
HUMAN RE-IDENTIFICATION THROUGH DISTANCE METRIC
LEARNING BASED ON JENSEN-SHANNON KERNEL
Yoshihisa Ijiri
1
, Shihong Lao
2
, Tony X. Han
3
and Hiroshi Murase
4
1
Corporate R&D, OMRON Corp., Kizugawa, Kyoto, Japan
2
OMRON Social Solutions Co. Ltd., Kizugawa, Kyoto, Japan
3
Electrical & Computer Engineering Dept., Univ. of Missouri, Columbia, MO, U.S.A.
4
Graduate School of Information Science, Nagoya Univ., Chigusaku, Nagoya, Japan
Keywords:
Human Re-identification, Distance Metric Learning, Jensen-Shannon Kernel.
Abstract:
Human re-identification, i. e., human identification across cameras without an overlapping view, has important
applications in video surveillance. The problem is very challenging due to color and illumination variations
among cameras as well as the pose variations of people. Assuming that the color of human clothing does
not change quickly, previous work relied on color histogram matching of clothing. However, naive color
histogram matching across camera network is not robust enough for human re-identification. Therefore, we
learned an optimal distance metric between color histograms using a training dataset. The Jensen-Shannon
kernel is proposed to learn nonlinear distance metrics. The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated
by experimental results.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the continuous drop of hardware costs, the num-
ber of surveillance cameras deployed havebeen grow-
ing drastically, leaving the available human analysts
far behind. To fill this gap, many automatic video
surveillance techniques and systems have been pro-
posed. Among them, human identification, which is
one major problem in video surveillance, enables us
to match human tracks in surveillance areas such as
stores and shopping malls for the purposes of secu-
rity or marketing. For law enforcement, with one or
more images of suspects, automatic human identifi-
cation speeds up the process of finding them from a
large amount of surveillance camera records. Con-
sidering the cost effectiveness and the psychological
effects on the citizenry, it is impractical to fully cover
the entire surveillance area without any blind spot us-
ing the camera network. Therefore, in general, human
identification needs to be done across cameras with
non-overlapping views. In this paper, this human re-
identification problem is studied.
It is natural to tackle the human re-identification
through the face recognition approach, which has
been studied extensively in the computer vision com-
munity. However, as shown in Fig. 1, people tend
to vary their poses a lot unless they are asked not
to do so. Surveillance cameras are also intended to
watch a large area. Hence it is unrealistic to assume
that clear human faces can always be viewed. There-
fore, for practical surveillance, face recognition alone
is insufficient to guarantee the human identification
accuracy. As a approach complementary to the face
recognition approach, human identification based on
clothing colors is studied in this paper. Taking most
of the surveillance scenarios into consideration, we
assume that people do not change their clothing in a
short time duration, Noticing the symmetry character-
istic of human clothing, we conclude that the colors of
most clothing are view-angle insensitive.
Human re-identification is a very challenging
problem for the following reasons. Among surveil-
lance cameras, color calibrations are not always the
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f)
Figure 1: Sample images from VIPeR dataset: (a)(b) are
from ID 302, (c)(d) from ID 188, and (e)(f) from ID 358.
603
Ijiri Y., Lao S., X. Han T. and Murase H..
HUMAN RE-IDENTIFICATION THROUGH DISTANCE METRIC LEARNING BASED ON JENSEN-SHANNON KERNEL.
DOI: 10.5220/0003850506030612
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2012), pages 603-612
ISBN: 978-989-8565-03-7
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

same. Also, the illuminations of different camera
views usually varies a lot. In addition, the pose
variations of people make it infeasible to expect
identical appearances among cameras. Many works
have addressed these difficulties and can be summa-
rized into the following three groups: (i) appearance-
based methods, (ii) color calibration or color transfer
function estimation between cameras, and (iii) inter-
camera relationship modeling.
For appearance-based methods, various features
have been proposed to represent clothing colors and
textures (Bird et al., 2005; Gheissari et al., 2006;
Wang et al., 2007; Gray and Tao, 2008; Lin and
Davis, 2008; Hamdoun et al., 2008; Schwartz and
Davis, 2009; Kuo et al., 2010; Bak et al., 2010; Alahi
et al., 2010; Berdugo et al., 2010; Bazzani et al.,
2010; Farenzena et al., 2010; Hirzer et al., 2011).
Among them, Farenzena et al. (Farenzena et al.,
2010) combined weighted HSV histograms, Maxi-
mally Stable Color Regions (MSER), and Recurrent
High-Structured Patches. The former two features are
used to represent clothing colors, and the last one
is for texture description. In the feature extraction
process, according to the symmetric and asymmetric
axes, the human body is divided into sub-regions to
deal with pose variations using an algorithm called the
Symmetric Driven Accumulation of Local Features
(SDALF). More recently, Bak et al. (Slawormir et al.,
2011) proposed to use mean Riemannian covariance,
which consists of covariance matrices of RGB colors,
corresponding gradient magnitudes, and orientations
from multiple shots.
These state-of-the-art appearance-based algo-
rithms achieve high accuracy through extraction of
multiple features. More specifically, color histograms
in various color spaces and local descriptors are com-
bined. These redundant feature extractions contribute
higher accuracy at the expense of computational effi-
ciency. Among these features, clothing color-based
features are exploited extensively, because they are
robust to pose variation. For the color histogram
matching, traditional distances are used in various
color spaces. However, since the color calibrations
from different cameras are different, matching di-
rectly with traditional distances may lead to bias. So
the estimation of color relationships between cam-
eras, i.e. the algorithm group (ii) mentioned above,
has been studied in (Javed et al., 2008; Prosser et al.,
2008b; Prosser et al., 2008a; Gilbert and Bowden,
2006). Among these algorithms, the brightness trans-
fer function (BTF) method achieves quite good per-
formance. One disadvantage of BTF is that the BTF
between each pair of cameras has to be estimated. If
we have N cameras, then N(N −1)/2 BTFs must be
estimated. The computational complexity of the al-
gorithm w.r.t number of cameras is O (N
2
), which is
not practical for surveillance systems with many cam-
eras.
