
DISTRIBUTED TEAM FORMATION
FOR HUMANOID ROBOT SOCCER
Onuralp Ulusoy and Sanem Sariel-Talay
Department of Computer Engineering, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul, Turkey
Keywords: RoboCup competitions, Humanoid robot soccer, Team strategy, Multi-robot cooperation, Distributed team
formation.
Abstract: In this paper, we propose an adaptive team formation strategy for humanoid robot soccer. The proposed
strategy involves distributed cooperative decisions through both communication and observations. Two
agent groups, namely defenders and attackers, are formed by a case-based group formation method.
Attackers are formed for constructing an attacking formation around the ball and scoring a goal whenever
possible while defenders are for blocking and constructing a defensive obstacle against the opponent team.
Cooperative decisions are made using communication among team members. Distribution of agents on the
field is ensured by Voronoi cell construction of each agent through observations in a distributed manner.
Experiments are set in the RoboCup 3D Soccer Simulation League environment where our method is
compared to earlier team formation methods. The results illustrate that a distributed Voronoi cell
construction method combined with a case-based grouping algorithm outperforms the others. Furthermore,
it has been shown that our method is also robust to communication failures.
1 INTRODUCTION
RoboCup competitions provide convenient tools to
test and validate multi-agent team strategies.
Specifically, simulation competitions are suitable for
analyzing complicated team strategies in the face of
realistic constraints such as limitations on
observability, communication and teleoperation.
This paper presents a team formation approach for
humanoid soccer teams which deal with both
competition and cooperation issues. Just like real
soccer games, the main objective of a humanoid
soccer team is scoring goals against an opponent
team. Efficiency of cooperation is an important key
factor to win a game. There are mainly two
behaviors which involve cooperation issues, namely,
passing the ball to a teammate or spreading out to
the field of play to gain control of the ball whenever
needed. Both behaviors require agents to be in
appropriate positions to achieve the desired
outcomes. These positions usually belong to special
formations which may dynamically change their
shapes for different situations during a game. The
performance of the overall team is highly dependent
on these adaptive formations and the corresponding
positions of robotic agents. Contrary to human
soccer games, there are not generic formations for
humanoid soccer especially because these are also
dependent on the underlying motion model.
Therefore, the set of mobility constraints of a team
plays an important role in the selection of an
appropriate team strategy.
We propose an adaptive team formation strategy
which can be applied to robot soccer. However, the
focus of this paper is on the RoboCup 3D simulated
humanoid soccer competitions. Our team strategy is
used in the top layer of the software for team
beeStanbul (Asta et al., 2011) for RoboCup 3D
Soccer Simulation League (SSL). Experiments are
set in the RoboCup 3D SSL Environment, Simspark
(Simspark Official Website, 2011). Simspark
provides an environment for multiplayer soccer
games of two competing teams of simulated
autonomous humanoid agents (RoboCup 2011 3D
Simulation League hosted 9 x 9 agent games on a
21x14 m field.). The team scores more goals in a
ten-minute-long match wins the game. Simspark
uses ODE (Open Dynamics Engine) for physical
agent simulation of Nao humanoid robots by
Aldebaran Robotics (Aldebaran Robotics Official
Website, 2011). The real Nao robot has a height of
57 cm, a weight of 4,5 kg and 22 degrees of
605
Ulusoy O. and Sariel-Talay S..
DISTRIBUTED TEAM FORMATION FOR HUMANOID ROBOT SOCCER.
DOI: 10.5220/0003881006050613
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (SSIR-2012), pages 605-613
ISBN: 978-989-8425-95-9
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

freedom. The robot is equipped with special sensors
including a gyroscope, an accelerometer and a force
resistance perceptor on each foot. Simspark can
simulate all these features and model some realistic
limitations including sensor and actuator noise. The
simulator also provides limited communication
among robots through special effectors and
perceptors and visual information in the form of
noisy distance and angle values for the objects in the
viewpoint of agents.
Some rules of humanoid soccer are different
from real soccer due to the limitations of mobility of
agents. At present, fouls are not penalized in the
RoboCup 3D SSL but crowding the ball. According
to the crowding rule, at most two players are
allowed to be in the 0.8 m radius circle around the
ball; only a single player from a team in a circle with
a radius of 0.4 m and at most two teammates in a
circle with a radius of 1 m. Failure to comply with
either of these rules results in a repositioning of an
agent out of the field. All these rules should be taken
into account in the team strategy for avoiding any
penalties.
