
BROWSING THE SENSOR WEB
Pervasive Access for Wide-area Wireless Sensor Networks
Jie Wan
1
, Michael J. O’Grady
1
, Gregory M. P. O’Hare
1
and Todor Colakov
2
1
CLARITY: Centre for Sensor Web Technologies, School of Computer Science and Informatics, University College Dublin
Dublin, Ireland
2
University of West Bohemia, Pilsen, Czech Republic
Keywords:
Sensor Web, Human Computer Interaction, Pervasive Computing.
Abstract:
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) are almost exclusively regarded as data gathering entities. Various sensed
data elements are captured and routed back to a central server for processing, visualization and interpretation.
However, it can be realistically conjectured that scenarios will increasingly emerge that demand a facility
for ad-hoc interaction with individual sensor nodes. Moreover, such interaction will occur in the physical
environment in close proximity to where the sensor node is physically located. In this paper, the need for
in-situ ad-hoc interaction is motivated. A methodology for facilitating such interaction is presented, and the
implementation of a sensor browser is described.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pervasive Computing envisages a world of embed-
ded artifacts connected by pervasive networking tech-
nologies. Moreover, seamless and intuitive interac-
tion is perceived as a key characteristic of such sys-
tems. While Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) are a
fundamental enabling technology for pervasive com-
puting, and have been harnessed in a diverse range
of applications for example, surveillance and environ-
mental monitoring, access to such networks is inher-
ently centralized, and support for point-to-point ad-
hoc interaction with individual sensor nodes is lack-
ing. Cases where such interaction would be desirable
might include law enforcement where, after an inci-
dent, officials at the scene could obtain instant access
to security cameras within their immediate vicinity.
Crowd-sourcing activities are another avenue where
such access would be useful. For the purposes of
this discussion, the practical issue of network main-
tenance in the field is considered.
Section 2 outlines some documented approaches
to interaction with WSNs. In Section 3, the need for
ad-hoc interaction with WSNs is motivated through
a practical example in network Operation and Main-
tenance (O&M). A methodology for enabling ad-hoc
interaction is described in Section 4. A prototype sen-
sor browser is outlined in Section 5 after which the
paper is concluded.
2 RELATED RESEARCH
Interaction and visualization in WSN contexts are re-
ceiving increasing attention by the research commu-
nity. Initially, there is a focus on WSN management
issues, and a number of frameworks have been de-
scribed in this area. Examples include SNMS (Tolle
and Culler, 2005), TASK (Buonadonna et al., 2005),
Mote-View (Turon, 2005), SensibleDoctor (Cha et al.,
2008), Wireless Sensor Network Remote Interaction
Tool (Tirkawi and Fischer, 2008) and Octopus (Jur-
dak et al., 2008). Another approach describes how
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and web tech-
nologies may be integrated to enable online visualiza-
tion (Fan and Biagioni, 2004). However in all these
cases, the predominant model is one of centralized ac-
cess and control.
Other researchers have considered issues relating
to WSN access while in the physical WSN environ-
ment. SensAR is an innovative approach that har-
nesses Augmented Reality (AR) for the visualiza-
tion of real-time environmental data using a hand-
held computer (Goldsmith et al., 2008). Likewise,
the speckled computing consortium harness AR as
an interaction paradigm for micro-sensor networks
(Leach and Benyon, 2006). Gauger et al explore dif-
ferent physical modalities for interaction with individ-
ual nodes, including gesture and light (Gauger et al.,
2009). Tricorder (Lifton et al., 2007) is a dedicated
device for browsing and navigating WSNs. It can
query local sensor nodes directly or remote sensor no-
109
Wan J., J. O’Grady M., M. P. O’Hare G. and Colakov T..