For camera networks, if people walk away from
one camera to another, and the entrance/exit times
of each camera can be modeled statistically. For in-
stance, a person exiting from a camera usually ap-
pears in another camera within a certain elapsed time.
Based on this concept, inter-camera relationship mod-
eling methods, categorized as algorithm group (iii),
have been proposed in (Javed et al., 2008; Huang and
Russell, 1997; Pasula et al., 1999; Song and Roy-
Chowdhury, 2007). The disadvantage of this scheme
is that such methods assume correct correspondence
between people and people walking in almost the
same elapsed time between cameras. Such assump-
tions may not be true in many practical situations. It
also requires people correspondences for all possible
pairs of cameras. Thus these algorithms also have the
computational complexity of O (N
2
), where N is the
camera number.
Considering the facts listed above, we believe that
the clothing color-based human re-identification is
one of the most promising approaches. Thus im-
proving the color matching for this approach is very
important. For color matching problems, however,
the importance of distance metrics has not been em-
phasized enough: only simple distance metrics have
been exploited. Therefore in this paper, we propose
a method for learning optimal distance metrics be-
tween color histograms from different cameras. The
proposed method reduce the complexity of the BTF
from O (N
2
) to O (1), since it does not assume that
the camera configuration is known. It is robust to
differences of color calibration between cameras as
well. To obtain better accuracy, we apply nonlinear
kernel functions to learn a nonlinear distance metric.
We experimentally validated the approach based on
the combination of large margin component analysis
(LMCA) and the Jensen-Shannon kernel. The pro-
posed method improves the identification accuracy
for clothing color matching approach. Therefore, the
proposed method and many previous works are com-
plementary.
In summary the contribution of this paper is two-
fold: (a) the use of nonlinear distance metric learn-
ing is proposed to achieve better accuracy compared
with conventional simple distance metrics, and (b) the
combination of LMCA and the Jensen-Shannon ker-
nel function is proposed. The basic idea of the pro-
posed method is illustrated in Fig. 2(b) and compared
with the conventional methods shown in Fig. 2(a).
In contrast to the conventional methods that match
VISAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
604

!"#$%&'
()*%!+,-"*
!"#$%&'
()*%!+,-"*
!"#$%&'
.)*%-/0&*
!$%#$%'1/-2'
*0!,&
(a)
!"#$%&'
()*%!+,-"*
!"#$%&'
()*%!+,-"*
!"#$%$&$'($!"#%)(*+"$,!%-!+#(,%($%&.($!
/&-01+!%
)(*+"$,!*%2(+3%
)(*+"$,!%-!+#(,%
4&$'($!"#%
5(*+"$,!%
-!+#(,%
.$%#$%'
*/!,&
(b)
Figure 2: (a) conventional and (b) proposed color matching
schemes.
clothing color histograms in a simple distance metric,
the proposed framework computes the distance with a
learned optimal distance metric.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. In Section 2, the proposed method is described
in depth with a review of some basic algorithms. In
Section 3 the experimental results are presented to
validate the proposed approach. Finally in Section 4,
concluding remarks are given.
2 PROPOSED METHOD
In this paper, we assume that the human region in a
camera view is given by a human detector or back-
ground subtraction algorithm. The training datasets
from many surveillance cameras under different con-
ditions and corresponding subject labels are assumed
available for metric learning. As mentioned above,
different cameras under different conditions cause
different color calibration. Hence the direct use of his-
tograms affects the identification accuracy adversely.
In contrast, the optimal distance metric is learned with
a training dataset in the proposed work.
To learn the optimal metric, color histograms X =
{x
i
;i = 1,...,n} are firstly computed for the train-
ing dataset, where n is the total number of training
samples in the dataset. Then using histograms X and
corresponding labels Y, the optimal distance metric
is learned. By including most of the possible vari-
ations in practical situations in the training dataset,
we expect this approach to work in real applications.
During the registration process, every time people en-
ter the fields of views of cameras, they are registered.
For each person, color histograms m
c
are extracted
as models. Denoting the number of people registered
as C, M = {m
c
;c = 1,...,C} are obtained. In the
re-identification process, color histograms of test im-
ages, T = {t
k
;k = 1,... ,K} are obtained, where K is
the number of images to be matched. Histograms M
and T are matched using the learned distance metric.
In the proposed method, the large margin criterion
is used to learn the optimal distance metric. Nonlin-
ear projection φ(x
i
) is used to project the input his-
tograms onto a higher dimensional space. For non-
linear projection, several types of kernel functions are
investigated; the final results are shown in experimen-
tal results section.
2.1 Clothing Color Histograms
Traditionally, color histograms are extracted in the
color spaces including RGB HSV, Lab, and YCbCr.
