
USING PROVENANCE IN SENSOR NETWORK APPLICATIONS
FOR FAULT-TOLERANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING
Position Paper
Gulustan Dogan and Theodore Brown
Graduate Center, City University of New York, New York City, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Provenance, Fault-tolerance, Troubleshooting, Sensor Networks.
Abstract:
Provenance is a rapidly progressing new field with many open research problems. Being related to data and
processes, provenance research is at the cross-roads of research from several research communities. With
the huge amount of information and processes available in sensor networks, provenance becomes crucial
for understanding the creation, manipulation and quality of data and processes in this domain too. Sensors
collaboratively carry out sensing tasks and forward their data to the closest data processing center, which may
further forward it. Provenance provides the means to record the data flow and manipulate snapshots of the
network. Consequently given enough data, provenance can be used in sensor network applications to find
out causes of faulty behavior, to figure out the circumstances that will affect the performance of the sensor
network, to produce trustworthy data after elimination of the causes, etc. In this position paper, we describe
provenance work in the sensor network community to sketch a panoramic view of the recent research and
give a provenance model of a binary target localization sensor network as a real life example to show how
provenance can be used in sensor network applications for fault-tolerance and troubleshooting.
1 INTRODUCTION
Wireless sensor networks are used in many appli-
cations such as battlefield surveillance, air pollution
monitoring, forest fires detection, biological, chem-
ical attack detection. Due to their nature, wireless
sensor networks are more error-prone than traditional
networks. However most of the sensor network ap-
plications are real-time and mission critical. There-
fore fault-tolerance and troubleshooting become very
crucial in order to sustain the network. In this posi-
tion paper, we argue that sensor networks should have
provenance support for many benefits including fault-
tolerance and troubleshooting.
Although sensor networks is an area of research
for years, provenance management should be a con-
cern too in order to have an understanding of how
the results are obtained for fault tolerance and trou-
bleshooting purposes. In some sensor networks such
as ad hoc sensor networks, in which data is copied,
moved, created, updated and deleted in an uncontrol-
lable way, provenance can play an important role in
deciding about data qualities such as trustworthiness,
accuracy, verifiability.
Maintaining provenance information makes it po-
ssible to have a clearer picture of the movement of
the data and its manipulation in a sensor network
by tracking the evolution of the data systematically.
There can be many reasons why the data values gen-
erated are not accurately received at the sink. For
instance one reason could be the sensors themselves
may be sending faulty data. Provenance can be used
to keep track of the state of the sensors and more gen-
erally to find out the causes of faulty behavior, to fig-
ure out the circumstances that will determine the con-
nectivity of the network, and to produce trustworthy
data after elimination of the causes.
We present a dataflow-oriented provenance model
for sensor networks. Although our dataflow-oriented
provenance model is generic, we use a particular
scenario to support our argument modeling it on a
proximity binary target localization sensor network.
This model works best with networks sensing dy-
namic objects, and we introduce a provenance di-
rected network-level fault-tolerance mechanism by
using the cognitive strength of provenance models.
Our provenance model reduces the limitations of
faulty data by decreasing the possibility of errors in
wireless sensor networks. By determining faulty data
early in the stream, our model also makes it advanta-
47
Dogan G. and Brown T..
USING PROVENANCE IN SENSOR NETWORK APPLICATIONS FOR FAULT-TOLERANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING - Position Paper.
DOI: 10.5220/0003803300470052
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Sensor Networks (SENSORNETS-2012), pages 47-52
ISBN: 978-989-8565-01-3
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

geous to have a self-adjusting sensor network so that
the sensor data that is produced results in more accu-
rate results at the receiving end.
This paper is organized as follows. Related work
is presented in Section 2. In Section 3 we give some
background information on provenance. In Section 4
we describe how provenance information can be used
in sensor network applications for fault-tolerance and
troubleshooting. In Section 5 we describe the prove-
nance model for a target localization sensor network.
