
TOWARDS PERSONALIZED TRAINING OF ELECTRIC POWER
GENERATION OPERATORS
Ricardo Molina
1
, Guillermo Rodriguez
1
, Yasmin Hernandez
1
, Israel Paredes
2
,
Gustavo Arroyo
1
and Liliana Argotte
1
1
Instituto de Investigaciones Electricas, Department of information Technologies, Reforma 113,
Cuernavaca Morelos, 62490, Mexico
2
Comisión Federal de Electricidad (CFE), Subdirección de Generación, Mexico DF., Mexico
Keywords: Personalized Training, e-learning, Labor Competences.
Abstract: This paper presents an approach to personalize the training of operators of power electricity generation.
Although the approach is described in the context of electric power generation, it can be adapted to other
cognitive training environments. The training courses are personalized on the basis of job position and the
operator‘s training history. The personalized training is complemented with the certification of labor
competences.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Web offers the perfect technology and
environment for personalized learning where
learners can be uniquely identified, content can be
specifically presented, and progress can be
individually monitored, supported, and assessed.
(Martinez 2001).
2 COMPLEX DOMAIN
LEARNING
What one regards as simple or complex is somewhat
dependent on the individual making the judgment
[Adelsberger 2008]. Besides individual differences
in terms of prior knowledge and experience,
however, there are some particular characteristics of
complex domain problem and problem-solving skills
associated with the situation. A complex cognitive
skill is one that consists of multiple constituent
skills; some of them involve thoughtful processing.
Multiple measures and reflective treatment can be
found in many work situations and problems in the
operation and maintenance of equipment for
generating electricity.
2.1 Cognitive and Psychomotor
Learning
Currently, electric power generation operators (like
other operators of complex equipment as airplanes,
helicopters, etc.), are trained, first, with theoretical
courses to gain cognitive knowledge. Then, to
acquire psychomotor experience they are sent to
power plant simulators and after that they practice in
the actual power plants supervised by a human tutor,
the trainees become real operators. The psychomotor
training is by definition personalized.
In this paper we describe the personalization of
cognitive knowledge courses for power generation
plant operators.
3 INTELLIGENT
ENVIRONMENT
ARCHITECTURE FOR
PERSONALIZED TRAINING
Our proposed architecture of an intelligent
environment is based on dynamic course generating
systems proposed by [Brusilovsky 2003]. The
intelligent environment is composed of four main
components (see Figure 1): the domain knowledge
