
ON-LINE 3D BODY MODELLING FOR AUGMENTED REALITY
Luis Almeida
1,2
, Paulo Menezes
1
and Jorge Dias
1
1
Institute of Systems and Robotics, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Coimbra,
Coimbra, Portugal
2
Institute Polytechnic of Tomar, Tomar, Portugal
Keywords:
Augmented Reality, 3D Reconstruction, Tele-presence, Virtual View Synthesis.
Abstract:
Building 3D body models is an important task for virtual and augmented reality applications in tele-
rehabilitation, education, 3DTV, entertainment and tele-presence. We propose a real-time full 3D reconstruc-
tion system that combines visual features and shape-based alignment using low cost depth sensor and video
cameras targeting three-dimensional conferencing applications. With this approach we overcome the classic
video based reconstruction problem in low-texture or repeated pattern regions. Alignment between succes-
sive frames is computed by jointly optimizing over both appearances and shape matching. Appearance-based
alignment is done over 2D SURF features annotated with 3D position. Shape-based alignment is performed
using the motion transformation estimation between consecutive annotated 3D point clouds through a linear
method. A solution to avoid wrong annotated 3D matched points is proposed. 3D mesh model representation
is used to lower the processed data and create a 3D representation that is independent of view-point.
1 INTRODUCTION
Immersive virtual applications are common technolo-
gies nowadays demanding new human machine inter-
actions approaches. This paper presents an on-line
incremental 3D reconstruction framework that can be
used on mixed or augmented reality (AR) applications
based on tele-presence. The project intends to create
an affordable 3D acquisition and display system use-
ful for socialization and entertainment using low cost
depth sensors and video cameras. Exploring comput-
ers graphics, spatial audio and artificial vision, tech-
niques enable us to induce sensations of being phys-
ical in the presence of other people useful on sev-
eral domains like elderly loneness minimization prob-
lem(Lange et al., 2010), tele-rehabilitation(Kurillo
et al., 2011)(Rizzo and Kim, 2005), education, social-
ization, 3DTV, entertainment, tele-presence (Nahrst-
edt et al., 2011), etc.
Internet chat/audio/video conferencing programs
like Skype, VOIP, NetMeeting and phones have been
used for socialization, nevertheless they are not able
to create the remote person presence feeling. Means
of communications that enable eye contact, facial
expressions, body language, gestures reconnaissance
are required to avoid this sense of disconnectedness.
The concept goal is depicted on Figure 1. An example
scenario consist on a system providing immersive
tele-presence and natural representation of two re-
mote checker players in a friendly and shared mixed
reality space to enhance the quality of human-
centered communication. The example, based on the
principle of a shared virtual checkers board, tries to
describe the correct eye contact and gestures repro-
duction.
Figure 1: The concept explores computers graphics, spatial
audio and artificial vision techniques to induce sensations
of being physical in the presence. Checkers mixed reality
space example.
472
Almeida L., Menezes P. and Dias J..
ON-LINE 3D BODY MODELLING FOR AUGMENTED REALITY.
DOI: 10.5220/0003866304720479
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (GRAPP-2012), pages 472-479
ISBN: 978-989-8565-02-0
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Augmented reality and particularly tele-immersion
(Jung and Bajcsy, 2006)(Azuma et al., 2001)(Lanier,
2001) provides the technology means that enable
users to interact remotely while experiencing the
benefits of a real face-to-face meeting. The tele-
immersive technology integrates virtual reality for
rendering and display purpose, artificial vision for
image acquisition and 3D reconstruction, and vari-
ous networking technologies for transmitting data be-
tween distant sites in real-time without significant de-
lays. Virtual meeting spaces allows the possibility of
socialization, collaborative work on 3D data, 3DTV,
remote training and monitoring, and remote teaching
of physical activities (e.g., rehabilitation, dance).