Section 6 concludes the paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Provenance in the sensor network community is an
area of research that is new and open to many di-
rections. Provenance management in sensor net-
works should be considered in order to have an un-
derstanding of how the results are obtained. Having
this motivation, although not as extensive as prove-
nance research in database (Cui et al., 2000; Buneman
and Tan, 2007; Moreau et al., 2008; Cheney et al.,
2009) and eScience community (Davidson and Freire,
2008a; Barseghian et al., 2010; Crawl and Altintas,
2008; Feng and Lee, 2008; Freire et al., 2008), there
has been research on provenance in sensor networks
community.
To our knowledge, there is not any work on us-
ing provenance specifically for fault tolerance in sen-
sor networks. Some research has leveraged prove-
nance in extracting metadata from weather sensors
(Stephan et al., 2010), in answering domain specific
complex queries (Patni et al., 2010; Park and Heide-
mann, 2008a), in building provenance aware sensor
data storage (Ledlie et al., 2005). In our previous
work we used provenance for network restructuring
(Dogan et al., 2011) and assessing trust (Govindan
et al., 2011).
The nature of provenance in sensor networks is
different from eScience and database community in
several ways (Park and Heidemann, 2008a), this is
why research on provenance in sensor network com-
munity should be done more extensively to make ro-
bust provenance systems for sensor networks.
3 BACKGROUND
Provenance has been defined broadly as the origin,
history, chain of custody, derivation or process of an
object. In disciplines such as art, archeology, prove-
nance is crucial to value an artifact as being authen-
tic and original (Cheney, 2010). However prove-
nance has also become a crucial component in fields
that rely on digital information. For instance Home-
land Security and Governmental Affairs highlighted
provenance as one of three key future technologies
for securing their critical infrastructure (Wynbourne
et al., 2009). Provenance has grown in importance in
its use in helping to understand how the digitally cap-
tured data is manipulated at the source and used at the
destination.
The literature often divides provenance into data
and workflow provenance (Moreau and Ludascher,
2007). Data provenance gives a detailed record of
the derivation of a piece of data that is the result of
a transformation step (Tan, 2007) whereas workflow
provenance is the information or metadata that char-
acterizes the processing of information from input to
output (Davidson and Freire, 2008b).
4 PROVENANCE FOR
FAULT-TOLERANCE AND
TROUBLESHOOTING
Provenance is needed to be transmitted to where a de-
scription of the data namely metadata is needed. Ba-
sically, if there is any input data (data provenance),
any process chain (workflow provenance) or informa-
tion flow (dataflow provenance), provenance can be
included. There are many areas in sensor networks
where provenance can be used. In this paper, we
concentrate on showing how provenance can improve
fault-tolerance and troubleshooting capability of sen-
sor networks.
In a sensor network, there can be many unpre-
dictable events such as broken sensors, unstable con-
nections, lack of energy which will cause corruption
in system. For example a sensor can get many streams
at the same time such as temperature, audio and video.
When it transmits the stream, the metadata will spec-
ify what kind of stream the sent data is, when it was
transmitted, the id of the node transmitting the stream,
whether the data was modified or not. If later this
data is found to be faulty, by using dataflow prove-
nance graph the responsible node can be determined
and marked as an untrusted node. Another example
will be if a video sensor changes its angle, zoom, or
resolution, provenance can record the path the image
travels(Tilak et al., 2005) which can be later used to
track the source if the user is not satisfied with the im-
age.
It is beneficial to store provenance information
for historical value for the sensor data (its metadata).
Mostly sensor data is treated as data with a real time
SENSORNETS 2012 - International Conference on Sensor Networks
48

value but Ledlie et al point out that it has historical
value too if thought in a broader sense. To heal, adjust
and manage sensor networks, historical sensor data is
required. For instance, for finding the patterns related
to snowfall and traffic, sensor data monitoring traffic
and snowfall and their provenance data can be useful
(Ledlie et al., 2005). In our model, dataflow prove-
nance graphs are stored in a central storage which is
further described in Section 4. The stored historical
metadata of paths is a good source in determining the
behavior patterns of the network. We can make use of
the historical metadata to extract statistical informa-
tion that is related to fault-tolerance such as misreport
frequency of a node, unsuccessful transmissions of a
link, inconsistent data retrievals, etc.