We use the HSV joint histograms in the HSV color
space because they showed better accuracy than other
color spaces according to our experiments. Since
clothing colors generally do not vary drastically
among front, back, right, and left views, for view-
point invariantmatching, vertical combination of such
clothing colors as the upper and lower body colors are
robust in many cases. Based on this observation, Bird
et al. (Bird et al., 2005) divided the entire human re-
gion into several vertically segmented regions to ob-
tain regional histograms. Following this scheme, in
this paper, the human region is segmented vertically
into P pieces, and for each sub-region p(p= 1,...,P),
HSV joint histograms x
ip
∈ R
b
h
×b
s
×b
v
are computed,
where b
h
,b
s
,b
v
are the number of bins in the H, S
and V color channels and x
ip
is vectorized from the
2D joint histogram. Then to describe all the human
region features, these histograms in each region are
concatenated as x
i
= {x
i1
,...,x
iP
} ∈R
D
and normal-
ized so that
∑
i
|x
i
| = 1, where D = b
h
×b
s
×b
v
×P.
We apply this procedure for training, model, and test
images to obtain color histograms X, M, and T, re-
spectively.
HUMAN RE-IDENTIFICATION THROUGH DISTANCE METRIC LEARNING BASED ON JENSEN-SHANNON
KERNEL
605

2.2 Distance Metric Learning
Many supervised/unsupervised distance metric learn-
ing algorithms have been proposed (Yang, 2006). We
adopt a supervised learning algorithm in this work.
Among supervised algorithms, linear discriminant
analysis (LDA) is a major algorithm. However, LDA
has some limitations. For example, it cannot be ap-
plied when there are not enough data to estimate intra-
class scatter or insufficient classes to make the be-
tween class scatter matrix be non-singular. On the
other hand, not only the linear distance metric but also
the nonlinear distance metric using kernel functions
have been proposed to improve accuracy. Among
them, the support vector machine (SVM) has gained
much popularity due to its good performance. How-
ever, since it was originally formulated as a binary
classification problem, it cannot be applied directly
to multi-class problems. To extend the binary clas-
sification to the multi-class case, we can discrimi-
nate matching scores that share the same labels and
those between different labeled data. In the prac-
tice of this scheme, the number of differently la-
beled pairs often becomes extremely larger than that
of the pairs sharing the same labels, causing the un-
balanced training problem. To avoid this, sampling
is often adopted from a large number of differently
labeled pairs. However, there is no guarantee that
appropriate data can always be sampled, which may
cause over-fitting. For these problems, Prosser et
al.(Prosser et al., 2010) proposed ensemble rankSVM
to solve this problem as ranking problem. Although
it shows good performance, it is noted that the tuning
of this algorithm is computationally expensive(Zheng
et al., 2011). To improve the ensemble RankSVM
further, recently Zheng et al.(Zheng et al., 2011) pro-
posed ”Probabilistic Relative Distance Comparison”
(PRDC), which is one of variants of distance metric
learning. This algorithm is promising, however, train-
ing process is still computationally expensive. On
the other hand, while a number of distance metric
learning have been proposed, the large margin near-
est neighbor (LMNN) (Weinberger and Saul, 2009) is
viewed as one of the best methods (Kulis, 2010) in
terms of accuracy. To further improve LMNN and al-
leviate the difficulties in processing high dimensional
data, Torresani et al. proposed large margin com-
ponent analysis (LMCA) (Torresani and Lee, 2007).
Furthermore, the algorithm was kernelized to learn
the distance metric in higher dimensional and non-
linear space for better performance. In this paper we
use it to learn the large margin distance metric. In the
following description, we briefly review the algorithm
and describe how to apply it to the re-identification
problem.
Linear LMCA:
Given color histogram features X = {x
i
;i =
1,...,n} ∈ R
D×n
and corresponding labels
Y = {y
i
;i = 1, ...,n} ∈ {0,1}
n
, LMCA minimizes
the following loss function ε(L):
ε(L) =
∑
ij
η
ij
||L(x
i
−x
j
)||
2
+ c
∑
ijl
η
ij
(1−y
il
)
·h(||L(x
i
−x
j
)||
2
−||L(x
i
−x
l
)||
2
+ 1), (1)
where L ∈ R
d×D
is a linear projection for X, η
ij
∈
{0,1} takes 1 iff x
j
and x
i
shares the same label
(y
i
= y
j
) and x
j
is the k-nearest neighbor of x
i
, c > 0
is an appropriate balancing parameter, y
il
∈ {0,1} is
a variable that takes 1 iff y
i
= y
l
, and h(s) is a hinge
function that is defined as h(s) = max(s,0). The first
term minimizes projected distances between the data
pairs that share the same labels to encourage the in-
variance property, and the other term is for discrimi-
nation, which makes projected distances between the
data pairs with the same labels and those with dif-
ferent labels distant with unit distance 1. The hinge
function gives a loss for the invasive data and does
not affect those data that have enough margins. Opti-
mizing L by gradient descent based on this objective
function, optimal linear discriminative projection can
be obtained. Here the distance metric can be given by
L
T
L:
Kernel LMCA:
For nonlinear projection φ(x
i
), the inner product is ex-
pressed as k(x
i
,x
j
) = φ
T
i
φ
j
. In subsequent descrip-
tion, the following notation is used: φ
i
= φ(x
i
)CΦ =
[φ
1
,...,φ
n
]
T
Ck
i
= Φφ
i
= [k(x
1
,x
i
),...,k(x
n
,x
i
)]. Us-
ing nonlinear projection, the loss function in the pro-
jected space is expressed as:
ε(L) =
∑
ij
η
ij
||L(φ
i
−φ
j
)||
2
+ c
∑
ijl
η
ij
(1−y
il
)
·h(||L(φ
i
−φ
j
)||
2
−||L(φ
i
−φ
l
)||
2
+ 1). (2)
The gradient of the loss function becomes
∂ε(L)
∂L
=
∑
ij
η
ij
L(φ
i
−φ
j
)(φ
i
−φ
j
)
T
+ c
∑
ijl
η
ij
(1−y
il
)
·h
′
(s
ijl
)L[(φ
i
−φ
j
)(φ
i
−φ
j
)
T
−(φ
i
−φ
l
)(φ
i
−φ
l
)
T
], (3)
where
s
ijl
= ||L(φ
i
−φ
j
)||
2
−||L(φ
i
−φ
l
)||
2
+ 1. (4)
Considering the parameterizations of L as L = ΩΦ,
Eq. (3) yields
VISAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
606

∂ε(L)
∂L
= 2Ω
∑
ij
η
ij
[E
(k
i
−k
j
)
i
−E
(k
i
−k
j
)
j
]Φ
+ 2cΩ
∑
ijl
η
ij
(1−y
il
)h
′
(s
ijl
)
·[E
(k
i
−k
j
)
i
−E
(k
i
−k
j
)
j
−E
(k
i
−k
l
)
i
+ E
(k
i
−k
l
)
l
]Φ, (5)
where
s
ijl
= {||Ω(k
i
−k
j
)||
2
−||Ω(k
i
−k
l
)||
2
+ 1}, (6)
E
v
i
= [0, . . . , 0,v,0,...,0] is a n ×n matrix that only
takes value v at the i-th column, and h
′
(s) is a dif-
ferential of h(s). To avoid the discontinuity of h
′
(s)
around 0, approximation by a smooth hinge function
was proposed(Rennie and Srebro, 2005). Using Eq.
