
A STANDARD AND INTEROPERABLE
TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED ASSESSMENT SYSTEM
FOR SKILL AND KNOWLEDGE ACQUIREMENT
Enosha Hettiarachchi
1
, Maria Antonia Huertas
2
, Enric Mor Pera
2
and Ana Elena Guerrero Roldan
2
1
Internet Interdisplinary Institute (IN3), Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC), Barcelona, Spain
2
Department of Computer Science, Multimedia and Telecommunication, Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC),
Barcelona, Spain
Keywords: e-Assessment, Formative, Summative, Diagnostic, Learning Management System, Online Assessments.
Abstract: There are some subjects that require a high level of skill practice and knowledge acquisition. Many of these
are related with mathematical content. In particular, logic for computer science is a good example. There are
some interesting tools and systems available for e-assessments of this kind of subjects in higher education,
but none of them is providing rich feedback in a qualitative manner. In this paper, we describe a technology-
enhanced assessment system for assessing both skill and knowledge acquisition in online higher education
while adhering to e-learning and e-assessment standards and specifications. This technological requirement
is achieved through designing a system which allows the integration of existing partially effective tools with
common Learning Management Systems (LMSs) according to standard conformance. The system is
designed and developed in a way that it can be used as modules to existing systems or LMSs. The reason for
doing this is that institutes who are interested in the system can use the tool as a module integrated to their
existing system which maintains interoperability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Technology-Enhanced Assessment (TEA) can be
noted as the end-to-end electronic assessment
process where Information and Communication
Technology (ICT) is used for the presentation of
assessment activity, and the recording of responses.
This includes the end-to-end assessment process
from the perspective of learners, tutors, educational
institutions; awarding bodies as regulators, and the
general public (JISC, 2007). Technology-enhanced
assessments, which is most commonly known as e-
Assessment or online assessments has become an
integral part of e-learning based study programmes,
ordered by educational institutes. The main reason is
that teachers are seeking to expand assessment tasks,
while at the same time broaden the range of skills
assessed and provide students with more timely and
informative feedback on their progress.
There are a wide range of tools which can be
used for both learning and assessment. But most of
the tools are focused towards learning and only few
can be used for assessment. Technology-enhanced
assessment can have questions and activities that
have a predetermined correct answer or questions
and tasks that have more than one way of giving the
solution. Currently, most of the tools support only
predetermined questions such as Multiple Choice
Questions (MCQ) and True/False questions.
However these types of questions are good for
assessing knowledge levels of students but when it
comes to assessing skill levels, it is needed to go
beyond these types of questions to provide rich
feedback.
Both in learning and assessment, sharing of
learning resources as well as communicating with
similar systems has become a major challenge.
Therefore different standards and specifications have
been defined to represent the e-learning systems and
components. In order to have a high quality
technology-enhanced assessment system, a set of
features and requirements have been identified. One
of these requirements is e-learning standard and
specification conformation while designing and
implementing the systems. Standards help to ensure
five abilities to the e-learning and e-assessment
system such as Interoperability, Reusability,
Manageability, Accessibility and Durability (Al-
157
Hettiarachchi E., Huertas M., Mor Pera E. and Guerrero Roldan A..
A STANDARD AND INTEROPERABLE TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED ASSESSMENT SYSTEM FOR SKILL AND KNOWLEDGE ACQUIREMENT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003913401570160
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2012), pages 157-160
ISBN: 978-989-8565-07-5
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Smadi et al., 2009).
e-Assessment systems which can be used for
both skill and knowledge assessment while adhering
to most common standards and specifications are an
interesting research and development goal.
The rest of the paper is organized into five
sections where section 2 gives a general introduction
about the standards and specifications used. In
section 3, goals for developing a TEA system will be
explained with more emphasis on logic course while
also considering about e-assessments in general.
Last two sections will explain about the design and
architecture of the system and discussions
consecutively.