Aiming an incremental on-line 3D human body
reconstruction solution useful for shared mixed re-
ality workspace (Aliakbarpour et al., 2011)(Kurillo
et al., 2008)(Petit et al., 2008)(Kurillo et al., 2011),
we estimate the 3D world information using 2D image
sequences and depth information using a depth cam-
era, e.g. a structured light camera or time of flight
camera (ToF). With this approach we overcome the
classic video based reconstruction problem in low-
texture or repeated pattern regions. The presented
real-time 3D full reconstruction system combines vi-
sual features and shape-based alignment. By detect-
ing image point features for which tri-dimensional
coordinates can be measured, a correspondence be-
tween 3D and 2D is established. Using those anno-
tated 3D points, between consecutive point clouds,
it is possible to estimate the motion transformation
through a linear, closed form or iterative method, reg-
ister them on one same referential and create a global
model. Correspondence between consecutive image
features in images is performed using SURF method
(Bay et al., 2006). Virtual view synthesis and mod-
eling is based on 3D mesh from dense depth maps in
order lower the data to be processed and to create a
3D mesh representation that is independent of view-
point.
Mesh simplification is performed reducing the
number of vertices’s and facets while keeping impor-
tant object features or interest points in the model.
The aim is to continuously generate a realistic body
model, transfer the model and reconstruct on a re-
mote common display or virtual environment accord-
ing each users viewpoint by a tracking process. Figure
2 presents an overview of the algorithm.
The existence of 3D human model that is incre-
mentally updated according the user movements low-
ers the computational scanning resources and stands
as an ideal data input solution for the emergent 3D
display technology. New display devices are now able
to provide a stereoscopic perception of 3-D depth to
RGB
Depth
RGB-D Camera
SURF Sparse Features
Dense Point Clouds
RGB-D Features
Rotation, Translation
SVD
Refine Transformation
RANSAC
Alignment
Point Clouds Maps
Mesh
Representation
Model
Figure 2: Algorithm overview. The proposed real-time
3D full reconstruction system combines visual features and
shape-based alignment between consecutive point clouds.
The model representation is updated incrementally.
the viewer either using head mounted displays, light
active shutter glasses, passive polarized glasses or
without glasses, using flat-panel auto stereoscopic so-
lutions employing lenticular lenses or parallax barri-
ers. Even with an accurate viewer’s head tracking and
images view dependent rendering on common screens
(ex: TV’s, LCD’s) is possible to create the illusion
of a real window. Our incremental on-line 3D hu-
man reconstruction solution should provide models
easily rendered on any of those referred display tech-
nologies. The reminder of this paper is organized as
follows. First a related work is presented on section
1.1 concerning the psychology nature of the sense of
presence followed by the technological approaches to
accomplish that. Section 2 describes the suggested
methodology and section 3 present some experimen-
tal results and discussion. Finally, section 4 presents
the future work and conclusions.
1.1 Background
Virtual reality (VR) and Augmented reality (AR) cre-
ates a sensory and psychological experience for users
as an alternative to reality (Bohil et al., 2009). The
more one can provide the system with sensory inputs
that simulate and effectively mimic those encountered
in nature, the more convincing the resulting percep-
tual and cognitive experience will be for the user (Bo-
hil et al., 2009). Immersive VR and AR perceptu-
ally surrounds the user, increasing his or her sense of
presence (Steuer, 1992) or actually being within it. In
immersive VR, sensory information is more psycho-
logically prominent and engaging than the sensory in-
formation gleaned from other types of media (Lanier,
2001)(Bailenson et al., 2008).
