
A MULTI-CRITERIA
APPROACH TO LOCAL ENERGY PLANNING
The Case of Barreiro Municipality
Ana Rita Neves
1
, João Carlos Lourenço
2
and Vítor Leal
1
1
IDMEC, Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias, Porto, Portugal
2
Centre for Management Studies (CEG-IST), Instituto Superior Técnico, Technical University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords: Local energy planning, Multi-criteria evaluation, MACBETH.
Abstract: Energy planning is at the top priorities of local authorities nowadays. Problems such as the depletion of
natural resources, the wellbeing of human population and the security of energy supply have became the
main drivers to change the current fossil fuel-based energy paradigm. In order to put into practice energy
planning processes at the local level, there is a need to provide support methods and tools to local
authorities. In this paper we present a decision support methodology for sustainable local energy planning
that combines energy modelling and multi-criteria evaluation techniques. The focus of the paper is on the
building process of a multi-criteria evaluation model for the municipality of Barreiro, in Portugal. The
municipality case revealed that multi-criteria evaluation is a suitable tool for local energy planning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today’s energy systems are largely driven by the
combustion of fossil fuels, which cause negative
impacts in the environment, in the society and in the
economy. Impacts such as the greenhouse gases
(GHG) emissions are considered to be the principal
cause of climate change (IPCC, 2007). The depletion
of natural resources affects the ecosystems and the
wellbeing of human population, and the risks on the
security of energy supply due to the dependence of a
country in imported fossil fuels affect negatively the
economy.
Energy challenges encompass an urgent change
of the current fossil fuel-based energy paradigm and
the promotion of sustainable energy systems. It is
recognized nowadays that local authorities have an
important role to play in the promotion of
sustainable energy systems. Indeed, recent policies
and initiatives, such as the Covenant of Mayors and
the C40 Cities, stress the fact that cities are
important actors for implementing sustainable
energy policies and that their actions must be
encouraged and supported. The emerging calls for
action at the local level must be accompanied by
methods and tools to assist local authorities in their
processes of energy planning. In particular, local
authorities need a decision support methodology to
help them identifying their fundamental objectives
and selecting actions to achieve these objectives.
This paper presents the application of a decision
support methodology for energy planning to the
municipality of Barreiro in Portugal. The
methodology was applied combining energy
modelling and multi-criteria evaluation techniques.
The focus of the paper is on the building process of
the multi-criteria evaluation model. Problem
structuring methods such as causal mapping (Bryson
et al., 2004) were employed in order to identify the
objectives of sustainable energy planning.
The application of the methodology to the
municipality of Barreiro encompassed the task of
energy modelling for the base year 2008 and for the
time horizon of 2020 in a business-as-usual
perspective. In this way, it was possible to see the
expected evolution in terms of energy consumption
and GHG emissions. Afterwards, the selection of a
set of actions allowed the generation of alternative
energy action plans that were evaluated with the
multi-criteria model. In this work, it was adopted a
MACBETH socio-technical approach (Bana e Costa
and Vansnick, 1999; Bana e Costa et al., 2011; see
also Bana e Costa et al., 2008, for an application in
the energy sector, and Bana e Costa and Oliveira,
313
Neves A., Lourenço J. and Leal V..
A MULTI-CRITERIA APPROACH TO LOCAL ENERGY PLANNING - The Case of Barreiro Municipality.
DOI: 10.5220/0003797603130320
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES-2012), pages 313-320
ISBN: 978-989-8425-97-3
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2002, for an application in a municipality) involving
actors from the Barreiro City Council and the
Barreiro energy agency (S.Energia), who built a
value function for each objective and weight the
objectives in an one-day decision conference
(Phillips, 2007). At the end of the decision
conference it was possible to obtain an overall
benefit value score for each alternative energy action
plan under evaluation. The expected result of the
application of the methodology is to provide support
to decision-making in local energy planning
processes.
