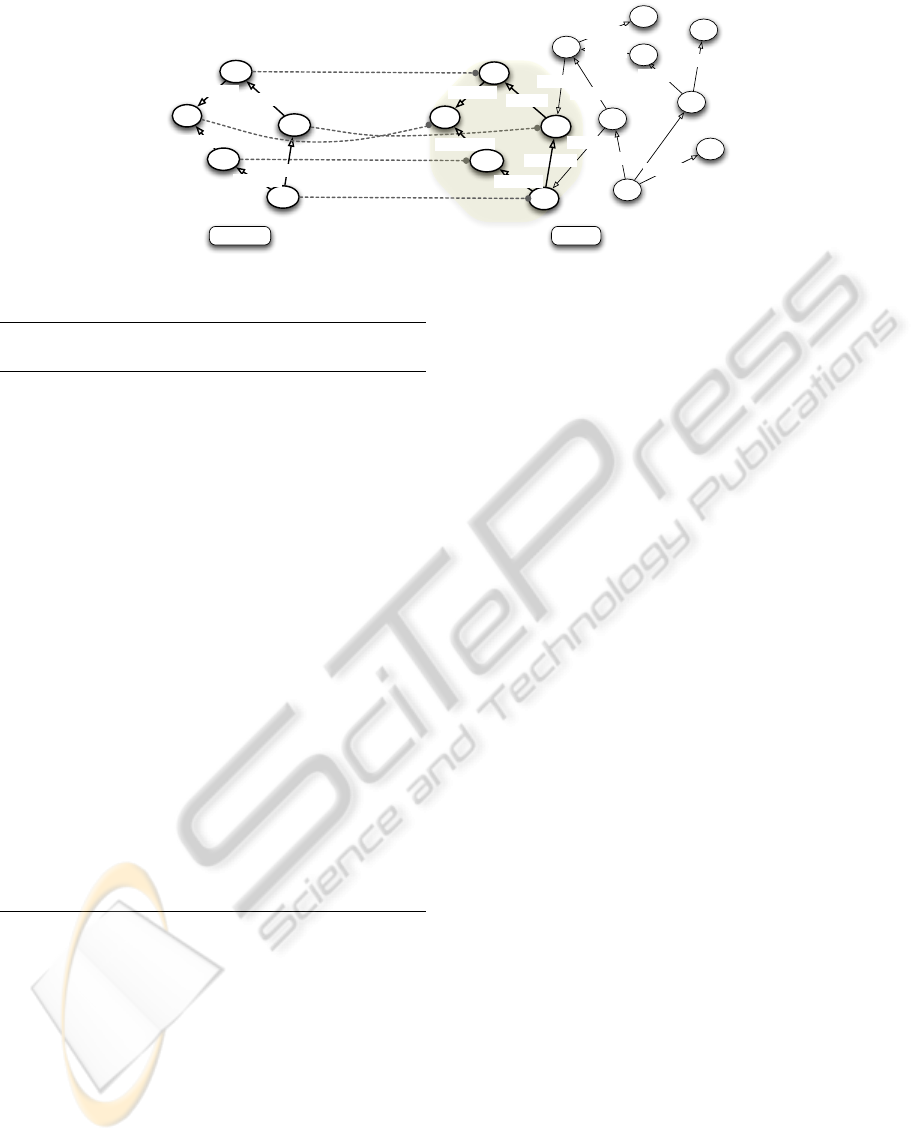
prototype
o14
cAbove,70
o15
o13
o11
o12
cRight,60
tRight,1
cAbove,68
cRight,70
image
cRight,20
cRight,10
cAbove,70
o9
cAbove,72
o10
o3
o1
o2
cRight,61
tRight,3
cRight,65
cAbove,70
o7
cRight,60
tRight,1
o6
cRight,65
o5
cAbove,70
o8
o4
...
...
...
cRight,70
tRight,2
cAbove,70
Figure 4: Graph representations of a prototype (left) and an image interpretation (right).
Algorithm 1: Delineates one image (visual entities V , pro-
totypes ζ).
function DELINEATE(V,ζ)
C ← GENERATE (V )
set of relevant composite entities from V
C
eval
← CLASSIFY(C,ζ)
classification w.r.t ζ
S ← SELECT(C
eval
)
selection w.r.t a set of constraints
S
∗
← POST PROCESSING(S)
return S
∗
end function
function CLASSIFY(C,ζ)
return for each c ∈ C a triple hy,d,ci where y,d are
the class, respectively distance w.r.t. the prototypes in ζ
according to a k-NN classifier.
end function
function SELECT(C
eval
)
RANK 3-tuples (y,d,c) ∈ C
eval
according to d
FILTER 3-tuples candidates:
C
∗
= {(y,d,c) ∈ C
eval
| #C
∗
≤ threshold}
{(S,Qual)} ← OPTIMIZE(C
∗
)
return S
∗
= argmax
Qual
{(S,Qual)}
select the best solution
end function
of noisy information, composite entities representing
a small number of visual entities are also needed. For
example, if the image contains some parts of a (hypo-
thetical) house, they can be regarded as configurations
on their own (e.g. the partial house ic
3
in Figure 2(b)).
II Composite Entity Classification (CLASSIFY). At
all layers, except the primitive, a k-nearest-neighbor
approach based on a distance measure between two
composite entities is used for composite entity classi-
fication. Each composite entity is represented by its
corresponding visual interpretation I. A matching be-
tween any two interpretations I
1
and I
2
, is a mapping
such that each entity in I
1
is mapped to at most one
entity in I
2
. In terms of the graph representation, this
corresponds to mapping the vertices from I
1
to those
of I
2
(Figure 4). The mapping induces a distance func-
tion d(I
1
,I
2
) which has two components. One charac-
terizes the structure similarity, the other the appear-
ance. Our choice is justified by the fact that both as-
pects can have impact on the matching score.