Virtual view synthesis and modeling are the po-
tential graphic tools to create the eye to eye con-
tact illusion on tele-presence communications(Isgro
et al., 2004) (Bohil et al., 2009). Real time 3D re-
construction approaches can be divided in three cat-
egories: silhouette-based reconstruction, voxel-based
methods with space sampling and image-based recon-
struction with dense stereo depth-maps. Usually the
body surface is reconstructed by merging sensors data
from different views. Two types of information are
ON-LINE 3D BODY MODELLING FOR AUGMENTED REALITY
473

required: depth data and sensor pose data. When
there is no prior information about depth and pose,
the reconstruction techniques bases on structure from
motion. On such cases, the sensor ego-motion esti-
mation is based on corresponding features found in
consecutive images. The depth information, without
absolute scale, is then computed using the obtained
ego-motion information. When depth information is
available a priori, but sensor pose is still unknown, us-
ing data resulting from a ToF or structured light depth
camera, a laser scanner or a stereo camera without
inertial sensors, the reconstruction techniques usually
bases on the Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithm
(Besl and McKay, 1992). 3D point clouds acquired
from different views are registered onto one same ref-
erential by iteratively matching overlap surfaces. This
method is computationally heavy for real time appli-
cations. When depth data and sensor pose data are
known a priori, no registration procedure is required
to merge the data onto a global referential. The pre-
cision of depth measurements and sensor pose esti-
mation act on the final surface reconstruction qual-
ity. Recent depth sensor devices provide precise 3D
measurements and also RGB data, enabling the use
of 2D image algorithms. It is possible to improve the
2D feature mapping between consecutive RGB im-
ages, associating the respective depth data and creat-
ing a 3D feature tracking. 2D image features mapping
approaches are generally based on Kanade-Lucas-
Tomasi (KLT) method (Shi and Tomasi, 1994), Scale-
Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) method (Lowe,
2004) or Speed Up Robust Features (SURF) method
(Bay et al., 2006). Several works use these techniques
to track 3D pose sensor changes either for object de-
tection, path planning, for gesture recognition or for
reconstruction purposes (Henry et al., 2010)(Mirisola
et al., 2007)(Akbarzadeh et al., 2006)(May et al.,
2009)(Menezes et al., 2011). Our work intends to per-
form a real-time incremental body modeling.
2 METHODOLOGY
We propose a real-time full 3D reconstruction sys-
tem that combines visual features and shape-based
alignment using Xbox Kinect device. Alignment
between successive frames is computed by jointly
optimizing over both appearance and shape match-
ing. Appearance-based alignment is done over 2D
SURF features annotated with 3D position. Al-
though SIFT descriptor present better accuracy, we
have choosen SURF method in order to achieve the
real-time characteristic. Shape-based alignment is
performed using the motion transformation estima-
tion between consecutive annotated 3D point clouds
through a linear method. There are several possible
closed form solutions for rigid body transformation
(Eggert et al., 1997): SVD (Arun et al., 1987)(Chal-
lis, 1995)(Eggert et al., 1997) or iterative methods like
Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) (Fischler and
Bolles, 1981)(Akbarzadeh et al., 2006)(Konolige and
Agrawal, 2008). Once obtained a 3D point model a
mesh is generated through Delaunay triangulation.
2.1 Registration
Suppose the existence of two corresponding 3D
points sets {x
t
i
} and {x
t+1
i
}, i = 1..N, from consec-
utive t and t + 1 scans, related through the following
equation (1):
x
t+1
i
= Rx
t
i
+ T +V
i
(1)
ε
2
=
N
∑
i=1
x
t+1
i
− Rx
t
i
− T
2
(2)
R represents a standard 3x3 rotation matrix, T stands
for a 3D translation vector and V
i
is a noise vector.
The optimal transformation [R,T] that maps the set
{x
t
i
} on to {x
t+1
i
} can be obtained through the mini-
mization of the equation (2) using a least square crite-
rion. The least square solution is the optimal transfor-
mation only if a correct correspondence between 3D
point sets is guaranteed. Complementary methods are
used to robust the correspondence (e.g. RANSAC).
The singular value decomposition (SVD) of a ma-
trix can be used to minimize Eq. (2) and obtain the
rotation (standard orthonormal 3x3 matrix) and the
translation (3D vector) (Arun et al., 1987)(Challis,
1995)(Eggert et al., 1997). In order to calculate ro-
tation first, the least square solution requires that {x
t
i
}
and {x
t+1
i
} point sets share a common centroid. With
this constraint a new of equation can be written using
the following definitions:
x
t
i
=
1
N
n
∑
i=0
x
t
i
x
t+1
i
=
1
N
n
∑
i=0
x
t+1
i
(3)
x
t
ci
= x
t
i
− x
t
i
x
t+1
ci
= x
t+1
i
− x
t+1
i
(4)
ε
2
=
N
∑
i=1
x
t+1
ci
− Rx
t
ci
2
(5)
Maximizing Trace(R H) enable us to minimize the
generated equation (5), with H being a 3x3 corre-
lation matrix defined by H = x
t+1
ci
(x
t
ci
)
T
. Consider-
ing that the singular value decomposition of H re-
sults on H=UDV
T
, then the optimal rotation matrix,
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
474

R, that maximizes the referred trace is R= U diag(1;
1; det(UV
T
)) V
T
:
R = UV
T
(6)
The optimal translation that aligns {x
t+1
i
} centroid
with the rotated {x
t
i
} centroid is
T = x
t+1
i
− Rx
t
i
(7)
2.2 Model Mapping
Suppose that the mapping from the world coordinates
to one of the scans of the sequence, is known (ex:
to scan 0) and it is represented by the transformation
0
H
w
. As described before, for any consecutive pair
of scans (t, t+1) from tracked points it is possible to
measure rotation and translation and combine them
into a single homogeneous matrix 4x4,
t+1
H
t
, H =
[R,T]. Therefore it is possible to compute equations:
i
H
0
=
i
H
i−1
i−1
H
i−2
... ..