The next section presents the structuring of the
local energy planning problem, where the objectives
and respective attributes are identified as well as the
actions and the generation process of alternatives to
be subjected to the multi-criteria evaluation. It is
also presented how the local actors were involved in
this process Section 3 focuses in the building of the
multi-criteria evaluation model for the municipality
of Barreiro. Section 4 draws some conclusions.
2 STRUCTURING THE LOCAL
ENERGY PLANNING
PROBLEM
2.1 Identification of Objectives
and Attributes
The process of structuring the objectives aims to
provide a deeper understanding of the decision
context. The objectives were identified through a
literature review and through interviews with local
actors. Each interview made with a single actor lead
to a cognitive map, which represents “a person’s
thinking about a problem or issue” (Eden, 2004, p.
673). The individual cognitive maps were
subsequently merged into a group causal map
(Bryson et al., 2004), which was validated by the
interviewees with minor changes. The objectives
were then structured according to the procedure
described by Keeney (2007). This allowed
separating the fundamental objectives from the
means objectives. To do this, for each objective, we
asked “Why is this objective important in the
decision context?” (Keeney, 2007, p. 114) If the
response to the question identified that the objective
was important because of its implications for some
other objective, this was a means objective. If the
response was that the objective was one of the
essential reasons for interest in the situation, this was
a candidate for a fundamental objective.
Figure 1 presents the objectives hierarchy, where
the fundamental objectives (in the grey boxes) were
used to build the multi-criteria evaluation model.
Table 1 summarizes the selected objectives and
their attributes for local sustainable energy planning.
Observe that the attributes (that are also known as
descriptors of performance; see Bana e Costa et al.,
2008) are used to measure the extent to which the
objectives are achieved by alternative sets of actions
(Keeney, 2007).
Figure 1: Objectives hierarchy.
Table 1: Objectives and attributes.
Objectives Attributes
O1 Reduce GHG emissions
Tonnes of CO
2
equivalent reduced
O2
Reduce air pollution from
transport
Tonnes of NO
x
emissions
reduced
O3
Maximize employment
benefits
Net jobs gained
O4
Improve long-term energy
independence
Tonnes of oil equivalent
of imported fossil fuels
reduced
O5
Minimize the negative
impacts on human health
caused by noise from
transport
Number of people that
benefit from noise levels
reduction
O6
Minimize the negative
impacts on human health
by improving the thermal
comfort conditions of
homes and offices
Tonnes of oil equivalent
(final energy) reduced
for space heating and
cooling
O7
Minimize the negative
impacts on human health
caused by automobile
dependence
Number of passenger-km
