
THREE DIFFERENTIAL EMOTION CLASSIFICATION
BY MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS
USING PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNALS
Discriminantion of Emotions by Machine Learning Algorithms
Eun-Hye Jang
1
, Byoung-Jun Park
1
, Sang-Hyeob Kim
1
and Jin-Hun Sohn
2
1
BT Convergence Technology Research Department, Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute,
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2
Department of Psychology/Brain Research Institute, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Keywords: Emotion classification, Machine learning algorithm, Physiological signal.
Abstract: In HCI researches, human emotion classification has done by machine learning algorithms based on
physiological signals. The aim of this study is to classify three different emotional states (boredom, pain,
and surprise) by 5 machine learning algorithms using features extracted from physiological signals. 200
college students participated in this experiment. The audio-visual film clips were used to provoke emotions
and were tested their appropriateness and effectiveness. EDA, ECG, PPG, and SKT as physiological signals
were acquired for 1 minute before each emotional state as baseline and for 1-1.5 minutes during emotional
state and were analyzed for 30 seconds from the baseline and the emotional state. 23 parameters were
extracted from these signals: SCL, NSCR, mean SCR, mean SKT, maximum SKT, sum of negative SKT,
and sum of positive SKT, mean PPG, mean RR interval, standard deviation RR interval, mean BPM,
RMSSD, NN50, percenet of NN50, SD1, SD2, CSI, CVI, LF, HF, nLF, nHF, and LF/HF ratio. For emotion
classification, the difference values of each feature subtracting baseline from the emotional state were used
for analysis using 5 machine learning algorithms. The result showed that an accuracy of emotion
classification by SOM was lowest and SVM was highest. This could help emotion recognition studies lead
to better chance to recognize various human emotions by using physiological signals. Also, it is able to be
applied on human-computer interaction system for emotion detection.
1 INTRODUCTION
Emotion recognition in studies on human-computer
interaction is the one of topic that researcher are
most interested in. To recognize human's emotions
and feelings, various physiological signals have been
widely used to classify emotion (Wagner, Kim, &
Andre, 2005), because signal acquisition by non-
invasive sensors is relatively simple and
physiological responses are less sensitive in social
and cultural difference (Drummond & Quah, 2001).
Also, it is known that physiological responses are
significantly correlated with human emotional state.
Many studies have reported relation between
emotion and physiological responses and mainly
focused on physiological responses induced by basic
emotions such as happiness, sadness, anger, fear,
and disgust (Ax, 1953; Boiten, 1996; Kanade &
Tian, 2000; Palomba, Sarlo & Angrilli, 2000). On
the other hand, other emotions such as boredom,
pain and surprise have been least investigated and
reported by single-channel physiological signal such
as respiratory (de Melo, Kenny & Gratch, 2010;
Flor, Knost & Birbaumer, 2002; Jolliffe & Nicholas,
2004). But it is needed to study the emotion
classification using multi-channel physiological
signals because emotion is related to other signal
such as GSR, EMG, HR, Cortisol response, etc.
Recently, although emotion recognition based on
physiological signals was performed by various
algorithms such as FP (Fisher Projection), SFFS
(Sequential Floating Forward Search), KNN (k-
Nearest Neighbor algorithm), and SVM (Support
Vector Machines), it needed to study for
development of methods and algorithm to exactly
classify some emotion.
528
Jang E., Park B., Kim S. and Sohn J..
THREE DIFFERENTIAL EMOTION CLASSIFICATION BY MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS USING PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNALS - Discriminantion
of Emotions by Machine Learning Algorithms.
DOI: 10.5220/0003880605280531
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2012), pages 528-531
ISBN: 978-989-8425-95-9
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
The purpose of this study was to classify three
different emotions (boredom, pain, and surprise) by
using multi-channel physiological signals. Surprise
emotion may be divided into ‘wonder’ that people
feel when perceiving something rare or unexpected
(Collet et al., 1997), and ‘startle’ response to a
sudden unexpected stimulus such as a flash of light,
a loud noise, or a quick movement near the face
(Nasoz et al., 2004; Verhoef et al., 2009). In this
study, ‘startle’ surprise emotion was induced by
emotional stimuli and 5 machine learning
algorithms, linear discriminant function (LDF),
classification and regression tree (CART), self
organizing map (SOM), Naïve Bayes and support
vector machine (SVM) for emotion classification
were used.
