
SEGMENTATION OF VESSEL GEOMETRIES FROM MEDICAL
IMAGES USING GPF DEFORMABLE MODEL
Si Yong Yeo
1
, Xianghua Xie
2
, Igor Sazonov
1
and Perumal Nithiarasu
1
1
College of Engineering, Swansea University, Swansea , U.K.
2
College of Science, Swansea University, Swansea , U.K.
Keywords:
Vessel segmentation, Geometric potential force, Deformable model, Image segmentation, Level set methods.
Abstract:
We present a method for the reconstruction of vascular geometries from medical images. Image denoising is
performed using vessel enhancing diffusion, which can smooth out image noise and enhance vessel structures.
The Canny edge detection technique which produces object edges with single pixel width is used for accurate
detection of the lumen boundaries. The image gradients are then used to compute the geometric potential field
which gives a global representation of the geometric configuration. The deformable model uses a regional
constraint to suppress calcified regions for accurate segmentation of the vessel geometries. The proposed
framework show high accuracy when applied to the segmentation of the carotid arteries from CT images.
1 INTRODUCTION
The human circulatory system consists of vessels that
transport blood throughout the body, providing the
tissues with oxygen and nutrients. It is known that
vascular diseases such as stenosis and aneurysms are
often associated with changes in blood flow patterns
and the distribution of wall shear stress. Modelling
and analysis of the hemodynamics in the human vas-
cular system can improveour understanding of vascu-
lar disease, and provide valuable insights which can
help in the development of efficient treatment meth-
ods. In recent years, computational fluid dynamics
(CFD) has been widely used for patient-specific mod-
elling of blood flow in vascular structures (Steinman,
2002; Cebral et al., 2003; Taylor and Figueroa, 2009;
Taylor and Steinman, 2010). Despite the involve-
ment of numerous groups working in this field, and
rapid advancement in efficient computational meth-
ods, there has been limited applications of compu-
tational hemodynamics in clinical practice. This is
largely due to the challenges involved in the design of
an integrated framework which can efficiently and ac-
curately automate the interdisciplinary computational
modelling process, which includes image segmenta-
tion, mesh generation and CFD simulation.
One of the main challenges in the computational
modelling of hemodynamics is the accurate recon-
struction of the vascular geometry. Anatomically ac-
curate geometric models of the vascular structures are
essential for realistic flow simulations and analysis.
The anatomical information used to reconstruct the
geometric models are usually provided in the form of
medical image datasets (scans) from imaging modal-
ities such as computed tomography (CT) and mag-
netic resonance (MR) imaging. Manual reconstruc-
tion of the vasculature geometries can be tedious and
time consuming. There is also the issue of variabil-
ity between the geometries extracted manually by dif-
ferent individuals, and variability of geometries ex-
tracted by the same individual at different occasions.
In order to allow computational flow modelling to be
efficiently applied as a diagnostic or predictive tool,
the amount of user intervention required in the pro-
cess should be reasonably small. In particular, a con-
siderable amount of user intervention is often required
in the reconstruction of an accurate geometric model
for the simulation of flow dynamics. Therefore a ro-
bust and efficient method that can be used to accu-
rately segment the geometric structures from medical
image datasets can be very useful and advantageous
in the modelling process. Here, we propose a robust
framework for the segmentation of vessel geometries
using the GPF deformable model. The framework is
then applied to efficiently segment the geometries of
carotid arteries from CT images.
Although several techniques exist for the segmen-
tation of vascular structures from medical images, it
remains an intricate process due to factors such as im-
age noise, partial volume effects, image artifacts, in-
323
Yeo S., Xie X., Sazanov I. and Nithiarasu P..
SEGMENTATION OF VESSEL GEOMETRIES FROM MEDICAL IMAGES USING GPF DEFORMABLE MODEL.
DOI: 10.5220/0003849303230332
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (SADM-2012), pages 323-332
ISBN: 978-989-8425-98-0
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

tensity inhomogeneity and changes in topology. In
(Mori and Yamaguchi, 2001), the coordinate points
for the center line of the aortic arch were extracted
from volume rendered MR images. A cubic spline
was then used to represent the aortic centerline, and
cross-sectional grids were generated on normal planes
at equidistant points along the curve. This generated
a curved tube with circular cross section of uniform
radius, which is not representative of the geometry
of the aorta. In (Tokuda et al., 2008), the centerline
and diameter information of the vessels was extracted
from the image dataset, and the vascular model was
reconstructed using non-uniform rational B-splines
(NURBS). Such techniques may often smooth out ge-
ometric information that can be important to the com-
putation of accurate flow dynamics, such as those at
bifurcations.