Our proposed approach considers the mentioned
rules to escape from penalties. According to our
strategy, robots can be in four different roles,
namely, goalkeeper, defender, midfielder and
forward. Forward and goalkeeper roles have their
own planners. Midfielder and defender roles share
the same planner but they differ in positioning on the
field. Goalkeeper is a static role which is assigned to
an agent for the entire match. The forward role is
assigned dynamically based on a voting mechanism
through communication. Each agent sends its time
cost to be able to control the ball and determine
whether it can be in the forward role based on the
information from the incoming messages and a self-
calculation.
Two groups (attackers and defenders) are formed
with a case-based group formation method and the
remaining roles are assigned based on the messages
from the team’s captain (goalkeeper is selected as
the captain due to its widest viewpoint). When there
is a failure in communication, agents decide on their
roles based on only observations.
The attackers group involves the forward agent
and the midfielders. Attackers usually target to
control the ball and score a goal, while defenders
prevent the opponent from scoring. Team formation
is shaped by the positions of defender or midfielder
agents. These agents calculate their next positions
based on a distributed Voronoi cell construction
which is the main contribution of this work. Voronoi
cell decomposition method is previously applied to
robot soccer. However, our method differs from
earlier work in the construction of cells both as the
calculation and the way the overall diagram is
formed. First, there is no supervision of cell
construction which is performed in a completely
distributed manner. Second, our method neither
relies on communication nor need a high
communication bandwidth among agents. However,
if communication is available, this channel is also
used to improve the solution quality. Since the
approach is not heavily dependent on explicit
communication, failures in communication could
also be handled. This feature is especially useful in
real-world settings. Another contribution of our
method lies in the automatic online determination of
targets for agents. Therefore, there is no need to
previously determine special formations.
This paper’s structure is as follows: Section 2
reviews earlier work in the field. Section 3 presents
the main team strategy for robotic soccer games and
the proposed procedures: the case-based group
formation approach and the distributed adaptive
formation. Experimental results and performance
analysis of the approach in terms of ball possession
ratio and use of communication are presented in
Section 4. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Dynamic team formation problem has been
investigated in earlier work for both humanitarian
and military applications (Balch and Arkin, 2000;
Stone and Veloso, 1999). Successful results of these
works have been used in RoboCup environments as
well (Candea, Hu, Iocchi, Nardi and Piaggio, 2011;
Nair, Tambe and Marsella, 2003; Röfer, 2003).
Multirobot coordination approaches used in
RoboCup environments mostly rely on continuous
communication among agents. However, RoboCup
3D SSL doesn’t provide a supervisor and
communication among agents is limited.
Several team formation algorithms were applied
in RoboCup soccer competitions (Dashti et al., 2006;
Nakanishi, Murakami and Naruse, 2008; Reis, Lau
and Oliviera, 2001; Ros, Arcos, de Mantaras and
Veloso, 2009). Dashti et al. (2006) use Voronoi cells
to position and distribute players in the field for
RoboCup 2D SSL. With this method, each agent
calculates its own Voronoi cell and moves to the
center of its own cell. Dynamically calculating the
cells ensures the agents to scatter throughout the
field. After the distribution is achieved, agents move
to better positions by attraction vectors and calculate
ICAART 2012 - International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
606

their Voronoi cells dynamically to be distributed in
the field again. Even though this method is efficient
for fast-moving 2D soccer agents, slower humanoid
agents in 3D SSL should maintain proximity to each
other in order to gain control of the ball quickly
when it is lost. Therefore, distributing the agents
throughout the field may not result in the desired
outcome in 3D SSL.
Nakanishi et al. (2008) propose Dominant
Region (DR) diagrams to create a formation. DR
diagrams look like Voronoi diagrams, but the
required calculation is based on the arrival time of
all agents to their future positions. Each agent forms
its region based on an area where it can reach to
faster than its teammates. Players can move in their
regions in order to be positioned on the field. With
this approach, the agent which is closest to the ball
approaches to the ball and the others can follow it
while staying in their dominant regions. This method
can be useful in 3D humanoid soccer but needs a
supervisor or a high communication bandwidth
among the agents to calculate a general DR diagram.
Therefore, it may not be suitable for environments
with limited communication.