2 METHODS FOR EMOTION
CLASSIFICATION
200 college students (mean age: 21.7years ± 2.3)
participated in this experiment. They reported no
history of medical illness due to heart disease,
respiration, or central nervous system disorder or
psychotropic medication. They were introduced to
the experiment protocols and filled out a written
consent before the beginning of experiment. Also,
they were paid $30 USD per session to compensate
for their participation.
The audio-visual film clips that had been tested
their appropriateness and effectiveness were used to
provoke three different emotions (Figure 1). The
appropriateness of emotional stimuli means the
consistency between the emotion designed to
provoke each emotion and the category (e.g., boring,
painful, and surprising) of participants’ experienced
emotion. The effectiveness was determined by the
intensity of emotions that participants rated on a 1 to
7 point Likert-type scale (e.g.., 1 being “least bring”
or “painful” and 7 being “most boring” or
“painful”).
Figure 1: The example of emotional stimuli.
The apporiateness and effectiveness of these stimuli
were as follows; boredom had appropriateness of
86.0% and effectiveness of 5.23±1.36, the results
showed appropriateness of 97.3% and effectiveness
of 4.96±1.34 in pain and appropriateness of 94.1%
and effectivess of 6.12±1.14 in surprise.
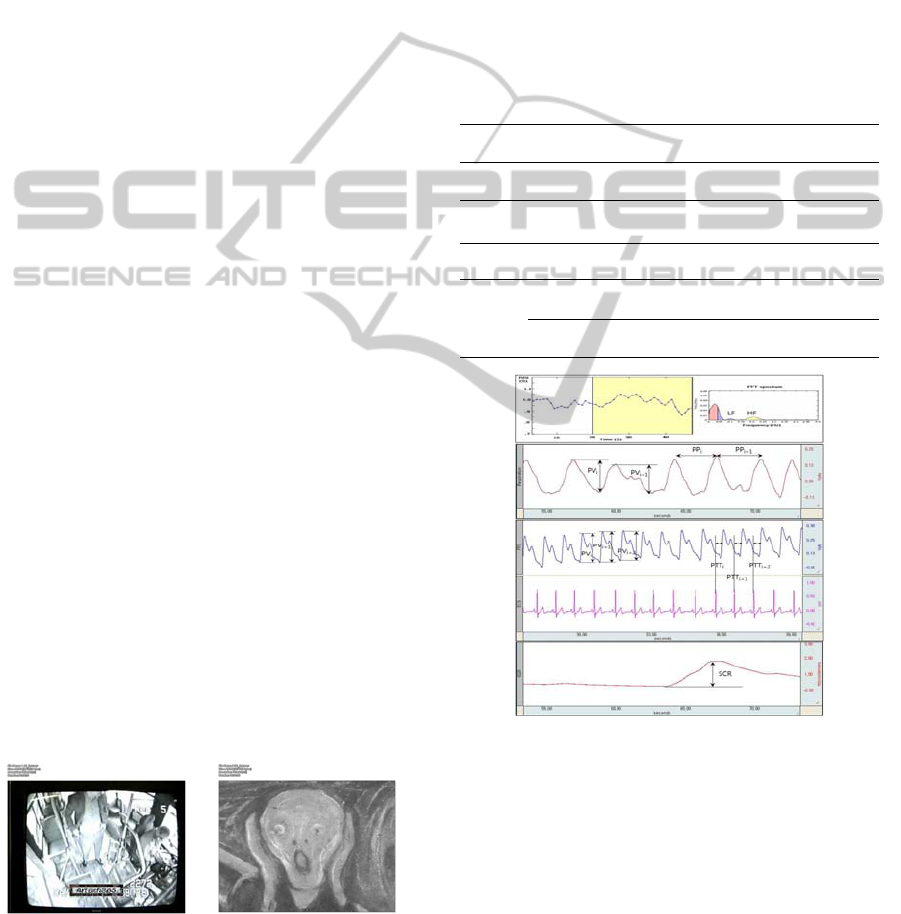
EDA, ECG, PPG, and SKT were acquired by
MP150 Biopac system Inc. (USA) during 1 minute
long baseline prior to the presentation of emotional
stimuli and for 1 to 1.5 min long while participants
watch emotional stimuli as emotional state. The
obtained signals were analyzed for 30 sec from the
baseline and the emotional state by AcqKnowledge
(Ver. 3.8.1) software (USA). Total 23 features were
extracted from these signals (Table 1).
Table 1: Features extracted from physiological signals.
signal feature
EDA SCL, NSCR, mean SCR
SKT
mean SKT, maximum SKT, sum of negative SKT,
sum of positive SKT
PPG Mean PPG
ECG
time domain
mean RRI, std RRI, mean HR,
RMSSD, NN50, pNN50, SD1, SD2,
frequency
domain
LF, HF, nLF, nHF, LF/HF ratio
Figure 2: The example of feature extraction.
