
TEAM LEARNING PROGRAM FOR INFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERS USING PROJECT-BASED LEARNING
Case Study of the “Upper Process” in IT Engineering
Minoru Nakayama
1
, Manabu Fueki
2
, Shinji Seki
3
, Toshikazu Uehara
4
and Kenji Matsumoto
4
1
Human System Science, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Ookayama 2–12–1, Meguro, 152–8552, Tokyo, Japan
2
Computer College Niigata, Benten 2–3–13, Chuou-ku, 950–0901, Niigata, Japan
3
Computer College Hokkaido, Kikusui 6–3, Shiroishi-ku, 003–0806, Sapporo, Japan
4
Software Consultant Corporation, Nakano 5–62–1, Nakano-ku, 164–8505, Tokyo, Japan
Keywords:
Team Learning, Project based Learning, Learning Management System, Learning Evaluation, Upper Process.
Abstract:
This paper reports the case of an educational practice and evaluation of team learning in an Engineering
course. This course uses project-based learning and is supported by a learning management system. Its
subject is the “Upper Process” of Information Technology systems development. The course was conducted
at a computer college which trains information technology engineers to meet the demands of industry. The
course content consists of team practice sessions to understand “requests for proposals” (RFP) and to learn
how to propose “requirement definitions”. Student’s communication skills are also taught throughout the team
learning sessions. To assess what was learned, the results of the team learning sessions were evaluated and self
evaluations of learning activities were conducted. After this, a feasibility study of the team learning activity
was discussed. Also, the evaluation scores of the functions of the learning management system were correlated
with the assessment scores.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of engineers in various disciplines
requires human resources training in the higher and
vocational education systems and the improvement
of the educational system (Japanese Ministry of Ed-
ucation, Sports, Culture, Science and Technology
(MEXT), 2010). The development of educational
programs and evaluation methodologies have been
discussed and disseminated (Shinoda, 2011), result-
ing in many revisions to these programs.
Also in the area of information technology
(IT), human resource development issues such as
the amount of engineers needed and the quality
of engineering performance(Information-Technology
Agency, 2010) have been discussed. In particu-
lar, the IT industrial sector claims that informa-
tion technology engineers should have systems de-
velopment experience as members of a team which
has practiced resolving problems while they were
learning fundamental engineering theory. Addition-
ally, it is often suggested that IT engineering gradu-
ates from departments of computer science have in-
sufficient communication skills, leadership qualities
and project management experience (Information-
Technology Agency, 2010).
Since most IT engineers have been trained at com-
puter colleges, these colleges have to develop educa-
tional program to meet the above requirements. Most
college students in Japan are around 20 years old, and
have little experience as engineers. Also, IT engi-
neers have to learn business manners in order to bet-
ter communicate with customers and business part-
ners. One approach is to employ team learning as a
form of project based learning (PBL). Team learn-
ing means that students work together as a project
team, and resolve problems collectively. These teams
require collaboration, and members have to play in-
dividual roles which are assigned in advance (Itoh,
2011). Therefore, team learning is different from
group learning or collaborative learning (Ichikawa,
1995; Bransford et al., 2000). Team learning may
consist of discussions, learning through experience,
and teaching each other. There have been some dis-
cussions about team learning (Decuyper et al., 2010;
Yazici, 2005), and the difference between team learn-
ing and other group learning styles is not clear. How-
ever, our purposeis not to clarify the difference. Stud-
105
Nakayama M., Fueki M., Seki S., Uehara T. and Matsumoto K..
TEAM LEARNING PROGRAM FOR INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERS USING PROJECT-BASED LEARNING - Case Study of the “Upper
Process” in IT Engineering.
DOI: 10.5220/0003897101050111
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2012), pages 105-111
ISBN: 978-989-8565-06-8
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

ies have reported that team learning can provide train-
ing which improves academic achievement and hu-
man performance,two measures of work related skills
(Hanabusa, 2008). It can also be applied to various
areas of engineering education (Shirabe, 2006). On-
line learning management systems can play a learning
support role, as a kind of virtual learning environment
(VLE), even for PBL (Leng et al., 2006). However,
enhanced computer supported collaborative learning
(CSCL) environments cannot always promote team
learning as a form of PBL because some of the hu-
man factors of the teams are so important. Therefore,
careful design and support will be important if team
learning is to be effective.