Situation Based Strategic Positioning (SBSP)
(Reis et al., 2001) is another team formation
approach which uses game information including the
current position of the agent and its current role, the
selected formation for the team and the positions of
others. Maintaining this information, agents move to
their positions according to their roles. This method
requires dynamically assigning roles to the agents
during the game. SBSP suffers from a complicated
rule-based algorithm to reach a final formation in
non-deterministic and noisy environments like
RoboCup 3D SSL due to the computation
requirements.
Forming groups in the team usually results in
better team performance. Ayanian, Kumar and
Koditschek (2011) introduce a method which
coordinates the agents within each group by explicit
communication. Forming groups with optimal
number of agents can prevent unnecessary crowds.
Therefore, agents in different groups can achieve
multiple tasks which might help completing those
tasks faster. While inter-group communication is
kept limited, intra group communication demands
are high.
Ros et al. (2009) propose a Case-Based
Reasoning (CBR) method to position the agents.
Cases represent both the action sequences and the
formations by keeping the game situations including
positions of the agents, game time, current score etc.
CBR is an applicable formation method but in some
of the CBR methods, the cases should be hand-
coded before and usually the number of them is
limited. Some of the CBR approaches update their
case libraries in runtime to modify cases but this is a
costly process.
Our approach uses Voronoi cell decomposition
as in Dashti et al. (2006) but differs from this
approach by its initial frame construction and its
adaptability based on the ball location. The objective
is not spreading out all players on the field but
constructing a formation around the ball to easily
possess it whenever possible.
3 DISTRIBUTED TEAM
STRATEGY
The proposed distributed team formation strategy
involves four sequential processes to determine a
target for an agent. Figure 1 presents the main
modules for the team strategy. Initially two groups,
namely attackers and defenders, are formed by using
a Case-Based group formation strategy (Aamodt and
Plaza, 1994). The role of each agent is determined
based on these groups. The attackers group involves
the forward and the midfielder agents while the
defenders group involves only the defender agents.
Our adaptive formation method relies on the
construction of Voronoi cells, which are generated
distinctly by each agent that has the role of
midfielder or defender. The centers of these cells
form the initial targets for these agents. Target
locations are finalized by applying Potential Fields
Method (Arkin, 1998) for obstacle avoidance and
path planning. Because controlling the ball is crucial
in soccer, its location is used in cell initialization and
forming groups. All agents except goalkeeper
continuously send their time costs to control the ball
and they decide on the forward agent role according
to the incoming cost information and a self-
calculation.
The Partial Fourier Series (PFS) model is used as
the motion model for our RoboCup 3D SSL
beeStanbul team software (Asta and Sariel-Talay,
2011). Different types of body motions, including
straight walks (forward, back, diagonal and side
walk), inward turn, outward turn, rotate, kick and
stand-up are available for agents. Based on the
assigned role of an agent, the corresponding planner
is activated. Each plan has a set of behaviors which
activate a set of motions. Figure 2 shows the
decomposition of an example plan (dribble-to-goal)
for an agent that has the forward role.