II-A Classification: Structure. To evaluate how
well two logical interpretations match structurally, we
must calculate their generalization (common part).
We employ a recent result of (De Raedt and Ra-
mon, 2009) on metrics. It targets the minimally gen-
eral generalizations of two interpretations, but ap-
plies to different types of objects, including graphs.
We choose the object identity (OI)-subsumption or-
der (Ferilli et al., 2003), which, for graphs, corre-
sponds to subgraph isomorphism. The minimally
general generalization (mgg) then is the maximal
common subgraph. This means that vertices in the
subgraph can be mapped to at most one vertex in
the supergraph, imposing an exact structure matching,
and thus the mgg is not necessarily unique (De Raedt,
2008). Example 1 illustrates the mgg under OI-
subsumption.
Example 1. Let I
1
= {cRight(o
1
,o
2
,2)} and
I
2
= {cRight(o
3
,o
4
,2),cRight(o
5
,o
4
,2)}.
Under OI-subsumption there are two possible mggs:
mgg
0
OI
(I
1
,I
2
) = {cRight(X
1
,X
2
,2)} with
θ
0
1
= {X
1
/o
1
,X
2
/o
2
}, θ
0
2
= {X
1
/o
3
,X
2
/o
4
}
mgg
1
OI
(I
1
,I
2
) = {cRight(X
1
,X
2
,2)} with
θ
1
1
= {X
1
/o
1
,X
2
/o
2
}, θ
1
2
= {X
1
/o
5
,X
2
/o
4
}.
Consequently, the mgg for two interpretations I
1
and
I
2
results in the set mgg
all
= {mgg(I
1
,I
2
)}. Using one
mgg from the set, the distance between two interpre-
tations I
1
and I
2
is equivalent to:
d
s
= |I
1
| + |I
2
| − 2|mgg(I
1
,I
2
)| (1)
where | · | is the number of the vertices in the inter-
pretation. From this, it is straightforward to derive
a normalized structural distance d
ns
(I
1
,I
2
). Similar
distance measures are defined in (Nienhuys-Cheng,
1997; Horv
´
ath et al., 2001; Kirsten et al., 2000).

II-B Classification: Appearance. In addition to
structural similarities, properties of entities (e.g.,
color) are important. If mgg represents the maxi-
mal common structure between two interpretations I
1
and I
2
, then mggθ
1
and mggθ
2
are specialized maxi-
mal common parts of mgg that correspond to I
1
and
I
2
, respectively. The substitutions θ
1
and θ
2
spec-
ify the mapping between different entities. Indeed, if
V /e
1
∈ θ
1
and V /e
2
∈ θ
2
then e
1
is mapped onto e
2
.
We can now define a normalized appearance distance
between the two interpretations I
1
and I
2
as:
d
na
(I
1
,I
2
) =
1
|mgg|
×
∑
a∈mgg
d
0
(aθ
1
,aθ
2
),
where a is an atom in mgg. Since mgg gives the
common structure of the two interpretations, in or-
der to compute d
na
(I
1
,I
2
) we start from mgg and spe-
cialize each atom a ∈ mgg, such that aθ
1
and aθ
2
are ground atoms with the same predicate symbol a.
Let S denote the set of all symbols, then the distance
d
0
: S × S → [0,1] is a normalized distance measure
defined for our particular application in the following
way. Let t
i
,s
i
be attributes, then:
d
0
(a(t
1
,...t
n
),a(s
1
,..., s
n
)) =
1
n
×
n
∑
i=1
d
0
(t
i
,s
i
) (2)
For discrete attributes we employ the hamming dis-
tance d
0
(t
1
,t
2
) = 1 if t
1
= t
2
, otherwise 0. For numer-
ical attributes in the range [min,max]:
d
0
(t
1
,t
2
) =
abs(t
1
−t
2
)
max − min
(3)
The structural and appearance-based aspects of the
distance measure are combined into a single measure
using a (normalized) weighted average:
d
sa
(I
1
,I
2
) = w
s
× d
ns
(I
1
,I
2
) + w
a
× d
na
(I
1
,I
2
), (4)
where w
s
+ w
a
= 1. These weights can be supplied or
learned. Because the mgg of interpretations I
1
and I
2
is not unique, the global normalized distance between
I
1
and I
2
finally is:
d(I
1
,I
2
) = min
m∈mgg
all
d
sa
(I
1
,I
2
). (5)
Next, we employ a k-nearest neighbor classifier
(KNN in function CLASSIFY). Given the set of com-
posite entities C and the set of prototypes ζ, the al-
gorithm evaluates the quality of each composite en-
tity by computing the distance to the prototypes and
classifies it based on the majority vote of its neigh-
bors. The algorithm returns the set C
eval
of 3-tuples
(y, d
ζ
,c), where y is the class of c ∈ C and d
ζ
is the
mean distance from c to the elements of the subset
ζ
y
⊆ ζ describing only concepts of class y.
III Composite Entity Selection (SELECT). In the
function SELECT we first rank the set of composite
entities of interest C according to their distances to
the nearest prototypes in ζ, and use a threshold on the
number of candidates to select the best set C
∗
. This
step is optional, but recommended as a large space of
composite entities C is usually generated. From this
reduced set, we then want to select those that together
explain best (most of) the visual features at that layer.
To this end, we formulate the composite entity selec-
tion problem as a maximum weighted independence
set problem.