Furthermore, provenance ensures authenticity of
data which is helpful in creating a safe platform for
fault-tolerance and troubleshooting. In sensor net-
works, data can be modified along its path to its des-
tination and can be used for maliciously. If there is
provenance tracking on the node, the data can be ver-
ified as authentic or not. Although this verification is
not foolproof, it adds a layer of protection. For in-
stance the system can be configured so that before a
change, the identity of the node making the change
would be verified. If the node’s identity cannot be ver-
ified, this will be the sign of an attack and the modifi-
cations will not be allowed, making the network more
resistant and fault-tolerant.
By making use of logs of provenance information,
tracing and monitoring can be done efficiently and
changes between two time slots can be found out if the
later information is considered faulty. The logs can
be used in troubleshooting and fault-tolerance mak-
ing network more fault-tolerant as mistakes will be
more quickly detected at a closer destination before
data travels long distances.
4.1 Where Provenance Comes In
As stated above provenance answers questions such
as “how was data created?”, “on what other data
does computed data value depend upon?”, “how do
the ancestries of these two data differ?”(Muniswamy-
Reddy, 2010). Therefore, in sensory data systems,
sensors can also have the provenance information of
data dependency. For instance there will be a data
dependency representing the data binding relation be-
tween the outputs of sensor nodes A, B, C, D, E and
input of fusion node F shown in Figure 1. Opera-
tion of fusion node F depends on availability of the
data provided by nodes A, B, C, D, E. This depen-
dency provenance will be helpful in analyzing data
flow graphs of sensor networks.
Dataflow provenance is the path that data is trans-
mitted over until it comes to the fusing node. Then
if there is a misreport, using dataflow provenance we
can find out the sensor creating the false information
and it can be replaced by reconfiguring the network
or waking up an appropriate sensor before a system
malfunction.
Value Dependency:
Nodes A, B, C, D, E
Fusion
Node F
Node E
Node D
Node C
Node B
Node A
Figure 1: Value dependency between nodes.
4.2 How to Model Provenance
For standardization purposes, a provenance model
called Open Provenance Model (OPM) has being
crafted (Moreau and Ludascher, 2007). An alterna-
tive model is the W3C SSN-XG. We will use OPM
for modeling provenance and for lack of space we
will not further discuss this latter model. However
the OPM model does not support some requirements
that are specific to sensor networks such as record-
ing provenanceof streaming data, capturing times be-
tween sensing. It is an ongoing research issue to com-
pletely adapt this model to sensor networks (Park and
Heidemann, 2008b) and it is in our future agenda.
In OPM, provenance is modeled as a directed
acyclic graph (DAG). The nodes in the DAG represent
objects whose provenance the system describes. The
edges between objects indicate relationships between
them. Both the nodes and edges can have attributes.
For nodes, the attributes consist of information such
as the name of the object it represents and the object
type. For edges, the attributes indicate the type of re-
lationships between objects. In our system, as energy
is an important consideration, we keep the forwarded
provenance data as small as possible and we do not la-
bel attributes of nodes in our provenance graphs. We
only transmit id of the node, edge label and data at
each transmission.
Apart from being modeled as a DAG, our model
specifically is an Information Flow Model (Sabelfeld
and Myers, 2003). Information flows between
a source object and its destination object. The
USING PROVENANCE IN SENSOR NETWORK APPLICATIONS FOR FAULT-TOLERANCE AND
TROUBLESHOOTING - Position Paper
49
graph timestamps localization
2011-01-19 03:14:07 λ
.......... ........ ..............
Figure 2: Central storage scheme.
source object is the ancestor of the destination object
(Muniswamy-Reddy, 2010). This model will be more
useful as we are interested in finding out the path that
created the target localization decision. In our system,
dataflow provenanceis kept as directed graphs in Cen-
tral Provenance Repository as illustrated in Figure 2.