DISTRIBUTED TEAM FORMATION FOR HUMANOID ROBOT SOCCER
607
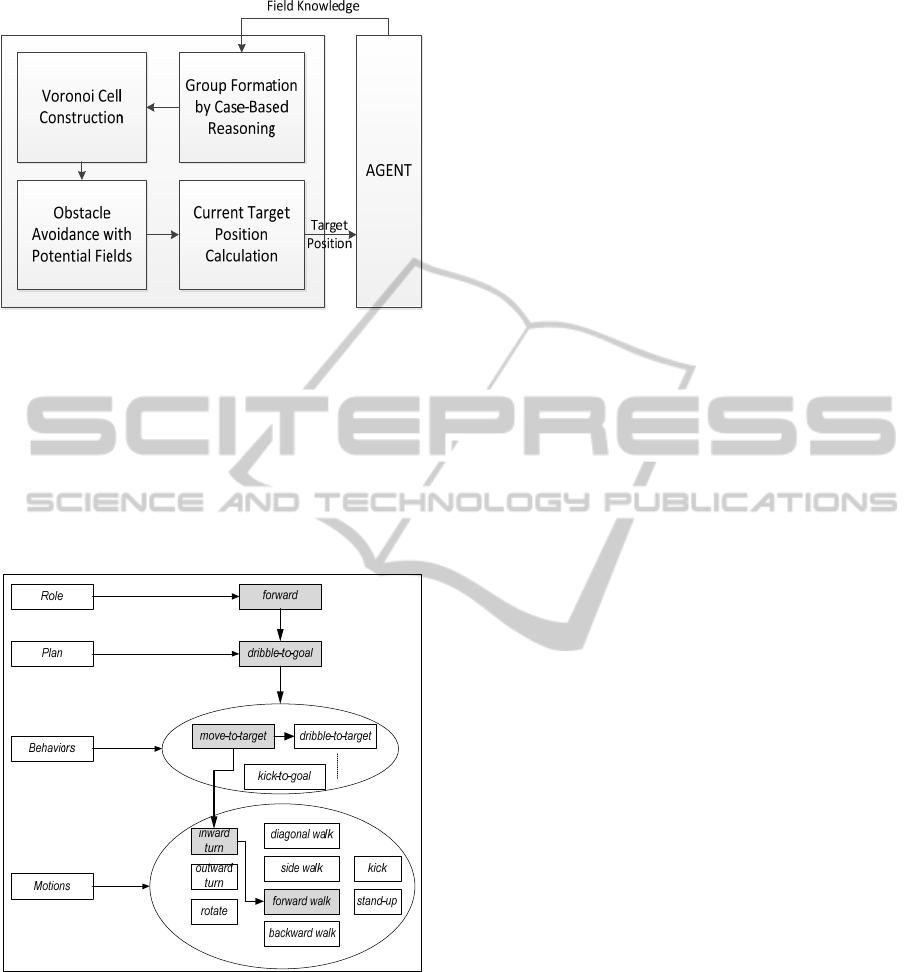
Figure 1: General structure of the distributed team
formation method.
As described in Section 1, goalkeeper positions
itself around the defense area regardless of the team
formation. The forward agent (i.e., the closest agent
to the ball) always targets to possess the ball. While
goalkeeper is a static role assigned to an agent, the
remaining agents switch between the other roles
according to their time costs to reach to the ball.
Figure 2: The decomposition of an example plan for an
agent that has the forward role. Lower level components
are hierarchically activated by selection at a higher level.
At the lowest level, primitive actions are selected and the
corresponding motion commands are sent to the server.
3.1 Case-based Group Formation
The current setup of the RoboCup 3D SSL involves
nine team players in each team. A single player is
assigned to the goalkeeper role. Our strategy divides
the rest of the team into two groups, namely,
defenders and attackers, for offensive and defensive
strategies. Attackers are formed for constructing an
attacking formation around the ball and scoring a
goal whenever possible. This group involves the
forward agent and the midfielders which usually
target to control the ball and score a goal. Defenders
are formed for blocking and constructing a defensive
obstacle against the opponent team. This strategy
prevents the opponent team from scoring.
We use a case-based group formation method
(Aamodt and Plaza, 1994) to determine the number
of defender agents and midfielder agents
dynamically. Since two agents are assigned to the
goalkeeper and the forward roles, the remaining
seven agents are to be assigned to these roles.
Instead of using a predetermined number for these
roles, a case-based method is applied to determine
the best separation.
The current game score and the positions of
agents and the ball are considered in the problem
description of cases. The general structure of cases is
shown in (1). Each case corresponds to a certain
number of agents for defenders and midfielders. For
example, if the team is losing in the middle of the
game, more players could be assigned as midfielders
to tie the game with more attacker agents while
taking the risk of conceding a goal.
= { , ,
, ,
}
(1)
The case library initially involves 12
predetermined cases which are allowed to be
modified in runtime according to the success of
applying them.
The maximum bandwidth for RoboCup 3D SSL
agents is 20 B for each cycle which can be used by a
single agent. This communication channel can be
used by a single agent to send role assignments for
group formations. We have selected the goalkeeper
as the captain of the team because it has the widest
line of sight of the field. The time period to
communicate is shared effectively by each agent.
The goalkeeper is responsible to send group
formation messages according to the results of the
case-based grouping method while other agents send
their costs to reach at the ball position. If agents fail
to communicate with each other, they behave
according to their field knowledge and observations.
Figure 3 shows each agent’s role selection
strategy and its decision for joining to a group. The
agent that is closest to the ball assigns itself the
forward role and directly looks for ball possession to
score against the opponent. The other agents in the
ICAART 2012 - International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
608

attackers group take midfielder role and follow the
forward agent in a close proximity for handling
passes or failures. The defenders position themselves
at a distance behind the ball to defend the goal.
