
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE NEW GENERATION OF HOSPITAL
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
I. Evgeniev and V. Gueorguiev
Technical University Sofia, blvd. „Kliment Ohridski” 8, Sofia, Bulgaria
Keywords: Hospital information system, Telemedicine, Medical data analysis, Data mining.
Abstract: The aim of this paper is to present some ideas about new directions in hospital information systems’ design.
They are based on results obtained in the context of joint research with Medical University Sofia,
requirements from other hospitals and discussions with industrial providers of such systems. We target
investigations, design, organisation and future expansion of a hospital information system, new concepts
and methods for continuous acquisition of patient’s vital data, transmission, collection and binding of that
data for diagnostic and disease tracking purposes, investigations on relevance of life quality and healthcare
based on the e-Health technologies and medication and drug tracking. Some of these new investigations are
oriented to build data mining background.
1 INTRODUCTION
The aim of this paper is to present results and based
on them ideas about new directions for design of
Hospital Information Systems (HIS). Part of these
ideas is obtained in the context of a joint research
project for investigation, design, organisation and
future expansion of a hospital information system
DAPSEpro. Extending our work in the years and
cooperating with other providers and research
groups we found some new possibilities for HIS
extension and reorganisation.
The primary research started with investigation
of current status of installed and operating hospital
information systems on the territory of the Medical
University Sofia. Elimination of the usual paper-
based information exchange to IT-based one is one
of the primary topics.
Medical University Sofia is a huge distributed
hospital complex. It has tens of different clinics,
laboratories and buildings.
Results of this investigation and some of
implemented solutions are presented in (Evgeniev et
al., 2010). It was focused on the following main
problems:
Distributed, heterogeneous and varying data-
Hospital systems collect a diverse variety of patient
information represented in many digitized or hard-
written types. Creation and support of patient’s
analyses library is a problem solved under presented
project.
Data validity, security and protection - Data
validity is very important to make decision-making
process stable and safe. This includes time validity
and safety and security of delivery. Data access and
privacy are very important and have to provide end-
to-end security and validation in the system.
Tracking patients when they are out of the
hospital – technical, medical and economical
aspects.
IT problems of archiving and digitalisation of
paper-based images and documents.
Improvement of analyses of medical images.
In the design and implementation time we found
some new targets. They were found to be problems
first. After some work they became new targets.
Some of this new targets and interrelations
encouraged writing of this paper. This paper does
not pretend to cover all possible aspects of HIS –
problems, solutions and similar but to point to some
of them and to share some experience.
2 SYSTEM STRUCTURE
The implemented under DAPSEpro Intelligent
Medical Information System’s (IMIS) structure and
subsystems are shown on figure1. It offers the
following features:
471
Evgeniev I. and Gueorguiev V..
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE NEW GENERATION OF HOSPITAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003885004710475
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2012), pages 471-475
ISBN: 978-989-8425-88-1
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Unified environment for data exchange between
installed apparatus and systems in the hospital;
Access to the information resources via
heterogeneous communication environment (mesh).
Tracking the full process of hospitalization of
every single patient.
Data collection and storage for every medication
and procedures.
Offers Remote Medical WWW Services for out-
of-hospital health tracking and care.
Management of all procedures and medications.
Administrative tracking of all patients.
Remote messaging of medical personnel about
health status of selected patients based on remote
vital data acquisition and control.
The initial DAPSEpro covers now two clinics –
clinics of nephrology and pulmonology. All
activities are oriented to answer requirements for
supporting Electronic Health Record standards and
Bulgarian requirements for health records.
According to figure 1, the Fixed clinical network
provides connectivity for all machines and apparatus
in the hospital from one side and servers and
personnel terminals from the other side.
The Wireless medical sensor network provides
access for the medical personnel to data servers and
connects sensors and apparatus having wireless
possibilities to transfer small amount of data. This
makes both people and machines mobile on the
clinic’s territory.
The Management Server controls all
administrative processes and controls access to
database server which hosts all records about
manipulations, personnel and patients’ archives, etc.
The other system elements will be discussed
later.
2.1 Successive Parts
Starting with pure technical project supporting
administrative and medical activities we found that
the usual approach to implement some appropriate
solution and after that to study medical personnel
how to use it is not enough good. This is near to
“brute force” approach what is not applicable to so
sensitive area as medicine.