5 AN EXAMPLE: TARGET
LOCALIZATION SENSOR
NETWORK
To better illustrate our concepts, we will examine
a system that makes use of proximity binary sen-
sors. We assume that environment that sensors are
in is not under attack so that we can assume that the
provenance information is assured to be accurate. In
proximity-based wireless sensor networks, the like-
lihood of the target position is calculated using the
binary values reported by proximity binary sensors.
A proximity sensor acts as a tripwire i.e. it reports
a detection when a target close by triggers it. Exam-
ples of these sensors are seismic, acoustic, passive, in-
frared; they can be deployed in large numbers because
of their low cost. The binary proximity behavior in
sensors is achieved by implementing simple energy
detection algorithms where the signal is compared to
a threshold. If the signal exceeds the threshold, the
sensor node reports a “1” meaning a detection, oth-
erwise a “0” is reported for no detection. A network
of such sensors is used to localize and track targets(Le
and Kaplan, 2010). Provenance data is captured in our
model for this network as a support for fault-tolerance
and troubleshooting of the target localization.
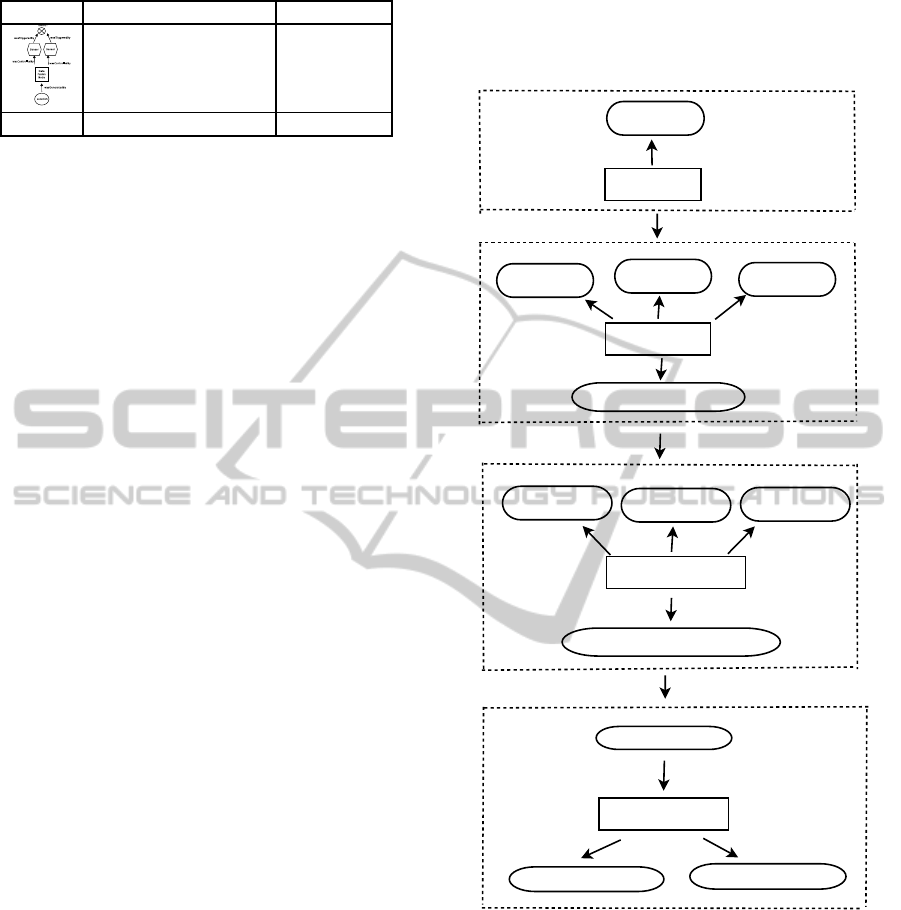
A detailed picture of open provenance model of our
system is illustrated in Figure 3. Basically network
snapshots are taken at time intervals when a target is
detected and they are stored in the Central Provenance
Repository. Later these network snapshots are used
in order to get a better understanding of the behavior
of the network for fault-tolerance and troubleshoot-
ing. Traditional sensor network systems deal with real
time data and they lack the ability to remember past
detections and which nodes were actively participat-
ing in the target localization. As clearly can be seen
in Figure 3 below, our system records the dataflow
pictures.