In this paper, the feasibility of developing a team
learning style for practical learning by IT engineers
is examined, and also the interaction between team
learning activities and functions of learning manage-
ment system have been discussed. Team learning
sometimes influences individual learning (Ellis et al.,
2003), so a key point is whether it is feasable to mea-
sure the effectiveness of positive learning. Another
hypothesis is that some functions of learning man-
agement systems may contribute to learning, such as
the team learning requirement for discussion between
participating members and the recording of their dis-
cussions.
This paper will address the following topics:
• The design and develop of an educational pro-
gram to provide practical job experience in IT sys-
tems development using face to face and online
learning, including communication skills training
in response to customer’s expectations. These are
taught as a subject called the “Upper Process”.
• The evaluation of learning performanceduring the
course, by develping and using evaluation items to
assess student’s performance.
• The enhancement of team learning, by developing
a learning management system. An evaluation of
this system by students is conducted, and the re-
lationship between learning performance and sys-
tem evaluation is analyzed.
2 METHOD
2.1 Learning Content
The “Upper Process” of IT systems development and
consulting was selected as a subject to determine the
feasibility of team learning using project-based learn-
ing. This topic was studied as project-based team
learning, which is the detailed analysis of “requests
System administrator
LMS
Teaching resources
(Materials, FAQ ducuments)
Learning management system
(User management, Logs)
Lecturer / Mentor
Lecturer
Mentor
Team learning support
(Forum, etc.)
Student
Student
Student
Student
Lecture room
Figure 1: Experimental environment.
Table 1: Learning management system functions.
Item Contents
Task summary Objectives, required learning time
Task materials
The downloading of materials
Lecture materials
The downloading of materials
Questions about the
task
Forum forquestioning lecturer and men-
tor
Team discussion
Forum for discussion with team mem-
bers
Individual session
report
The uploading of report documents
Team products Database of the team’s final products
Self evaluation
Online questionnaire for self evalua-
tion
for proposals” and the proposing of “requirement def-
initions” while students learned communication with
customer skills, business manners, and problem solv-
ing methods involving teamwork. This course is orig-
inally designed for on-the-job training, and it has been
modified for use in a college course, with consider-
ation given to course content and evaluation criteria.
The course consisted of 15 sessions in a computer col-
lege. One lecturer and one mentor organized partici-
pants, who were 40 students (5 teams × 8 members).
The problem assigned involved the following two
tasks.
1. The first task
Analysis of “requests for proposals”: The team
members pointed out which questions should be
asked to better understand the needs and record-
ing detailed explanations while they talked with
someone in the role of customer. 6 sessions × 90
minutes each.
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
106

Work in progress by team
Performance and
undestanding
of presentation
Quality of behavioral and
language presentation
2.4
2.8
2.4
3.0
2.4
2.8
2nd Task
1st Task
1 2 3 4
Evaluation Score
Figure 2: Mean evaluation scores for products of group
work (N of teams=5).
2. The second task
Preparation of a “requirement definition”: The
team members summarised the proposed system
requirements after interviewing someone in the
role of customer and then analyzing and under-
standing the request as a team. 6 sessions × 90
minutes.
These two tasks are independent of each other.
Every team’s activity was evaluated as follows:
• Analysis of documentation and interviews with
customers
• Analysis of the session minutes which recorded
team activity
• Individual session reports
• Individual self assessments of team learning
• Assessments of proposals resulting from team
collaboration
Additionally, the first session was a course orien-
tation, the 8th session was an intermediate discussion
and the 15th session was used for overall reflection
and assessment.
2.2 Learning Environment
All students in this course used their notebook PCs,
which were connected together as a learning manage-
ment system. A diagram of the system is illustrated
in Figure 1. The system, which was developed us-
ing the Moodle system, provided learning materials
and recorded the learning process, the session min-
utes and individual reports. The main function of the
system is summarised in Table 1.
The role of each member was self assigned and the
team working sessions were also conducted at each
team’s own pace in a normal classroom. The role of
the customer was assigned to a lecturer, so that the
lecturer could introduce various business skills, such
Table 2: Evaluation of team products for the first task (N of
teams=5).