1
H
0
and
i
H
w
=
i
H
0
0
H
w
To update the reconstructed model, each acquired 3D
point set is transformed to the world coordinate sys-
tem using
i
H
w
. This alignment step adds a new scan
to the dense 3D model. Alignment between succes-
sive frames is a good method for tracking the body
position over moderate distances.
2.3 Tracking and Registration Refining
SURF features are detected and matched over consec-
utive undistorted images. These features are invari-
ant to affine transformations, so they allow detection
of the feature points from different angles and range.
Although SURF provides good distinctive descrip-
tors, undesirable matches can occur related with back-
ground static areas and image body boundaries. To
overcome this situation it possible to define a work-
ing reconstruction space for the body and a mask for
the SURF algorithm. After finding the set of matched
image features, a correspondence between 2D and 3D
is set up. These annotated 3D points pairs are then
used to estimate the motion between two time consec-
utive point clouds. Assuming that the identification
problem has been solved, we must compute the rigid
transformation (rotation and translation) that align the
two consecutive 3D scans. The solution should take
in account that the data are typically affected by noise:
correspondences may be false, and some key data
patches may be partially occluded.
Registration Refining using RANSAC: False cor-
respondent point pairs that wrongly biases the rigid
body transformation estimation are removed using the
RANSAC method. The approach randomly samples
three 3D points correspondent pairs from consecutive
scans and iteratively estimates the rigid body transfor-
mation (Arun et al., 1987) until find enough consen-
sus or reach a maximum number of iteration based
on the probability of outliers. The procedure starts to
use a small initial data set and enlarges the number
of samples consistent with the model. K iterations
are performed while the eligible solution with highest
number of inliers, based on sum of the distances be-
tween pair of correspondent point, is selected as the
best transformation model. The K iterations number
follows equation (8):
K =
log(1 − p)
log(1 − (n
inliers
/N
pts
)
S
)
(8)
p stands for the desired probability of finding at
least one model transformation without outliers
within K iteration, n
inliers
is the number of eligibles
pairs of points that fit the current estimation, N
pts
represents the total number of pairs of points and S
is the minimum number of eligible samples to fit the
transformation model. Registration refining method
is described in algorithm 1.
Algorithm 1: Registration refining algorithm - Outliers re-
moval.
1: Input :X
p
,X
q
{assumed correspondent 3D point pairs}
2: Output :[R,t]
{rigid body transformation estimation}
3: while (i < MAXIT ER) do
4: randomly select 3 pairs of points
5: [R
i
,t
i
] ← estimate 6DOF rigid body transformation for these 3 pairs
6: X
0
q
= R
i
∗ X
q
+t
i
{apply the transformation to X
q
scan to map it into X
p
reference
frame}
7: inliers
i
= |(X
0
q
− X
p
) < τ|, number o f inliers
i
{determine the set of data points which are within a Euclidean dis-
tance threshold τ}
8: if (sizeo f (inliers
i
) > T
threshold
) then
9: [R,t] ← re-estimate the transformation model using all inliers
i
10: EX IT
11: end if
12: if (number o f inliers
i
> bestscore) then
13: bestscore ← number o f nliers
i
14: best inliers ← inliers
i
{store cardinality of inliers
i
and inliers
i
}
15: update MAXIT ER {using eq. 8}
16: end if
17: i = i +1
18: end while
19: [R,t] ← re-estimate the transformation model using all points from
best inliers
Virtual View Synthesis: On a 3D video conference,
the real eye contact is preserved while each partici-
pant observes the others from their current perspec-
ON-LINE 3D BODY MODELLING FOR AUGMENTED REALITY
475

tive. Each user viewpoint changes according his
movements around the shared meeting environment.