module, the tutor, the operator model, and the
Learning Management System (LMS).
372
Molina R., Rodriguez G., Hernandez Y., Paredes I., Arroyo G. and Argotte L..
TOWARDS PERSONALIZED TRAINING OF ELECTRIC POWER GENERATION OPERATORS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003926603720375
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2012), pages 372-375
ISBN: 978-989-8565-06-8
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
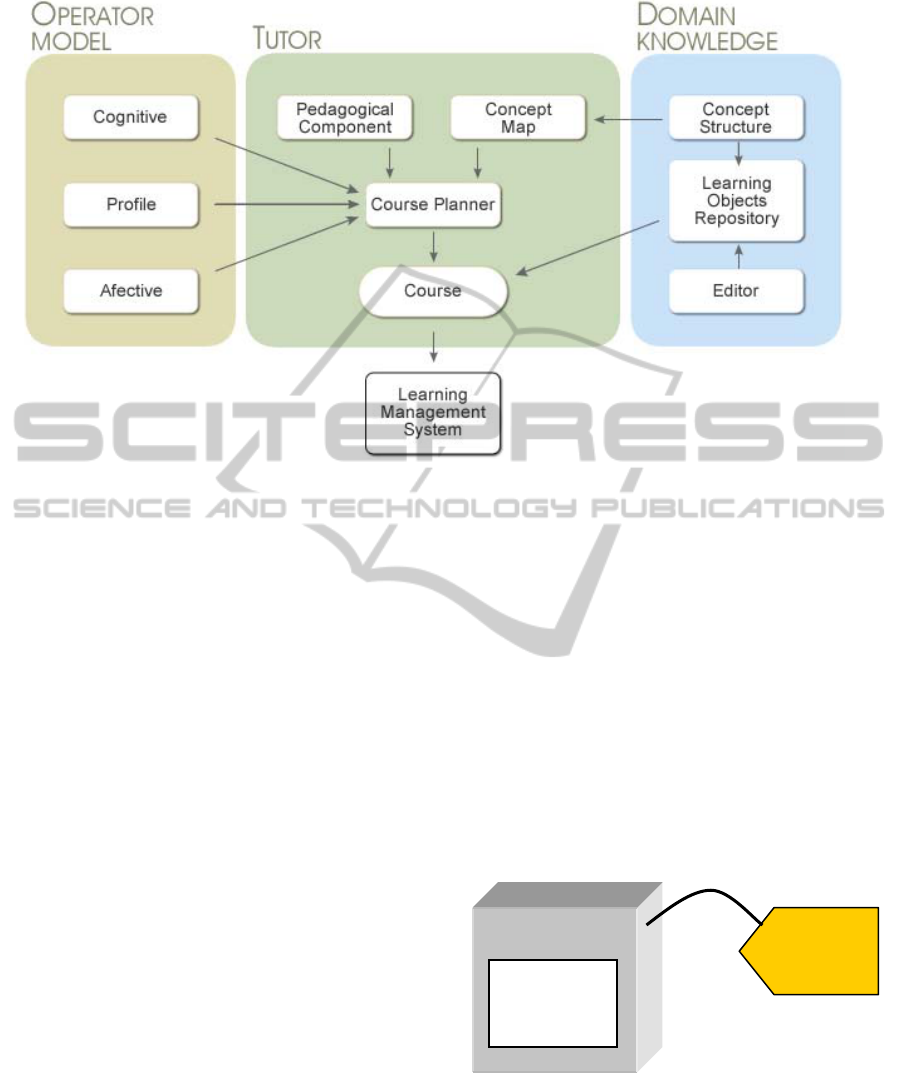
Figure 1: Architecture of the intelligent environment.
4 THE DOMAIN KNOWLEDGE
MODULE
The domain knowledge module has three main
components: the concept structure map, the editor
and the repository of learning objects.
4.1 The Concept Structure Map
The concept structure contains the concept/topic
structure of the subject knowledge to be taught. It is
possible to organize the domain concepts/topics into
a set of smaller, possibly interrelated AND/OR
graphs, representing relatively independent sub-
areas of the knowledge, different views, or different
levels of granularity. It is represented as an
AND/OR graph, where nodes represent the concepts
domain or elements of knowledge, such as electrical
topics, components of control board, rules,
procedures and so on; and arcs represent
relationships between concepts, such as a
prerequisite for learning a concept or a sequence.
Every node is associated with a set of teaching and
testing materials labeled as Reusable Learning
Object (RLO), which instantiate different ways to
teach the concept/topic (e.g. introduce, explain, give
an example, and give a simulation, exercise, or test).
For the training of power plant operators, the
concept structure map is made based on the
structural decomposition of the generation process
into unit, structure (boiler, condenser, turbine,
generator, etc.), systems (air-gas, water-steam, fuel-
oil, etc.), equipment (PI Control, etc.) and
component (pump, valve, pipe, thermometer, etc.).
4.2 Editor
The editor contains tools for edition of teaching and
testing materials based on learning objects. Each
material is labeled as Reusable Learning Object
(RLO) or Shared Content Object (SCO) according
with the SCORM (Sharable Content Object
Reference Model) terminology [ADL 2001].
Only for the generation process, CFE has a
collection of more than 400 instructional courses
developed in house during the last 10 years.
Figure 2: SCORM complaint learning objects (SLO).
The editor allows the repository manager to take
learning content, generate a SCORM 2004
compliant label o manifest and to compress all
together in a zip file (see Figure 2). The result is a
SCORM compliant Learning Object (SLO) that can
SCO
Html, WAP, GIF,
JScript, VRML, etc.