Let G = (V,E,W ) be an undirected graph, where
V , E and W are the set of vertices and edges and
a vertex weighting function, respectively. An in-
dependent set is a set S ⊆ V such that ∀e ∈ E the
two end vertices of e do not belong to S simultane-
ously. A maximum weighted independence set prob-
lem (WISP) is formulated as follows: given an input
graph G = (V,E,W ), find the independence set S of
vertices in V such that the value W (S) is subject to
maximization. In order to convert our problem to a
WISP problem we have to find the correspondence to
the input graph G = (V,E,W ) and the independence
set S. In our case:
• V becomes the set of composite entities C
∗
.
• we use the set of edges E to model constraints be-
tween composite entities, that is the solution must
contain only composite entities that do not share
any visual entities. This constraint is considered
through the independence property itself by in-
serting an edge between any two C which share
at least one visual entity:
E = {e(c
1
,c
2
)|c
1
,c
2
∈ C
∗
,V (c
1
) ∩V (c
2
) 6= ∅}
• the vertex weighting function W : V → N is
W
c
= σ(1 − d
ζ
(c,ζ)), ∀c ∈ C
∗
where σ is a function which proportionally ampli-
fies higher scores to ensure the selection of best
scored composite entities. The function that we
want to maximize is then W (S) =
∑
c∈S
W
c
, where
S is one independence set solution.
The solution to the WISP problem is given by the
function OPTIMIZE. This is known to be a NP-hard
optimization problem and both exact and approxima-
tion algorithms exist (Busygin, 2006). For the ex-
act case we use a branch-and-bound algorithm for the
maximum clique problem, which is computationally
equivalent to the maximum independent set problem
computed on the complement graph (see (
¨
Osterg
˚
ard,
2002) for more details). We therefore replace our OP-
TIMIZE function with the Cliquer optimizer
1
. For the
1
Available at http://users.tkk.fi/pat/cliquer.html.

approximation case we use the algorithm for the max-
imum weight clique problem proposed in (Busygin,
2006). We employ the QUALEX-MS optimizer
2
in-
stead of our OPTIMIZE function. Other approxima-
tion methods are also known to work in polynomial
time (Lozin and Milanic, 2010). However these are
adequate for particular (i.e., planar) graphs, while our
selection problem deals with general graphs. If the
size of C
∗
is in a certain range we use the exact op-
timizer, otherwise the approximate one. This gives
acceptable results in practice.
The algorithm follows the same principle for all
layers of the hierarchy. However there are differences
at each layer with respect to i) the interpretations gen-
erated (both size and structure) and therefore the com-
posite entities and ii) the distance function which is
tuned for each layer.
IV (POST PROCESSING). We employ two steps.
IV-A Bounding Box Prediction. The end goal of
our framework is to predict the bounding boxes of
detected objects. We use the subgraph V S
c
of the
composite entity to predict a bounding box for the ob-
ject c. This is implemented by mapping the bounding
boxes of the visual entities in V
c
(i.e., vectors of 2D
locations) to the corners of the object bounding box.
IV-B Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Either
the KNN classifier or the selection step may give
multiple spatially overlapping detections for each in-
stance of an object. The selection step ensures that
detections do not share any visual entities, however
their bounding boxes can still overlap. We use a
greedy procedure for eliminating repeated detections
via non-maximum suppression. After applying the
bounding box prediction described above we have
a set of detections for an object category in an im-
age. Each detection is defined by a bounding box
and a score. We sort the detections by score, and
greedily select the ones with highest score, while
suppressing detections with bounding boxes that are
more than some percentage (which varies depending
on the setting) covered by a bounding box of a previ-
ously selected detection. A similar NMS step is taken
in (Felzenszwalb et al., 2010).
6 APPLICATION AND
EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
Dataset and Application
We first describe the application of our method to
2
Available at http://www.stasbusygin.org.
2D street view images (Figure 5). These commonly
display a rich structure (and variety), yet are often
quite consistent in terms of structure in a row of
houses. We have annotated
3
60 images of rows of
house facades from different countries. A number of
20 images were collected by ourselves, the rest from
Google Street View. All images show near-frontal
views of the houses and no further rectification was
performed. Each image has a resolution of 600x800
pixels. On these images, windows, doors and houses
were manually annotated. We use the close to the
right (cRight), close above (cAbove) and touch to
the right (tRight) spatial relations as illustrated in
Example 2. An Euclidian distance threshold is used
for the close relation defined relatively to the size
of the objects. The background knowledge can easily
be extended with new relations, to enable even richer
relational representations of visual data.
Figure 5: Images of houses in Eindhoven; an annotated
training image is on the left; a testing image is on the right.
Example 2. The background knowledge for the spatial re-
lation cRight:
closeto(A,B, Dist) ← bb(A,BB
1
), bb(B,BB
2
), A 6= B,
distance(BB
1
,BB
2
,Dist), Dist < threshold.
cRight(A,B,Dist) ← bb(A,BB
1
), bb(B,BB
2
),
right(BB
1
,BB
2
), closeto(A,B,Dist).
where bb is the bounding box of a visual entity.
We make use of three layers in a four-level hierar-
chy: primitive, object and house layers (Figure 6).
Primitive Layer. This layer takes as input im-
age pixels and groups them in corner-like features
with local descriptors. We employ the KAS fea-
ture detector (Ferrari et al., 2008) to detect inter-
est points formed by chains of k connected, roughly
straight contour segments. We use k = 2 to de-
tect corner-like shapes and solve the classification
problem by attaching a category label from the set
Y = {cType00, cType01,cType10,cType11} to each
corner-like candidate. These labels represent top-
right, top-left, bottom-right and bottom-left corners
and are established based on the orientation of the
segments composing the 2AS feature. The selection
is done in two steps. Firstly, we only keep square-
like corners with an angle (90 − δ)
◦
< α < (90 +
δ)
◦
. Secondly, we describe the selected 2AS features
with HOG descriptors (Dalal and Triggs, 2005) and
3
Using the LABELME toolbox (Russell et al., 2008).