Therefore new perspectives views have to be pre-
sented at each time instant depending on the viewers
pose in front of the display. This requires a precise
estimation of the viewers pose in 3D space, which
can be accomplish by and head/body tracking mod-
ule. The selected approach is based on a facial feature
tracker using eye feature (Viola and Jones, 2001).The
purpose of use Haar-like features is to meet the real-
time requirement. The resulting eyes 2D position can
then be associated to 3D points for the calculation of
head 3D pose.
Algorithm 2: Model reconstruction algorithm.
1: Input :rgb images,depth images
2: Output :3D mesh model
3: initialize R
g
, t
g
, f
1
, f
1d
, f
1xyz
, f
1r
4: for (; ;) do
5: f
2
← undistort(adquire rgb image())
6: f
2d
← undistort(adquire depth image())
7: f
2xyz
← convert depth image to xyz data( f
2d
)
8: f
2r
← map rgbcolor to depth image( f
2xyz
, f
2
)
9: (sur f
1
,sur f
2
) ←
detect SURF f eatures( f
1r
, f
2r
)
10: matches2D ← SURF match(sur f
1
,sur f
2
)
11: matches3D ← correspond2D3D(matches2D)
12: [R,t] ← motion estimator(matches3D)
13: [R
g
,t
g
] ← update global trans f ormation(R,t)
14: f
1r
← f
2r
, f
1xyz
← f
2xyz
{update past data}
15: model ←
project points to world coordinates( f
2xyz
,R
g
,t
g
)
16: mesh model generation
17: end for
3 IMPLEMENTATION AND
RESULTS
Novel depth sensors like PrimeSense camera or Xbox
Kinect can capture video images along with per-pixel
depth information. To experimentally test the algo-
rithm we register several 3D point clouds in order to
create person model while he is rotating in front of
Kinect device.
Calibrations: The Kinect device combines a regu-
lar RGB camera and a 3D scanner, consisting of an
infrared (IR) projector and an IR camera (figure 7a).
A initial calibration step is required to undistort the
RGB and IR images, and to map depth pixels with
color pixels (6 DOF transform between RGB and IR
cameras) (Almeida et al., 2011).
Implementation: The system was developed us-
ing the C++ language, OpenCV library, OpenKinect
library, OpenAR framework (an augmented reality
framework under development on ISR-Coimbra) and
Ubuntu Linux v10.10.
Matching: On figure 3 we present an example of
correspondence between consecutive image features
using SURF method (white lines indicate correspon-
dent point). Some matches are undesirable and are
related with background static areas. Our solution is
to confine the reconstruction space with better limits
or develop a movement segmentation filter. The con-
tribution of erroneous matches is minimized by the
number of good matches while using the described
minimization method with outliers removal to obtain
the transformation.
Figure 3: SURF features matched on consecutive time
frames.
Outliers Removal: In order to analyze the regis-
tration refining improvement described on algorithm
1, we have measured the mean euclidean distance
between several consecutive registrations with and
with outliers removed after applying the transforma-
tion to X
q
scan that maps it into X
p
reference frame
(X
0
q
= R
i
∗ X
q
+ t
i
, |(X
0
q
− X
p
)|) (see figure 4). The
red balls line (without outliers) presents a much lower
error than considering all SURF matched point into
rigid body transformation. Figure 5, presents for each
consecutive rigid body transformation estimation the
total number of SURF matched points (blue bars) and
the number of inliers for that take (red bars).
Figure 4: Mean euclidean distance between several consec-
utive registrations with and without outliers removed.