Data Fusion and Computation
used by
Sun Jan 09 11:41:12 EST
Localization
Data: s01
Localization
Data: s02
Localization
Data: s03
Fused & Computed Data
Estimated
Location
Headquarters
Stream ID: s01
Provenance Data
Localization Data
Computed
Data: c01
Computed
Data: c02
Computed
Data: c03
Central Node
Estimated Location
User Interaction
Location Estimation
Data Retrieval
Internal Node
Localization Sensor
used
Sun Jan 09 11:44:12 EST
wasTriggeredBy
used
used
used
Sun Jan 09 11:43:01 EST
wasTriggeredBy
used
used
wasGeneratedBy
Sun Jan 09 11:41:54 EST
wasTriggeredBy
wasGeneratedBy
Sun Jan 09 11:40:02 EST
wasGeneratedBy
Sun Jan 09 11:39:57 EST
wasGeneratedBy
Sun Jan 09 11:39:57 EST
Figure 3: OPM graph of binary localization.
5.1 Fault Tolerance and
Troubleshooting
Consider the following scenario: A target steps into
the field and trips one or more sensors. Target lo-
calization is done at the base node within headquar-
ters. Administrators may see that the target is local-
ized wrongly. Provenance will be helpful at this point
to understand the reasons behind this. In our model,
provenance graphs of localizations (data flow from
one node toanother) can beexamined and causes for
SENSORNETS 2012 - International Conference on Sensor Networks
50

any change or fault can be detected. After finding the
root cause, the network can be reconfigured eliminat-
ing the faulty nodes.
There are many possible exceptions in a sensor
network which some of them can be listed as fol-
lows, sensor node failure, deadline expiry, resource
unavailability, path loss and unpredictable multipath
(Bal et al., 2010). On the other hand Zahedi et al
characterize a sensor measurement to be in one of sev-
eral states including normal, noisy, spike, frozen, sat-
uration, bias, spike, oscillation (Zahedi et al., 2008).
Our dataflow-oriented sensor network model that is
illustrated in Figure 3 will capture and tolerate fail-
ure patterns due to faulty data. As our flow model
has value dependencies stored, fault-tolerance will be
doable. For example when a sensor is failing, it can
be replaced and retransmission can be done. Another
example is, since provenance data flows to the central
provenance repository, the problem can be found out
earlier that the node is out of energy and be replaced
before it causes system to provide faulty or incom-
plete data.
At the headquarters, administrators can find out
wrong localizations. In traditional sensor networks,
it is hard to find faulty nodes because there may not
be historical data available. Network constantly de-
tects targets and reports their locations but the net-
work snapshot at the time of the detection is not ac-
cessible. However in our model, every time a tar-
get detection is sensed, the result and corresponding
provenance DAG is sent to the Central Storage. The
scheme of the Central Storage is given in Figure 2. As
the system has access to past right and wrong detec-
tions and the network snapshots at these times, it can
find out the common patterns in false detections. For
instance, comparing past 50 wrong detections and the
provenance graph, a graph traversal algorithm can fig-
ure out the common pattern in the graphs such as “ev-
ery time the target is nearby this group of sensors, the
localization is done wrongly”. Network can be healed
by replacing these nodes or omitting them. Although
building a graph mining algorithm is not in the scope
of this paper,the graph mining algorithm for bug find-
ing in graphs developedby Abdelzaher et al is suitable
to our model (Khan et al., 2009).