Evaluation item Mean
Understanding the assigned task procedure
Understanding the relationship between the task trigger
and the product
2.2
Recognition of the causal relationship between the current sit-
uation and background issues
Issues about preparing a written estimate
2.8
Issues regarding a long-term contract
2.6
Issues about responding to obstacles
2.0
Managing an account book and work progresses record
2.2
Evaluation of the team’s ability to discover original
problems
1.6
Table 3: Evaluation of team products for the second task (N
of teams=5).
Evaluation item Mean
Presentation of solutions to meet the requirements
There is a written proposal which meets the require-
ments
2.0
The propositions are created by the lecturers
2.4
Proposals for coping with obstacles
1.6
Proposals to confirm the progress of work
2.2
Evaluation of team’s original proposals
1.6
Appropriate description of the task flow
2.6
Missions of system operators are clearly indicated
2.4
New jobs are clearly listed in the proposal
2.2
as conventional communication formats during inter-
views. Students summarised the their work and re-
ported their meeting minutes. They could discuss un-
resolved points using online forums after the face-to-
face team working sessions.
2.3 Evaluation Methodology
The evaluation criteria of the two tasks were differ-
ent because the objectives were different. The evalu-
ation standard for student activities were designed in
advance as a rubric (Shinoda, 2011). The following
two types of team activities were rated using a 4-point
scale (1=the worst, 4=the best).
1. Evaluation of the team’s products
The number of evaluation items was 9 for the first
task and 11 for the second task. Three of these
were common for both evaluations: (1) Quality
of behavioral and language presentation (2) Per-
formance and understanding of presentations (3)
Progress of work as a team, individual session re-
ports and the meeting minutes.
2. Self evaluation
Students were asked to evaluate their learning
activities themselves twice, using questionnaires.
The first questionnaire contained 10 questions and
the second questionnaire contained 12.
TEAMLEARNINGPROGRAMFORINFORMATIONTECHNOLOGYENGINEERSUSINGPROJECT-BASED
LEARNING-CaseStudyofthe"UpperProcess"inITEngineering
107
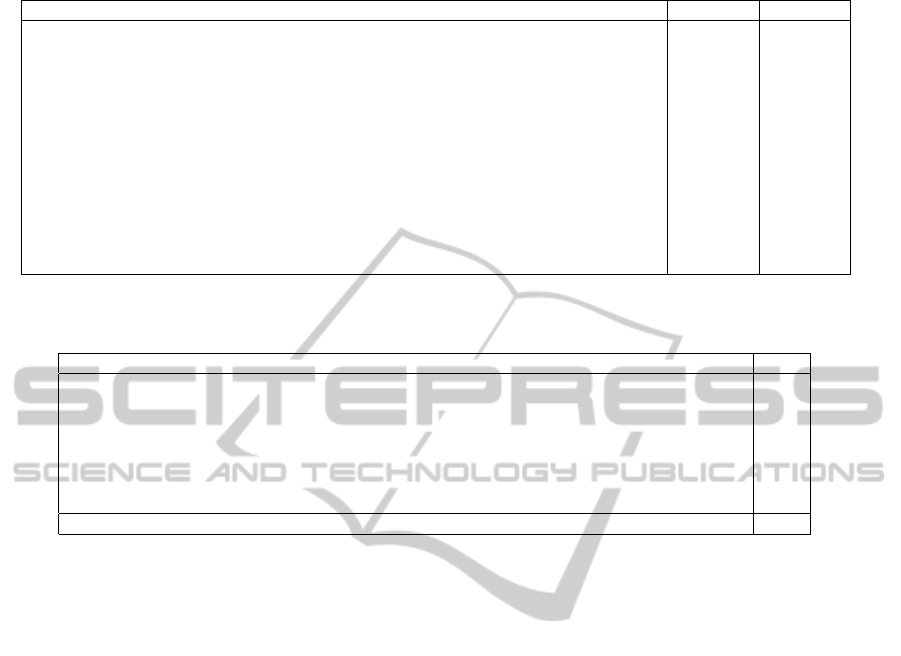
Table 4: Self evaluation results for the first and second tasks (N of participants=40).
No. Question item 1st task 2nd task
1
Can you extract unclear points from the RFP document on your own?
2.20(0.76)# 2.35(0.66)
2
Can you clarify documents intended for meetings with customers using team discussions?
2.85(0.70)* 2.75(0.59)*
3
Can you retrieve sufficient responses to your questions in the customer interviews?