Label or
Manifest
(XML)
TOWARDSPERSONALIZEDTRAININGOFELECTRICPOWERGENERATIONOPERATORS
373
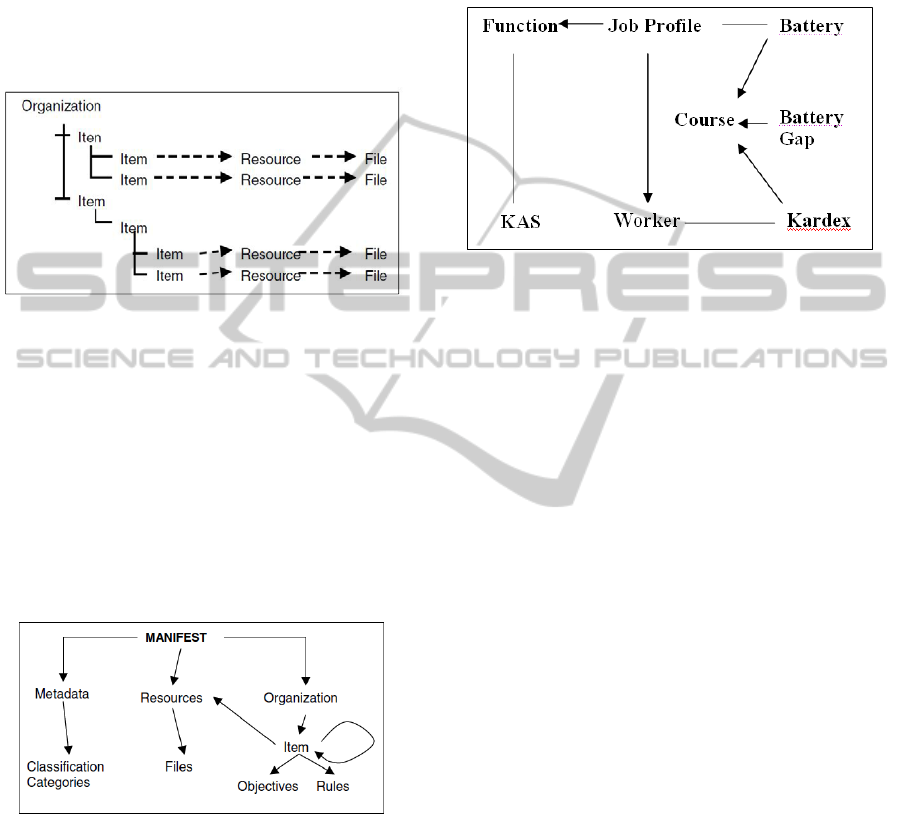
be managed by any SCORM compliant LMS.
The SCORM compliant manifest contains
metadata for the classification and recovery of the
SLO. The classification categories have been
extended to satisfy the needs of CFE, some were
inspired from concept structure map.
The SLO is a set of items to structure a course,
workshop, or other aggregation of learning
resources, the organization of the SLO is as shown
in Figure 3.
Figure 3: The organization of a SLO.
4.3 Learning Object Repository
The Domain Knowledge module has a Learning
Object Repository (LOR). The LOR is a central
database in which learning content (SLO) is stored
and managed. The Repository main component is
the database.
The repository is implemented using a relational
database management system and an abstraction
model of the database using a semantic network is
shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: The semantic network for the database structure.
Other authors [Gascueña 2005] use ontologies to
model the database but in this case a semantic net is
simpler and is a closer representation of the
relational database.
5 THE COURSE PLANNER
MODULE
First we present the basic approach and then the
competences are integrated.
5.1 Basic Course Planner
Figure 5 shows a semantic network that represents
the data used personalized courses.
Figure 5: Data used to personalized courses.
5.2 Integration of Competences
The objective is that the traditional training model
supports to the employees' labor skills certification
without affecting the training contractual rights.
The approach followed to integrate the labor
skills concept with personalized training is centered
in the concept of thematic content that the training
course programs will have to include to support the
employee in the labor skills certification process.
The idea is to establish and achieve thematic
consistency between the elements of the labor skills
norms of the key functions and the specialty courses
of the employee position profiles.
The integration process includes the set of
specialties (SP1, SP2,... SPn) obtained from the
position profiles of the productive organizational
functions and the configuration of specialties based
on skills or competences (c1, c2, … cn) achieved by
correlating the thematic content of the skills norm
with the content of the specialties courses and
adapting them or creating new contents to impact the
competence certification.
In this fashion, a specialty is a group of
competences, Sp1 = C1 + C2 +. + Cn, (see Figure
6). The specialties can be classified in more than one
specialization level, where the highest level contains
the lower levels.