(5), the steepest descent update rule is given by
L ← L−λ
∂ε(L)
∂L
. (7)
However in Eq. (5), all the terms in
∂ε(L)
∂L
have Φ and
L = ΦΩ by assumption, and Φ in Eq. (7) can be re-
moved. Hence the update rule is reduced to the fol-
lowing simple gradient descent update of Ω:
Ω ←Ω −λΓ, (8)
Γ = 2Ω
∑
ij
η
ij
[E
(k
i
−k
j
)
i
−E
(k
i
−k
j
)
j
]
+ 2cΩ
∑
ijl
η
ij
(1−y
il
)h
′
(s
ijl
)
·[E
(k
i
−k
j
)
i
−E
(k
i
−k
j
)
j
−E
(k
i
−k
l
)
i
+ E
(k
i
−k
l
)
l
]. (9)
By assumption, projection onto higher dimen-
sional space can be obtained easily:
Lφ
q
= ΩΦφ
q
= Ωk
q
. (10)
Here the distance metric can be represented as
k
T
q
Ω
T
Ωk
q
.
Since this algorithm automatically selects data
that fall within the margin through the learning pro-
cess, we expect better generalization compared to the
methods that sample fixed pairs in advance, which is a
simple extension of the binary classification problem
to the multi-class problem.
2.3 Kernel Functions
In this section, kernel functions that are suitable for
matching two distributions a,b ∈ R [0,1]
D
are inves-
tigated, such as normalized histograms or probability
distributions.
Histogram intersection kernel:
One popular distance between histograms is the his-
togram intersection. The histogram intersection ker-
nel, which satisfies Mercer’s condition, was proposed
in (Odone et al., 2005; Grauman and Darrell, 2005):
k(a, b) =
∑
i
min(a
i
,b
i
). (11)
χ
2
kernel:
Another popular distance between histograms is the
χ
2
distance. Here, the χ
2
kernel function, satis-
fies Mercer’s condition as well (Zhang et al., 2006;
Fowlkes et al., 2004). It is defined as:
k(a, b) = exp
−
1−
∑
i
(a
i
−b
i
)
2
1
2
(a
i
+b
i
)
σ
2
. (12)
Bhattacharyya kernel:
Hellinger distance
1
2
∑
i
√
a
i
−
√
b
i
2
is effective be-
tween two probability distributions. Here a and b are
normalized histograms such that
∑
i
a
i
= 1,
∑
i
b
i
= 1,
and thus the distance yields 1 −
∑
i
√
a
i
b
i
, which is
called the Bhattacharyya distance. Based on the Bhat-
tacharyya distance, the following Bhattachayya ker-
nel is derived that satisfies Mercer’s theorem (Jebara
and Kondor, 2003):
k(a, b) =
∑
i
p
a
i
b
i
. (13)
Jeffrey divergence kernel:
In human re-identification based on clothing color
histogram matching, one key point is that the ro-
bust matching between histograms is affected heav-
ily by noises. Due to the big appearance changes,
the shape of the color histograms are often altered,
which complicates robust matching. Thus we can-
not rely on histogram shape matching, while Gauss
kernel or other correlation-based kernels strongly rely
on histogram shape. For comparing and matching
such uncertain information, one popular way is an
information-based measure. For this problem, the
Kullback-Leibler divergence (KLD) H(a||b) is an ef-
fective measure of the differences between two prob-
abilistic pieces of information. However, due to its
asymmetry(H(a||b) 6= H(b||a)) the KLD cannot be
used directly as a kernel function. Symmetric Jeffrey
divergence (JD) H(a||b) + H(b||a)(Jeffreys, 1946) is
used to define the Jeffrey divergence kernel function
as exp(−JD/σ
2
). The definition is given by
k(a, b) = exp
−
∑
i
a
i
log
a
i
b
i
+ b
i
log
b
i
a
i
σ
2
=
∏
i
b
i
a
i
a
i
σ
2
a
i
b
i
b
i
σ
2
, (14)
HUMAN RE-IDENTIFICATION THROUGH DISTANCE METRIC LEARNING BASED ON JENSEN-SHANNON
KERNEL
607
where σ is another parameter that provides tuning
flexibility. We don’t have proof for the positive def-
initeness of this kernel function yet, even though ex-
periments show that it is always positive definite.