BROWSING THE SENSOR WEB - Pervasive Access for Wide-area Wireless Sensor Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0003809601090112
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Sensor Networks (SENSORNETS-2012), pages 109-112
ISBN: 978-989-8565-01-3
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
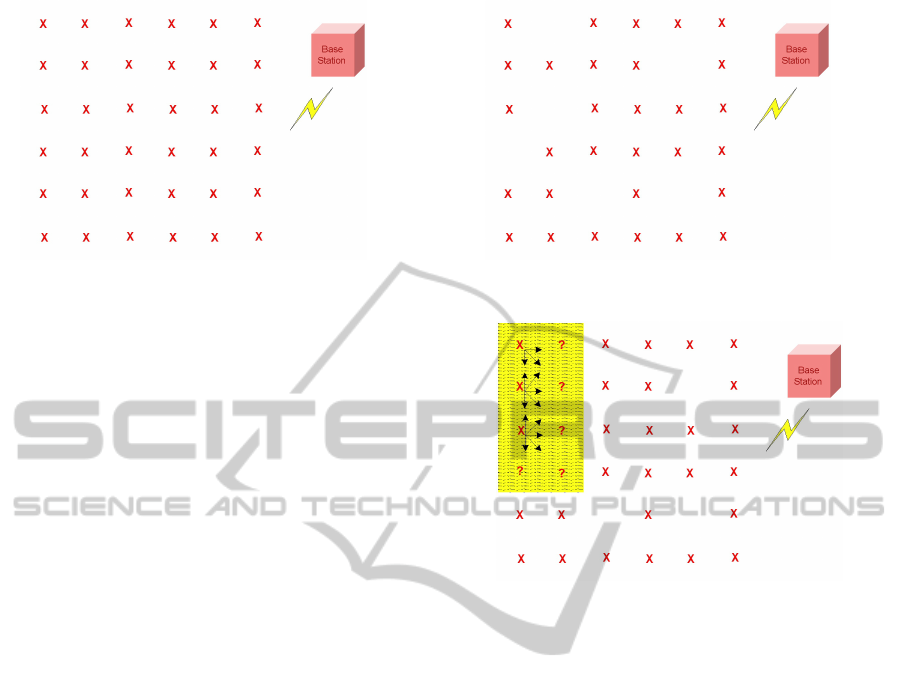
Figure 1: Topology of a ideal sensor field.
des by issuing a multi-hop request. Using an em-
bedded compass for orientation, and a signal strength
indicator for position, it can be used in a point-and-
browse fashion while physically in the WSN. Tri-
corder is designed to operate with the Plug sensor net-
work. Such a network has potential in domestic or
occupational environments; however, it is not suitable
for wide area sensor networks of the kind used for
environmental monitoring. Ringwald et al (Ringwald
et al., 2006) have developed a tool for interactively
inspecting WSNs in the field. It allows querying of
individual nodes and firmware upgrades on the nodes
as well as topology viewing. Extensive use is made of
Bluetooth, even at sensor level.
The Sensor Browser described in this paper com-
plements and builds upon these approaches, but is
more generic in its applicability in that it seeks to op-
erate on a range of popular smart phones, and support
a variety of sensor platforms.
3 CASE STUDY: OPERATIONS &
MAINTENANCE
The primary function of a sensor is to measure either
individual or multiple phenomena, and to report this
measurement to a dedicated sensor or base station.
This leads to the second key function: the routing of
data. Sensors may also serve as routers, routing data
from other sensors to the base station, or more likely,
to other sensors that are closer to the base station. A
failure in either of these functions would compromise
the operation of the WSN, requiring physical inter-
vention in the field to correct the problem.
Figure 1 illustrates what an uniform WSN topol-
ogy might be expected to look like. Sensors are laid
out in the coverage area in a grid-like fashion, all
equidistant such that the entire area is covered from
a sensing and routing perspective. Each sensor has a
number of paths for routing data to the base station,
Figure 2: Topology of a realistic sensor field.
Figure 3: Topology of a faulty sensor field.
which in turn can either process it in situ or pass it
further up the network stack for further analysis.
Over time, a WSN will deteriorate, resulting in a
number of sensors no longer functioning (Figure 2).
However, the WSN itself is still functioning; data can
still be routed to the base station, and the gaps in
the sensing function may be estimated using various
modeling techniques.
A major problem arises when a combination of
sensors fail such that either the sensing or routing
function is seriously compromised for part of the
WSN coverage area. Figure 3 illustrates a case of
routing failure where part of the network is isolated
and cannot communicate with the base station. To
remedy this situation, physical intervention is re-
quired - this would frequently demand a capability for
in situ ad-hoc interaction with individual nodes.
4 ENABLING AD-HOC
INTERACTION
From a hardware perspective, three components are
necessary to realize a sensor browsing experience.