Goalkeeper continuously sends the ball position and
the numbers of the teammates that are going to be in
attackers group according to the case-based
grouping method. If a player hears its number in the
latest message string, it positions itself as one of the
attackers. Otherwise, it takes the defender role. If
the goalkeeper fails to send messages to the others
due to falling down or any other reason, it sends a
failure message to inform them. If the other players
don’t hear any messages or hear the failure message,
they act on their behalf through observation. In this
case, five players closest to the ball assign
themselves the attackers group and three players the
defenders group in a static manner. If a player
observes five teammates that are closer to the ball
than itself, it acts like a defender and uses a
defensive Voronoi cell calculation method. In the
opposite situation, it acts as either the forward agent
or a midfielder agent. Midfielder agents calculate
Voronoi cells to determine their targets while the
forward agent directly targets the ball.
Figure 3: FSM for agents’ group formation behavior
according to the team captain messages or observations.
d
i
: i
th
lowest Euclidean distance between the ball and the
agents in the viewpoint, d: Euclidean distance between the
agent and the ball, k: the maximum number of attackers.
3.2 Target Selection by Adaptive
Voronoi Cell Construction
The midfielder and defender agents need to position
themselves for maintaining close proximity to the
forward agent and defending the goal respectively.
This is accomplished by a distributed Voronoi cell
construction approach in which each agent
calculates its own cell independent from that of the
others. Therefore, every agent has a different shaped
cell and these can overlap.
In conventional Voronoi diagram computation,
Fortune Algorithm (FA) (de Berg, van Kreveld,
Overmars, and Schwarzkopf, 2000) is used. Our
approach differs from FA in the construction of the
final cell. The initial cell is constructed by
considering the ball location and then, iteratively
narrowed down to get the final cell for the agent. In
FA, the lines that construct the cells are
perpendicular bisectors of the line segment between
teammate locations. In our approach, a line from the
corresponding teammate position parallel to the
perpendicular bisector is used. The main procedure
for our distributed cell construction approach for
each agent is given in Algorithm 1.
After constructing the cell for itself, each agent
determines the center of the cell as its new target.
Agents become closer to each other by using this
strategy, which is more beneficial for attacking in
soccer. However, RoboCup 3D SSL league have
some rules to prevent crowding an area with
multiple agents. According to these rules, a player is
repositioned out of the field if it is in a circle that has
a radius of 1 meter with two other teammate players.
In order to overcome the situation where there is a
teammate closer than 2 m, the cell is adjusted to
keep at least 1 m distance from that teammate.
Applying these alterations on the construction of a
cell, the distance to any teammate is guaranteed to
be greater than 1 m. In RoboCup 3D SSL, each
agent has a 120 degrees angle of view. Therefore,
agents only consider the positions of teammates they
can see and the ball’s last seen position to construct
their Voronoi cells. Euclidean distance is used for
distance calculations. (2) shows the distance formula
for two coordinates (A(x
1
,y
1
), B(x
2
,y
2
)) that is used in
Algorithm 1.
(
,
)
=
(
−
)
+(
−
)
(2)
Algorithm 1: Voronoi cell construction for agent a
k
Input:
P
B
: the ball’s last seen position (b
x
,b
y
)
P
i
: the current position of a
i
(p
ix
,p
iy
)
P
G
: the midpoint of the team’s goal line
P
S
: the initial cell start point
l: the distance limit for cell initialization (4 m)
m: the distance limit for the crowding rule (2 m)
Output:
cell
k
: the Voronoi cell for a
k
c:
the center of
cell
k
t
k
: target destination of a
k
DISTRIBUTED TEAM FORMATION FOR HUMANOID ROBOT SOCCER
609

L
i
: Line between L
i1
and L
i2
m
Li
: Slope of L
i
if agent = midfielder
P
S
= P
B
end if
if agent = defender
P
S
= (P
B
+ P
G
)/2
end if
L
0
: Line between P
S
and P
k
(L
01
= P
S
, L
02
= P
k
)
L
1
: Line between L
11
and L
12
where
(L
1 ⊥
L
0
), P
S
∈L
1,
(
,
)
=
(
,
)
=
(
,
)
=/2
L
2
: Line between L
21
and L
22
where (L
2 ⊥
L
0
)
, P
k
∈L
2,
,
(
,
)
=
(
,
)
=
(
,
)
=/2
L
3
: Line between L
11
and L
21
, where m
L3
= m
L0
L
4
: Line between L
12
and L
22
, where m
L4
= m
L0
create cell
k
which is the enclosed area between the
intersection points of L
1
, L
2
, L
3
and L
4
for all teammates (a
i
≠ a
k
) in point of view
p: Coordinate to draw line according to a
i
L
p
: Line between P
k
and P
i
if
(
,
)
>
p = P
i
else if
(
,
)
≤/2
p = x where x ∈ L
p
,
(
,
)
=/2
else
p = x where x ∈ L
p
,
(
,
)
=
(
,
)
– /2
end if
create line L where p∈L, (L
⊥
L
p
)
if L intersects cell
k
//L divides cell
k
into 2 cells: cell
1
and cell
2
cell
k
= cell
j
(j ∈{1,2}andP
k
∈cell
j
)
end if
end for
calculate center coordinate of cell
k
(c)
calculate t
k
by altering c according to obstacles using
Potential Fields
Algorithm 1 is used for both midfielders and
defenders. Defenders create their cells with the same
algorithm, but their initial cell is calculated
according to the midpoint of the line connecting the
ball position and the center of the team’s goal
position while midfielders use the ball location.
