
ENTERPRISE NETWORK REDESIGN THROUGH
SERVER CONSOLIDATION
Abeer Al-Fadhel, Paulvanna N. Marimuthu and Sami J. Habib
Kuwait University, Computer Engineering Department, P. O. Box 5969 Safat, 13060 Kuwait
Keywords: Utilization, Server Consolidation, Redesign, Optimization, Simulated Annealing.
Abstract: In this paper, we have explored the utilization of existing servers within an enterprise information network
(EIN), and we have proposed redesign operations on servers to identify and remove the low-utilized servers.
The low-utilized servers consume unnecessary power and increase the operational and maintenance cost.
The removal of low-utilized server is viewed as an EIN redesign problem, which removes the low-utilized
servers within the EIN and re-distributes the clients of the purged servers to the remaining servers, thereby
reducing a portion of expenditure on maintenance and operation. We have proposed three approaches on
distributing the clients of removed servers and the approaches are; single server pure random distribution,
selective distribution and multiple servers pure random distribution. We have employed Simulated
Annealing to search for best possible random server/servers in order to distribute the workload of the
removed server, thereby improving the utilization of the remaining servers. The simulation results for a
given EIN with 10 servers and 25 clusters show that our proposed server consolidation approaches improve
the initial average server utilization of around 25% to 60%, 68.5%, and 90% respectively in the proposed
three methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
An enterprise information network (EIN) is a
medium scale computer network, designed to
support the activities of an enterprise such as bank or
scientific institution. Typically, an EIN is comprised
of several servers offering specific services to a
number of clusters containing clients; Moreover, it
offers high quality service and enables enterprises to
coordinate their processes across all functional and
management levels. Many enterprises install
separate servers to house new applications mainly to
prevent the risk of negative effects of one
application on another, when both the applications
are installed on the same server. Commonly,
enterprise data centers use to have many servers to
handle their operations in various departments, as
the installation of a new application on an existing
server with several applications running on it,
sometimes leads to degrade the server performance.
Moreover, the servers purchased by different
decision makers over a period of time to offer
specific services to a group of clients may also
increase the number of servers. As years pass by, the
added servers within the enterprise network have
lead to a situation known as ‘server sprawl’,
whereby too-many servers are running at very low
utilization, consuming physical space and power, as
well as wasting the internal resources of servers such
as CPU, memory, and storage devices. On net result,
server sprawl increases the operational and
maintenance cost of the EIN.
The present economic crisis forces the enterprise
networks to cut unnecessary operational and
maintenance costs. In this paper, we have examined
the utilization of installed servers in an enterprise
network and apply server consolidation techniques
to remove the under-utilized servers and redistribute
the clients of the removed servers to the selected
server from the remaining servers. We have
extended the work of Abdulgafer et al (2010),
whereby the authors redesign a grid-based enterprise
information network through servers consolidation.
We have proposed three different approaches to
distribute the workload of the removed low utilized
server; single server pure random distribution,
selective distribution and multiple servers pure
random distribution. We have employed Simulated
Annealing to search for the best server to distribute
the clients of the removed server that improves the
186
Al-Fadhel A., N. Marimuthu P. and J. Habib S..
ENTERPRISE NETWORK REDESIGN THROUGH SERVER CONSOLIDATION.
DOI: 10.5220/0003854201860191
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES-2012), pages 186-191
ISBN: 978-989-8425-97-3
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

utilization of the existing servers. We have
compared the utilization of the servers present in the
EIN before and after the application of the redesign
process, whereby it shows a maximum increase of
65.2% in the average utilization.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2,
discusses the related work and Section 3 describes
the server sprawl problem. The server consolidation
methods are presented in Section 4. Section 5
elaborates on Simulated Annealing approach and
Section 6 presents the experimental results and
analysis, and Section 7 concludes our work.
2 RELATED WORK
Several studies were carried out by various
researchers to devise techniques to reduce the costs
of enterprise network by improving the utilization of
installed servers. A decision model for server
consolidation in data centers was presented by
Speitkamp and Bichler (2010) in order to minimize
the costs of servers in terms of hardware costs (e.g.,
CPU and memory bandwidth). By optimally
allocating virtual servers to physical servers, the
authors reduced the hardware cost.