shifting from passenger
cars to public transit,
walking and cycling
O8 Reduce the energy bill
Euros saved per
household per year
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
314
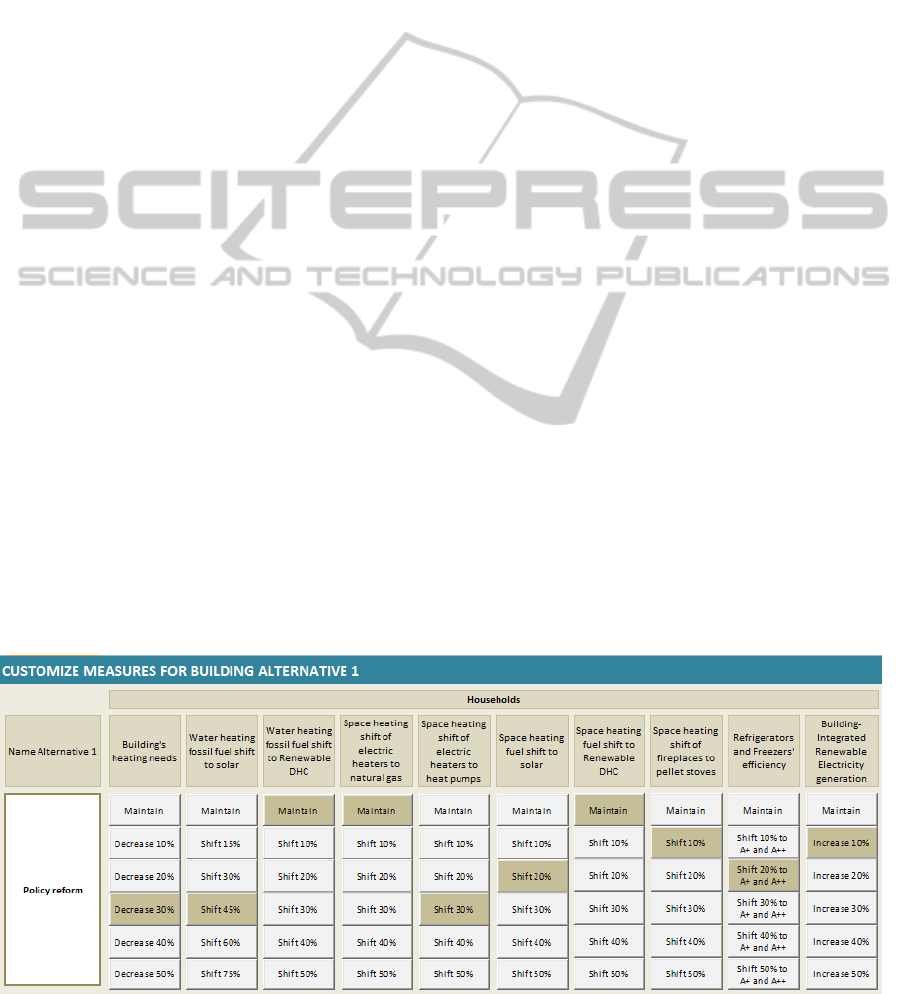
2.2 Identification of Actions
and Generation of Alternatives
The identification of actions was based on an
extended literature review, having into account three
selection criteria:
Local authority actions – the main focus of this
work was on the demand side, because it is
where the local authority can have a greater
power to act. The areas where the local
authority has no control of intervention were
excluded from this work, such as large-scale
energy supply and industry.
Technical actions – leaving the policy actions
or promotion mechanisms outside of the scope
of this work.
Community-scale actions – the focus of this
work is community-wide and Government
operations only.
Alternatives represent means of achieving the
objectives. They usually are a mutually exclusive set
of means among which a choice is possible. In
general, to be allowed not to choose is also
considered an alternative (Zeleny, 1982, chap. 4).
In this case, alternatives are combinations of 26
actions (10 actions in the households sector, nine
actions in the services sector, and seven actions in
the transport sector) in six different degrees of
implementation. Making all the possible
combinations between the actions and the possible
degrees of implementation would result in a very
large number of alternatives (precisely, 6
26
).
Although, it would be possible to generate them with
the help of a computer-based decision support
system it would be impractical due to the existence
of synergies between actions that needed to be
analysed. Therefore, it was decided to adopt a
pragmatic approach for the generation of alternatives
based upon a strategy-generation table procedure
(Kirkwood, 1997; Matheson and Matheson, 1998).
The actions and their degrees of implementation
were combined directly in the energy model
implemented in a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet,
allowing in this way to account for the synergetic
effects. The rows of the table represent the different
degrees of implementation for the different actions
that are presented in columns. The only exception is
the first row (named “Maintain”) that means “do not
implement the action”. The user builds an alternative
by selecting one cell from each of the 26 columns.
Figure 2 shows a screenshot of the spreadsheet
where the degrees of implementation of the 10
actions of the sector of households for alternative 1
are shown. At the end, the user can visualise if the
selected combination of actions/degrees of
implementation respect the constraint of GHG
emissions reduction (in this case a minimum level of
20% is required). If not, the user should redefine the
selection of actions/degrees of implementation in
order to accomplish the target reductions in GHG
emissions.