2 STANDARDS AND
SPECIFICATIONS FOR
E-ASSESSMENTS
Most used standards and specifications associated
with learning and assessment objects are; IMS Basic
LTI (Learning Tools Interoperability), IMS QTI
(Question and Test Interoperability), IMS LIP
(Learner Information Package) (IMS GLC, 2011),
IEEE PAPI (Public and Private Information) (CEN
WS-LT LTSO, 2011), LOM (EduTech Wiki, 2011),
and SCORM (Sharable Content Object Reference
Model) (ADL, 2011). Additionally there are some
assessment formats whose main objective is the
authoring and sharing of assessment resources. This
is an important factor which has to be considered
when communicating and exchanging information
between different systems, especially to maintain the
interoperability among systems. These assessment
formats should include the features such as response
and outcomes processing (Proc), metadata
capabilities (Meta), hybrid question management
(Hybrid), correct response indication (C.R.) and
multiple responses (M.R.) related to one question
(Gutiérrez et al., 2010). Based on the above features,
a comparison of some of the assessment formats are
illustrated in Table 1.
From the above table, mostly considering about
interoperability; IMS QTI, Hot Potatoes,
MoodleXML, OpenMark and Blackboard can be
taken into account. However, Blackboard is a
commercial software and both Hot Potatoes and
OpenMark are application specific (Gutiérrez,
Kloos, and Crespo, 2010). Some systems are
commercial/specific and they are not built according
to standards as with open source systems, which can
be easily integrated with other tools. As a result we
can take MoodleXML, a common format of the
popular and most used open source LMS, Moodle
(Moodle, 2011) and IMS QTI, a defector standard.
Table 1: Key features in assessment formats.
Formats Meta Proc M.R. C.R. Hybrid
IMS QTI x x x x x
Hot Potatoes x x x x x
MoodleXML x x x x x
OpenMark x x x x x
Blackboard x x x x x
DocBook x x
FML x
QAML x x
SuML x
To communicate between LMSs and other tools
while maintaining the interoperability, IMS has
introduced some standards such as IMS Basic LTI
and IMS-LIP. IMS Basic LTI, allow remote tools
and content to be integrated into a LMS in a secure
and interoperable manner. IMS-LIP specification
addresses the interoperability of internet-based
Learner Information systems with other systems that
support the Internet learning environment. Also for
tracking and transferring data between systems
SimpleOutcome (IMS GLC, 2011) service can be
used with OAuth (OAuth, 2011), an open protocol
which allows secure API authorization in a simple
and standard method for web applications.
3 KNOWLEDGE AND SKILL
ASSESSMENT
There are subjects in which the skill levels of
students are needed to be evaluated in order to
qualify students of that particular subject. When
considering mathematics as an example, the more
general e-assessment systems offer a range of
question types but they are not designed to offer a
specific assessment experience. Therefore, systems
and tools for e-assessment of mathematics have to