Spellmann, et al. (2003) applied a performance
modelling and stepwise refinement to analyze the
consolidation alternatives before making any
physical changes. They defined three consolidation
alternatives, which were centralization, physical
consolidation, and, data and application integration.
Servers were moved from different geographic data
centers to a common location (centralization),
several small servers were replaced with fewer large
servers to achieve storage consolidation (physical
consolidation) and data was consolidated into a
single server, and similar applications were merged
into a single server (data and application
integration).
Gupta et al. (2008) discussed the problem of
server sprawl. The authors modelled the problem of
server consolidation as a variant of the bin packing
problem, where the items to be packed were the
servers being consolidated and bins were the target
servers. The authors developed a new heuristic
algorithm for determining the number of destination
servers in the presence of the incompatibility
constraints including bin-item incompatibilities.
The problem of data-centers consolidation was
formulated as a minimization problem (Anselmi,
Cremonesi and Amaldi, 2009). The weighted sum of
server costs comprised of cost of energy
consumption, and maintenance, subject to satisfying
performance constraints on utilizations and data-
center response times was studied. Server costs were
minimized by reducing the number of servers used
in the data-center, which was achieved through
installing a given software application on a number
of servers, while maintaining a maximum utilization
thresholds.
Uddin and Abdul Rahman (2010) presented a
server consolidation solution to reduce the energy
consumption from underutilized servers and reach
energy efficient data centers using virtualization.
They defined virtualization as a technology that
combines multiple virtual servers on a single server,
and thus, increased the utilization of server. The
utilization of a server was estimated by measuring
its performed workloads and executed applications.
Dhyani et al. (2010) presented a constraint
programming approach for the service consolidation
problem in data-centers. The problem was to find an
allocation of applications to servers while
minimizing the data-center costs and satisfying
constraints on the resource utilizations. The authors
developed a constraint programming approach using
the Comet programming language to assess the
impact of the rule-based constraints in reducing the
problem search space and to improve the solution
quality and scalability.
Cardosa et al. (2009) presented a suite of
techniques for placement and power consolidation of
virtual machines in data centers taking advantage of
the min-max and shared features inherent in
virtualization technologies. The objective was to
place virtual machines among a set of physical
servers in the data center and estimated the shares
that should be given to each VM.
The behavior of server consolidation workloads was
studied by Jerger, Vantrease and Lipasti (2007),
which focused particularly on sharing of caches
across a variety of configurations. The authors
presented a study of a variety of last level cache
sharing arrangements to illuminate some of the
pressures felt by the cache hierarchy, and showed
that both performance and fairness were affected.
They presented a simulation methodology which
was designed to mimic a dynamically partitioned
system running a hypervisor or virtual machine.
Our work focuses on redesign of an existing EIN
through the removal of underutilized servers and the
distribution of their clients' to the remaining servers.
3 PROBLEM FORMULATION
The server consolidation problem is formulated as
ENTERPRISE NETWORK REDESIGN THROUGH SERVER CONSOLIDATION
187

an optimization problem, where the objective
function is to maximize the servers’ utilization as
shown in Equation (1). The term represents the
utilization for server j, and S is the total number of
servers in the system
Utilization of Servers = max
∑
=
S
j
j
U
1
(1)
Here, we highlight the core constraints, which
facilitate the uniform distribution of clients to the
existing servers. Constraint (2) states that each
cluster of clients is attached to only one server,
thereby ensuring that each client is served by one
server.
∑
=
=
S
j
jij
1
,1
βα
Cj ,...,2,1=∀
(2)
In constraint (2), represents the binding of ith
cluster to jth server. represents the allocation of
server j in the EIN.
Constraint (3) ensures that an installed server
serves more than one cluster. Moreover, it ensures
that the number of connected clusters is less than the
total number of clusters in the system so that the
server will not be over-utilized. The term C
represents the total number of clusters within EIN.