• Mobile phone - As the de facto standard for ubiq-
uitous communication, high-end mobile phones
SENSORNETS 2012 - International Conference on Sensor Networks
110
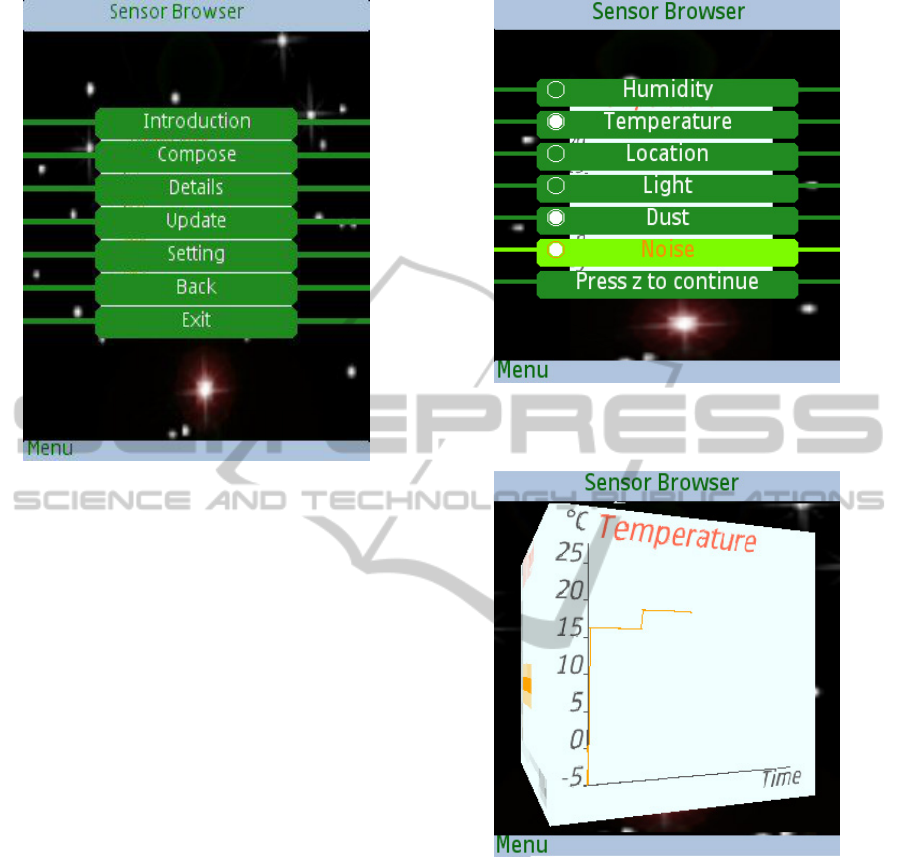
Figure 4: Sensor Browser: introduction screen.
and smart phones increasingly incorporate a suite
of technologies that enables them to host spe-
cialized third-party and custom-developed appli-
cations. In this case, a Nokia N97 was harnessed.
• Sensor platform - a Mica2 unit was adopted as it
was considered an archetypical sensor device, ca-
pable of sensing a number of common phenom-
ena. For communications it uses RF (868/916
MHz).
• Protocol Convertor - mobile phones and sensor
platforms use different communications technolo-
gies so it is necessary to enable a protocol con-
vertor through hardware. A base station was con-
structed using a second Mica2 mote mounted on
a PC Interface board. This was then augmented
with a BlueSnapXP Mobile Bluetooth RS-232
dongle from Serialio.com. This supports the stan-
dard Bluetooth Serial Port profile.
All motes were programmed using NesC. The
browser itself on the mobile phone was developed in
Java ME.
5 THE SENSOR BROWSER
Figure 4 illustrates the introduction screen of the Sen-
sor Browser. This enables access to various function-
ality supported by the browser. In practice, a sensor
may support a multitude of sensed modalities, for ex-
ample, temperature, humidity, ambient noise levels
Figure 5: Sensor Browser: identifying the temperature, dust
and noise as the sensed values of interest.
Figure 6: Sensor Browser: trends are plotted on the individ-
ual faces of a rotating cube for the sensed phenomena under
investigation.
and so on. But users may only be interested in some of
these, depending on their need. Thus, they can spec-
ify multiple modalities that are interesting to them, for
example, temperature, dust and noise (Figure 5), and
visualize the sensed data via the browser. A number
of other modalities such as the battery level, air pol-
lution level can also be monitored while might not be
of interest for general users, additional data about the
network topology, link quality can be gathered if it is
available.
A key feature of the browser is that it continuously
records the required sensed values as they are encoun-
tered. In this way trends can be visualised. The sensor
BROWSING THE SENSOR WEB - Pervasive Access for Wide-area Wireless Sensor Networks
111

adopts a cube metaphor, showing the trends for each
required sensed parameter on an individual face (Fig-
ure 6).