2.33(0.80) 2.43(0.68)
4
Can you resolve the unclear points through summarizing responses in customer interviews using
team discussions?
2.78(0.66)* 2.78(0.77)*
5
Can you state your opinion or have significant discussions in the online forum?
2.63(0.93) 2.45(0.96)
6
Can you play the role of a good business person with appropriate behavior and speech?
2.18(0.75)# 2.48(0.72)
7
Can you make documents such as session reports and session minutes?
2.78(0.73)* 2.95(0.60)*
8
Can you propose an appropriate solution plan?
2.33(0.66) 2.10(0.63)#
9
Can you propose a solution plan for a long-term contract?
2.33(0.69) 2.43(0.81)
10
Can you propose a solution plan to overcome obstacles?
2.30(0.69) 2.13(0.85)#
11
Did you consider requirements which are out of scope?
– 2.13(0.72)#
12
Did you consider the feasibility of the proposed solution?
– 2.13(0.69)#
Mean (STD): Bold*: significantly higher, Bold#: significantly lower than the median
Table 5: Result of factor analysis (factor loading).
No. Question item Load
2
Can you clarify documents for meetings with customer using team discussions?
0.63
3
Can you obtain sufficient responses to your questions in the customer interview?
0.69
4
Can you resolve the unclear points through summarizing responses of customer interviews using
team discussions?
0.51
5
Can you state your opinion or have significant discussions in the on-line forum?
0.37
6
Can you play the role of a good business person with appropriate behavior and speech?
0.42
7
Can you make documents such as session reports and session minutes?
0.37
Chronbach α coefficient 0.73
2.4 Evaluation of Learning
Environment
The usability of the learning environment may affect
the effectiveness of team learning and self evaluation,
so five aspects of the system are evaluated in 13 of the
questions. The five system aspects are:
1. Team discussion forums
2. Individual session reports
3. Team product uploads
4. Schedule management
5. Overall evaluation
Though students assessed their own grades, the
responses were scored using a 4-point scale (1=the
worst, 4=the best). The questionnaires were given to
40 participants after the completion of the course.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Learning Evaluation
The lecturer rated the products of the 5 teams using
evaluation items which were designed in advance as
a rubric. First, the means of three common items
across the two tasks are summarised in Figure 2. All
means for the first task are comparable with the me-
dian 2.5, but the ones for the second task have in-
creased slightly. Though practical education may pro-
vide a few improvements, there are no significant dif-
ferences between means for the two tasks.
Second, the means for the other items are sum-
marised separately in Tables 2 and 3, because their
evaluation points are different. To confirm the differ-
ences across the evaluation items, interval estimation
is conducted. In the results, all means are not signifi-
cantly different from the median of 2.5. Therefore, as
all evaluations are located around the median rate, this
suggests that all team performances are acceptable by
the lecturer. Additionally, these means suggest that
the lecturer does not reject the team products.
The means of self evaluation across 10 question
items were calculated for both the first and second
tasks, and for the two additional questions in the sec-
ond task. The results are summarised in Table 4.
Means for some questions are higher than the median,
such as those regarding team discussions, session re-
ports and minute reports. Again, interval estimation
was conducted for all means. Symbols are used for
mean values significantly higher or lower than the me-
dian. “*” represents mean values that are significantly
higher, and “#” represents mean values that are sig-
nificantly lower. As the results show, some negative
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
108
results from the first task improved significantly in the
second task. In particular, means for questions from
the second task (Nos. 10-12) are significantly smaller
than the median, so that participants may have recog-
nized that they have not performed these tasks suffi-
ciently.
To extract factors of self evaluation, exploratory
factor analysis was conducted for responses to com-
mon and identical questions about the two tasks. As
a result, one factor model consisting of 6 items is ex-
tracted in Table 5. The internal consistency is eval-
uated using a Chronbach α coefficient, where α is
0.73. Therefore, the sum of these rates can be defined
as an index of self evaluation. The mean scores for
each task are calculated as 2.59 for the first task and
2.64 for the second task. There is no significant dif-
ference between scores of the two tasks, and they are
also comparable with the median. Though the tasks
are independent of each other, the scores are compa-
rable, and the sums of the two scores are calculated as
the self evaluation score.