The time complexity of the algorithm is O(n
2
)
where n is the number of agents in the team. Figure
4 shows the iterations for calculating the final cell
and the corresponding target as the center of this cell
for agent #2 (a
2
), which is a midfielder and draws its
initial cell according to the ball position. As
mentioned before, only teammates in the viewpoint
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 4: Step-by-step calculation of the Voronoi cell for
a
2
. (a) construction of the initial cell according to the ball
position, (b) cell iteration due to the intersections with a
5
,
(c) cell iteration due to the intersections with a
6
, (d) the
final cell for a
2
. The corresponding target position is
marked with a red point.
of the agent are considered. The area that is out of
a
2
’s point of view is shown as the shaded area.
Figure 4 (a) shows the initial cell construction by
considering the ball position (P
b
). In Figure 4 (b),
(c), and (d), the cell is modified according to the
locations of a
5
, a
6
, a
8
and a
9
, respectively. The line
for a
9
doesn’t have any intersection points with the
current cell, so it doesn’t make any changes in the
cell. The final Voronoi cell of a
2
is shown with the
red frame and the center of that cell is marked with a
red point in Figure. 4 (d).
Agents continually form their Voronoi cells and
move toward their targets. Due to the distributed
calculation of cells, a complete diagram is not
formed. Cells of different agents may overlap in
some situations, but the relevant precautions taken to
overcome the crowding rule and the Potential Fields
Method ensures that the targets are not too close to
ICAART 2012 - International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
610

each other. This approach also protects agents from
collusions.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Two sets of experiments are set to analyze the
performance of our proposed team strategy.
rcssserver3d is used for the simulation, which is the
official server software for RoboCup 3D SSL
competitions and RoboViz (Stoecker and Visser,
2011) as a visualization tool.
In soccer game, keeping possession of the ball is
one of the key factors for scoring a goal. Our first
experiment targets to analyze this issue and the
average position of the ball in the field. Ball position
fields are determined by dividing the 21 x 14 m field
horizontally into 3 equal areas (defense, midfield and
forward) each 7 x 14 m. The area next to the team’s
goal is called the defense area, the area next to the
opponent’s goal is called the forward area and the
area between these two fields is the midfield area.
The proposed method is compared to our earlier
method Situation Based Strategic Positioning
(SBSP) that we used in RoboCup German Open
2011 competitions, our previous Voronoi cell based
method which uses a static grouping strategy instead
of case-based grouping and DPVC method (Dashti
et al., 2006). In DPVC, Voronoi cells are used to
scatter the agents throughout the field. In SBSP,
each agent has a predetermined role and they shape
formations according to predefined positions around
the ball based on their roles. All the approaches are
applied on the latest motion model of our team.
RoboCup 2011 binary of Nao Team Humboldt
(Burkhard et al., 2011)
is used as an opponent because
the motion model of Nao Team Humboldt
is close in
speed to that of our PFS model. Also Nao Team
Humboldt
has a successful defensive team formation
which blocks the opponent. We run 10 games for
each method against Nao Team Humboldt. A
snapshot is shown in Figure 5 from an instance
during these games where the blue agents are from
beeStanbul team and the red agents from Nao Team
Humboldt. This figure also illustrates the Voronoi
cell of each midfielder agent in beeStanbul. The
agent closest to the ball assigns itself the forward
role while the rest of them are assigned to the
midfielder role in the attackers group. As can be
seen from the figure, the Voronoi cells of
midfielders may overlap as it is allowed. However,
target positions as the centers of these cells are
always different if agents see each other.