The 3D models of the vascular structures in (Wang
et al., 1999) were reconstructed by extracting the 2D
contours of the vessels at each of the image slices
of the MR image dataset, and then lofting through
the contours to create the surface models of the ves-
sels. The different vessels were then merged using
boolean operations in solid modelling. The cross
sections of a particular vessel may however intersect
with cross sections of branching vessels, and the ge-
ometry at these positions have to be approximated.
Other authors such as (Xu et al., 1999; Augst et al.,
2003; Younis et al., 2004; Giordana et al., 2005; Peiro
et al., 2008) also reconstructed 3D surface models of
the vessels from 2D contours extracted from image
slices. This sometimes requires positioning and ori-
enting the 2D contours according to the medial axis
of the vessels, and curve and surface interpolation are
used to approximate and reconstruct the surface mod-
els. However, the 2D contour extraction techniques
used do not provide control over 3D smoothness, and
3D geometric properties from the image datasets are
not considered.
A simple thresholding technique was used in
(Nanduri et al., 2009) to extract the binary image of
the vessels, and the vascular model was reconstructed
using an isosurface algorithm. The thresholding tech-
nique however does not consider the spatial charac-
teristics of the image, and is sensitive to image noise
and inhomogeneous intensity. In (Yi and Ra, 2003;
Sekiguchi et al., 2005), region growing algorithms
were applied to segment the vascular structures from
CT and MR angiography data. The region grow-
ing techniques are, in general, sensitive to noise, and
can often lead to non-contiguous regions and over-
segmentation. In addition, thin structures are often
not extracted due to variations in image intensities.
The watershed transform was used in (Abdel-Dayem
and El-Sakka, 2005; Ding et al., 2007) to extract the
geometry of the carotid. In this approach, the im-
age is interpreted as a landscape or topographic sur-
face, with the pixel intensity representing the eleva-
tion of the topographic surface. Consider water on
the landscape flowing towards regions with local min-
ima, the watersheds are the lines that partition these
regions. In this way, the image is partitioned into ho-
mogeneous regions with the watersheds defining the
boundaries of the regions. The watershed transform
tends to be sensitive to noise and often produces over-
segmentation. It is also difficult for the watershed
technique to extract thin structures and weak object
edges.
In (Ladak et al., 2000; Gil et al., 2000), a 3D dy-
namic surface model was used to delineate the bound-
ary of carotid arteries. An initial triangulated model
was placed within the interior of the carotid ves-
sels, and an inflation force was applied to deform the
model towards the vessel wall. In particular, the in-
flation force is applied only when the vertices of the
model are within the lumen, i.e., at locations with im-
age intensity below a user-specified threshold. An
image-based force is further applied to the surface
model to better localize the boundary. It may however
be difficult to select an appropriate threshold value
that delineates the vessel wall closely due to inho-
mogeneous image intensity. This approach is sensi-
tive to noise, and manual editing is often required to
move the vertices towards the vessel wall. In (Stein-
man et al., 2002), a 2D discrete dynamic contour was
first used to extract the vessel contours, a dynamic
surface model was then inflated to reconstruct the sur-
face model using the binary images of the extracted
contours. This however does not consider the 3D ge-
ometric information from the image dataset. In (Yim
et al., 2001; Cebral et al., 2001; Cebral et al., 2004),
the surface models for each of the vessel branches of
the carotid artery were reconstructed independently
using a tubular deformable model. A surface merg-
ing algorithm is then required to reconstruct the sur-
face model of the carotid bifurcation from the trian-
gulated surfaces of the vessel branches. This particu-
lar approach requires the determination of the axis of
each of the vessels, which can be done manually by
selecting a reasonable amount of points from image
slices to represent the curves of the structure. Due
to the smoothing effect of this technique, regions of
high curvature such as those at bifurcations or steno-
sis may not be modeled accurately. These explicit
deformable models represent contours and surfaces
parametrically, which requires the tracking of points
on the curves and surfaces during deformation. It is
therefore difficult for explicit deformable models to
ICPRAM 2012 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
324

deal with topological variation and complex shapes.
Implicit deformable models have been applied in
the segmentation of vascular structures in (Nilsson
and Heyden, 2003; Antiga and Ene-Iordache, 2003;
Deschamps et al., 2004; Svensson et al., 2006; Antiga
et al., 2008). However, many of these techniques use
an attraction force field which acts on contours or sur-
faces only when they are close to the object bound-
aries. As such, initial contours have to be placed
close to the object boundaries, which can be tedious in
complex geometries. A constant pressure term such
as the one in (Malladi et al., 1995), is often used to
monotically expand or shrink the deformable model
towards the image object boundaries, which can over-
whelm weak object edges. In addition, the initial con-
tours have to be placed either inside or outside object
boundaries, which can be difficult for compact and
narrow structures. Many of these techniques are also
sensitive to image noise, and have difficulties in ex-
tracting deep boundary concavities.