Jensen-Shannon kernel:
Another way to circumvent KLD’s asymmetry is the
Jensen-Shannon divergence (JSD)(Lin, 1991). Not
only it is symmetric but it also has other numerous de-
sirable properties. As shown in (Huang et al., 2005),
it is numerically more stable than KLD or JD and pro-
vides a theoretical upper bound in terms of the vari-
ational distance; no general upper bound exists for
KLD or JD. Therefore the JSD-based kernel func-
tion, which satisfies Mercer’s theorem, is proposed
(Chan et al., 2004). To give one more parameter
σ for flexibility, an exponential function is used as
exp(−JSD/σ
2
). The resulting kernel function is
k(a, b) = exp
−
∑
i
a
i
2
log
2a
i
a
i
+b
i
+
b
i
2
log
2b
i
a
i
+b
i
σ
2
=
∏
i
a
i
+ b
i
2a
i
a
i
2σ
2
a
i
+ b
i
2b
i
b
i
2σ
2
. (15)
This kernel is positive definite (Chan et al., 2004).
Even though a variety of kernel functions exists, this
kernel has not received enough attention yet.
To investigate the effectiveness of this kernel for
our problem, a preliminary experiment using syn-
thetic data generated using Gaussian mixture model
is conducted. As shown in experimental section, we
use HSV joint histograms in the HSV color space. In
HSV joint histograms, hue, saturation and value com-
ponents can be easily shifted circularly by illumina-
tion changes or color calibration differences. To sim-
ulate data pairs from the same person, a pair of circu-
larly shifted and original distributions are used. For
data pairs from different persons, mutually different
distributions are used. An example of data pair is il-
lustrated in Fig.3. 500 samples of data pair is used to
draw a distribution of distances by each kernel. The
result can be shown in Fig.4. The distances between
data pairs with circular shift should be small, while
those between data pair with different distributions
should be large. To quantify the effectiveness, the ra-
tio of mean distance for simulated intra-person pairs
against that for simulated different individualpairs are
computed. The results can be seen in Table.1, where
the mean distance for simulated intra-person pairs is
denoted by m
shift
and that for simulated different in-
dividual pairs m
dif f
. The larger the ratio is, the better.
Viewing these results, we can see that the proposed
Jensen-Shannon kernel function is the most appropri-
ate for our HSV color space based matching problem.
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
distribution 1
dist.1 shifted circularly
distribution 2
Figure 3: Synthetic test distributions; the bold line and the
regular dotted line indicate a pair of color histograms of a
person from different cameras, which simulates circularly
shifted hue histogram in HSV color space, and the bold line
and the bold dotted line indicate a pair of color histograms
from different person.
0 0.5 1
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
Bhattacharyya kernel
0 0.5 1
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
hist. intersec. kernel
0 0.5 1
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
χ
2
kernel
0 0.5 1
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
Jensen−Shannon kernel
Figure 4: Distance distribution in each kernel function; dot-
ted line indicates a distribution of distances between data
pairs with different color distributions, the other one indi-
cates a distribution of those between shifted and original
color distributions.
Table 1: Ratios of mean distance between shifted and orig-
inal data pairs against that between different data pairs.
Bhat. HI χ
2
JS
m
shift
m
dif f.
1.8059 1.9113 2.0271 2.3351
2.4 Matching
Normalized color histograms are projected onto opti-
mized nonlinear space, as shown by Eq. (10), which
yields Ωk(X,M), Ωk(X, T), where Ω is learned by
Eq. (8), and X, M, and T are color histograms com-
puted from training dataset, model images, and test
images, respectively. Here matching can be done as:
s
ck
= f(Ωk(X,m
c
),Ωk(X,t
k
)), (16)
where f(·, ·) is an arbitrary similarity function. Esti-
mated identity
ˆ
ω
k
for input data t
k
is given by taking
VISAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
608

20
40
60
80
100
120
Figure 5: Subregion
division.
(a) Correct match: ID 126 (b) Correct match: ID 351 (c) False match: ID 006 & 135 (d) False match: ID 078 & 107
Figure 6: Successful and failure cases by the proposed method.
the maximum for similarity scores s with respect to
registered models M = {m
c
;c = 1,. . . ,C}:
ˆ
ω
k
= max
c
(s
ck
). (17)
Although any similarity function can be used as f in
Eq. (16), in the following experiments, we used cor-
relation.
3 EXPERIMENTS
We conducted experiments using the Viewpoint In-
variant PEdestrian Recognition (VIPeR) dataset by
Gray et al. (Gray and Tao, 2008) to show the ef-
fectiveness of the proposed method. This dataset
is constructed to evaluate viewpoint invariant human
re-identification algorithms. Several examples from
VIPeR can be seen in Fig. 1. Due to the pose and
illumination variations, the clothing colors are signif-
icantly different between the two images of the same
person. Furthermore, in the dataset, the camera labels
are not available to indicate from which camera the
images were taken. Since estimating such color cali-
bration functions as BTF is impossible, this dataset is
quite difficult for human re-identification.
In this dataset, two images for each of 632 sub-
jects are included: one for the model and one for
matching. The training dataset is constructed by ran-
domly selecting 200 individuals from the 632 people.
Since there are two images for each subject, the train-
ing dataset has 400 images. The remaining 432 in-
dividuals are used for evaluation. In all experiments,
through ten cross validations, we estimated the mean
accuracy and the corresponding standard deviations.