train a binary classifier on these descriptors to dis-
card irrelevant corner features found on other struc-
tures than buildings (e.g., vegetation or cars). Object
layer annotations represent training data for this step.
Object Layer. Visual entities at this level are sparse
detected corner features. Each corner has a lo-
cal HOG descriptor
4
as an attribute on which an
appearance-based distance component can be com-
puted. We solve this by using first a trained a classifier
to map the attribute to either a window or door label,
and then computing a discrete distance between these
labels. An additional attribute is the corner type (e.g.,
cType00). Based on our spatial theory, attributes rep-
resenting the Euclidean distance between bounding
boxes of spatially related entities, contribute also to
the appearance-based distance. Composite entities
represent possible doors or windows and are defined
by subgraphs consisting of 3 up to 4 visual entities.
House Layer. Visual entities here are doors and win-
dows found at the object layer, and composite entities
represent possible houses. Again we employ our spa-
tial theory to find potential composite entities, and de-
rive attributes for the spatial relations between visual
entities. Attributes of visual entities at this layer are
the labels door and window. Composite entities are
defined by subgraphs consisting of 2 up to 6 visual
entities, estimated from the training data.
Experimental Evaluation
The experiments were performed in two different
phases. In a first phase, we performed experiments at
single layers independently. More precisely, we used
as input for the learning task at one single layer the
annotated (or segmented, for the object layer) train-
ing data at that layer and then employed our method
to compute the output. In this way, it is possible to
get an appreciation of how difficult the learning prob-
lem is and what are the limitations of the data at each
layer. In a second phase, we performed experiments
in the full hierarchical setting, that is, the inputs are
image pixels and the outputs are at the house layer.
This allows us to estimate how good the hierarchical
approach works.
Because we deal with a detection problem we
adopt the evaluation measures used in information
retrieval. We measure performance in terms of the
number of true and false detections in a test dataset.
In our setting the positives are all the composite en-
tities selected via the selection function. We evalu-
ate the performance using the overlap measure, which
4
A variation of the HOG descriptor with 16 orientation
bins instead of 9 showed improved results. We used a win-
dow size of 128x128 pixels and a block size of 8x8 cells.
is also the PASCAL VOC (Everingham et al., 2008)
criterion. We compare the bounding box BB
d
corre-
sponding to the detected concept to the ground-truth
bounding box BB
t
in manually annotated data. If
area(BB
d
∩BB
t
)/area(BB
d
∪BB
t
) > 0.5, then BB
d
is
a true positive (TP), otherwise it is a false positive
(FP). The precision P is TP divided by the total num-
ber of predicted components. The recall R is TP di-
vided by the number of ground-truth components in
the test set. The F1 score is a measure of accuracy
and is the harmonic mean of precision and recall.
The problem of detection is often posed as a clas-
sification task, namely distinguishing in the image the
class of interest with some score. Such a classifier can
be turned into a detector by sliding it across the im-
age and thresholding the scores of the hypothesis to
obtain a precision-recall curve. Differently, our for-
mulation builds on top of a kNN classifier by select-
ing interesting (already scored) candidates which to-
gether find the best semantic segmentation of the im-
age. Since they are together part of the solution, they
are all predicted positive instances (except the spa-
tially overlapping ones solved by the final NMS step).
As a result, there is no obvious threshold that can be
varied to trade-off precision vs. recall and instead of
a precision-recall curve, the performance is measured
as a precision-recall point. Since we are interested to
measure the impact of structure on our detection prob-
lem, we vary the parameter w
s
of our model and show
its influence on precision and recall values.
We have as parameters k (in the KNN) and the rel-
ative weights w
s
and w
a
(structure vs. appearance for
classification). We experiment with different values
of k to evaluate the influence of the structure parame-
ter w
s
on precision/recall values
5
.
Results
We have tested different values of w
s
at single layers
independently and with the full hierarchy.