2 PROPOSED METHOD
In this section, a robust framework is proposed for
the reconstruction of vascular geometries from medi-
cal images. The approach consists of image denoising
using vessel enhancing diffusion (Enquobahrie et al.,
2007; Manniesing et al., 2006), optimal edge detec-
tion using the Canny edge filter (Canny, 1986), and
robust segmentation of the vascular geometries using
GPF deformable model (Yeo et al., 2011).
2.1 Vessel Enhancing Diffusion Filtering
The formulation of the vessel enhancing diffusion fil-
ter (Enquobahrieet al., 2007; Manniesing et al., 2006)
is based on a smoothed version of the vesselness mea-
sure used in (Frangi et al., 1998). In this approach, an
anisotropic diffusion filter with strength and direction
determined by the vesselness measure is applied to
enhance the geometric structures of the vessel. The
vesselness measure is determined by analyzing the
eigensystem of the Hessian matrix given as:
H =
I
xx
I
xy
I
xz
I
yx
I
yy
I
yz
I
zx
I
zy
I
zz
(1)
which describes the geometric information at each
point of a 3D image I based on the local intensity vari-
ations. Here, the derivatives of the image I are com-
puted as convolution with derivatives of the Gaussian
function, i.e. I
x
= I(x) ∗
∂
∂x
G
σ
(x), where G
σ
denotes
the Gaussian function with standard deviation σ. The
principal curvatures and directions are given by the
maximum and minimum eigenvalues and the corre-
sponding eigenvectors. With the eigenvalues given
such that |λ
1
| ≤ |λ
2
| ≤ |λ
3
|, the vesselness measure
is defined as: if λ
2
≥ 0 or λ
3
≥ 0, V
σ
(λ) = 0; other-
wise
V
σ
(λ) =
1− e
−R
A
2
2α
2
·e
−R
B
2
2β
2
·
1− e
−S
2
2γ
2
·e
2c
2
|λ
2
|λ
3
2
(2)
with
R
A
=
|λ
2
|
|λ
3
|
(3)
R
B
=
|λ
1
|
p
|λ
2
λ
3
|
(4)
S =
q
λ
1
2
+ λ
2
2
+ λ
3
2
(5)
in which R
A
and R
B
can be used to differentiate tubu-
lar structures from blob-like and plate-like structures,
while S is used to differentiate between foreground
vessel structures and background noise. The parame-
ters α, β and γ are weighting factors which control the
sensitivity of the vesselness measure, and c is a small
constant.
For a multiscale analysis, the vesselness function
is computed for a range of scales, and the maximum
response is selected using the following equation:
V = max
σ
min
≤σ≤σ
max
V
σ
(λ) (6)
A diffusion tensor is then defined such that vessel dif-
fusion takes place in the direction of the vessel, while
diffusion perpendicular to the vessel direction is in-
hibited. The diffusion tensor can therefore be used to
preserve vessel structures and is given as:
D = Qλ
′
Q
T
(7)
where Q is a matrix containing the eigenvectors of the
Hessian matrix H, and λ
′
is a diagonal matrix with
elements given as:
λ
1
′
= 1+ (w− 1) ·V
1
s
(8)
λ
2
′
= λ
3
′
= 1+ (ε − 1) ·V
1
s
(9)
with w, ε and s as tuning parameters. The anisotropic
diffusion is then defined as:
L
t
= ∇· (D∇L) (10)
where L(0) is set as the input image. Figure 1 demon-
strates that the vessel enhancing diffusion filter can be
applied to enhance the vessel structures and smooth
out noise in the image. The algorithm for the vessel
enhancing diffusion filter has been implemented us-
ing the Insight Toolkit (Ibanez et al., 2005).
SEGMENTATION OF VESSEL GEOMETRIES FROM MEDICAL IMAGES USING GPF DEFORMABLE MODEL
325

Figure 1: Vessel enhancing diffusion and image object edge representation of CT image dataset 1, from left to right - orig-
inal image, image with vessel enhancing diffusion, image gradient magnitude, Canny edge with image gradient intensities,
geometric potential field.