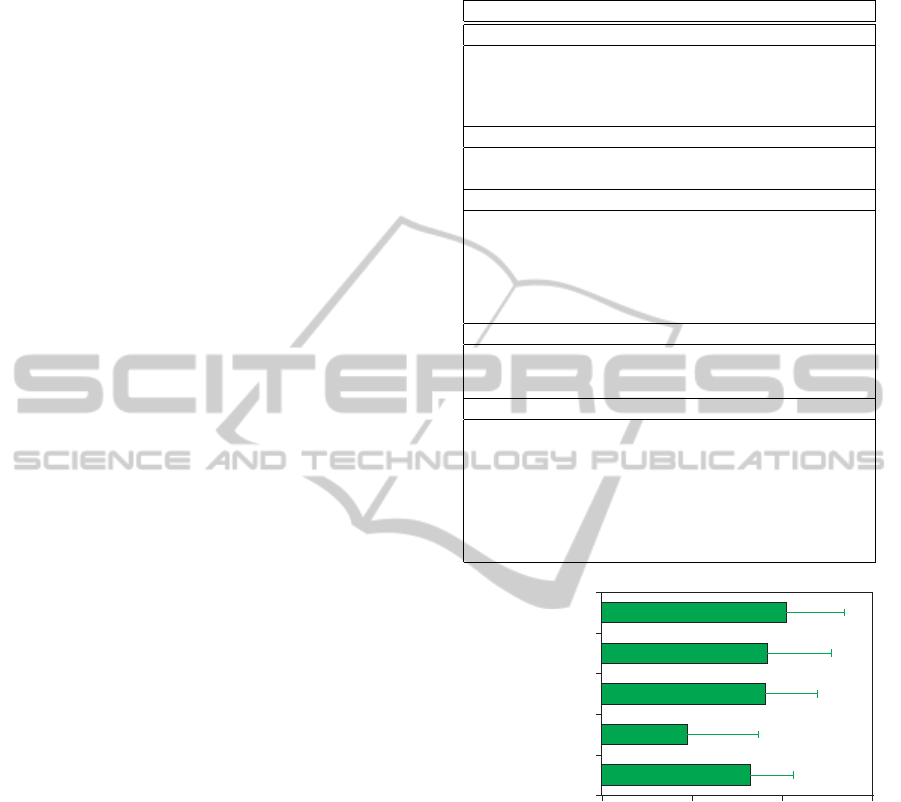
3.2 Effectiveness of Learning Support
Systems
Five major functions of the learning environment
were evaluated using 4-point scale questionnaires.
The 13 question items are listed in Table 6. Mean
scores for the 5 major functions were calculated and
are shown in Figure 3. The error bars in the figure
show standard errors. The mean for the team dis-
cussion forum is the highest, and the means for in-
dividual session reports, team product database and
overall evaluations are also high. According to the
results of interval estimation, the four means for the
above functions are significantly higher than the me-
dian (p < 0.05). However, the mean for the sched-
ule management function is significantly lower than
the median. The team sessions were conducted pe-
riodically, so that additional scheduling might not be
required. As most means for functions are relatively
high, students have positively evaluated this system.
According to the results of the system evaluation,
students agreed that the functions of the LMS as a
learning environment helps their team learning activ-
ities. It is hypothesized that there are some corre-
lational relationships between team learning perfor-
mance and system evaluation. The correlation coef-
ficients between these were calculated. The results
are summarised in Figure 4. First, the coefficient for
evaluation of team products and the function of the
team product database is the highest, at 0.44. This
means that members of teams whose presented prod-
ucts which scored highly evaluated the function of
Table 6: Question items for system evaluation.
No. Question items
Team discussion forum
1
Records of team discussion dialogs were useful for
team learning
2
This function was easy to use to summarise team dis-
cussions
Individual session reports
3
This function was easy to use to present session re-
ports to the lecturer
Team product database
4
This function was easy to use to submit team products
5
The function of reviewing the results of other teams
was useful
6
This function was easy to use to review products of
other teams
Schedule management
7
The schedule management function was useful
8
This function was useful to manage the team schedule
Overall evaluation
9
I would like to use this system frequently
10
I found this system unnecessary complex (reverse
scoring)
11
This system was easy to use
12
This system provided many functions
13
Most students would learn to use this system very
quickly
5: Overall evaluation
4: Schedule management
3: Team product database
2: Individual session report
1: Team discussion forum
System evaluation score
1 2 3 4
Figure 3: Mean score of system evaluations (N of partic-
ipants=40) [All values are significantly different from the
median score (2.5)(p < 0.05)].
team product database positively. The system may
contribute to the results of team work activities. How-
ever, as the coefficients for other functions are rela-
tively small, their effectiveness may be small.