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
476
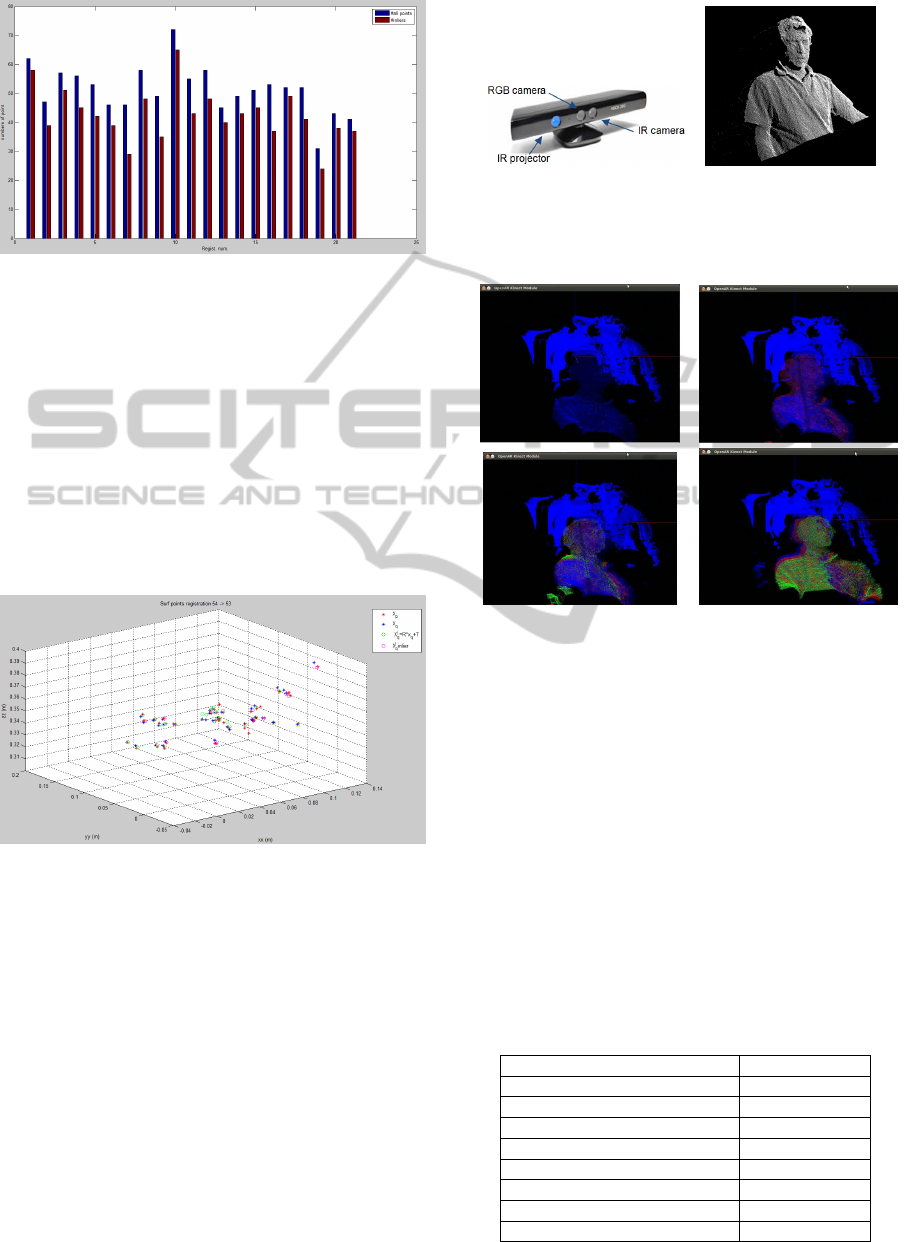
Figure 5: Number of points number (blue bars) vs Number
of inlier’s (red bars) on each registration.
Experimental results shows that considering a
high number of inliers (not all SURF point features)
makes the transformation estimation more robust and
increases the alignment accuracy. Figure 6 depicts
two correspondent 3D points sets, result from SURF
algorithm that should be aligned. After applying the
transformation to X
q
scan to map it into X
p
reference
frame we obtain a new set of points X
0
q
= R
i
∗ X
q
+ t
i
(green ball points). Applying the transformation to
inlier’s points only, we obtain magenta balls point.
Figure 6: Applying the transformation to X
q
scan to map it
into X
p
reference frame (X
0
q
= R
i
∗ X
q
+t
i
), result into green
ball for all points and magenta balls just for inliers.
3D Modeling: An example of off-line mesh genera-
tion, using unorganized kinect 3d points, is provided
on figure 7b. Delaunay triangulation computation re-
sults on 99334 vertices and 1223930 faces.