2.2 Edge Representation for Vessel
Geometries
Image object edges are usually represented as regions
with high intensity contrasts. Image gradients can be
determined using the gradient operator or the Sobel
filter. These techniqueshowever produces object edge
width of a few pixels. This can easily cause nearby
structures to be connected. For complex geometries
such as those in medical images, it is often neces-
sary to determine fine edges using more robust edge
detection techniques (Deriche, 1987; Petrou and Kit-
tler, 1991) for accurate representation of the image
structures. The Canny edge detection (Canny, 1986)
can produce object edges with single pixel width, and
can therefore be used for accurate edge detection of
the vessel structures. In the Canny edge detection
technique, image smoothing is first applied to reduce
noise interference. This can be performed using the
Gaussian filter or other smoothing techniques such as
vessel enhancing diffusion (Manniesing et al., 2006).
The image gradients are then computed to determine
the magnitudes and directions of the edges. Image
pixels with magnitudes which are not local maxima
in the directions of the edges are suppressed. Hyster-
isis thresholding is then applied to filter out spurious
edges caused by noise. Image pixels with edge mag-
nitude greater than a high threshold, i.e. f
edge
(x) > T
h
are considered as edges, while pixels with edge mag-
nitude lower than a low threshold, i.e. f
edge
(x) < T
l
are removed. Image pixels with edge magnitudes in
between the threshold values, i.e. T
l
≤ f
edge
(x) < T
h
,
which are connected to edge pixels are also consid-
ered as edges. The image gradients at the detected
edges are then used to compute the geometric poten-
tial field, see (Yeo et al., 2011) for more detail. As
shown in Figure 1, the geometric potential field gives
a more coherent representation of the image object
boundaries as it utlizes global edge pixel interactions
across the image.
2.3 Segmentation of Vessel Geometries
using GPF Deformable Model with
Region Constraint
It is shown in (Yeo et al., 2009a; Yeo et al., 2009b;
Yeo et al., 2011) that the GPF deformable model can
be used to efficiently segment complex geometries
from biomedical images. By using pixel or voxel
interactions across the whole image domain, the de-
formable model is more robust to image noise and
weak edges. The dynamic vector force field changes
according to the relative postition and orientation be-
tween the geometries, which allows the deformable
model to propagate through long tubular structures.
Here, the GPF deformable model is applied to seg-
ment the geometries of human carotid arteries from
CT images. Some of the main challenges in the seg-
mentation of the carotid geometries include intensity
inhomgeneity, weak edges and adjacent veins with
similar intensities to the carotids. In addition, calcifi-
cations which are attached to the arterial walls should
not be included in the reconstructed geometries. Al-
though, the calcified plaques often appear as relatively
bright regions compared to soft tissues, plaques with
lower densities may have similar intensities to the lu-
men. As the intensities of the plaques vary with the
ICPRAM 2012 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
326

Figure 2: Image slice from CT image dataset 2 showing contours (top row) and corresponding pixels (bottom row) extracted
using: from left to right - GPF deformable model, GPF deformable model with intensity threshold and GPF deformable model
with region constraint.
Figure 3: Image slice from CT image dataset 4 showing contours (top row) and corresponding pixels (bottom row) extracted
using: from left to right - GPF deformable model, GPF deformable model with intensity threshold and GPF deformable model
with region constraint.
densities, it is not easy for techniques such as global
intensity threshold to remove the plaques from the ex-
tracted geometries. In this section, a region constraint
is added to the deformable model such that it does not
propagate across the calcified regions. This is done by
constraining the deformable model from propagating
across regions with image gradient magnitude larger
than a user specified value, T
max
. As the calcified re-
gions usually have relatively large image gradients,
the threshold value can be easily selected by observ-
ing the histogram of the image gradient magnitude.
The deformable model with region constraint can thus
be expressed as:
∂φ
∂t
=
0 if |∇I| > T
max
αgκ|∇φ| − (1− α)(F· ∇φ) otherwise
(11)
where α is a weighting parameter, g is the edge stop-
ping function, κ is the curvature and F is the geo-
metric potential force defined in the GPF model (Yeo
et al., 2011).
Figures 2 and 3 depict a z-axis slice of the ex-
tracted geometry. As shownin the figures, some calci-
fied regions have similar intensity to the lumen, which
caused the deformable model to include them in the
extracted geometries. The intensities of the plaques
vary which makes it difficult for a global intensity
threshold to suppress them. It is shown that by adding
the region constraint, the deformable model can easily
get around the calcified regions to segment the carotid
geometries accurately.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this section, experimental results on the segmen-
tation of the cartoid geometries using the proposed
framework are shown. In particular, 6 datasets from
CT imaging (provided by Wolverhampton NHS trust)
are used in the experiment. The volumes of interest
containing the carotid arteries are extracted from the
image datasets to reduce the size of the input datasets.
