
ICT EDUCATION FOR HIGHER COMPETITIVENESS
OF THE UNIVERSITY STUDENTS
Ladislav Burita
1,2
and Pavel Rosman
1
1
Department of Industrial Engineering and Information Systems, Tomas Bata University,
Mostni 5139, Zlin, Czech Republic
2
Communication and Information Systems Department, University of Defence, Kounicova 65, Brno, Czech Republic
Keywords: Computer Science, Education, Evaluation, Experience, Knowledge Management System, Research.
Abstract: The paper summarizes the experience of teaching Computer Science at the Faculty of Management and
Economics at Tomas Bata University in Zlín. Furthermore, the implementation of a knowledge management
system in education at the Faculty of Military Technology at the University of Defence in Brno is
mentioned. The methodology, an overview of subject areas, application of information and communication
technologies (ICT) in instruction and its organization are also presented herein. The results of some research
activities in the field of Informatics instruction are introduced; and options for future development of the
courses are proposed. The introduction of new approaches and methods into teaching with the use of ICT is
offered.
1 INTRODUCTION
In this paper authors raise a question whether
students and teachers in education are adequately
prepared to use all the opportunities and approaches
leading to effective teaching, particularly in the field
of learning supported by modern ICT, which offer
new possibilities and how to prepare students in ICT
areas to gain more competitiveness. The potential of
the knowledge management system in education is
described.
Authors mentioned two different courses: one
course is Computer Science to prospective
economists and managers at the Faculty of
Management and Economics (FaME), Tomas Bata
University (TBU) in Zlín (http://www.utb.cz), and
the second course is Project of ICT at the Faculty of
Military Technology (FMT), University of Defence
(UoD) in Brno (http://www.unob.cz), Czech
Republic.
The course of FaME is more elaborated (see
chapter 2-3) in the paper and the results are included
of research in teaching. It is mentioned elaborate
only on one of the research goal: to what extent the
course meets the expectations of prospective
economists and managers for the use in practice
(competitiveness). The analysis of the research
results makes it possible to suggest options for
further development of the course. The structure of
the course is in the table 1. There is difference of
teaching the course to full-time and part-time
students. The part-time students have only
consultations (lectures and discussion) and the full-
time students have in addition practice.
The Computer Science for Economists (CSE)
course might serve as an example when a whole
range of literature is available on the market as well
as plenty of interactive courses on the Internet. The
development of the Internet has brought about new
alternatives to traditional forms of study – and ICT
play a key role in them. The content of computer
science instruction has been a long-term discussion
(Rosman and Burita, 2011).
One of the outcomes of these debates is the
understanding of the importance of professional
working with the Office Automation (OA), which is
also reflected in the recognition of the qualification
level achieved by gaining the European Computer
Driving License (ECDL).
The course at FMT includes three main parts:
project, information, and knowledge management.
Only the third part is mentioned in the paper (see
chapter 4) to illustrate the quick transfer of
knowledge from research to education and to shows
the possibilities of knowledge system as an
education theme.
283
Burita L. and Rosman P..
ICT EDUCATION FOR HIGHER COMPETITIVENESS OF THE UNIVERSITY STUDENTS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003904302830286
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2012), pages 283-286
ISBN: 978-989-8565-07-5
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 EVOLUTION OF COMPUTER
SCIENCE EDUCATION
The main objective of the course still lies in
providing an overview of modern ICT, with regard
to all the necessary components of information
systems and applications, particularly OA including
their essential characteristics and reciprocal links.
Furthermore, we were interested in the student
attitude to this type of education, including the
willingness to invest money in it. General views on
the acquisition and development of computer and
information literacy have been changing in the
course of history and still differ.
As a unifying requirement for achieving a
measurable level of knowledge and practical skills
might serve, for example, the requirements specified
for earning the ECDL. This fact is reflected in our
methodology: the students who present a valid
ECDL certificate have fulfilled the requirements and
are not obliged to enrol in the course. The objectives
and description of the course are stated on the
university portal (http://portal.utb.cz) in the course
syllabus.