In the human body extraction, if an automatic seg-
mentation algorithm was employed, the result would
be affected by its accuracy. To avoid this and evaluate
only the effect by difference of distance metrics, the
human body region is segmented manually. In prac-
tical situations, this can be done relatively easily by
background subtraction, for example.
Table 2: CMC in comparison.
CMC (1) CMC (10)
Baseline (Euclidean dist.) 8.7±0.8 24.2±1.0
Baseline (NCC) 10.8±1.0 28.6±0.8
Baseline (hist. intersec.) 13.2±1.1 35.3±1.0
Baseline (Bhat. dist.) 17.2±0.8 39.2±1.0
LMCA with lin. 13.0±1.0 37.3±2.4
LMCA with Gauss(5.0) 15.0±1.2 43.8±1.9
LMCA with hist. intersec. 17.1±2.4 51.1±2.3
LMCA with χ
2
19.6±1.5 53.6±1.5
LMCA with Bhat. 18.8±1.3 50.9±1.5
LMCA with JD 16.6±0.1 53.2±1.3
LMCA with JS 20.5±1.5 55.7±1.5
For feature extraction, we used HSV joint his-
togram in the HSV color space. We used five bins for
HS channels and three bins for V channel for quan-
tization. For division into sub-regions, the best ac-
curacy was given by segmentation into eight regions,
as illustrated in Fig. 5. The blue lines represent the
boundaries of each region and color histograms are
computed from the red areas in each sub-region. Con-
catenating these histograms in each image, we ob-
tained 5×5×3×8= 600 dimensional features.
We used a cumulative match characteristic (CMC)
curve to evaluate the matching performance. CMC (n)
represents the probability that correct matches appear
in the top n-th. CMC (1) and CMC (10), which rep-
resent the probability that correct matches are always
placed first and within top 10 respectively, are shown
in Table 2. In the table, each cell includes estimated
mean value ± corresponding standard deviation. For
comparisons, such basic techniques as simple Eu-
clidean distance, normalized correlation, histogram
intersection, and Bhattacharyya distance are listed as
baselines. In the LMCA evaluation, in addition to lin-
ear LMCA, we tested various kernel LMCAs, includ-
ing Gauss, histogram intersection, χ
2
, Bhattacharyya,
Jeffrey divergence, and Jensen-Shannon kernels. The
combination of LMCA and the Jensen-Shannon ker-
nel gave the best result. On the other hand, for the
HUMAN RE-IDENTIFICATION THROUGH DISTANCE METRIC LEARNING BASED ON JENSEN-SHANNON
KERNEL
609

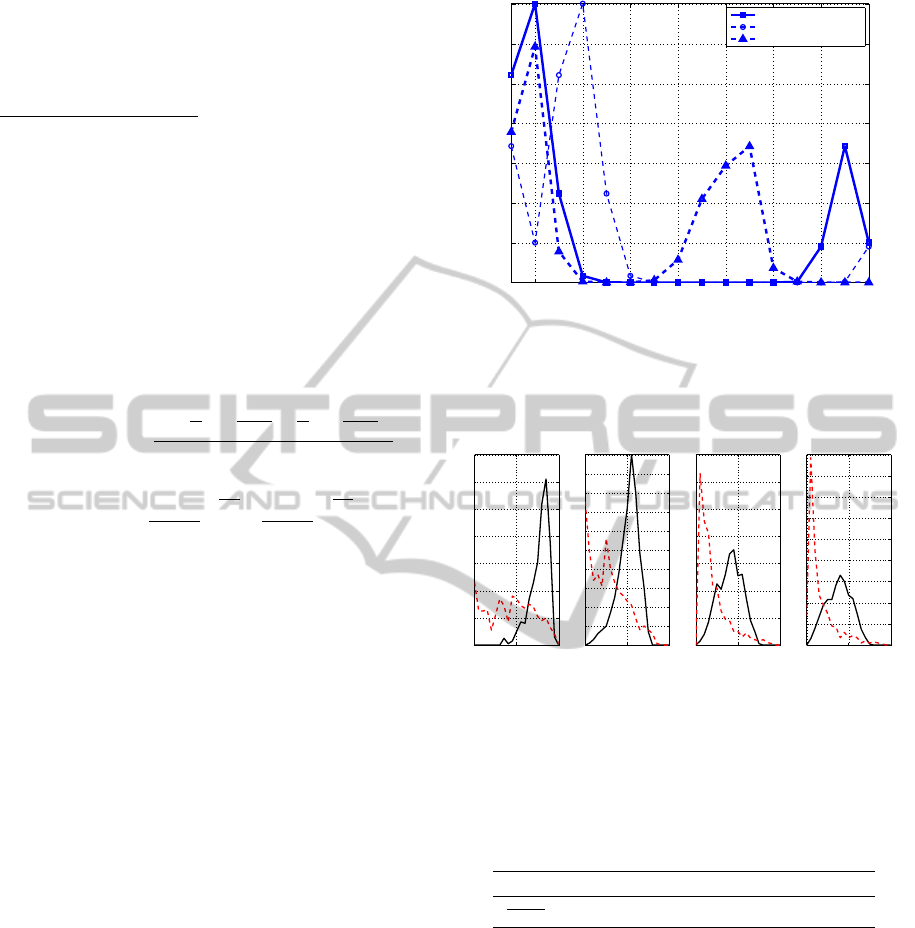
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Cumulative Match Characteristics
Rank
Recognition rate
LMCA(JS)
LMCA(χ
2
)
LMCA(Bhat.)