To identify the difference of physiological
signals between baseline and emotional state,
statistical analysis were done as paired t-test (SPSS
16.0). And for emotion classification, five different
machine learning algorithms were applicated by
difference values substracting signals of baseline
from emotional state. The used algorithms are as
follows; LDA which is one of the linear models,
CART of decision tree model, SOM of Neural
Network, Naïve Bayes of probability model, and
SVM of non-linear model, which are used the well-
THREE DIFFERENTIAL EMOTION CLASSIFICATION BY MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS USING
PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNALS - Discriminantion of Emotions by Machine Learning Algorithms
529
known emotion algorithms.
3 RESULTS OF EMOTION
CLASSIFICATION
The result of difference between baseline and each
emotional state showed that physiological responses
during emotional states were significantly differed
from baseline (Table 2). Boredom significantly
differed from baseline in SCL, NSCR, meanSCR,
s_n SKT, meanRRI, stdRR, meanHR, and SD2. The
features of SCL, NSCR, mean SCR, s_n SKT, s_p
SKT, meanPPG, stdRR, RMSSD, NN50, pNN50,
SD1, SD2, CVI, and LF during painful state showed
significant difference from baseline. In surprise,
there were significant differences between baseline
and emotional state at all parameters except for max
SKT and LF, HF, nLF, nHF, and LF/HF ratio.
Table 2: The result of difference between baseline and
emotional states.
emotion
p
arameter
boredom pain surprise
SCL 2.59* 5.53*** 14.36***
NSCR 3.55*** 11.64*** 10.75***
meanSCR 2.68** 8.45*** 7.45***
meanSKT 0.20 -1.05 2.04*
s_n SKT -2.49* -9.93*** -4.62***
s_p SKT -1.75 -5.86*** -4.84***
meanPPG 0.93 2.66** -4.64***
meanRRI -3.11** -0.44 -4.29***
stdRR 2.00* 2.97** 5.43***
meanHR 3.00** 0.93 3.32**
RMSSD 1.31 3.21** 3.45**
NN50 -0.16 4.19*** 5.95***
pNN50 -0.42 4.10*** 4.72***
SD1 1.11 3.09** 3.68***
SD2 2.07* 2.71** 5.73***
CSI 0.65 -1.30 5.56***
CVI 1.68 4.10*** 9.66***
LF 1.48 2.78** 1.49
* p < .05, ** p < .01, *** p < .001
23 features extracted from physiological signals
were applied to emotion classification algorithms for
emotion classification of 3 emotions. Table 3 shows
the result of emotion classification by 5 algorithms.
Table 3: Result of emotion classification.
algorithm accuracy (%) features (N)
LDA 78.6 23
CART 93.3 23
SOM 70.4 23
Naïve Bayes 83.4 23
SVM 100.0 23
In analysis of LDA, accuracy of all emotions was
78.6% and in each emotion, boredom was
recognized by LDA with 77.3%, pain 80.0%, and
surprise 78.6% (Table 4). CART provided accuracy
of 93.3% when it classified all emotions. In
boredom, accuracy of 94.3% was achieved with
CART, 95.9% in pain, and 90.1% in surprise (Table
5). The result of emotion classification using SOM
showed that according to orders of boredom, pain,
and surprise, recognition accuracy of 80.1%, 65.1%,
and 66.2% were obtained by SOM (Table 6).
Table 4: Result of emotion classification by LDA.
boredom pain surprise total
boredom
77.3 4.5 18.2
100.0
pain
1.2 79.9 18.9
100.0
surprise 4.2 17.2 78.6 100.0
Table 5: Result of emotion classification by CART.
boredom pain surprise total
boredom
94.3 1.1 4.5
100.0
pain
1.2 95.9 3.0
100.0
surprise 5.7 4.2 90.1 100.0
Table 6: Result of emotion classification by SOM.
boredom pain surprise total
boredom
80.1 5.1 14.8
100.0
pain
7.7 65.1 27.2
100.0
surprise 13.0 20.8 66.2 100.0
The accuracy of Naïve Bayes algorithm to classify
all emotion was 83.4%. And each emotion was
recognized by Naïve Bayes with 84.7% of boredom,
82.8% of pain, and 84.4% of surprise (Table 7).
Finally, accuracy of SVM was 100.0% and
classifications of each emotion were 100.0% in all
emotions (Table 8).