The robust framework which consits of vessel diffu-
sion enhancing, computation of optimal object edge
representation and deformable model with regional
constraint is then applied for the reconstruction of
vessel geometries.
Figures 4 to 7 depict the segmentation of the
carotid geometries using the GPF deformable model
with region constraint. As shown in Figures 4 and 6,
the bidirectional and dynamic vector force allows the
flexible cross-boundary intializations of the model to
easily propagate and convergeto the geometries of the
SEGMENTATION OF VESSEL GEOMETRIES FROM MEDICAL IMAGES USING GPF DEFORMABLE MODEL
327

Figure 4: Segmentation of carotid artery from CT image dataset 1 (61x71x125) using GPF deformable model (CPU-time,
276s).
Figure 5: Segmentation of carotid artery from CT image dataset 3 (70x80x120) using GPF deformable model (CPU-time,
206s).
Figure 6: Segmentation of carotid artery from CT image dataset 5 (70x80x120) using GPF deformable model (CPU-time,
1379s).
Figure 7: Segmentation of carotid artery from CT image dataset 6 (70x80x120) using GPF deformable model (CPU-time,
185s).
ICPRAM 2012 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
328

Figure 8: Comparison of geometry segmented from CT image dataset 1 using image slices taken along z-axis direction: blue
- manual, orange - GPF deformable model.
Figure 9: Comparison of geometry segmented from CT image dataset 3 using image slices taken along z-axis direction: blue
- manual, orange - GPF deformable model.
carotid arteries. The extraction of the vessel geome-
tries from image datasets 1 and 4 took only 276s and
494s, while the extraction from image datasets 2 and 5
took 1216s and 1379s due to factors such as intensity
variation, low constrast, multiple branches and com-
plex topologies. A graphical user interface has been
developed, which can be used to set multiple initial
contours for fast convergence. It can also be used
to remove inconsistency in object boundaries due to
low resolution of the images, artifacts, etc., or small
branches which do not affect the computational flow
analysis. As shown in Figure 5 and Figure 7, one can
easily speed up the segmentation process by placing
multiple initial contoursor surfaces, as the model con-
verges to the vessel geometries in 206s and 185s when
applied to image datasets 3 and 6 respectively. Note
that the deformable model easily propagate through
the stenotic carotid bifurcations and get around the
calcified regions to efficiently segment the carotid ge-
ometries from the CT images.
The reconstructed vessel geometries using the
proposed framework are compared against geome-
tries from manual segmentation. Figures 8 to 11 de-
pict the comparison of the extracted geometries us-
ing random cross-section slices taken along the z-
axis direction. The blue and orange contours rep-