To confirm the relationship between self evalu-
ation and system evaluation, correlation coefficients
for each function were calculated. The variation in
these coefficients is illustrated as a bar graph in Figure
5. The coefficients for team discussion forums, indi-
vidual session reports and overall evaluations of the
system are higher than 0.4. The system performance
may affect individual self evaluation.
TEAMLEARNINGPROGRAMFORINFORMATIONTECHNOLOGYENGINEERSUSINGPROJECT-BASED
LEARNING-CaseStudyofthe"UpperProcess"inITEngineering
109
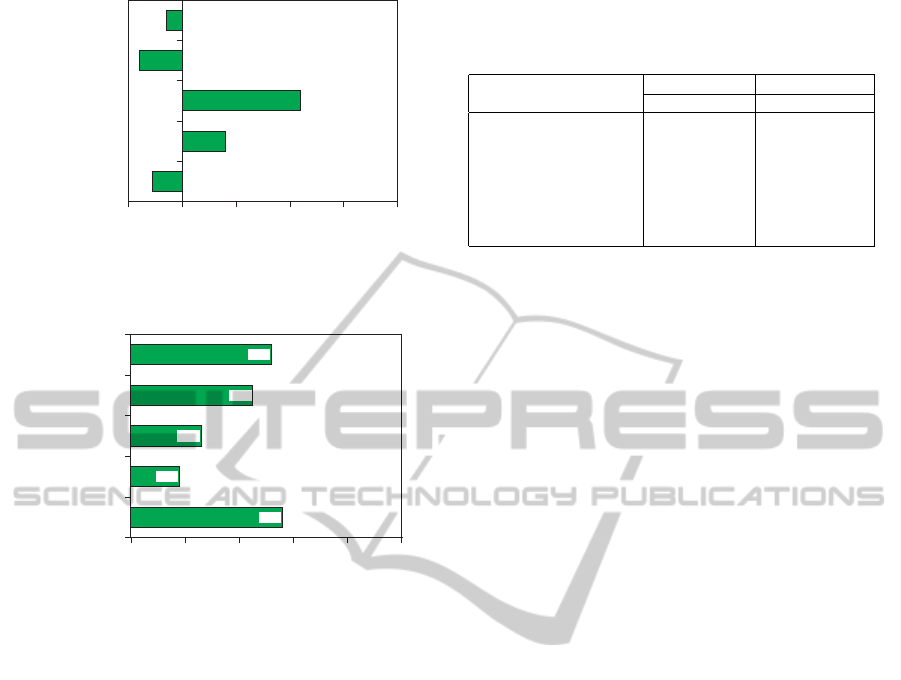
-0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
Correlation coefficient(r)
-0.06
-0.16
0.44
0.16
-0.11
5: Overall evaluation
4: Schedule management
3: Team product database
2: Individual session report
1: Team discussion forum
Figure 4: Correlation coefficients between assessments of
group’s products and system evaluation scores (N of partic-
ipants=40).
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
0.52
0.45
0.26
0.18
0.56
Correlation coefficient(r)
5: Overall evaluation
4: Schedule management
3: Team product database
2: Individual session report
1: Team discussion forum
Figure 5: Correlation coefficients between self evaluation
scores and system evaluation scores (N of participants=40).
4 SUMMARY
This study examined a course which used team learn-
ing in a project based learning course to develop IT
engineers who could adapt to the requirements of the
industry. The course was conducted at a computer
college, and the evaluation of team products used
rubric criteria. Self evaluation by students and their
evaluation of a learning management system were
also conducted.
As a result of the team learning work observed in
the study, team product proposals reached an accept-
able level of competence, and students reflected ap-
propriately on their learning activity. Certainly, both
lecturer and mentor had to provide detailed instruc-
tion and support to promote team learning activities,
as they had designed the course content and prepared
the materials. Also, they were able to evaluate stu-
dent learning activities using the rubric. As a result,
the possibility of a team learning approach to IT sys-
tem development education was confirmed.