add to more general characteristics of e-assessment
systems, the possibility to represent mathematical
notation first, to recognize symbolic representations,
secondly and to asses complex processes and not
only knowledge
These raised the need to go beyond ‘usual’ type
of questions and incorporate a dynamic and an
interactive user-friendly dimension into e-
assessments. In particular, it is needed to develop a
system for e-assessments of skill acquirement, which
can communicate with currently available LMSs,
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
158
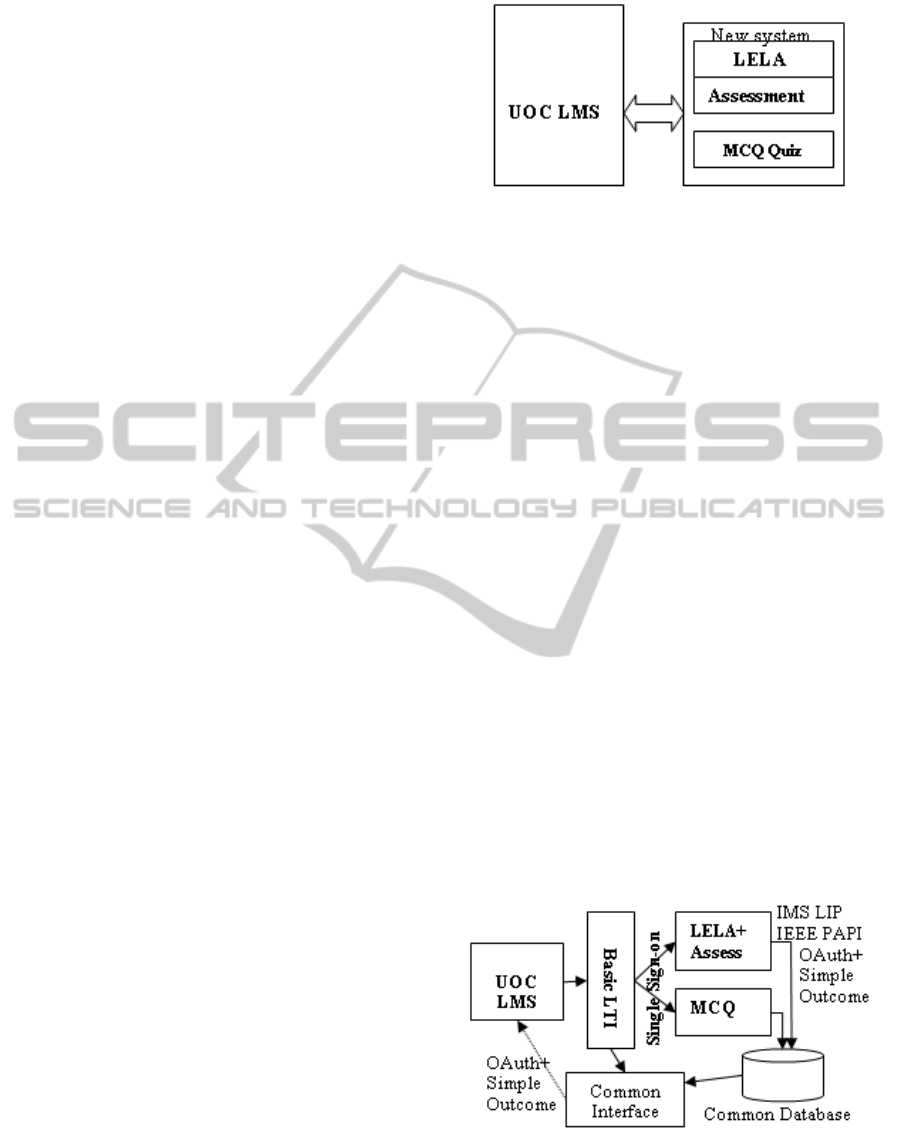
and which adheres to most commonly used
standards allowing interoperability among systems.
As the case study, Mathematical Logic courses at
the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC), a fully
online university) will be considered. Logic is a
subject which requires a high level of skill and
knowledge. At the moment, UOC use a particular
tool developed especially for mathematical logic
called Logic E-Learning Assistant (LELA), which is
an intelligent tutoring system for assisting the
learning of Logic (Huertas et al., 2011). The current
LELA system will be used as a module in the new e-
assessment system along with other tools. At the
same time, the data gathered from the new system
can be used to measure the impact of e-assessments
which in turn can be used to improve the assessment
process. It will also help to gather knowledge on
which methods/strategies are suitable for conducting
formative and summative assessment as well as
which indicators/variables should be gathered to
draw conclusions in e-assessment. General
requirements are being considered when designing
and developing the system for both formative and
summative assessments and it will be proved by
using mathematical logic subject of the UOC.
4 SYSTEM DESIGN AND
ARCHITECTURE
Following User Centred Design (UCD) approach,
firstly we identified the problems related to skill and
knowledge acquisition in online higher education.
Existing tools and research projects used for
evaluating both skills and knowledge acquisition in
formative and summative assessments were
analyzed. Then we identified the features and pitfalls
in those systems and decided to develop a new
technology enhanced e-assessment system. As our
main case, we use Mathematical logic subject of the
UOC. We designed scenarios for the system, which
was evaluated and revised based on the feedback of
the teachers and students. Since the system is being
developed as a series of modules, it was needed to
identify open source tools compatible with
assessment formats such as IMS QTI and Moodle
XML. It is highly important that these tools adhere
to standards and specifications. LELA, will also be
enhanced into an e-assessment tool. Then the
architecture of the system was designed. Here we
decided on few tools (eg: Moodle Quiz module, IMS
QTI compatible tools) and how they can be
integrated with the most common LMSs as shown in
Figure 1.
Figure 1: Architecture of the system – Level I.