The adoption of the strategy-generation table
approach for the generation of alternatives provides
a structured procedure to sort out alternatives that
the user considers to make sense to analyse in more
detail. The energy model allowed the creation of five
alternatives that were subjected to a multi-criteria
evaluation process.
2.3 Involvement of the Local Actors
The involvement of local actors took place in two
stages. First, the process of identification of the
Figure 2: The strategy-generation table.
A MULTI-CRITERIA APPROACH TO LOCAL ENERGY PLANNING - The Case of Barreiro Municipality
315

Figure 3: Reference levels “Good” and “Neutral” defined on each attribute.
objectives had the participation of the City
Councilman for Environment of Barreiro City
Council and the director of the energy agency
(S.Energia). This process also involved the
participation of local actors from other
municipalities in Portugal. Second, a decision
conference was held with the participation of two
technicians from the Environmental Sustainability
Division of Barreiro City Council and two
technicians and the director of the energy agency.
The actors involved represented the points of view
of those two organizations concerning the
implementation of the sustainable energy action
plan.
During the decision conference, a facilitator
guided the decision process helped by an analyst.
The facilitator started by remembering the model
structure created until then, namely by presenting
the objectives and their attributes. The facilitator
also had the task of stimulating the group discussion
concerning the development of the multi-criteria
value model without contributing to the content of
discussion (Phillips, 2007). The analyst used the
decision support system M-MACBETH (www.m-
macbeth.com) to display on-the-spot the model
being developed.
3 BUILDING THE
MULTI-CRITERIA
EVALUATION MODEL FOR
THE MUNICIPALITY OF
BARREIRO
3.1 Building a Value Function for Each
Objective
The objectives and attributes presented in table 1
were used in the model of the municipality of
Barreiro after having the agreement from the local
actors involved. The exception was in the objective
“Reduce noise impacts from transport”, which was
dropped from the model due to lack of data.
For each attribute the group was asked to define
a “neutral” reference level; this means to define a
performance that would be neither positive nor
negative in the linked objective. The group was also
asked to define a “good” reference level for each
attribute, i.e. a performance level considered
significantly attractive in the light of the objective.
Figure 3 shows the performance reference levels
defined upon each attribute.
For each attribute the group was asked to define
a “neutral” reference level; this means to define a
performance that would be neither positive nor
negative in the linked objective. The group was also
asked to define a “good” reference level for each
attribute, i.e. a performance level considered
significantly attractive in the light of the objective.
Tonnesof
CO2eq.
emissions
reduced
Tonnesof
Nox
emissions
reduced
Netjobs
gained
Toeof
imported
fossilfuels
reduced
Toeoffinalenergy
reducedforspace
heatingandcooling
ofhomesand
offices
NumberofPkm
shiftingfrom
passengercarsto
publictransit,
walkingandcycling
Euros
savedper
household
peryear
20%
00
0
00
0
tCO
2
eq.