C
C
j
iij
pp
∑
=1
1
βα
Si ...,3,,2,1=
∀
(3)
4 REDESIGN THROUGH
SERVER CONSOLIDATION
4.1 Server Utilization
The server utilization is calculated by taking the
average CPU usage over a period of time (during
one hour) (Abdulgafer et al., 2010), which includes
the number of file requests received by each server
and time taken by each server to process the file
requests. The performance of each server is
estimated based on its utilization and higher server
utilization leads to higher server performance.
We have defined define the server utilization (U)
as the amount of time the server is busy during a
period of time, (for example; duration of one hour)
as in Equation (4).
U = (amount of time the server is busy during
one hour / 3600 seconds) * 100
(4)
With known server capacity, which is the
maximum number of files the server can handle
during one hour, the amount of time (T) the server is
busy during one hour can be calculated using
Equation (5). The average file size is measured in
Megabytes and server capacity is measured in
Megabytes/hour.
T = (average file size * average number of
requested files per one hour) / server capacity)
(5)
4.2 Load Redistribution Approaches
We have proposed three approaches on distributing
the clients of the removed servers; single server pure
random distribution, selective distribution into the
second lowest utilized server and multiple servers
pure random distribution as shown in Figure 1. In all
the three methods, the utilization of each server is
computed and the server with lowest utilization is
selected for removal from the EIN. The single server
pure random distribution method selects a server
randomly from the remaining servers list and it
distributes the clients of the removed server. The
second approach allocates the clients of the removed
server to the second lowest utilized server in the
EIN. The third approach distributes the clients of the
removed server to two servers selected randomly
from the remaining servers in the EIN. Since the
first approach distributes the workload to only one
server, the probability of the randomly selected
server to become over utilized may occur more
frequently than the other methods. But the
overloading of server is decreased in the second
approach as it adds the clients to the second lowest
utilized server. However, the third approach
balances the workload by distributing the clients
over two servers, which result in overall
improvement in the servers’ utilizations.
5 ROLE OF SIMULATED
ANNEALING IN EIN
REDESIGN
Simulated Annealing (SA) is used widely to solve
different optimization problems. SA starts with an
initial solution S
0
, and then, it generates a new
solution using a function called neighbor in the
optimization process (Kirkpatrick et al., 1983). The
neighbor function is defined with a function known
as the Metropolis, which accepts a new solution
based on the dominance of cost of new solution or
based on a probabilistic function. We have
employed SA in our consolidation algorithm to
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
188

Figure 1: Load redistribution techniques utilized by neighborhood functions within SA.
optimize the utilizations of servers in the given EIS.
If the cost of the computed solution is positive,
then, the new solution gives a higher average
utilization and it is accepted. Otherwise, if the
random number in the Metropolis satisfies the given
condition, then the new solution is accepted.
Metropolis consolidation function is considered
as the solution modification function, which