Table 1 shows the overall results of all methods.
These results illustrate that, the new approach
outperforms our previous approaches and DPVC in
terms of ball possession, keeping control of the ball
and carrying the ball to the opponent’s area. Our
previous approach that uses Voronoi cells combined
with a static grouping method also gives good
results but using a case-based method for grouping
further improves the overall performance. According
to these results, the key factors for the success of the
proposed team strategy can be listed as the
distributed online construction of Voronoi cells and
dynamic positioning to the centers of these cells.
Even when the forward agent falls over during an
attack, by this approach, midfielders maintain close
proximity with the forward agent and regain control
of the ball. Communication is also used to
dynamically form attacker and defender groups.
Another advantage of the new approach is the
unpredictability of the team strategy as a competitive
strategy. There are not fixed formations that can be
learned and predicted by the opponent during a
game.
Figure 5: An instance from a game using rcssserver3d of
Simspark for simulation and RoboViz for the visualization.
Blue polygons indicate the cells of the agents and red
circles indicate their centers.
As expected, the performance of DPVC is better
than that of SBSP in terms of carrying the ball to the
opponent’s area due to the dynamism. In SBSP, on
the other hand, predetermined formations are easy to
be predicted by the opponent in a later time step
during the game. However, ball possession
performance of DPVC is worse than that of SBSP
because it scatters the agents throughout the field. In
that case, if the motion model of the agents is not
fast enough, they may not responsively regain the
control of the ball when it is lost.
DISTRIBUTED TEAM FORMATION FOR HUMANOID ROBOT SOCCER
611

Table 1: Comparison among the methods used in beeStanbul team software against Nao Team Humboldt in terms of ball
possession and ball position.
Distributed Voronoi
Approach with case-
based grouping
Distributed Voronoi
Approach with static
grouping
DPVC SBSP
Ball Possession
Ratio
53.23177%
(σ = 0.04441)
52.92768%
(σ = 0.08248)
47.83140%
(σ = 0.07796)
50.45958%
(σ = 0.06877)
Ball in Own
Area
15.95018%
(σ = 0.04423)
17.11815%
(σ = 0.11013)
27.76341%
(σ = 0.13851)
37.04670%
(σ = 0.18277)
Ball in Midfield
37.48712%
(σ = 0.08912)
38.37606%
(σ = 0.14637)
31.74228%
(σ = 0.11037)
33.22326%
(σ = 0.10827)
Ball in
Opponent Area
46.56270%
(σ = 0.11047)
44.50579%
(σ = 0.18259)
40.49431%
(σ = 0.13937)
29.73004%
(σ = 0.24710)
(a) (b)
Figure 6: Test results for each message loss rate presented as the averages of 5 games against Nao Team Humboldt. (a)
Average goal difference (positive values show the scores in favor of our team) (b) Average ball possession ratio of our
team.
In the second set of experiments, we measure the
performance of our method for different message
loss rates. In rcssserver3d, a team is allowed to send
a message periodically in 0.06 seconds. In our
current implementation, we use all the available
messaging periods in order to perform better. In this
experiment, we manually switched off
communication based on the message loss rate to
simulate communication failure. The reported results
indicate that our method is robust to communication
failures for most of the instances. Even for no
communication cases, agents can still make
decisions and calculate their Voronoi cells based on
observations and they position themselves to
appropriate target locations for maintaining an
efficient formation. This is achieved by the
distributed implementation of Voronoi cell
construction. However, as expected, ball possession
performance is degraded gradually with the worst
value 47.7%.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
We have presented an adaptive team formation
method for RoboCup 3D SSL. Our proposed
Voronoi Diagram based formation generation
method requires less computational cost than the
standard Voronoi Diagram generation. The ball
position is also taken into account during these
calculations. We combined our Adaptive Voronoi
Diagram with a Case-Based group formation method
controlled by an agent (i.e., goalkeeper) through
explicit communication. The agents are divided into
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
Goal Difference
Message Loss Rate
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
1
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
Ball Possession Ratio
Message Loss Rate
ICAART 2012 - International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
612

defender and attacker groups according to this
agent’s messages. We compared our method against
our previous Voronoi cell approach that is combined
with a static group formation algorithm, and earlier
methods. The results illustrate that the new approach
outperforms the other approaches. In our future
work, we plan to change the team leader to
determine the group behaviors dynamically in run
time. In order to provide a better formation, we plan
to assign the captain role to the agent that has the
best angle of view on the field dynamically.