At the beginning of the semester, the students
use the university information system (IS) to enrol in
courses and chose particular seminars and practical
exercises in laboratories. Thus they optimize their
own study schedule. Communication between
teachers and students of both study forms is
performed through the CSE portal (http://ipe.fame.
utb.cz/). Students access their study materials in the
distance learning courses in the Moodle Learning
Management System at portal Vyuka (http://vyuka.
fame.utb.cz/), including course books and guidelines
for exercises in laboratories. Furthermore, students
have at disposal a large number of sample
documents created in OA, and thus they can
compare their products to the standards.
3 RESEARCH ON THE
INNOVATION OF
APPROACHES TO TEACHING
In the 2010/2011 academic year, over 550 students
(355 full-time, 196 part-time and 14 life-long
learning) were admitted to the FaME/TBU in Zlín.
To obtain adequate feedback of the quality
education, an extensive research was carried out at
the end of the semester in the academic year
2010/2011. It confirmed the correct aiming of the
course, but also identified possible areas of
improvement.
To obtain the results, two target groups of
students who have successfully completed study
requirements were addressed. After finishing the
course, the part-time students (KIPE) were asked to
fill in a paper questionnaire. The full-time students
(PIPE) were asked to fill in an online questionnaire.
The intention was not only to gain the views of
students, including the assessment, but also to
compare the two approaches in research and
teaching the subject. Almost 70% of questionnaires
were completed and submitted, which borders on a
successful research (in theory 75% questionnaires
should be submitted).
Two examples of the evaluation process
continue. The first example analyses the students’
response of the item: “Benefits of lectures to
students and the difficulty of the course.” In both
tests, the benefit of the CSE (IPE) course subject
areas was examined in detail. Individual subject
areas were marked; the average mark in test 1 is 1.89
(1.68 is the best and 2.14 the worst one); the average
mark in test 2 is 2.27 (1.80 is the best and 2.76 the
worst one), see Table 1. The scale is 1 to 5; 1 is the
best.
Table 1: Importance of the CSE (IPE) subject areas for
students [Source: authors].
The least beneficial subject areas marked by the
students were areas 3 and 7; the full-time students
identified areas 3, 6, 7 and 8. The subject area which
also includes the issues of enterprise computer
science earned the average mark of 1.97 by the part-
time students and 2.50 by the full-time students.
Regarding the fact that lectures at the
FaME/TBU are not mandatory, students’ attendance
was decreasing steadily from almost 100% at the
beginning of the course to less than a half. The full-
time students lacked motivation to participate in
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
284

lectures, and therefore they challenged the benefits
and importance of the lectures. They expressed more
criticism; however, it is vital to state here that they
have less or no practical experience in the use of
ICT in practice. They have not been able to assess
the importance of the course in view of the future
needs so far, and thus their marks were lower than
the marks suggested by the part-time students.
The question of the appropriateness of the choice
of subject areas presented in lectures was assigned to
the PIPE students only. The teaching should reflect
the requirement for getting the ICT skills of students
from various schools on the same level, preparing
them for work with ICT at the FaME, and enhancing
the professionalism of work with ICT for enterprise
computer science. Table 2 shows the result of the
responses. The vast majority of students consider the
subject’s areas are beneficial for them.
Table 2: Importance of the CSE (IPE) subject areas for
students [Source: authors].
4 KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
SYSTEM FOR EDUCATION
The information and knowledge society needs well
trained professionals who will be able to work with
knowledge in enterprises, government and public
organizations, and will be able to innovate
processes. Meeting such demands is not an easy
task. Therefore, besides an increase in the potential
of knowledge, the students should develop creative
skills and personality traits that would lead them to
the enhancement of their problem solving skills.
The procedure and method of teaching the
knowledge approaches at the University of Defence
(UoD) in Brno, Faculty of Military Technology
(FMT) and creation of knowledge-based systems to
students model the methodology used in the research
project MENTAL, Knowledge Management of the
Network Enabled Capability of the Army of the
Czech Republic (ACR) in 2008-2011.
The research defence project MENTAL was
oriented at the research of the knowledge and KMS
development for the NEC administration in the
ACR. NEC concept includes all ideas and measures
about warfare in the information age.