On the other hand, central repository of prove-
nance information makes restructuring for the pur-
pose of healing the network easier. For instance, if
a faulty node has to be removed, it can be replaced
by a close accurate node. For determining the closest
accurate node, we can search the central provenance
repository. Central repository also makes possible ex-
amining redundant sources that may come from dif-
ferent parts of the network. For instance a mobile de-
vice on a vehicle and a fixed sensor can sense the same
data but the data from the vehicle may be captured in
the network later after it moves far from where it col-
lected the data. By using the provenance repository,
we can trace back to the ancestors of the data and see
that both data are captured in the same location and
they are redundant.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this position paper, we have built a provenance
model for sensor networks. We illustrated our
model on a binary target localization network. Our
model makes it possible to build fault-tolerant sensor
networks leveraging historical dataflow information.
There are many opportunities for further research of
using provenance in sensor networks. Open Prove-
nence Model (OPM) was not designed primarily for
sensor networks, it is lacking some important fea-
tures such as handling real-time provenance. A model
of provenance collection and dissemination for sen-
sor networks requires further work. There are many
research problems to consider. For instance prove-
nance information may overwhelm the amount of ac-
tual data being collected. By storing the provenance
data in a central store, errors can be found more effi-
ciently than if the provenance data is stored within the
network. However the amount of additional commu-
nications should be weighed with the this. The best
way to model the provenance, what to keep as prove-
nance and how to make use of it in an efficient way
can depend on the application, but general guidelines
are still not well understood. As a future direction, af-
ter adapting OPM to sensor networks, we would like
to do simulations of our revised model on real-world
data sets.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was sponsored by the Army Research
Laboratory and was accomplished under Cooperative
Agreement Number W911NF-09-2-0053. The views
and conclusions contained in this document are those
of the authors and should not be interpreted as rep-
resenting the official polices, either expressed or im-
plied, of the Army Research Laboratory or the U.S.
Government. The U.S Government is authorized to
reproduce and distribute reprints for Government pur-
poses notwithstanding any copy right notation here
on.
USING PROVENANCE IN SENSOR NETWORK APPLICATIONS FOR FAULT-TOLERANCE AND
TROUBLESHOOTING - Position Paper
51

REFERENCES
Bal, M., Shen, W., and Ghenniwa, H. (2010). Collabora-
tive signal and information processing in wireless sen-
sor networks: a review. In 2009 IEEE International
Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, pages
3240–3245.
Barseghian, D., Altintas, I., Jones, M., Crawl, D., Potter, N.,
Gallagher, J., Cornillon, P., Schildhauer, M., Borer, E.,
and Seabloom, E. (2010). Workflows and extensions
to the kepler scientific workflow system to support en-
vironmental sensor data access and analysis. Ecolog-
ical Informatics, 5(1):42–50.
Buneman, P. and Tan, W. (2007). Provenance in databases.
In Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGMOD inter-
national conference on Management of data, pages
1171–1173. ACM.
Cheney, J. (2010). Causality and the semantics of prove-
nance. Arxiv preprint arXiv:1004.3241.
Cheney, J., Chiticariu, L., and Tan, W. (2009). Provenance
in databases: Why, how, and where. Foundations and
Trends in Databases, 1(4):379–474.
Crawl, D. and Altintas, I. (2008). A provenance-based
fault tolerance mechanism for scientific workflows.
International Provenance and Annotation Workshop
(IPAW).
Cui, Y., Widom, J., and Wiener, J. (2000). Tracing the
lineage of view data in a warehousing environment.
ACM Transactions on Database Systems (TODS),
25(2):179–227.
Davidson, S. and Freire, J. (2008a). Provenance and sci-
entific workflows: challenges and opportunities. In
SIGMOD Conference, pages 1345–1350. Citeseer.
Davidson, S. and Freire, J. (2008b). Provenance and sci-
entific workflows: challenges and opportunities. In
SIGMOD Conference, pages 1345–1350. Citeseer.