REFERENCES
Aamodt A. and Plaza E., 1994. Case-Based Reasoning:
Foundational Issues, Methodological Variations, and
System Approaches. Artificial Intelligence
Communications 7:1, pp. 39-52.
Aldebaran Robotics Official Website, 2011.
http://www.aldebaran-robotics.com/
Arkin, R., 1998. Behavior-Based Robotics. MIT Press,
Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Asta, S., Sonmez T., Ulusoy O., Alimoglu A., Ersen M.,
Sozmen O. and Sariel-Talay S., 2011. beeStanbul
RoboCup 3D Simulation League Team Description
Paper 2011. RoboCup 2011, Istanbul 5-11, July, 2011.
Asta, S. and Sariel-Talay S., 2011. Nature-Inspired
Optimization for Biped Robot Locomotion and Gait
Planning. The 6th European Event on Nature-inspired
Techniques in Scheduling, Planning and Timetabling,
Torino, Italy, 27-29 April, 2011, pp. 434-443.
Ayanian, N., Kumar, V. and Koditschek, D., 2011.
Synthesis of Controllers to Create, Maintain, and
Reconfigure Robot Formations with Communication
Constraints. Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics,
Volume 70/2011, pp. 625-642.
Burkhard, H. D., Krause, T., Mellmann, H., Ritter, C. N.,
Xu, Y., Scheunemann, M., Schneider, M. and
Holzhauer, F., 2011. NaoTH 2011 The RoboCup
Team of Humboldt-Universitat zu Berlin. RoboCup
2011, Istanbul 5-11, July, 2011.
Candea, C., Hu, H., Iocchi, L., Nardi, D. and Piaggio, M.,
2001. Coordination in multi-agent RoboCup teams.
Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Volume 36, Issues
2-3, pp. 67-86.
Balch, T. and Arkin, R., 2000. Behavior-Based Formation
Control for Multirobot Teams. Proceedings of Fourth
International Conference on Multi-Agent Systems, pp.
363-364.
Dashti, H. T., Aghaeepour, N., Asadi, S., Bastani, M.,
Delafkar, Z., Disfani, F.M., Ghaderi, S.M., Kamali, S.,
Pashami, S. and Siahpirani, A.F., 2006. Dynamic
Positioning based on Voronoi Cells. RoboCup 2005.
LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4020, pp. 219–229.
de Berg, M., van Kreveld, M., Overmars, M. and
Schwarzkopf, O., 2000. Computational Geometry.
Springer–Verlag, New York, 2000.
Nair, R., Tambe, M. and Marsella, S., 2003. Team
Formation for Reformation in Multiagent Domains
Like RoboCupRescue. RoboCup 2002: Robot Soccer
World Cup VI, Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
Volume 2752/2003, pp. 150-161.
Nakanishi, R., Murakami, K. and Naruse, T., 2008.
Dynamic Positioning Method Based on Dominant
Region Diagram to Realize Successful Cooperative
Play. RoboCup 2007: Robot Soccer World Cup XI
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Volume
5001/2008, pp. 488-495.
Reis L. P., Lau N., Oliveira E.C., 2001. Situation Based
Strategic Positioning for Coordinating a Team of
Homogeneous Agents. Springer’s Lecture Notes in
Artificial Intelligence, Vol.2103, Berlin, pp. 175–197.
Ros, R., Arcos, J. L., de Mantaras, R. L. and Veloso, M.,
2009. A case-based approach for coordinated action
selection in robot soccer. Artificial Intelligence, v.173
n.9-10, pp. 1014-1039.
Röfer, T., 2003. An Architecture for a National RoboCup
Team. RoboCup 2002: Robot Soccer World Cup VI,
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Volume
2752/2003, pp. 417-425.
Simspark Official Website, 2011. http://simspark.
sourceforge.net/
Stoecker, J. and Visser, U., 2011. RoboViz:
Programmable Visualization for Simulated Soccer.
RoboCup 2011, Istanbul 5-11, July, 2011.
Stone, P. and Veloso, M., 1999. Task Decomposition and
Dynamic Role Assignment for Real-Time Strategic
Teamwork. Intelligent Agents V: Agents Theories,
Architectures, and Languages, Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, Volume 1555/1999, pp. 293-308.
DISTRIBUTED TEAM FORMATION FOR HUMANOID ROBOT SOCCER
613