Figure 8 depicts a sequence of scans that creates a
3D person model. They result from several 3D point
clouds fused in real time after applying successive 3D
rigid body transformations.
Processing Time Measurements: Typically the
system has a performance of 2 HZ. The time consum-
ing stage is related with the surf feature extraction and
it takes an average of 300 ms. It depends on the num-
ber of detected good feature of the image, although
(a) (b)
Figure 7: a) Kinect Sensor b) Mesh model with 99334 ver-
tices and 1223930 faces.
Figure 8: 3D Model, real time sequence of point clouds be-
ing registered on the same referential, each color represent
time sequential scans.
we expect to speed up significantly this step by mak-
ing use of GPU. The involved number of points also
influences the transformation time calculus. On table
1 we present some typically time measure involving
some algorithm steps.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The future work also includes studies conducing to
a technological testbed that allow us to measure the
sense of presence. Our approach explores virtual view
Table 1: Processing time measurements.
Algorithm Steps (ms)
Acquisition 1.55
Undistort Images 10.61
DepthRGB Map and last frame update 36.13
SURF feature extraction 314.853
Matching and transformation calculus 78.0282
Alignment, display and interaction 30.377
Total 471.56 (f=2.12 Hz)
ON-LINE 3D BODY MODELLING FOR AUGMENTED REALITY
477

synthesis through motion body estimation and hybrid
sensors composed by video cameras and a low cost
depth camera based on structured-light. The solu-
tion addresses the geometry reconstruction challenge
from traditional video cameras array, that is, the lack
of accuracy in low-texture or repeated pattern region.
We present a full 3D body reconstruction system that
combines visual features and shape-based alignment.
Experimental results shows that considering a high
number of inliers (not all SURF point features) in-
creases the alignment accuracy. Modeling is based
on meshes computed from dense depth maps in order
lower the data to be processed and create a 3D mesh
representation that is independent of view-point. This
work presents an on-line incremental 3D reconstruc-
tion framework that can be used on low cost telep-
resence applications to enable socialization and en-
tertainment.
REFERENCES
Akbarzadeh, A., Frahm, J.-M., Mordohai, P., Clipp, B., En-
gels, C., Gallup, D., Merrell, P., Phelps, M., Sinha,
S. N., Talton, B., Wang, L., Yang, Q., Stew
´
enius, H.,
Yang, R., Welch, G., Towles, H., Nist
´
er, D., and Polle-
feys, M. (2006). Towards urban 3d reconstruction
from video. In 3DPVT, pages 1–8. IEEE Computer
Society.
Aliakbarpour, H., Almeida, L., Menezes, P., and Dias,
J. (2011). Multi-sensor 3d volumetric recon-
struction using cuda. 3D Research, 2:1–14.
10.1007/3DRes.04(2011)6.
Almeida, L., Menezes, P., Seneviratne, L., and Dias, J.
(2011). Incremental 3d body reconstruction frame-
work for robotic telepresence applications. In Robo
2011: The 2nd IASTED International Conference on
Robotics, Pittsburgh, USA.
Arun, K. S., Huang, T. S., and Blostein, S. D. (1987). Least-
squares fitting of two 3-d point sets. IEEE Trans. Pat-
tern Anal. Mach. Intell., 9:698–700.
Azuma, R., Baillot, Y., Behringer, R., Feiner, S., Julier, S.,
and MacIntyre, B. (2001). Recent advances in aug-
mented reality. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl., 21:34–
47.
Bailenson, J., Patel, K., Nielsen, A., Bajscy, R., Jung, S.-H.,
and Kurillo, G. (2008). The Effect of Interactivity on
Learning Physical Actions in Virtual Reality. Media
Psychology, 11(3):354–376.
Bay, H., Tuytelaars, T., and Gool, L. V. (2006). Surf:
Speeded up robust features. In In ECCV, pages 404–
417.
Besl, P. J. and McKay, N. D. (1992). A method for registra-
tion of 3-d shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach.
Intell., 14:239–256.
Bohil, C., Owen, C., Jeong, E., Alicea, B., and Biocca, F.
(2009). Virtual Reality and presence, 21st Century
Communication: A reference handbook. SAGE Pub-
lications, Inc.