The design group did wide exploration of needs
and requirements of the personnel.
Requirements were grouped in several groups.
Starting work was oriented to the general
administration, patients’ health records, clinical
orders and result delivery, wireless access to
database, fast connection to all available image
machines.
These parts were designed and implemented.
They offer planned basic functionality and have
embedded possibility for extensions.
2.2 New Parts
One unpredicted part of the system was connection
of Microbiology laboratory to the hospital system.
The Microbiology laboratory has smooth process for
cultures analyses and results report based on paper
control and tracking. Antimicrobial resistance check
is based on the WHONET v.5.5. This forced design
of a local system with two-level structure. On the
first level are connected all analyses machines
having outputs to computer. All analyses results that
need human interactions (like microscope analyses)
are recorded manually using unified fill-in-the-
blanks forms.
The upper level includes WHONET server, local
database server and administrative terminals.
Network server is positioned over this level and
connects laboratory micro-network to the hospital
network.
2.3 Questionable Parts
Here we will present some elements of the work
which became questionable or simply opened new
targets.
2.3.1 Unified Machine and Apparatus
Connection
One of the basic tasks for the DAPSEpro was to
investigate all available medical machines and to
design some hardware abstraction layer (HAL). It
should offer functionality making connection of a
new machine relatively simple and make possible
design and implementation of generalised control
and data acquisition interface to the upper system’s
levels.
Today this part is not finished and do not
promise to be finished easily. The problem is that
machines from different vendors offer different
hardware and software interfaces. Implementation of
a HAL in most cases needs simply to position
additional intermediating controller to implement
hardware and software transformations and logical
isolation. This is complicated and expensive task.
2.3.2 Security and Safety
Requirements about data security and safety
HEALTHINF 2012 - International Conference on Health Informatics
472
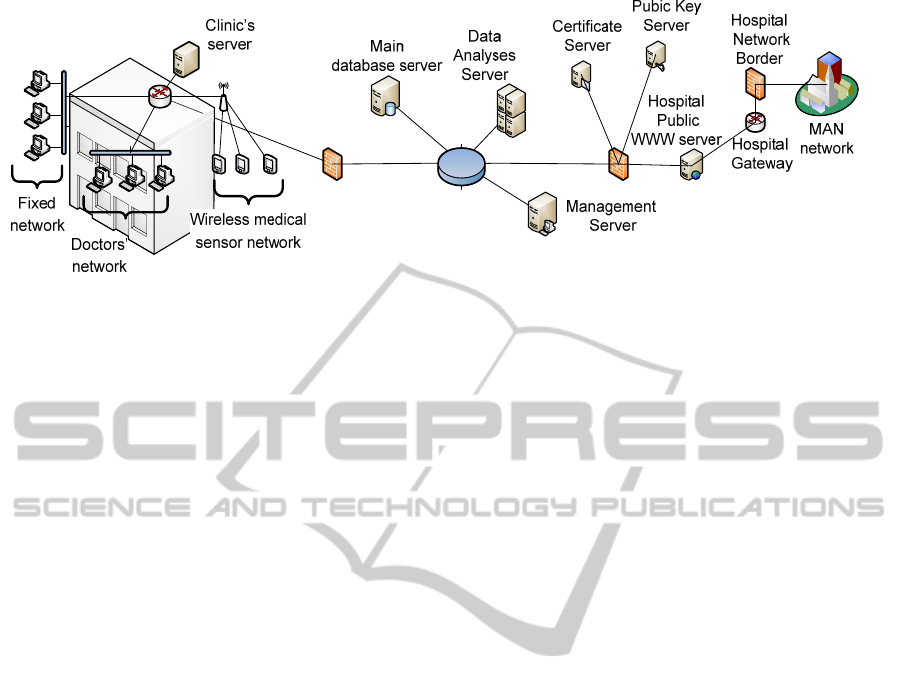
Figure 1: General structure of IMIS.
increased all the time in the implementation process.
HIS requires general security as every operator
operating personal data. Here were found the
following number of problems:
Uncontrollable number of access points to the
systems. All terminals, mobile access devices and
similar are generating hard to solve problem for
unauthorized access prevention.