The following example of individual student’s
work was taken from the „conferences” domain. At
first, the basic concepts and work with information
sources are introduced to students, and
simultaneously, the TOVEK SW modules are
described and used (www.tovek.cz). Consequently,
the students are introduced to knowledge
approaches, creating ontology in the AToM2 SW
environment (www.aion.cz).
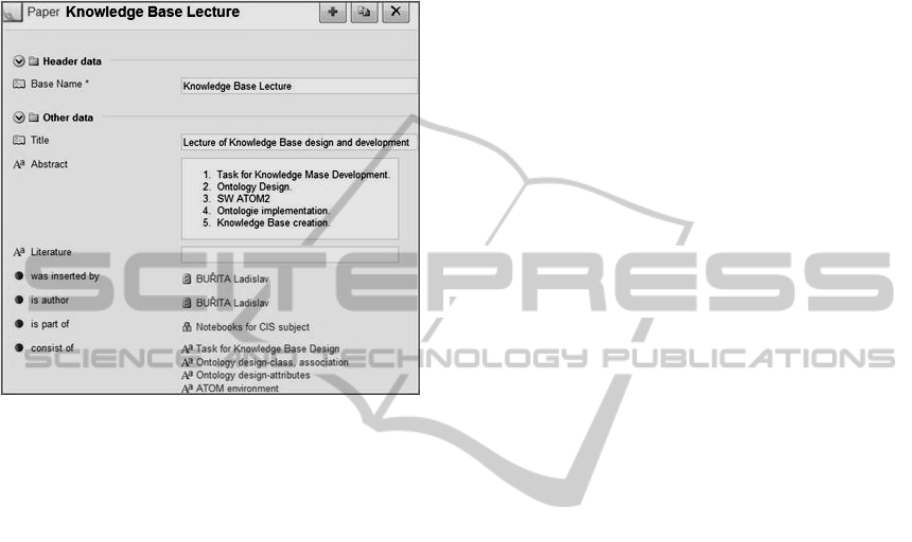
Figure 1: Ontology design [Source: authors].
The key problem of the knowledge management
system (KMS) development is ontology preparation
(model of the system). Classes and associations of
the ontology see at Figure 1.
Figure 2: Example of knowledge base on conferences in
the ATOM2 environment [Source: authors].
The procedure of the ontology elaboration
consists of typical software engineering steps:
analysis, design, implementation, testing, and
production. The implementation environment is the
ATOM2 SW, see Figure 2.
The opportunity of the KMS for the education is
resulting from its characteristics. The embedded
information and knowledge can be divided into
small parts and connected into requirement nets.
ICTEDUCATIONFORHIGHERCOMPETITIVENESSOFTHEUNIVERSITYSTUDENTS
285
Ontology driven KMS offers the chance to study
various themes according ontology concepts
(classes). Each occurrence of the class is a start point
for the new study problem, see Figure 3. The next
advantage is a complex environment where there is
no problem to add or change new study material.
Figure 3: The various starting points for the study [Source:
authors].
5 CONCLUSIONS
The first part of the paper analyses state of the
university teaching and explains the ICT role in
education process; it is followed by the description
of the teaching of Computer Science at TBU/FaME
in Zlín. The second part of the paper describes the
procedure of teaching the knowledge approach at
UoD/FMT in Brno and illustrates quick transfer
knowledge from research to education.
It states the objective, overview of subject areas and
methodology of teaching as well as the use of
information and communication technologies. The
second part contains some results of the research on
the Computer Science for Economists course and its
importance for students, focusing mostly on
enterprise computer science. The analysis of the
research results makes it possible to suggest options
for further development of the course.
The evaluation by students of both forms of
study (full-time and part-time) was positively
influenced by a number of measures and operational
changes leading to more effective communication
towards students, including innovation of the SCE
course content, which was introduced in the
2011/2012 academic year.
These include the implementation of the CSE
course portal, new FTP server and a range of
measures aimed at the improvement of the
preparation, course content and conduction of the
CSE course. They resulted from our research report,
which intended to streamline the issue of university
education, using ICT as a means for not only
obtaining information, but especially for education
and communication.
REFERENCES
Rosman, P., Burita, L., 2011. Experience of the
Integration of ICT into University Education. In
Information and Communication Technology in
Education ICTE´2011. University of Ostrava Press.
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
286