Challis, J. (1995). A procedure for determining rigid body
transformation parameters. Journal of Biomechanics,
28(6):733–737.
Eggert, D. W., Lorusso, A., and Fisher, R. B. (1997). Esti-
mating 3D rigid body transformations: a comparison
of four major algorithms. MAchine Vision and Appli-
cations, 9:272–290.
Fischler, M. A. and Bolles, R. C. (1981). Random sample
consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with appli-
cations to image analysis and automated cartography.
Commun. ACM, 24:381–395.
Henry, P., Krainin, M., Herbst, E., Ren, X., and Fox, D.
(2010). RGB-D Mapping: Using Depth Cameras for
Dense 3D Modeling of Indoor Environments. In RSS
Workshop on Advanced Reasoning with Depth Cam-
eras.
Isgro, F., Trucco, E., Kauff, P., and Schreer, O. (2004).
Three-dimensional image processing in the future of
immersive media. Circuits and Systems for Video
Technology, IEEE Transactions on, 14(3):288 – 303.
Jung, S.-H. and Bajcsy, R. (2006). A framework for con-
structing real-time immersive environments for train-
ing physical activities. Journal of Multimedia, 1(7):9–
17.
Konolige, K. and Agrawal, M. (2008). Frameslam:
From bundle adjustment to real-time visual mapping.
Robotics, IEEE Transactions on, 24(5):1066 –1077.
Kurillo, G., Koritnik, T., Bajd, T., and Bajcsy, R. (2011).
Real-time 3d avatars for tele-rehabilitation in virtual
reality. Stud Health Technol Inform, 163:290–6.
Kurillo, G., Vasudevan, R., Lobaton, E., and Bajcsy, R.
(2008). A framework for collaborative real-time 3d
teleimmersion in a geographically distributed environ-
ment. In Multimedia, 2008. ISM 2008. Tenth IEEE
International Symposium on, pages 111 –118.
Lange, B., Requejo, P., Flynn, S., Rizzo, A., Valero-Cuevas,
F., Baker, L., and Winstein, C. (2010). The potential
of virtual reality and gaming to assist successful aging
with disability. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
Clinics of North America, 21(2):339 – 356.
Lanier, J. (2001). Virtually there. j-SCI-AMER, 284(4):66–
75.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-
invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 60:91–
110.
May, S., Droeschel, D., Holz, D., Fuchs, S., Malis,
E., N
¨
uchter, A., and Hertzberg, J. (2009). Three-
dimensional mapping with time-of-flight cameras. J.
Field Robot., 26:934–965.
Menezes, P., Lerasle, F., and Dias, J. (2011). Towards hu-
man motion capture from a camera mounted on a mo-
bile robot. IVC, 29(6):382–393.
Mirisola, L. G. B., Lobo, J., and Dias, J. (2007). 3d map
registration using vision/laser and inertial sensing. In
EMCR.
Nahrstedt, K., Yang, Z., Wu, W., Arefin, M. A., and Rivas,
R. (2011). Next generation session management for
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
478

3d teleimmersive interactive environments. Multime-
dia Tools Appl., 51(2):593–623.
Petit, B., Lesage, J.-D., Franco, J.-S., Boyer, E., and Raf-
fin, B. (2008). Grimage: 3d modeling for remote col-
laboration and telepresence. In ACM Symposium on
Virtual Reality Software and Technology.
Rizzo, A. A. and Kim, G. J. (2005). A swot analysis of the
field of virtual rehabilitation and therapy. Presence,
14(2):119–146.
Shi, J. and Tomasi, C. (1994). Good features to track. In
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1994. Pro-
ceedings CVPR ’94., 1994 IEEE Computer Society
Conference on, pages 593 –600.
Steuer, J. (1992). Defining virtual reality: Dimensions de-
termining telepresence. JOURNAL OF COMMUNI-
CATION, 42:73–93.
Viola, P. and Jones, M. (2001). Rapid object detection using
a boosted cascade of simple features. In Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition, 2001. CVPR 2001. Pro-
ceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Confer-
ence on, volume 1, pages I–511 – I–518 vol.1.
ON-LINE 3D BODY MODELLING FOR AUGMENTED REALITY
479