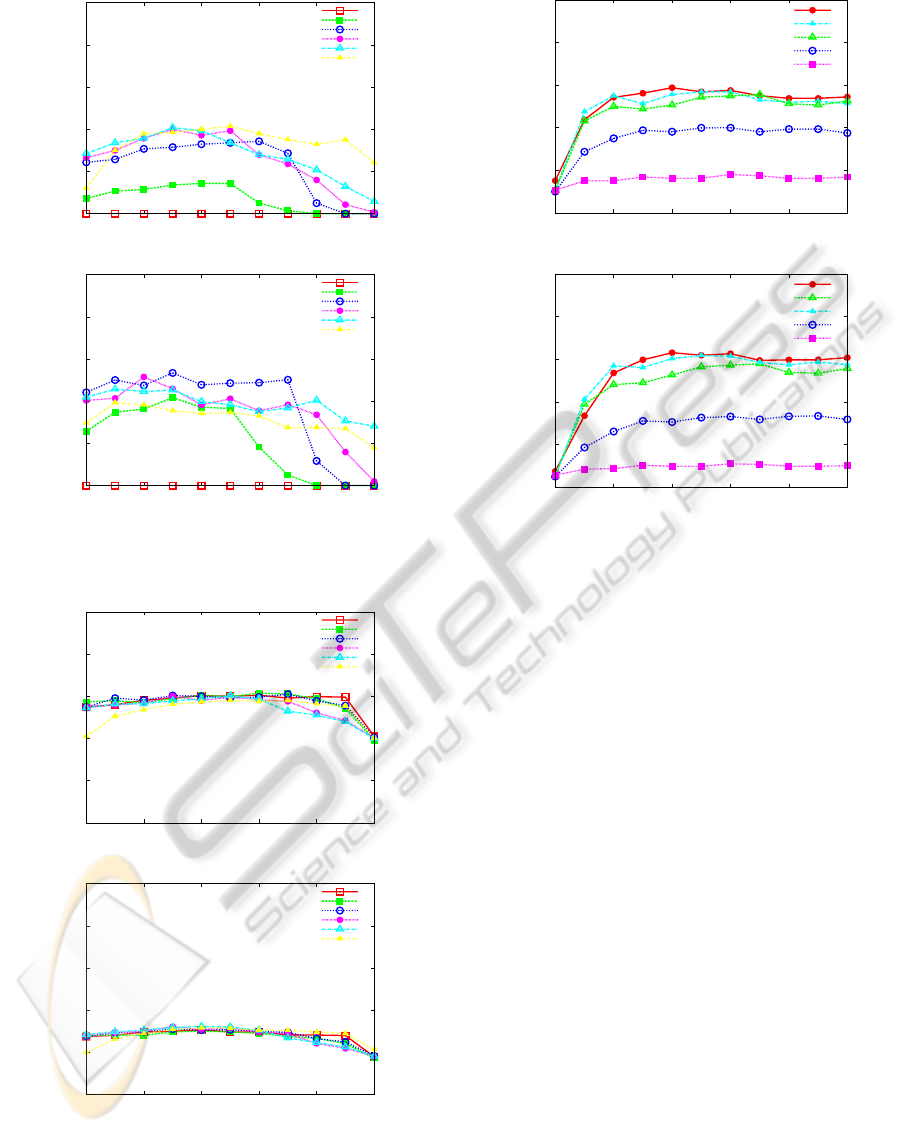
Experiment 1. Single Layer Segmentation –
Houses. At the house layer, we first test our approach
directly on the ground-truth annotations of the un-
derlying layer, that is, objects such as windows and
doors. We vary w
s
from 0 to 1 to plot recall and pre-
cision in Figure 7. We stress that w
s
is not a threshold
to trade precision for recall, but we use it to show the
influence of using structure on the performance. We
observe that if k is large enough (k ≥ 30), the increase
of the amount of structure increases precision/recall
values. Indeed, in our setup the use of structure is
essential to obtain good results. We notice that the
approach is not very sensitive to a precise value of w
s
5
We choose w
s
as the free parameter; w
a
= 1 − w
s
.

Figure 6: Data flow in the four-level hierarchy of the fa-
cades domain. Input layers: pixels, corner primitives and
object entities. Corresponding output layers: corner primi-
tives, object entities and house entities, respectively.
when w
s
> 0.1. For k = 60 we obtain optimal values
R=0.86, P=0.83; for k = 90, R=0.91 and P=0.9; for
k = all, R=0.88 and P=0.85. They are all obtained
when w
s
= 0.4 and we observe that the appearance
component w
a
= 0.6 has also influence on obtaining
optimal values of precision and recall. We also note
that, due to the selection procedure, precision and re-
call are highly coupled. For small values of k recall
and precision are much lower for any w
s
. Given the
structural variability at the house layer, a comparison
with enough prototypes is needed.
Experiment 2. Single Layer Segmentation – Ob-
jects. At the object layer the experiments are per-
formed directly with available detected KAS from the
primitive layer (not with annotations). They show
that the variation of the structure still has an influ-
ence, though it is more limited. This can be explained
by the fact that windows and doors have mostly the
same structure. However, at the object layer the struc-
ture still has an indirect influence, as it is needed for
computing appearance-based aspects. We ran experi-
ments with different values for k and w
s
. The results
are shown in Figures 8 and 9 for classes door and
window, respectively. The maximal values R=0.42,
P=0.47 for class door and R=0.61, P=0.35 for class
window are obtained for parameters k = 50, w
s
= 0.3,
w
a
= 0.7 and k = 50, w
s
= 0.5, w
a
= 0.5, respectively.
However, results for k = 10, k = 75 and k = 150 are
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Recall
Ws
k=all
k=90
k=60
k=30
k=10
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Precision
Ws
k=all
k=60
k=90
k=30
k=10
Figure 7: House layer segmentation (annotations). The
influence of structure on precision/recall for different k.
also close. A NMS step with 50% overlap was ap-
plied after the selection phase and before the evalua-
tion.
Experiment 3. Hierarchical Segmentation –
Houses. We evaluate detection results at the house
layer using the full hierarchy. From the raw image we
first detect the KAS primitives. These are then em-
ployed further as input to detect windows and doors.
At this point there are 2 possible ways to proceed.
We can select relevant windows and doors (via the
described selection step) at the object layer and use
this result as input for the house layer. However, this
gives less good results (R=0.32 and P=0.5), as a high
enough recall is required from the object layer to ob-
tain rich enough visual interpretations of images.
Alternatively, instead of the full selection step, we
consider the top ranked composite entities. In this
way, the full selection is replaced by a less selec-
tive mechanism, improving recall at the object layer.
The selected candidates become visual entities at the
house layer. This improves the results, as shown in
Figure 10, to obtain for k = 90, R=0.6 and P=0.63,
while for k = all, R=0.61 and P=0.65. The optimal
results are obtained when w
s
= 0.4.