Table 7: Result of emotion classification by NAÏVE BAYES.
boredom pain surprise total
boredom
84.7 0.6 14.8
100.0
pain
1.2 82.8 16.0
100.0
surprise 5.2 10.4 84.4 100.0
ICAART 2012 - International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
530

Table 8: Result of emotion classification by SVM.
boredom pain surprise total
boredom
100.0 0.0 0.0
100.0
pain
0.0 100.0 0.0
100.0
surprise 0.0 0.0 100.0 100.0
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study was to classify three different emotional
states (boredom, pain, and surprise) by machine
learning algorithms using physiological features.
Our results showed that physiological responses of
three emotions were differed and SVM were the best
algorithm for classification of three emotions. This
result could help emotion recognition studies lead to
better chance to recognize human emotions by using
physiological signals. Also, it can be useful in
profiling various emotion-specific physiological
responses or establishing the basis for emotion
recognition system in human-computer interaction.
However, this result was the classification
accuracy using only training set which didn’t divide
training and test sets. An average accuracy of
classification is necessary for repeated sub-sampling
validation using training and test sets as the choice
of training and test sets can affect the results.
Therefore, we will perform the average classification
in further analysis. Also, although it is known that
physiological signals offer a great potential for the
recognition of emotions in computer systems, in
order to fully exploit the advantages of physiological
measures, standardization needs to be established on
the emotional model, stimulus used for the
identification of physiological patterns,
physiological measures, parameters for analysis, and
model for pattern recognition and classification
(Arroyo-Palacios & Romano, 2008).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by the Converging
Research Center Program funded by the Ministry of
Education, Science and Technology (No. 2011K000
655 and 2011K000658).
REFERENCES
Wagner, J., Kim, J., Andre, E., 2005. From physiological
signals to emotions: Implementing and comparing
selected methods for feature extraction and
classification, IEEE International Conference on
Multimedia and Expo, Amsterdam, pp. 940-943.
Drummond, P. D., Quah, S. H., 2001. The effect of
expressing anger on cardiovascular reactivity and
facial blood flow in Chinese and Caucasians,
Psychophysiology, vol. 38, pp. 190-196.
Ax, A. R., 1953. The physiological differentiation between
fear and anger in humans, Psychosomatic Medicine,
vol. 15, pp. 147-150.
Boiten, F. A., 1996. Autonomic response patterns during
voluntary facial action, Psychophysiology, vol. 33, pp.
123-131.
Kanade, T. C., Tian, Y., 2000. Comprehensive database
for facial expression analysis, Proceeding of the 4th
IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face
and Gesture Recognition, pp. 46-53.
Palomba, D., Sarlo, M., Angrilli, A., Mini, A., 2000.
Cardiac responses associated with affective processing
of unpleasant film stimulus, International Journal of
Psychophysiology, vol. 36, pp. 45-57.
de Melo, C. M., Kenny, P. G., Gratch, J., 2010. Influence
of autonomic signals on perception of emotions in
embodied agents, Applied Artificial Intelligence, vol. 6,
pp. 494-509.
Flor, H., Knost, B., Birbaumer, N., 2002. The role of
operant conditioning in chronic pain: an experimental
investigation pain, Pain, vol. 95(1-2), pp. 111-118.
Jolliffe, C. D., Nicholas, M. K., 2004. Verbally reinforcing
pain reports: an experimental test of the operant model
of chronic pain, Pain, vol. 107(1-2), pp. 167–175.
Collet, C., Vernet-Maury, E., Delhomme, G., Dittmar, A.,
1997. Autonomic nervous system response patterns
specificity to basic emotions, Journal of the
Autonomic Nervous System, vol. 62, pp. 45-57.
Nasoz, F., Alvarez, K., Lisetti, C. L., Finkelstein, N., 2004.
Emotion recognition from physiological signals using
wireless sensors for presence technologies, Cognition,
Technology and Work, vol. 6, pp. 4-14.
Verhoef, T., Lisetti, C., Barreto, A., Ortega, F., Zant, T.,
Cnossen, F., 2009. Bio-sensing for emotional
characterization without word labels, Human-
Computer Interaction: Ambient, ubiquitous and
intelligent interaction, 13th International Conference,
San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 693-702.
Arroyo-Palacios, J., Romano, D. M., 2008. Towards a
standardization in the use of physiological signals for
affective recognition systems, Proceedings of
Measuring Behavior 2008.
THREE DIFFERENTIAL EMOTION CLASSIFICATION BY MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS USING
PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNALS - Discriminantion of Emotions by Machine Learning Algorithms
531