Dogan, G., Brown, T., Govindan, K., Khan, M., Abdelza-
her, T., Mohapatra, P., and Cho, J. (2011). Evaluation
of network trust using provenance based on distributed
local intelligence. MILCOM.
Feng, T. and Lee, E. (2008). Real-time distributed discrete-
event execution with fault tolerance. In IEEE Real-
Time and Embedded Technology and Applications
Symposium, pages 205–214. IEEE.
Freire, J., Koop, D., Santos, E., and Silva, C. (2008). Prove-
nance for computational tasks: A survey. Computing
in Science & Engineering, 10(3):11–21.
Govindan, K., X., W., Khan, M., Dogan, G., Zeng, K. Pow-
ell, G., Brown, T., Abdelzaher, T., and Mohapatra, P.
(2011). Pronet: Network trust assessment based on
incomplete provenance. MILCOM.
Khan, M., Abdelzaher, T., Han, J., and Ahmadi, H. (2009).
Finding symbolic bug patterns in sensor networks.
Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems, pages 131–
144.
Le, Q. and Kaplan, L. (2010). Target localization using
proximity binary sensors. In Aerospace Conference,
2010 IEEE, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Ledlie, J., Ng, C., and Holland, D. (2005). Provenance-
aware sensor data storage. IEEE Computer Society.
Moreau, L. and Ludascher, B. (2007). The first provenance
challenge. Concurrency and Computation: Practice
and Experience.
Moreau, L., Ludascher, B., Altintas, I., Barga, R., Bow-
ers, S., Callahan, S., Chin, J., Clifford, B., Cohen, S.,
Cohen-Boulakia, S., et al. (2008). Special issue: The
first provenance challenge. Concurrency and Compu-
tation: Practice and Experience, 20(5):409–418.
Muniswamy-Reddy, K.-K. (2010). Foundations for
Provenance-Aware Systems. PhD thesis, Harvard Uni-
versity, Massachusetts.
Park, U. and Heidemann, J. (2008a). Provenance in sensor-
net republishing. Provenance and Annotation of Data
and Processes, pages 280–292.
Park, U. and Heidemann, J. (2008b). Provenance in sensor-
net republishing. In Freire, J., Koop, D., and Moreau,
L., editors, Provenance and Annotation of Data and
Processes, volume 5272 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 280–292. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Patni, H., Sahoo, S., Henson, C., and Sheth, A. (2010).
Provenance Aware Linked Sensor Data. In 2nd Work-
shop on Trust and Privacy on the Social and Semantic
Web, Co-located with ESWC2010, Heraklion Greece.
Sabelfeld, A. and Myers, A. C. (2003). Language-based
information-flow security. IEEE Journal on Selected
Areas in Communications, 21.
Stephan, E., Halter, T., and Ermold, B. (2010). Lever-
aging The Open Provenance Model as a Multi-Tier
Model for Global Climate Research. In Proc. of 3rd
International Provenance and Annotation Workshop
(IPAW10), Troy, NY.
Tan, W.-C. (2007). Provenance in databases : Past, current,
and future. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin, 30:”3–
12”.
Tilak, S., Chiu, K., Abu-Ghazaleh, N., and Fountain, T.
(2005). Dynamic resource discovery for sensor net-
works. Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing, pages
785–796.
Wynbourne, M., Austin, M., Palmer, C., on Homeland Se-
curity, U. S. C. S. C., and Affairs, G. (2009). Na-
tional Cyber Security Research and Development
Challenges Related to Economics, Physical Infras-
tructure and Human Behavior: An Industry, Academic
and Government Perspective. Institute for Information
Infrastructure Protection.
Zahedi, S., Szczodrak, M., Ji, P., Mylaraswamy, D., Sri-
vastava, M., and Young, R. (2008). Tiered architec-
ture for on-line detection, isolation and repair of faults
in wireless sensor networks. In Military Communica-
tions Conference, 2008. MILCOM 2008. IEEE, pages
1–7. IEEE.
SENSORNETS 2012 - International Conference on Sensor Networks
52