In all experiments we perform a 5-fold cross vali-
dation on the dataset with the same folds. The imple-
mentation combines code written in Prolog, Matlab
and C. We are able to delineate houses and to separate
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Recall
Ws
k=all
k=200
k=150
k=75
k=50
k=10
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Precision
Ws
k=all
k=200
k=150
k=75
k=50
k=10
Figure 8: Object layer segmentation for class door. The
influence of structure on precision/recall for different k.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Recall
Ws
k=all
k=200
k=150
k=75
k=50
k=10
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Precision
Ws
k=all
k=200
k=150
k=75
k=50
k=10
Figure 9: Object layer segmentation for class window. The
influence of structure on precision/recall for different k.
them from neighboring houses, even when attached.
Some qualitative results are presented in Figure 12–
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Recall
Ws
k=all
k=90
k=60
k=30
k=10
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Precision
Ws
k=all
k=60
k=90
k=30
k=10
Figure 10: Hierarchical segmentation. The influence of
structure on precision/recall for different k.
14. The higher we get in the hierarchy and therefore
richer in the semantics, the more relevant the struc-
tural aspect becomes.
Comparison to Baselines. The goal of this work is
not so much to compete with powerful detectors, of-
ten building on dense representations from the litera-
ture, but rather to evaluate how structure can be flex-
ibly exploited in detection problems in general. We
show that even when starting from relatively sparse
and simple cues (Figure 6, primitive layer), detection
and delineation of complex objects is feasible, thanks
to the use of structure. Moreover, rather than just
detecting bounding boxes of objects, our method re-
turns a full semantic hierarchical interpretation of the
scene, decomposing each object into its constituents
parts. Nevertheless, for reference, we compare our
method with several baseline detectors to assess the
difficulty of the dataset.
Baseline 1. Objectness. As a first baseline, we use
the object detector proposed in (Deselaers and Ferrari,
2010) and employ the objectness measure to quantify
how likely it is for an image window (i.e., patch) to
contain an object. The measure combines several im-
age cues, such as: multi-scale saliency, color contrast,
edge density and straddleness. Its main purpose is to
predict, given an image, location priors in the form
of image windows to boost class specific object de-
tectors. The window sampling is done according to
the objectness distribution in the image. We use it
here as a first baseline house detector
6
. We run the
detector with 100 window samples
7
and then employ
the PASCAL VOC (Everingham et al., 2008) over-
lapping criterion to establish the correct label of each
sample (i.e., house or none).
Baseline 2. Objectness + HOG. As a second baseline
we combine the objectness measure with a separate
classifier trained
8
for the class house on HOG feature
descriptors (Dalal and Triggs, 2005). The objectness
classifier is used as a prior distribution to sample rel-
evant hypotheses in the image, while the HOG clas-
sifier is used to re-score them. We first sample 100
house candidates in each image and then employ the
specialized classifier to improve the predictions.
Baseline 3. Template Matching with Boosting. As a
third baseline we use the boosting approach
9
in (Tor-
ralba et al., 2004) to train an ensemble of weak detec-
tors for the class house. Each weak detector computes
template matching with a localized patch in object
centered coordinates. The features are obtained using
a convolution mask tailored to the normalized correla-
tion between the search patch and the template. Indi-
vidual houses can be more effectively detected using a
template matching approach than a texture-based one,
since houses in the same row have the same texture
and most street scenes greatly vary in texture across
the dataset. In our experiments we use different num-
bers of weak classifiers (see Figure 11).
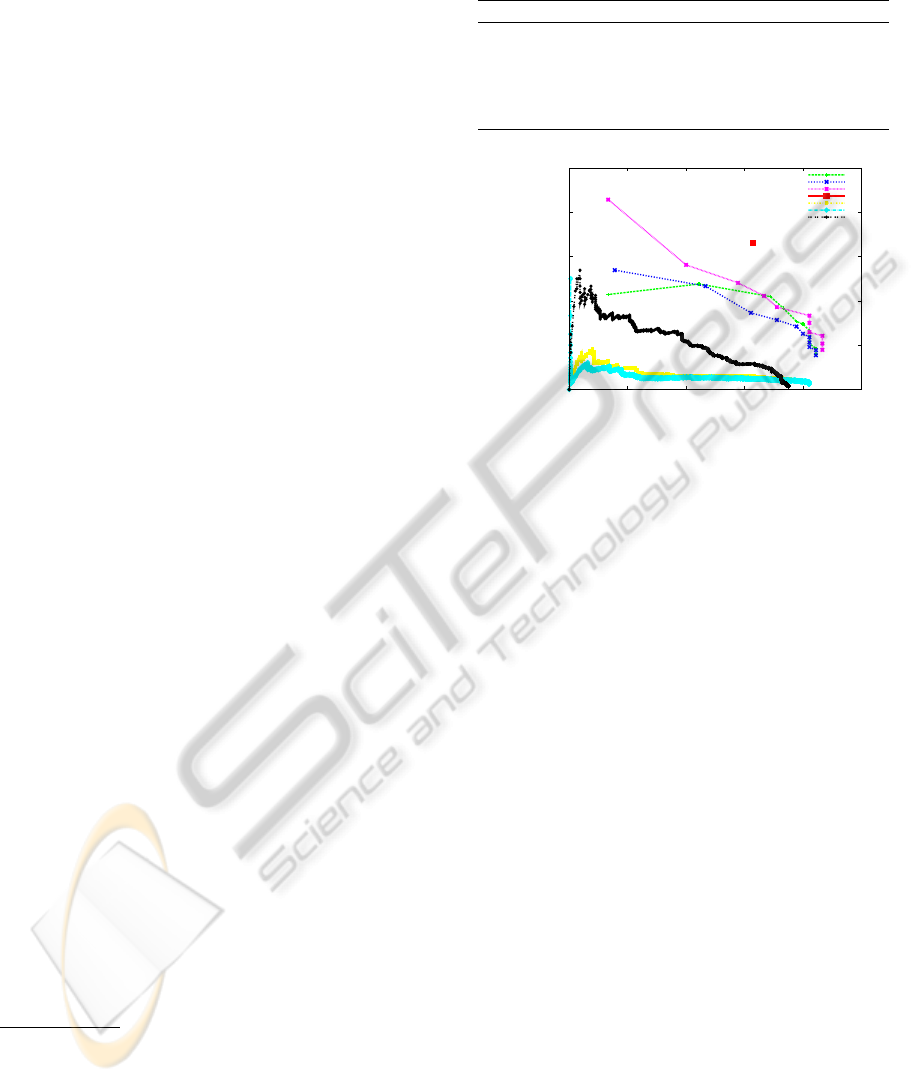
Table 1 shows the results for all baselines and
our method. The F1 values showed are the maxi-
mum F1 scores over all precision-recall points in the
precision-recall curves as in Figure 11. We also in-
clude results of the intermediary classification step to
show the benefits of the selection function. Although
the baseline detectors perform reasonably well for the
house detection problem, none of these detectors in-
corporates a fine-grained decomposition of a house, in
the form of structured output which explains the im-
age in the same way as our framework. In addition,
our method still outperforms the baselines although
we start from sparse features and therefore, a less rich
appearance-based component. We only use as fea-
tures the corners estimated from 2AS and a HOG de-
scriptor on its (reduced) neighborhood. This is op-
posed to the employed baselines which are optimized
6
Version 1.5, available at http://www.vision.ee.ethz.ch/
∼calvin/software.html.