In the hospital people are in hurry all the time
and sophisticated security system requiring slow or
repetitive log-in / log-out will be disabled fast.
Static security is not enough. This type of system
needs dynamic security but it is more complex and
hard to implement.
Data safety is the next problem. Today IT offers
many different solutions. The problem is that data
have to be delivered fast and without modifications.
Data are very sensitive. They include medication
orders, results from analyses, diagnoses and so on.
Data have huge amounts – images and
permanent sensors.
2.3.3 Image Analyses
Current approaches for analyses of images from
different sources become more important. The new
generations of image machines are producing
directly digital images. They are mostly in DICOM.
This format is a standard for this area but it is a
source of new type of problems:
Generated images are huge and need much disk
space.
Analyses and manipulation of all metrics,
comparison and other need deep non-medical
knowledge what is not well understood by doctors.
Much more problematic are sources producing
output on material carrier (paper, film or other).
Even today digitalization of images from paper or
films is problematic. There are a number of
problems. If the image is simple graphic every flat-
bad scanner is enough good. Digitalisation of film
images is much more sophisticated. Simple scanning
is impossible. The film image has much more details
than directly digitised picture. One qualitative
scanning can extract all these details from the
picture and to present them to the doctors.
In some previous research we proposed some
new approaches to solve the problem with
digitalisation of mages from X-Ray and ultrasound
machines which were proved in practice. The new
step in this work is implementation of dynamic
filtering and HDR transformations. Results are very
promising but need more work with medical doctors
to make results clear and free of artificial artefacts.
The other challenge is the human-machine
interface making analyses, interpretation and control
of work close to the understanding of medics.
One new question found by our group was the
problem of 3D reconstruction based on one or very
few pictures. This approach is different from that
one used in computer tomography (CT). The idea is
to recover not 360
0
image but part of it. This saves a
lot of radiation load of patients. Some results are still
available but again work in dynamic filtering and
shadows selection/ zoning/ distraction is in progress.
Absolutely new request to us in the time of work
was preparation for realistic body model that can be
manipulated and modified to be representative for
the origin at every stage of his life. This area is new
for our group but we started collaborative work with
teams from other European universities. The state-
of-the-art here is availability of 3D skeletal models
and models of some of organs. How all of this will
be combined in one representative model and how it
will be modified to present changes in someone’s
body is still open question.
Image collection for long time archives is hard
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE NEW GENERATION OF HOSPITAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS
473

problem as was mentioned above. A small hospital
produces only images in size of 5 to 10 TBytes per
year. To keep this amount of data “forever” becomes
a problem with many dimensions.
3 OPEN PROBLEMS
3.1 Technical Questions
It is obvious that today HIS are distributed. The
problem here is that they are classical mesh systems.
They are hierarchical systems of systems. A lot of
currently available subsystems have to be integrated
in new systems. Constantly part of them has some
specifics that need special patches or convertors to
enable inclusion.
More problematic is the fact that wireless
connection from different mobile devices becomes
widely used.
We see two general thing needing theoretical and
practical solutions.
1) First is that current distributed HIS architectures
generate problems for the medical personnel if it has
to acquire data from different sources connected to
different servers or subsystems. In many cases this
needs to know the exact system structure, to have
access rights to its different elements and so.
Hospitals are geographically distributed and their
divisions have to be connected properly and to look
like single object. The addressed solution here is
similar to the “cloud”. This is the so-called virtual
mono machine. The idea is old but can be
implemented today because of technological
revolution and performance bust. On abstract level
the system is represented like a single computer
implementing all system’s functionality. This is the
way the user sees telephone network. All layering,
abstractions and networking are hidden inside. Part
of this idea is designed and implemented in
DAPSEpro system.
This approach has one important drawback. It needs
very formal approach on the boundary between the
abstract mono-machine and real distributed systems.
The advantages of this approach comparable to
“cloud” are much a) better security and b) flexibility
for future extensions.
2) The second general problem for solving is the
mentioned above mobile access to HIS and medical
services. It covers two very different objects – any
kind of people’s access device (smart phones, tablets
and so) and mobile medical equipment (wearable
sensors, equipment in ambulances, autonomous
devices with wireless connectivity). All this is part
of today’s mHealth technologies.