tNO
x
Numbe r toe
toe millionpkm €/household/year
30%
200 150
27000
3000 600 500
QualityofLifeEnvironment EconomicDevelopment
Good
Neutral
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
316
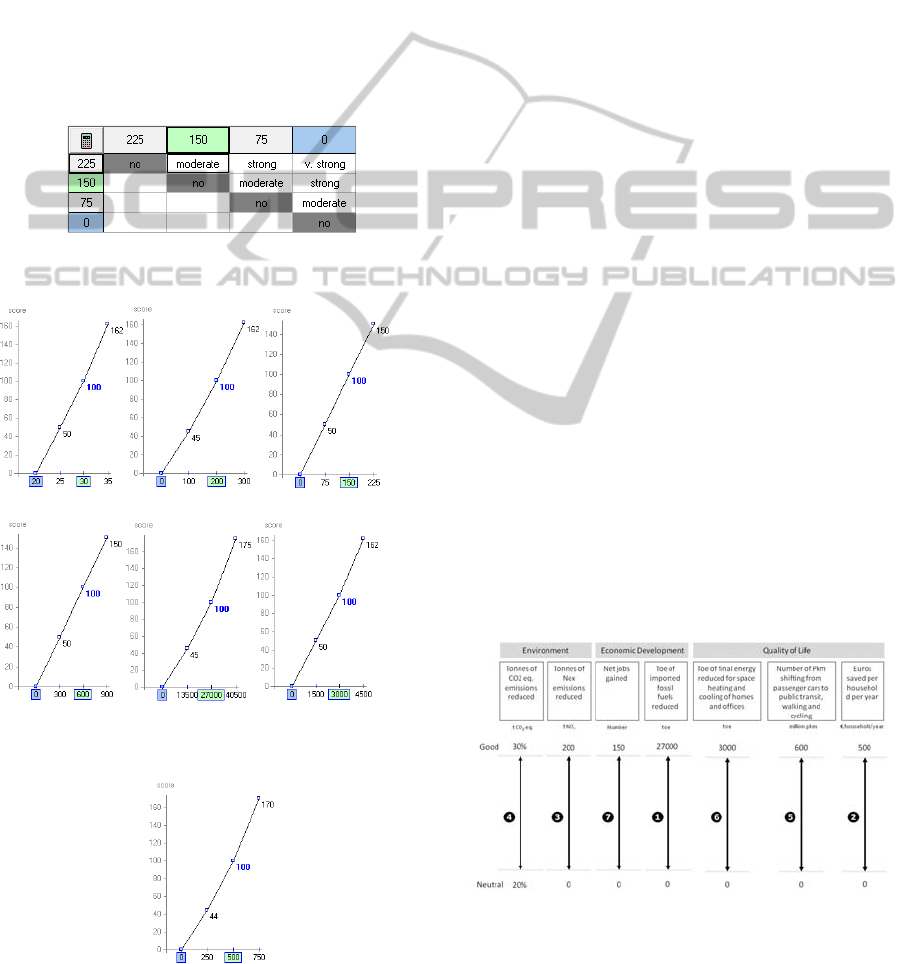
Figure 3 shows the performance reference levels
defined upon each attribute.
Afterwards, more levels were added to the
attributes such that each attribute had four
performance levels equally spaced in the attribute
scale.. The group was then asked to judge the
differences in attractiveness between each two levels
of performance, choosing one of the MACBETH
semantic categories: very weak, weak, moderate,
strong, or extreme. For each objective, the process
was initiated by asking the difference of
attractiveness of changing from the “neutral”
performance level to the “good” performance level
and followed by asking the difference between each
two of the other levels.
Figure 4: MACBETH judgements matrix for the objective
“Maximize employment benefits”.
Figure 5: Value functions for the objectives.
Figure 4 presents the group judgments matrix for the
objective “Maximize employment benefits”.The M-
MACBETH decision support system proposes a
numerical value scale based on the set of qualitative
judgments inputted in the matrix of judgments
(figure 4) using linear programming (see details in
Bana e Costa et al., 2011). The numerical scale is
anchored on the two predefined reference levels
(neutral and good) to which were assigned the scores
0 and 100. The proposed MACBETH scale is then
subjected to group analysis and discussion in terms
of proportions of the resulting scale intervals. In the
case of Barreiro, the group decided to make minor
scale adjustments on the value scales of some
objectives. Figure 5 represents the value functions
obtained for the objectives after the group
discussion.
3.2 Weighting the Objectives
The relative weights for the seven objectives were
defined using the MACBETH weighting procedure.
The group was first asked to rank the “neutral-good”
swings by their overall attractiveness. The facilitator
started by asking the question: “From the seven
objectives, if you could choose just one objective to
change from a neutral performance to a good
performance which objective would you choose?”
The questioning procedure continued till the final
ranking of “neutral-good” swings was achieved.
During the MACBETH questioning procedure to fill
in the weighting judgements matrix, the group
engaged in a deeper thinking and discussion about the
relative importance of the “neutral-good” swings and
decided to change the ranking of the second, third and
fourth most attractive swings. The final ranking of the
“neutral-good” swings is presented in figure 6.