LMCA(Gauss)
Bhat.
NCC
Figure 7: CMC curve.
Gauss kernel, the accuracy was degraded compared
to the simple distances, which means it is unsuitable
for matching normalized histograms. Moreover, the
result from LMCA plus the Jensen-Shannon kernel is
better than that from the PRDC(Zheng et al., 2011),
which can achieve 12.64% for CMC(1) and 44.28%
in CMC(10) in equivalentdata setup described in their
paper. Considering in (Zheng et al., 2011) 29 dif-
ferent feature channels such as Schmid and Gabor
filter for RGB, YCbCr, HSV color spaces are used,
the proposed method which uses only HSV joint his-
tograms is much more efficient and probably faster in
re-identification process.
The summarizing CMC curve is shown in Fig.
7. The proposed method (LMCA with the Jensen-
Shannon kernel) is the best for all ranks. Some suc-
cessful and failure examples by the proposed method
are shown in Figs. 6(a)-(d). Although the appearances
are quite different, for pairs in (a) and (b) from the
same ID, the proposed method effectively absorbed
the differences. However, pairs in (c) and (d) from
different IDs are falsely ranked first by the proposed
method. For the images in the pair (c), roughly speak-
ing, the only difference is the facial skin color, and
most of body region is the same color. This kind of
cases is still critical in the proposed method. The
other failure case in the pair (d), the only difference
is the upper body color. In addition, the upper body
region is including the same color. Presumably it is
due to the limitation of using histogram without spa-
tial information. Some extent of spatial ambiguity
is required for viewpoint invariance, so it is a trade-
off problem. Although seeking better features is out-
side the scope of this paper, more representative fea-
tures would give better accuracy using the proposed
method for these cases.
Finally we experimented with SDALF(Farenzena
et al., 2010), which is one of the current state-of-the-
Table 3: Combination with state-of-the-art algorithm.
CMC (1) CMC (10)
(a) SDALF (wHSVhist) 9.8±0.5 28.2±1.7
(b) SDALF (MSCR) 7.8±0.7 23.2±0.8
(a) + (b) 14.7±1.1 41.1±1.6
LMCA(JS) + (b) 21.3±1.2 57.7±2.6
art algorithm. The results are shown in Table 3. All
the experimental setups are the same as mentioned
above. The first three lines show the accuracy when
only the color features (MSCR, weighted HSV his-
tograms, and their combination) are exploited. Since
the proposed algorithm can be seen as an alternative
to weighted histogram matching, we used our pro-
posed method with MSCR. The results are in the last
line. The SDALF performance drastically improved
by only replacing the histogram matching part from
the original weighted histogram matching to the pro-
posed nonlinear distance metric learning-based his-
togram matching.
The result shows the top level accuracy on VIPeR
with the advantage of only using color features and so
fast processing. This suggests the effectiveness of the
proposed method.
The kernel LMCA learning took about 80 [sec]
with 400 training datasets
1
. Thus given a sufficient
number of training datasets, the algorithm can learn
optimal distance metrics relatively quickly. Com-
pared to the color calibration between cameras (such
as BTF) or inter-camera relationship modeling that re-
quires optimization for each pair of cameras, in the
proposed method, optimization can be done just once
at setup. Thus while BTF has computational com-
plexity of O (N
2
) w.r.t number of cameras N, that of
the proposed method is just O (1). Therefore the pro-
posed method is especially easy to implement when a
large number of cameras are employed.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we study the human re-identification
problem based on clothing colors. The re-
identification approach based on distance metric
learning is validated experimentally. The combina-
tion of LMCA and the Jensen-Shannon kernel pro-
vided the best accuracy in our experiments.
The proposed method does not assume that the
camera configuration is known. Our approach is dif-
ferent from the brightness transfer function estimation
1
The other experimental environments included Matlab
unoptimized code on Mac OS X, Core2Duo 2.2 GHz with
2GB memory.
VISAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
610

or inter-camera relationship modeling, where some
amount of the exact human correspondences in each
pair of cameras are needed. Therefore the advantage
of the proposed approach lies in the computational ef-
ficiency, which becomes obvious when a large num-
ber of cameras are deployed.
REFERENCES
Alahi, A., Vandergheynst, P., Bierlaire, M., and Kunt,
M. (2010). Cascade of descriptors to detect and
track objects across any network of cameras. CVIU,
114(6):624–640.
Bak, S., Corvee, E., Br´emond, F., and Thonnat, M. (2010).
Person Re-identification Using Spatial Covariance
Regions of Human Body Parts. In Proc. of AVSS.
Bazzani, L., Cristani, M., Perina, A., Farezena, M.,
and Murino, V. (2010). Multiple-shot Person Re-
identification by HPE signature. In Proc. of ICPR.
Berdugo, G., Soceanu, O., Moshe, Y., Rudoy, D., and Dvir,
I. (2010). Object Reidentification in Real World Sce-
narios Across Multiple Non-overlapping Cameras. In
Proc. of Euro. Sig. Proc. Conf.
Bird, N. D., Masoud, O., Papanikolopoulos, N. P., and
Isaacs, A. (2005). Detection of Loitering Individuals
in Public Transportation Areas. IEEE Trans. on ITS,
6(2):167–177.
Chan, A., Vasconcelos, N., and Moreno, P. (2004). A fam-
ily of probabilistic kernels based on information di-
vergence. Univ. of California, San Diego, Tech. Rep.
Farenzena, M., Bazzani, L., Perina, A., Murino, V., and
Cristani, M. (2010). Person Re-Identification by
Symmetry-Driven Accumulation of Local Features. In
Proc. of CVPR.