Also, a learning management system (LMS) was
introduced to promote team learning. The system
was used frequently and most functions of the system
were positively evaluated. In additional, the scores
Table 7: Correlation coefficients of evaluations between
Learning Management System and self assessment of learn-
ing (N of participants=40).
Team products Self evaluation
System evaluation 1st 2nd 1st 2nd
Team discussion fo-
rum
0.20 -.24 0.42* 0.49*
Individual session re-
ports
0.06 -.28 0.37* 0.42*
Team product database
0.59* 0.19 0.11 0.33
Schedule management
0.34* -.03 0.12 0.19
Overall evaluation
0.11 -.25 0.44* 0.53*
*: Level of significance coefficient: 5%
of system evaluations correlated with both the evalua-
tions of team products and with student’s self assess-
ments. These results provide evidence that since a
learning management system can assist students with
their education, a more appropriate system may bring
even better performance. This suggests that consider-
ation of the design of the system is quite important.
As these results are from a case study, it is not
easy to find the most appropriate way to conduct team
learning and design the learning environment. The
key design factors should be extracted and analyzed
using other educational topics. These processes will
be a subject of our further study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was partially supported by Japanese
Ministry of Education, Sports, Culture, Sci-
ence and Technology (MEXT), Grant-in-Aid
for Research on Human Resource Development
Projects (2010-2011). http://gp-portal.jp/src/ippan/
shoukaiPage.cfm?id=2261
REFERENCES
Bransford, J. S., Brown, A. L., Cocking, R. R., and Council,
N. R. (2000). How People Learn. National Academy
Press, Washington, D.C., Expanded edition.
Decuyper, S., Dochy, F., and den Bossche, P. V. (2010).
Grasping the dynamic complexity of team learning:
An integrative model for effective team learning in
organisations. Educational Research Review, 5:111–
133.
Ellis, A. P. J., Hollenbeck, J. R., Ilgen, D. R., Porter, C.
O. L. H., West, B. J., and Moon, H. (2003). Team
learning: Collectively connecting the dots. Journal of
Applied Psychology, 88(5):821–835.
Hanabusa, T. (2008). Improvement of human ability
through students’ project activity. Journal of Japanese
Society for Engineering Education, 56(1):77–82.
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
110

Ichikawa, S. (1995). Psychology for Learning and Educa-
tion. Iwanami Shoten, Tokyo.
Information-Technology Agency (2010). White pa-
per of Information-Technology Human Resources.
URL: http://www.ipa.go.jp/jinzai/jigyou/docs/ ITjin-
zai2010 Hire 20101209 v1-1.pdf.
Itoh, M. (2011). Possibility of alternative educational exper-
iment programs based on behavioural, cognitive and
situated learning theories. Journal of Japanese Soci-
ety for Engineering Education, 59(1):62–68.
Japanese Ministry of Education, Sports, Culture, Science
and Technology (MEXT) (2010). Desirable Situation
of Practical Engineer Education at Universities.
URL: http://www.mext.go.jp/b menu/shingi/chousa/
koutou/41/houkoku/ icsFiles/afieldfile/
2010/06/07/1294583 1.pdf.
Leng, B. A. D., Dolmans, D. H. J. M., Muijtjens, A.
M. M., and van der Vleuten, C. P. M. (2006). Stu-
dent perceptions of a virtual learning environment for
a problem-based learning undergraduate medical cur-
riculum. Medical Education, 40:568–575.
Shinoda, S. (2011). Necessity and design of assessment and
evaluation tools for documenting and demonstrating
the degree to which the student outcomes are acquired.
The Journal of The Institute of Electronics, Informa-
tion and Communication Engineers, 94(2):114–129.
Shirabe, M. (2006). New approaches in engineering educa-
tion and their relation with engineering ethics. Jour-
nal of Japan Society of Information and Knowledge,
16(3):14–23.
Yazici, H. J. (2005). A study of collaborative learning style
and team learning performance. Education + Train-
ing, 47(3):216–229.
TEAMLEARNINGPROGRAMFORINFORMATIONTECHNOLOGYENGINEERSUSINGPROJECT-BASED
LEARNING-CaseStudyofthe"UpperProcess"inITEngineering
111