Figure 6: Final ranking of the swings.
The next step consisted in asking the group to judge
the overall attractiveness of each “neutral-good”
swing, which allowed filling in the last
Tonnes CO
2
eq. reduced (%) Tonnes of NO
x
reduced Net jobs gained
Toe of imported fossil
fuels reduced
Toe of final energy reduced
for space heating and cooling
of homes and offices
Number of Pkm shifting
from passenger cars to
public transit, walking
and cycling
Euros saved per
household per year
A MULTI-CRITERIA APPROACH TO LOCAL ENERGY PLANNING - The Case of Barreiro Municipality
317

Figure 7: The MACBETH weighting matrix.
Figure 9: Overall benefit scores of the alternatives.
column of the MACBETH matrix in figure 7.
Subsequently, the group was asked to pairwise
compare the most attractive swing to the second
most attractive. The pairwise comparison continued
between the most attractive swing and each of the
other swings till filling in the first row of the
MACBETH matrix (figure 7). Afterwards,
judgments concerning the comparison of each two
consecutive swings were also made and the
questioning procedure stopped. It was not necessary
to ask more judgments, once MACBETH is able to
create the weighting scale with the information
already present in the matrix of judgments (see
figure 7).
Figure 8: Weighting scale obtained for the objectives
presented in table 1.
Figure 8 presents the weighting scale proposed
by M-MACBETH. The facilitator asked the group to
check the resulting weights in order to validate them.
For example, the facilitator asked if the “neutral-
good” swing on objective “GHG emissions
reduction potential” is worth four times the “neutral-
good” swing on objective “Maximize employment
benefits” (note that the weights of these objectives
are 16% and 4%, respectively), and also if the
“neutral-good” swing on objective “Improve long-
term energy independence” is worth 1.9 times the
neutral-good swing on objective “Minimize the
negative impacts on human health by improving the
thermal comfort conditions of homes and offices”,
which the group agreed.
3.3 Aggregation and Robustness
Analysis
The performances of the six alternatives upon each
of the objectives were determined in the energy
model developed in the spreadsheet and were then
inputted in M-MACBETH. The decision support
system transformed these performances into benefit
scores, using the value functions previously built,
and determined an overall benefit score for each
alternative by weighted summation of its value
scores. At the end of the decision conference, it was
possible to visualize the overall benefit scores for
the six alternative sustainable energy action plans
created (see column “Overall” in figure 9).
The alternative A4 ranked first with 143.83
benefit units and alternative A3 ranked second with
128.25 benefit units. Both A4 and A3 obtained
overall scores higher than that of a hypothetical
alternative “Good all over”, which shows that they
are very attractive alternatives. The remaining
O4 O8 O2 O1 O7 O6 O3
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
318

Figure 10: Robustness analysis.
alternatives also had positive overall scores, i.e.
higher scores than that of a hypothetical alternative
“Neutral all over”, which means that all of them are
globally attractive.
Given the hesitations the group had during the
weighting process it is wise to analyze if A4 would
continue to rank first when the weights are modified.
A robustness analysis made with M-MACBETH
considering variations of ±3% on the weights of all
objectives revealed that A4 continues to be the most
attractive alternative from the set of six alternatives
evaluated (figure 10). Observe that a green cross in a
cell of figure 10 means that the alternative in row
additively dominates the alternative in column (in
this case the dominance relationship depends on the
constraints defined upon the parameters of the
additive model), and a red triangle indicates
dominance in the classic sense (the alternative in
row is always preferred to the alternative in column
irrespectively of the constraints defined upon the
parameters of the model).