generates new solution and passes it to a function
called neighbor in all the iterations. The neighbor
function tests the new solution and computes the
average utilizations of all servers for the new
solution without removing a server from EIN.
Metropolis algorithm accepts the new solution if the
cost of the new solution is greater than the previous
solution.
ENTERPRISE NETWORK REDESIGN THROUGH SERVER CONSOLIDATION
189
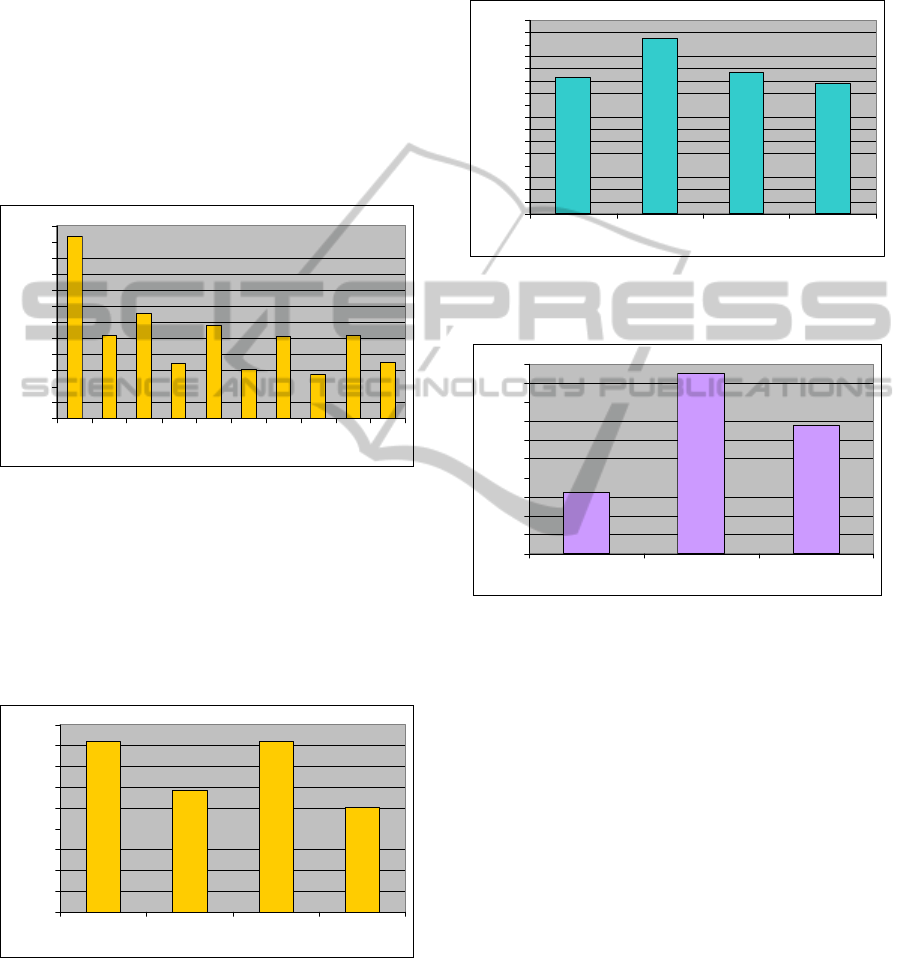
6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We have experimented with an enterprise
information network using all the three clients’
distribution approaches. EIN comprises of 10 servers
and 25 clusters. Figure 2 shows the distribution of
servers’ utilization within the initial EIN. The
average server utilization of the initial network is of
25.8%. The Simulated Annealing parameters are set
to the following values; initial temperature = 1000˚
C, α = 0.8, β = 1, and maximum-time = 100 time
units. We have coded all the three experiments
within Simulated Annealing in C++.
Figure 2: Server utilization in initial EIN network.
According to the first approach, the average
utilization of the remaining servers is computed for
an optimization period as in Figure 3, and it is equal
to 68.25%. In each of the iteration, the algorithm
removes one underutilized server and distributes
their clients' randomly to the remaining servers that
exist in the system.
Figure 3: Utilization of remaining servers in first
approach.
The second approach increases the server
utilization by 34.55% from 25.8 to 60.35% as shown
in Figure 4. In each of the iteration, the algorithm
removes one underutilized server and distributes
their clients' clusters to the lowest utilized server
selected from the remaining servers. For the similar
EIN, the third approach ends with a final redesign
solution consisting of 3 servers and with the average
utilizations of 91% as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 4: Utilization of remaining servers in second
approach.
Figure 5: Utilization of remaining servers in third
approach.
The first and second approaches reduce the servers
from 10 servers to 4 servers where it represents a
60% reduction after consolidation, whereas the third
approach reduced the servers to 3, where it
represents a 70% consolidation.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have proposed three server
consolidation approaches namely, single server pure
random distribution, selective distribution and
multiple servers pure random distribution to
distribute the clients of a low-utilized server in an
existing enterprise information network (EIN). The
three methods are tested on EIN with 10 servers and
25 clusters, and the utilization of the EIN improves
by 42.45%, 34.55% and 65.2% respectively. The
experimental results show that the redesign
56.5
26
32.5
17
29
15.2
25.5
13.5
26
17.2
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
12345678910
Servers ID
Utilizatio
n
82
58.5
82
50.5
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
1345
Servers ID
Utilizatio
n
56.5
72.4
58.5
54
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
12910
Servers ID
Utilizatio
n
84.5
97
91.5
78
80
82
84
86
88
90
92
94
96
98
139
Servers ID
Utilizatio
n
ICORES 2012 - 1st International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
190

algorithm reduces total number of servers from 10
servers to 4 servers, by eliminating most of the
under-utilized servers, and thereby reduces the EIN
operational and maintenance costs with acceptable
performance.