resent the cross-section of the geometries extracted
manually and using the GPF deformable model re-
spectively. As shown in the figures, the image dataset
consist of other tissue structures which may affect the
geometric reconstruction. In particular, vessels adja-
cent to the carotid artery can often cause other mod-
els to leak out due to the similar intensity. The ge-
ometric potential field provides a more coherent and
global representation of the object edges, and allows
the deformable model to extract the geometry accu-
SEGMENTATION OF VESSEL GEOMETRIES FROM MEDICAL IMAGES USING GPF DEFORMABLE MODEL
329
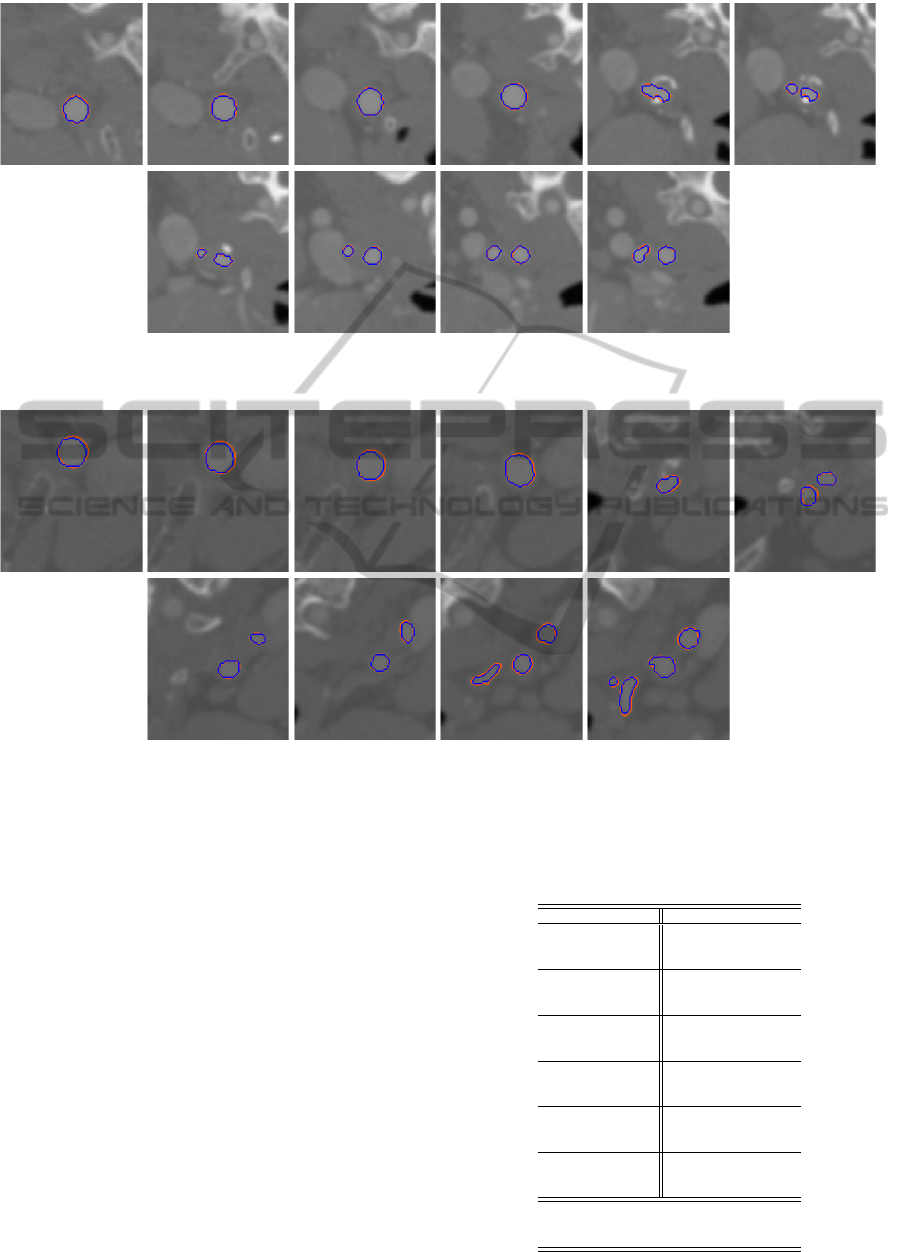
Figure 10: Comparison of geometry segmented from CT image dataset 4 using image slices taken along z-axis direction: blue
- manual, orange - GPF deformable model.
Figure 11: Comparison of geometry segmented from CT image dataset 6 using image slices taken along z-axis direction: blue
- manual, orange - GPF deformable model.
rately. By adding a region constraint, the proposed
model can easily get around the calcified regions as
the deformable model propagates through the tubular
structures to segment the vessel geometry as depicted
in Figures 9, 10 and 11. The proposed framework can
therefore be applied to segment the vessel geometries
efficiently from the images. As shown in the figures,
the vessel geometries segmented using the GPF de-
formable model with region constraint exhibit consid-
erably small deviations from the manually extracted
geometries.
Table 1 presents the accuracy of the segmented
geometries using the proposed method. The fore-
ground (FG) and background (BG) accuracy of the
geometries were measured as the percentages of true
foreground and background voxels which were seg-
mented as foreground and background respectively.
The normalized overall accuracy is given as the aver-
age of FG and BG to measure the accuracy of cor-
Table 1: Comparison of the segmented carotid geometries
using the GPF deformable model with manual segmenta-
tion: Foreground (FG), background (BG) and overall accu-
racy measured in %.
CT image dataset GPF
FG (%) 89.9
1 BG (%) 99.9
Overall (%) 94.9
FG (%) 89.8
2 BG (%) 99.9
Overall (%) 94.8
FG (%) 96.0
3 BG (%) 99.9
Overall (%) 97.9
FG (%) 99.1
4 BG (%) 99.8
Overall (%) 99.5
FG (%) 93.8
5 BG (%) 99.5
Overall (%) 96.7
FG (%) 94.4
6 BG (%) 99.6
Overall (%) 97.0
FG Average (%) 93.9
BG Average (%) 99.8
Overall Average (%) 96.8
ICPRAM 2012 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
330

rectly extracted voxels to reduce measurement bias
towards the large number of background voxels in
the image. It is shown that the proposed framework
provides significantly accurate geometries with over-
all acurracies of 94.9%, 94.8%, 97.9%, 99.5%, 96.7%
and 97.0% for image datasets 1 to 6, and an average
overall accuracy of 96.8%.