6 FUTURE WORK
A number of improvements are planned for this ini-
tial prototype. Managing scalability and sensor het-
erogeneity are essential, thus the possibility of stan-
dardizing on SensorML or MoteML (Ali et al., 2011)
is being explored. This would also form the basis
for a more robust approach to configuration and de-
bugging. Augmenting the user interface using GPS
and GoogleMaps would enable a realistic visualiza-
tion of the spatial relationship between the sensors.
Finally, until Zigbee and associated technologies are
integrated into mobile phones, it will be necessary to
support a protocol convertor. Mobile base stations of
the type described in (Angove et al., 2011) offer alter-
natives approaches in this instance.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has presented an initial prototype of a
mobile sensor browser; in contrast with previous ap-
proaches, this browser implements a number of novel
features. The adoption of the dynamic cube metaphor
enables an intuitive tool for users to view various
sensed parameters. Furthermore, an adaptive person-
alization mechanism has been harnessed; with the
consideration of individual user’s profile, user pref-
erences and physical environments attributes, select
sensor data can be gathered and visualized in a user-
specified manner. In addition, real-time sensing, data
collection and visualization have been implemented,
as well as short term historical data recording for
trend analysis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by Science Foundation Ireland
under grant 07/CE/I1147.
REFERENCES
Ali, F., Feaster, Y., Wahba, S. K., and Hallstrom, J. O.
(2011). A metadata encoding for memory-constrained
devices. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Southeast
Regional Conference, ACM-SE ’11, pages 191–196,
New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Angove, P., O’Grady, M. J., Hayes, J., O’Flynn, B., O’Hare,
G. M. P., and Diamond, D. (2011). A mobile gateway
for remote interaction with wireless sensor networks.
Sensors Journal, IEEE, 11(12):3309 –3310.
Buonadonna, P., Gay, D., Hellerstein, J., Hong, W., and
Madden, S. (2005). Task: sensor network in a box.
Wireless Sensor Networks, 2005. Proceeedings of the
Second European Workshop on, pages 133–144.
Cha, S., Shin, H., and Cha, H. (2008). Sensible doc-
tor - a mobile diagnosis tool for wireless sensor net-
works. Information Processing in Sensor Networks,
2008. IPSN ’08. International Conference on, pages
565–566.
Fan, F. and Biagioni, E. S. (2004). An approach to data
visualization and interpretation for sensor networks.
In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 37th Annual
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences
(HICSS’04) - Track 3 - Volume 3, HICSS ’04, Wash-
ington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Gauger, M., Saukh, O., and Marron, P. J. (2009). Talk to
me! on interacting with wireless sensor nodes. In
PERCOM ’09: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE In-
ternational Conference on Pervasive Computing and
Communications, pages 1–8, Washington, DC, USA.
IEEE Computer Society.
Goldsmith, D., Liarokapis, F., Malone, G., and Kemp, J.
(2008). Augmented reality environmental monitoring
using wireless sensor networks. iv, 0:539–544.
Jurdak, R., Ruzzelli, A. G., O’Hare, G. M. P., and Lopes,
C. V. (2008). Octopus: A dashboard for sensor net-
works visual control. The 14th Annual International
Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking,
Mobicom08 (Demo).
Leach, M. and Benyon, D. (2006). Interacting with a speck-
led world. In ADPUC ’06: Proceedings of the 1st in-
ternational workshop on Advanced data processing in
ubiquitous computing (ADPUC 2006), page 3, New
York, NY, USA. ACM.
Lifton, J., Mittal, M., Lapinski, M., and Paradiso, J. A.
(2007). Tricorder: A mobile sensor network browser.
In Proceedings of the ACM CHI 2007 Conference -
Mobile Spatial Interaction Workshop.
Ringwald, M., Y
¨
ucel, M., and R
¨
omer, K. (2006). Demo
abstract: Interactive in-field inspection of wsns. In
Adjunct Proceedings of the 3rd European Workshop
on Wireless Sensor Networks (EWSN 2006), Zurich,
Switzerland.
Tirkawi, F. and Fischer, S. (2008). Remote interaction
tool for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Perva-
sive Computing, 2008. ISWPC 2008. 3rd International
Symposium on, pages 360–364.
Tolle, G. and Culler, D. (2005). Design of an application-
cooperative management system for wireless sensor
networks. Wireless Sensor Networks, 2005. Proceeed-
ings of the Second European Workshop on, pages 121–
132.
Turon, M. (2005). Mote-view: A sensor network monitor-
ing and management tool. Embedded Networked Sen-
sors, 2005. EmNetS-II. The Second IEEE Workshop
on, pages 11–18.
SENSORNETS 2012 - International Conference on Sensor Networks
112