REFERENCES
Abdulgafer, A. R., Marimuthu P. N. and Habib, S. J. 2010.
Redesign of Grid-Based Enterprise Information
Network through Servers Consolidation, In the
Proceedings of the 5th International Conference of
Computer Sciences and Convergence Information
Technology, Nov 30
th
to Dec 2
nd
, Seoul, South Korea.
Abdulgafer, A. R., Marimuthu P. N. and Habib, S. J.
2009. Network Redesign through Servers
Consolidation, In the Proceedings of the 11th
International Conference for Information Integration
and Web-based Application and Services, December
14-16, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Anselmi, J., Cremonesi, P., and Amaldi, E. 2009. On the
Consolidation of Data-Centers with Performance
Constraints, In the Proceedings of the 5th
International Conference on the Quality of Software
Architectures: Architectures for Adaptive Software
Systems, East Stroudsburg, PA, USA.
Cardosa, M., Korupolu, M., & Singh, A. 2009. Shares and
Utilities based Power Consolidation in Virtualized
Server Environments. IFIP/IEEE International
Symposium on Integrated Network Management, Long
Island, New York- USA, pp. 327-334.
Dhyani, K., Gualandi, & Cremonesi, P. 2010. A
Constraint Programming Approach for the Service
Consolidation Problem. The International Conference
on Integration of AI and OR Techniques in Constraint
Programming, pp. 97-101, Bologna, Italy:
SpringerLink.
Frantzeskakis, L. F., and Luss, H. 1999. The Network
Redesign Problem for Access Telecommunications
Networks, Naval Research Logistics, Wiley, New
York, vol. 46, pp. 487-506.
Gupta, R., Bose, S. K., Sundarrajan, S., Chebiyam, M.,
and Chakrabarti, A. 2008. A Two Stage Heuristic
Algorithm for Solving the Server Consolidation
Problem with Item-Item and Bin-Item Incompatibility
Constraints, In the proceedings of IEEE International
Conference on Services Computing, Honolulu,
Hawaii, USA, pp. 39-46.
Jerger, N., Vantrease, D., & Lipasti, M. 2007. An
Evaluation of Server Consolidation Workloads for
Multi-core Designs. The IEEE 10th International
Symposium on Workload Characterization, Boston,
Massachusetts, USA, pp. 47 – 56.
Kokkinos, P. Christodoulopoulos, K., Kretsis, A., and
Varvarigos, E. 2008. Data Consolidation: A Task
Scheduling and Data Migration Technique for Grid
Networks, In the Proceedings of the 8th IEEE
International Symposium on Cluster Computing and
the Grid, Lyon, France, pp. 722 – 727.
Kirkpatrick, S., Gelatt, C. D., and Vecchi, M. P. 1983.
Optimization by Simulated Annealing, Science, vol.
220, pp. 671-680.
Marty, M. R., and Hill, M. D. 2007. Virtual Hierarchies to
Support Server Consolidation, In the Proceedings of
the 34th Annual International Symposium on
Computer Architecture (ISCA), San Diego, California,
USA.
Short, J. E., Bohn, R. E., and Baru, C. 2011. How Much
Information, 2010 Report on Enterprise Server
Information, Published on April 2011: http://hmi.ucsd.
edu/pdf/HMI_2010_EnterpriseReport_Jan_2011.pdf
Speitkamp, P. B., and Bichler, M. 2010. A Mathematical
Programming Approach for Server Consolidation
Problems in Virtualized Data Centers, IEEE
Transactions on Services Computing, vol. 3, no. 4, pp.
266-278.
Spellman, A., Erickson, K., and Reynolds, J. 2003. Server
Consolidation Using Performance Modelling, IT
Professional, vol. 5, pp. 31-36.
Uddin, M., and Abdul Rahman, A. 2010. Server
Consolidation: An Approach to Make Data Centers
Energy Efficient & Green, International Journal of
Scientific & Engineering Research, vol. 1, pp. 1-7.
ENTERPRISE NETWORK REDESIGN THROUGH SERVER CONSOLIDATION
191