We also decided on e-assessment standards (eg :
IMS Basic LTI, IMS LIP, IEEE PAPI) needed to
communicate with the LMS while maintaining
security and interoperability. Also web services and
security protocols (eg: SimpleOutcome and OAuth
protocol) needed for tracking data from several
databases and passing them to a common database
are begin studied. Here both MCQ Quiz module and
LELA will be used for formative assessments
modules. Knowledge will be assessed by using
MCQ and skills will be assessed by using LELA.
The processed results are displayed in a common
interface, which is accessible by students, teachers
and administrators. The most cost effective way of
displaying information to the users are studied,
either by passing information from the common
interface to the gradebook of the LMS or giving
access to the interface through single sign-on
facility. The ways to notify students and teachers
after processing the information such as final grade
or statistics of the system are also studied.
How to provide information rich feedback within
each module and also how often feedback should be
provided to improve the student learning process are
being studied. The final system will be implemented
with appropriate standards, web services and
security protocols. The architecture of the final
system is illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Architecture of the system – Level II.
After implementation, the system will be
validated in a real online learning environment in the
mathematical logic course. Through the
ASTANDARDANDINTEROPERABLETECHNOLOGY-ENHANCEDASSESSMENTSYSTEMFORSKILLAND
KNOWLEDGEACQUIREMENT
159

information/data obtained study whether it is
possible to track student learning over the duration
of the course. It is important to find out, which type
of e-assessment and what kind of feedback should
be provided to both teachers and students. It is also
important to analyze whether the information
obtained can be used to improve the system and the
assessment process.
5 DISCUSSION
Through the User Centred Design process, we will
be able to find out the most appropriate standards
that should be used for the communication between
systems while maintaining interoperability and also
the suitable web services and security protocols that
can be used to track, process, transfer and store data
between systems. The system validation is carried-
out with pilot studies in a real online classroom of
mathematical logic. With the results obtained, we
will be able to find an appropriate method for
conducting e-assessments, the importance of
feedback for e-assessment process, when to give
quantitative feedback with guidance for students and
also when to offer e-assessments in the learning
process. In turn check the impact of e-assessments in
the learning process.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is funded by the Internet Interdisciplinary
Institute (IN3) of the Universitat Oberta de
Catalunya (UOC).
REFERENCES
ADL, 2011. SCORM, Available at: <http://www.adlnet.
gov/Technologies/scorm/default.aspx>, [Accessed on 10
June 2011]
AL-Smadi, M., Guetl, C., and Helic, D., 2009. Towards a
Standardized e-Assessment System: Motivations,
Challenges and First Findings, Proceedings of the 4th
International Conference on Interactive Mobile and
Computer Aided Learning (IMCL2009) Conference.
Jordan, April 2009, 44-49.
CEN WS-LT LTSO, 2011. LTSC PAPI - Overview,
Available at: <http://www.cenltso.net/Main.aspx?put
=230> [Accessed on 10 June 2011]
EduTech Wiki, 2011. Learning Object Metadata
Standard, Available at: <http://edutechwiki.unige.ch/
en/Learning Object Metadata Standard>, [Accessed on
10 June 2011]
Gutiérrez, I., Kloos, C. D., and Crespo, R. M., (2010)
Assessing assessment formats: The current picture:
Special session: Assessing assessment formats,
Proceedings of IEEE Education Engineering
Conference, EDUCON (2010), Madrid, Spain. 1233-
1238.
Huertas, A., Humet, J. M., López, L., and Mor, E., 2011.
The SELL Project: a Learning Tool for E-learning
Logic. In P. Blackburn et al. (Ed.): Third International
Congress on Tools for Teaching Logic (TICTTL
2011), LNAI 6680, 123-130. Springer, Heidelberg.
IMS GLC, 2011. IMS GLC: Specifications Available at:
<http://www.imsglobal.org/specifications.html>
[Accessed on 26 September 2011]
JISC, 2007. Effective Practice with e-Assessment: An
overview of technologies, policies and practice in
further and higher education. Available at:
<http://www.jisc.ac.uk/media/documents/themes/elear
ning/effpraceassess.pdf> [Accessed on 20 October
2011]
Moodle, 2011. Welcome to the Moodle community.
Available at: <http://moodle.org> [Accessed on 20
October 2011]
OAuth, 2011. Getting Started - OAuth, Available
at:<http://oauth.net/documentation/getting-started/>
[Accessed on 20 October 2011]
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
160