7
According to the detector specifications. Increasing or
decreasing the number of samples did not improve results.
8
Using the LIBSVM library available at: http://
www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/∼cjlin/libsvm/.
9
Available at http://people.csail.mit.edu/torralba/ short-
CourseRLOC/boosting/boosting.html.
Table 1: Hierarchical segmentation and comparison to base-
lines; house layer.
Method Recall Precision F1
Objectness 0.14 0.1 0.12
Objectness + HOG 0.23 0.11 0.14
Feature boosting (120) 0.57 0.48 0.52
kNN classifier 0.4 0.3 0.35
Our method 0.61 0.65 0.63
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Precision
Recall
Boosting 120
Boosting 60
Boosting 30
Hierarchy
Objectness+HOG
Objectness
kNN
Figure 11: Baseline precision-recall curves; class house.
for dense cues and a richer appearance component.
To summarize, we show that our framework gives
promising results for the difficult detection tasks at
both individual levels and through the full hierarchy.
A challenging aspect is the propagation of candidates
up through the hierarchy. The recall of structures
needed at a higher level can limit good performance
at that layer. If the number of allowed candidates is
high enough – which means that we do not just prop-
agate the sole best solution, but a larger number of
candidate solutions – we enable the higher layer to se-
lect from more candidates and achieve better perfor-
mance. This balance between generating many can-
didates and propagating a suitable number of candi-
dates must be determined by the domain at hand, and
an interesting research question is how to computa-
tionally deal with this trade-off. Overall, our results
clearly show the feasibility and effectiveness of our
approach by combining relational knowledge repre-
sentations with computational vision.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
We have presented a novel general framework
for hierarchical image understanding, incorporat-
ing distance-based classifications, relational, spatial
knowledge representation and robust visual feature
recognition. The experiments show i) the interplay

Figure 12: Segmentation of images with partial occlusions
at single (house) layer.
Figure 13: Segmentation of images with partial occlusions
at the house layer using the hierarchy.
between structural and appearance-based aspects in
the recognition task and ii) good detection results both
at single layers and full hierarchy. This work explores
a new relational scheme for solving computer vision
tasks and we believe that there is still room for im-
provement. Three strong points of the approach are
that i) we do not assume availability of a full model
of the domain (e.g., a grammar) but only a set of an-
notated examples, which is more natural and easier
to obtain, ii) the framework can easily be extended
by adding relational/spatial background knowledge,
or replacing the classifiers by other similarity func-
tions or kernels and iii) the approach incorporates a
Figure 14: Segmentation of images at single (object) layer.
Door detections are marked in green.
fine-grained decomposition of a house in the form of
structured output which explains the image, as op-
posed to existing detectors.
In future work, we will extend the framework and
employ it for other recognition tasks (e.g., people de-
tection), suitable online annotated data, as well as in-
cluding denser cues as appearance features. We sus-
pect that extending the distance computations with
kernel-based learning for structured data (e.g., re-
lational representations) will boost recognition per-
formance. Another interesting direction is to pro-
vide more contextual knowledge in the recognition,
for example to take higher-levels into account di-
rectly when classifying structures at lower levels as
top-down feedback. A general goal is to explore
the boundaries between robust computer vision, high-
level knowledge representation and machine learning.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The first author gratefully wants to thank Gianluigi
Greco, Bernd Gutmann, Siegfried Nijssen and Paulo
Moura for their valuable comments, discussions, ad-
vice and support.
REFERENCES
Bar-Hillel, A. and Weinshall, D. (2008). Efficient learning
of relational object class models. IJCV, 77(1-3):175–
198.

Busygin, S. (2006). A new trust region technique for
the maximum weight clique problem. Discrete Appl.
Math., 154(15):2080–2096.
Caetano, T. S., McAuley, J. J., Cheng, L., Le, Q. V.,
and Smola, A. J. (2009). Learning graph matching.
TPAMI, 31(6):1048–1058.
Dalal, N. and Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented
gradients for human detection. In CVPR, pages 886–
893.
De Raedt, L. (2008). Logical and Relational Learning.
Springer.
De Raedt, L. and Ramon, J. (2009). Deriving distance met-
rics from generality relations. Pattern Recognition
Letters, 30(3):187–191.