REFERENCES
Abdel-Dayem, A. and El-Sakka, M. (2005). Carotid artery
ultrasound image segmentation using fuzzy region
growing. In International Conference on Image Anal-
ysis and Recognition, pages 869–878.
Antiga, L. and Ene-Iordache, B. Remuzzi, A. (2003). Com-
putational geometry for patient-specific reconstruc-
tion and meshing of blood vessels from mr and ct an-
giography. IEEE T-MI, 22(5):674–684.
Antiga, L., Piccinelli, M., Botti, L., Ene-Iordache, B., Re-
muzzi, A., and A., S. D. (2008). An image-based mod-
eling framework for patient-specific computational
hemodynamics. Medical and Biological Engineering
and Computing, 46(11):1097–1112.
Augst, A. D., Barratt, D. C., Hughes, A. D., McG Thom,
S. A., and Xy, X. Y. (2003). Various issues re-
lating to computational fluid dynamics simulations
of carotid bifurcation flow based on models recon-
structed from three-dimensional ultrasound images.
Proc Inst Mech Eng H, Journal of Engineering in
Medicine, 217(5):393–403.
Canny, J. (1986). A computational approach to edge detec-
tion. IEEE T-PAMI, 8(6):679–698.
Cebral, J. R., Castro, M. A., Lohner, R., Burgess, J. E., Per-
golizzi, R., and Putman, C. M. (2004). Recent devel-
opments in patient-specific image-based modeling of
hemodynamics. In ENIEF04.
Cebral, J. R., Hernandez, M., and Frangi, A. F. (2003).
Computational analysis of blood flow dynamics in
cerebral aneurysms from cta and 3d rotational angiog-
raphy image data. In International Congress on Com-
putational Bioengineering, pages 191–198.
Cebral, J. R., Lohner, R., Soto, O., Choyke, P. L., and Yim,
P. J. (2001). Patient-specific simulation of carotid
artery stenting using computational fluid dynamics. In
MICCAI, pages 153–160.
Deriche, R. (1987). Using canny’s criteria to derive a re-
cursively implemented optimal edge detector. IJCV,
1(2):167–187.
Deschamps, T., Schwartz, P., Trebotich, D., Colella, P., Sa-
loner, D., and Malladi, R. (2004). Vessel segmentation
and blood flow simulation using level-sets and embed-
ded boundary methods. In Computer Assisted Radiol-
ogy and Surgery, pages 75–80.
Ding, S., Tu, J., Cheung, C., Beare, R., Phan, T., Reutens,
D., and Thien, F. (2007). Geometric model generation
for CFD simulation of blood and air flows. In Interna-
tional Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical
Engineering, pages 1335–1338.
Enquobahrie, A., Ibanez, L., Bullitt, E., and Aylward, S.
(2007). Vessel enhancing diffusion filter. The Insight
Journal.
Frangi, A. F., Niessen, W. J., Vincken, K. L., and Viergever,
M. A. (1998). Multiscale vessel enhancement filter-
ing. In MICCAI, pages 130–137.
Gil, J. D., Ladak, H. M., Steinman, D. A., and Frenster,
A. (2000). Accuracy and variability assessment of
a semiautomatic technique for segmentation of the
carotid arteries from three-dimensional ultrasound im-
ages. Medical Physics, 27(6):1333–1342.
Giordana, S., Sherwin, S. J., Peiro, J., Doorly, D. J., Papa-
harilaou, Y., Caro, C. G., Watkins, N., Cheshire, N.,
Jackson, M., Bicknall, C., and Zervas, V. (2005). Au-
tomated classification of peripheral distal by-pass ge-
ometries reconstructed from medical data. Journal of
Biomechanics, 38(1):47–62.
Ibanez, L., Schroeder, W., Ng, L., and Cates, J. (2005). The
ITK Software Guide, 2nd Edition. Kitware, Inc.
Ladak, H. M., Milner, J. S., and Steinman, D. A. (2000).
Rapid three-dimensional segmentation of the carotid
bifurcation from serial MR images. Journal of Biome-
chanical Engineering, 122(1):96–99.
Malladi, R., Sethian, J. A., and Vemuri, B. C. (1995). Shape
modelling with front propagation: A level set ap-
proach. IEEE T-PAMI, 17(2):158–175.
Manniesing, R., Viergever, M. A., and Niessen, W. J.
(2006). Vessel enhancing diffusion: A scale space rep-
resentation of vessel structures. Medical Image Anal-
ysis, 10(6):815–825.