Fowlkes, C., Belongie, S., Chung, F., and Malik, J. (2004).
Spectral grouping using the Nystr¨om method. IEEE
Trans. on PAMI, 26(2):214–225.
Gheissari, N., Sebastian, T. B., and Hartley, R. (2006). Per-
son Reidentification Using Spatiotemporal Appear-
ance. In Proc. of CVPR.
Gilbert, A. and Bowden, R. (2006). Tracking Objects
Across Cameras by Incrementally Learning Inter-
camera Colour Calibration and Patterns of Activity. In
Proc. of ECCV.
Grauman, K. and Darrell, T. (2005). The Pyramid Match
Kernel: Discriminative Classification with Sets of Im-
age Features. In Proc. of ICCV.
Gray, D. and Tao, H. (2008). Viewpoint Invariant Pedestrian
Recognition with an Ensemble of Localized Features.
In Proc. of ECCV.
Hamdoun, O., Moutarde, F., Stanciulescu, B., and Steux,
B. (2008). Person re-identification in multi-camera
system by signature based on interest point descrip-
tors collected on short video sequences. In Proc. of
ICDSC.
Hirzer, M., Beleznai, C., Roth, P. M., and Bischof, H.
(2011). Person Re-identification by Descriptive and
Discriminative Classification. In Scandinavian Con-
ference on Image Analysis, pages 91–102.
Huang, T. and Russell, S. (1997). Object identification in
a Bayesian context. In Proc. of Joint Conf on AI &
IJCAI.
Huang, X., Li, S. Z., and Wang, Y. (2005). Jensen-shannon
boosting learning for object recognition. In Proc. of
CVPR.
Javed, O., Shafique, K., Rasheed, Z., and Shah, M. (2008).
Modeling inter-camera space-time and appearance re-
lationships for tracking across non-overlapping views.
CVIU, 109(2):146–162.
Jebara, T. and Kondor, R. (2003). Bhattacharyya and Ex-
pected Likelihood Kernels. In Proc. of Comp. Learn.
Theory.
Jeffreys, H. (1946). An invariant form for the prior proba-
bility in estimation problems. A Math. and Physical
Sciences, 186(1007):453–461.
Kulis, B. (2010). ICML 2010 Tutorial on Metric Learning.
Kuo, C.-H., Huang, C., and Nevatia, R. (2010). Inter-
camera Association of Multi-target Tracks by On-Line
Learned Appearance Affinity Models. In Proc. of
ECCV.
Lin, J. (1991). Divergence measures based on the Shannon
entropy. IEEE Trans. on Info. Theory, 37(1):145–151.
Lin, Z. and Davis, L. S. (2008). Learning Pairwise Dissim-
ilarity Profiles for Appearance Recognition in Visual
Surveillance. In Proc. of ISVC.
Odone, F., Barla, A., and Verri, A. (2005). Building kernels
from binary strings for image matching. IEEE Trans.
on Image Proc., 14(2):169–180.
Pasula, H., Russel, S. J., Ostland, M., and Ritov, Y. (1999).
Tracking many objects with many sensors. In Proc. of
IJCAI.
Prosser, B., Gong, S., and Xiang, T. (2008a). Multi-camera
Matching under Illumination Change Over Time. In
Proc. of Workshop on Multi-camera and Multi-modal
Sensor Fusion Algorithms and Applications.
Prosser, B., Gong, S., and Xiang, T. (2008b). Multi-camera
Matching using Bi-DirectionalCumulative Brightness
Transfer Functions. In Proc. of BMVC.
Prosser, B., Zheng, S., Gond, S., and Xiang, T. (2010). Per-
son Re-Identification by Support Vector Ranking. In
Proc. of BMVC.
Rennie, J. D. M. and Srebro, N. (2005). Fast maximum
margin matrix factorization for collaborative predic-
tion. In In proc. of ICML.
Schwartz, W. R. and Davis, L. S. (2009). Learning Discrim-
inative Appearance-Based Models Using Partial Least
Squares. In Proc. of Brazil. Symp. on Comp. Graph.
and Image Proc.
Slawormir, B., Corvee, E., Br´emond, F., and Thonnat, M.
(2011). Multiple-shot Human Re-Identification by
Mean Riemannian Covariance Grid. In Proc. of AVSS,
pages 179–184.
Song, B. and Roy-Chowdhury, A. K. (2007). Stochastic
Adaptive Tracking In A Camera Network. In Proc. of
ICCV.
Torresani, L. and Lee, K.-c. (2007). Large margin compo-
nent analysis. NIPS.
Wang, X., Doretto, G., Sebastian, T., Rittscher, J., and Tu,
P. (2007). Shape and Appearance Context Modeling.
In Proc. of ICCV.
HUMAN RE-IDENTIFICATION THROUGH DISTANCE METRIC LEARNING BASED ON JENSEN-SHANNON
KERNEL
611

Weinberger, K. Q. and Saul, L. K. (2009). Distance Metric
Learning for Large Margin Nearest Neighbor Classi-
fication. JMLR, 10:207–244.
Yang, L. (2006). Distance metric learning: A comprehen-
sive survey. Michigan State Univ. Tech. Report.
Zhang, J., Marszalek, M., Lazebnik, S., and Schmid, C.
(2006). Local Features and Kernels for Classification
of Texture and Object Categories: A Comprehensive
Study. IJCV, 73(2):213–238.
Zheng, W.-S., Gong, S., and Xiang, T. (2011). Person Re-
identification by Probabilistic Relative Distance Com-
parison. In Proc. of CVPR.
VISAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
612