Deselaers, T. and Ferrari, V. (2010). Global and efficient
self-similarity for object classification and detection.
In CVPR, pages 1633–1640.
Dubba, K. S. R., Cohn, A. G., and Hogg, D. C. (2010).
Event model learning from complex videos using ILP.
In ECAI, pages 93–98.
Esposito, F., Malerba, D., and Semeraro, G. (1992). Clas-
sification in noisy environments using a distance mea-
sure between structural symbolic descriptions. PAMI,
14(3):390–402.
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C. K. I., Winn,
J., and Zisserman, A. (2008). The PASCAL Visual
Object Classes Challenge 2008.
Felzenszwalb, P., Girshick, R., McAllester, D., and Ra-
manan, D. (2010). Object detection with discrimina-
tively trained part-based models. TPAMI, 32(9):1627
–1645.
Fergus, R., Perona, P., and Zisserman, A. (2007). Weakly
supervised scale-invariant learning of models for vi-
sual recognition. IJCV, 71(3):273–303.
Ferilli, S., Mauro, N. D., Basile, T. M. A., and Esposito, F.
(2003). A complete subsumption algorithm. In AI*IA
2003, pages 23–26.
Ferrari, V., Fevrier, L., Jurie, F., , and Schmid, C. (2008).
Groups of adjacent contour segments for object detec-
tion. TPAMI, pages 36–51.
Getoor, L., Koller, D., Taskar, B., and Friedman, N. (2000).
Learning probabilistic relational models with struc-
tural uncertainty. In Proceedings of the ICML-2000
Workshop on Attribute-Value and Relational Learn-
ing:Crossing the Boundaries, pages 13–20.
Hanson, A. and Riseman, E. (1978). Visions: A computer
system for interpreting scenes. In CVS78, pages 303–
333.
Harchaoui, Z. and Bach, F. (2007). Image classification
with segmentation graph kernels. In CVPR, pages 1–
8.
Hartz, J. (2009). Learning probabilistic structure graphs
for classification and detection of object structures. In
ICMLA ’09, pages 5–11.
Hartz, J. and Neumann, B. (2007). Learning a knowledge
base of ontological concepts for high-level scene in-
terpretation. In ICMLA, pages 436–443.
Horv
´
ath, T., Wrobel, S., and Bohnebeck, U. (2001). Re-
lational instance-based learning with lists and terms.
ML, 43(1/2):53–80.
Kirsten, M., Wrobel, S., and Horv
´
ath, T. (2000). Distance
based approaches to relational learning and clustering.
Relational Data Mining, pages 213–230.
Koutsourakis, P., Simon, L., Teboul, O., Tziritas, G., and
Paragios, N. (2009). Single view reconstruction using
shape grammars for urban environments. In ICCV,
pages 1795–1802.
Li, L.-J., Socher, R., and Fei-Fei, L. (2009). Towards
total scene understanding: Classification, annotation
and segmentation in an automatic framework. CVPR,
0:2036–2043.
Lippow, M. A., Kaelbling, L. P., and Lozano-Perez, T.
(2008). Learning grammatical models for object
recognition. In Technical Report.
Lozin, V. and Milanic, M. (2010). On the maximum
independent set problem in subclasses of planar
graphs. Journal of Graph Algorithms and Applica-
tions, 14:269–286.
Muggleton, S. and Buntine, W. L. (1988). Machine inven-
tion of first order predicates by inverting resolution. In
ML, pages 339–352.
M
¨
uller, P., Zeng, G., Wonka, P., and Van Gool, L. J. (2007).
Image-based procedural modeling of facades. ACM
Transactions on Graphics, 26(3):85.
Nienhuys-Cheng, S.-H. (1997). Distance between herbrand
interpretations: A measure for approximations to a
target concept. In ILP, pages 213–226.
¨
Osterg
˚
ard, P. R. J. (2002). A fast algorithm for the maxi-
mum clique problem. Discrete Appl. Math., 120:197–
207.
Petrou, M. (2008). The tower of knowledge: a novel ar-
chitecture for organising knowledge combining logic
and probability. In Logic and Probability for Scene
Interpretation, Dagstuhl Seminar Proceedings.
Pinz, A. J., Bischof, H., Kropatsch, W. G., Schweighofer,
G., Haxhimusa, Y., Opelt, A., and Ion, A. (2009).
Representations for cognitive vision: A review of
appearance-based, spatio-temporal, and graph-based
approaches. Electronic Letters on Computer Vision
and Image Analysis, 7(2):35–61.
Russell, B. C., Torralba, A., Murphy, K. P., and Freeman,
W. T. (2008). LabelMe: A database and web-based
tool for image annotation. IJCV, 77(1-3):157–173.
Sudderth, E. B., Torralba, A., Freeman, W. T., and Willsky,
A. S. (2008). Describing visual scenes using trans-
formed objects and parts. IJCV, 77(1-3):291–330.
Szeliski, R. (2010). Computer Vision: Algorithms and Ap-
plications. Springer.
Torralba, A., Murphy, K. P., and Freeman, W. T. (2004).
Sharing features: Efficient boosting procedures for
multiclass object detection. In CVPR, pages 762–769.
Tuytelaars, T. and Mikolajczyk, K. (2007). Local invariant
feature detectors: A survey. Foundations and Trends
in Computer Graphics and Vision, 3(3):177–280.
Zhao, P., Fang, T., Xiao, J., Zhang, H., Zhao, Q., and Quan,
L. (2010). Rectilinear parsing of architecture in urban
environment. In CVPR, pages 342–349.
Zhu, S.-C. and Mumford, D. (2006). A stochastic gram-
mar of images. Found. Trends. Comput. Graph. Vis.,
2(4):259–362.