Mori, D. and Yamaguchi, T. (2001). Construction of the
CFD model of the aortic arch based on mr images
and simulation of the blood flow. In International
Workshop on Medical Imaging and Augmented Real-
ity, pages 111–116.
Nanduri, J. R., Pino-Romainville, F. A., and Celik, I.
(2009). CFD mesh generation for biological flows:
Geometry reconstruction using diagnostic images.
Computers & Fluids, 38(5):1026–1032.
Nilsson, B. and Heyden, A. (2003). A fast algorithm for
level set-like active contours. Pattern Recognition Let-
ters, 24(9):1311–1337.
Peiro, J., Sherwin, S. J., and Giordana, S. (2008). Automatic
reconstruction of a patient-specific high-order surface
representation and its application to mesh generation
for CFD calculations. Medical and Biological Engi-
neering and Computing, 46(11):1069–1083.
Petrou, M. and Kittler, J. (1991). Optimal edge detectors
for ramp edges. IEEE T-PAMI, 13(5):483–491.
Sekiguchi, H., Sugimoto, N., Eiho, S., Hanakawa, T., and
Urayama, S. (2005). Blood vessel segmentation for
head MRA using branch-based region growing. Sys-
tems and Computers in Japan, 36(5):80–88.
Steinman, D. A. (2002). Image-based computational fluid
dynamics modeling in realistic arterial geometries.
Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 30(4):483–497.
Steinman, D. A., Thomas, J. B., Ladak, H. M., Milner, J. S.,
Rutt, B. K., and Spence, J. D. (2002). Reconstruction
of carotid bifurcation hemodynamics and wall thick-
ness using computational fluid dynamics and mri.
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 47(1):149–159.
SEGMENTATION OF VESSEL GEOMETRIES FROM MEDICAL IMAGES USING GPF DEFORMABLE MODEL
331

Svensson, J., Gardhagen, R., Heiberg, E., Ebbers, T., Loyd,
D., Lanne, T., and Karlsson, M. (2006). Feasibility of
patient specific aortic blood flow CFD simulation. In
MICCAI, pages 257–263.
Taylor, C. A. and Figueroa, C. A. (2009). Patient-specific
modeling of cardiovascular mechanics. Annual Re-
view of Biomedical Engineering, 11:109–134.
Taylor, C. A. and Steinman, D. A. (2010). Image-based
modeling of blood flow and vessel wall dynamics:
Applications, methods and future directions. Annals
of Biomedical Engineering.
Tokuda, Y., Song, M.-H., Ueda, Y., Usui, A., Toshiaki,
A., Yoneyama, S., and Maruyama, S. (2008). Three-
dimensional numerical simulation of blood flow in the
aortic arch during cardiopulmonary bypass. European
Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery, 33(2):164–167.
Wang, K. C., Dutton, R. W., and Taylor, C. A. (1999). Im-
proving geometric model construction for blood flow
modeling. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology
Magazine, 18(6):33–39.
Xu, X. Y., Long, Q., Collins, M. W., Bourne, M., and Grif-
fith, T. M. (1999). Reconstruction of blood flow pat-
terns in human arteries. Proc Inst Mech Eng H, Jour-
nal of Engineering in Medicine, 213(5):411–421.
Yeo, S. Y., Xie, X., Sazonov, I., and Nithiarasu, P. (2009a).
Geometric potential force for the deformable model.
In BMVC.
Yeo, S. Y., Xie, X., Sazonov, I., and Nithiarasu, P. (2009b).
Level set based automatic segmentation of human
aorta. In International Conference on Computational
and Mathematical Biomedical Engineering.
Yeo, S. Y., Xie, X., Sazonov, I., and Nithiarasu, P.
(2011). Geometrically induced force interaction for
three-dimensional deformable models. IEEE T-IP,
20(5):1373–1387.
Yi, J. and Ra, J. B. (2003). A locally adaptive region
growing algorithm for vascular segmentation. Inter-
national Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology,
13(4):208–214.
Yim, P. J., Cebral, J. J., Mullick, R., Marcos, H. B., and
Choyke, R. L. (2001). Vessel surface reconstruc-
tion with a tubular deformable model. IEEE T-MI,
20(12):1411–1421.
Younis, H. F., Kaazempur-Mofrad, M. R., Chan, R. C.,
Isasi, A. G., Hinton, D. P., Chau, A. H., Kim, L. A.,
and Kamm, R. D. (2004). Hemodynamics and wall
mechanics in human carotid bifurcation and its con-
sequences for atherogenesis: investigation of inter-
individual variation. Biomechanics and Modeling in
Mechanobiology, 3(1):17–32.
ICPRAM 2012 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
332