4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper had a particular focus on the multi-
criteria evaluation process and its application to the
municipality of Barreiro in the context of energy
planning. The multi-criteria evaluation model
presented is part of a comprehensive decision
support methodology which includes also an
extensive work on energy modelling of the local
energy system. The energy modelling was developed
in Microsoft Excel and has several features
necessary to the multi-criteria evaluation, namely the
process of generating alternatives and the
quantification of the performances of the alternatives
in each objective (which are required inputs to the
additive model developed with M-MACBETH). We
underline that the developed model not only allowed
to identify which alternative performed best out of
six alternatives, but also allowed to verify that it is a
very attractive alternative by comparing its overall
benefit score with those of the two reference profiles
– “good all over” and “neutral all over”. Indeed, in
this context, selecting the best alternative of a set of
unattractive alternatives would not be a wise
decision to make.
With respect to the multi-criteria evaluation
process, it is possible to conclude that this is a
suitable tool and with great potentiality to be applied
to local energy planning processes. In particular, it
promotes the participation of several local actors and
stimulates thinking and discussion about the key
issues for energy planning in their contexts. The
decision conference process and the M-MACBETH
software used were of valuable help to implement
the multi-criteria evaluation.
The development of the methodology had in
mind its replication for any local context, as so it is
expected that more municipalities will adopt this
common methodological framework in the
elaboration of their sustainable energy action plans.
Future research will still cover the assessment of
investment costs for each alternative to be traded-off
with the overall benefits of the alternatives.
A MULTI-CRITERIA APPROACH TO LOCAL ENERGY PLANNING - The Case of Barreiro Municipality
319

REFERENCES
Bana e Costa, C. A., De Corte, J. M. and Vansnick, J. C.
(2011). MACBETH (Measuring Attractiveness by a
Categorical Based Evaluation Technique). In Cochran,
J. J. (Ed.) Wiley Encyclopedia of Operations Research
and Management Science (Vol. 4, pp. 2945-2950).
John Wiley & Sons.
Bana e Costa, C. A., Lourenço, J. C., Chagas, M. P. and
Bana e Costa, J. C. (2008). Development of reusable
bid evaluation models for the Portuguese Electric
Transmission Company. Decision Analysis, 5(1), 22-
42.
Bana e Costa, C. A. and Oliveira, R. C. (2002). Assigning
priorities for maintenance, repair and refurbishment in
managing a municipal housing stock. European
Journal of Operational Research, 138(2), 380-391.
Bana e Costa, C. A. and Vansnick, J. C. (1999). The
MACBETH approach: Basic ideas, software, and an
application. In Meskens, N. and Roubens, M.R. (Eds.),
Advances in Decision Analysis (pp. 131-157).
Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Bryson, J. M., Ackermann, F., Eden, C. and Finn, C. B.
(2004). Visible Thinking: Unlocking Causal Mapping
for Practical Business Results. Chichester: John Wiley
& Sons.
Eden, C. (2004). Analyzing cognitive maps to help
structure issues or problems. European Journal of
Operational Research, 159(3), 673-686.
IPCC (2007). Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report,
Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the
Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental
Panel on Climate Change. In Pachauri, R.K. and
Reisinger, A. (Eds.) Core Writing Team. Geneva,
Switzerland.
Keeney, R. L. (2007). Developing objectives and
attributes. In Edwards, W., Miles, R.F. and von
Winterfeldt, D. (Eds.) Advances in Decision Analysis:
From Foundations to Applications (pp. 104-128).
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Kirkwood, C. W. (1997). Strategic Decision Making:
Multiobjective Decision Analysis with Spreadsheets.
Belmont: Duxbury Press.
Matheson, J. and Matheson, D. (1998). The Smart
Organization: Creating Value through Strategic R&D.
Boston: Harvard Business School Press.
Phillips, L. D. (2007). Decision conferencing. In W.
Edwards, W., Miles, R. F. and von Winterfeldt, D.
(Eds.) Advances in Decision Analysis: From
Foundations to Applications (pp. 375-399).
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Zeleny M. (1982). Multiple Criteria Decision Making.
New York: McGraw-Hill.
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
320