Here we have to meet security and safety
requirements. They are subject to be increased all
the time.
The direction of information exchange is the next
thing to be solved. Primarily the main direction was
from the sensors and apparata to the HIS. Today the
exchange is fully bi-directional. To the mobile user
area transferred data of any kind – numerical,
images and so. Moreover – there is a special kind of
education for students and for patients oriented to
modern mobile devices and networking
technologies.
All of this emphasizes the understandings of new
modalities and identification of opportunities for
implementing interoperable devices and systems,
and integration available HIS.
3.2 Medical Questions
We mentioned above that IT technologies can
provide to the medical society wide stream of new
possibilities.
Personal health record covering all aspects of
someone’s health history is still questionable.
Problems are coming from two sources – how and
where we can keep records and who needs life long
data tracking.
One of the challenges today is remote
consultancy. It needs in many cases transfer of
imaging and numerical information, held on paper
documents and similar. It has to be presented in
every HIS.
A special point is drug tracking in the context
complex analyses of how they influence patients,
combinations, age, gender and other cross-relations.
Mentioned above problems of creation of better
body and organ 3D models for every-day diagnosis
and health tracking and personal health profile
sustain.
3.3 Business Questions
A lot business questions have to be answered when
HIS is designed and implemented. They point to the
following different aspects:
The prise for data center – in exploitation time
this becomes really expensive.
Security support – depending on security level
planned to reach the price is becoming significant.
Every-day expenses for hospital activities,
patients care, medications, etc. have to be tracked.
HEALTHINF 2012 - International Conference on Health Informatics
474

Connections with health insurance companies.
Interdisciplinary work in the area of general
health and mHealth as the way to decrease
unnecessary stay in hospitals, preliminary
diagnosing, out-of-hospital support.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Here in this paper is presented an implementation of
first version of Intelligent Hospital Information
System. Together with this presentation are
discussed many open problems and new directions
for future research. They are discovered in three
separate sections. Some new solutions are proposed
here, too.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Different parts of this work are funded by Bulgarian
National Science Fund contracts DO02-113,
DRNF02-3 and DO02-175.
REFERENCES
Evgeniev, I., Trifonov, V., Gueorguiev, V., 2010. An
integral solution for hospital information system. In
Med-e-Tel 2010,Global Telemedicine and eHealth
Updates, vol. 3, Luxemburg.
www.hl7.org
www.OpenEHR.org
www.whonet.org
Ivan, E., Ivanov, V., Gueorguiev, V., Bodurski, E.,
Markov, Electronic Health Record: The State of The
Art, Computer Science'2009, 05 - 06 November 2009,
Sofia, Bulgaria
Ivan, E., Ivanov, V., Gueorguiev, N., Balgzhiev, B.,
Kehayov, Software Architecture For Medical
Information Systems, Computer Science'2009, 05 - 06
November 2009, Sofia, Bulgaria
Nakov O, V., Gueorguiev, I. E., Ivanov, V., Trifonov.,
Methadata organization in Electronic Health Record
(in Bulgarian), Computer Engineering, 2, 2009
Ivan Evg. Ivanov, Vesselin Gueorguiev, Velizar Bodurski,
Vencislav Trifonov, Telemedicine and Smart Phones
as Medical Peripheral Devices (Computational
Approaches), DESE 2010, London, UK, September
2010
Vesselin E., Gueorguiev, Ivan, E., Ivanov, Dessislava,
Georgieva, Digital Cameras as Low-cost Tools for
Telemedicine and e-Health: Opportunities and
Constraints, HEALTHINF 2011, Rome, Italy, January
2011
Momtchev I., Intelligent Agents – Issues Analysis and
Architecture Proposal, Proceeding of 18th int. conf.
“Systems for automation of Engineering and
Research” SAER 2004, Varna, Bulgaria, pp 201-206
Momtchev I., An Intelligent Agent Framework,
Proceeding of 19th int. conf. “Systems for automation
of Engineering and Research” SAER 2005, Varna,
Bulgaria, pp 211-215
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE NEW GENERATION OF HOSPITAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS
475