As an example of a competence oriented analysis
the design of a master degree curriculum in power
plant operation is briefly described. Table 1 shows a
5 semester master in engineering curriculum where
the courses in shady background represent
competence oriented courses with thematic contents
CSEDU2012-4thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
374
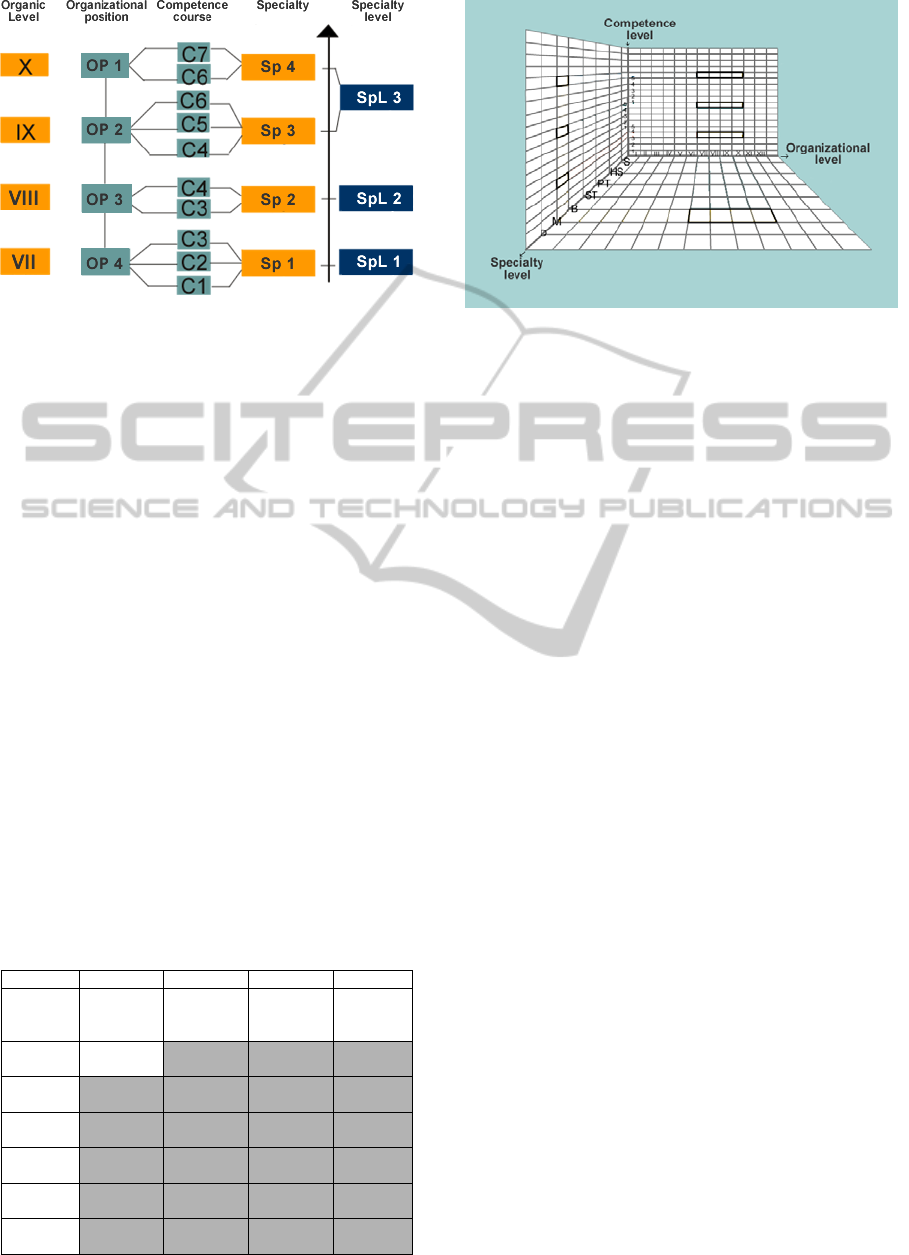
Figure 6: Competence oriented specialty courses.
matched to the thematic contents of labor skills. The
first generation of 15 employees graduated at the
end of the spring of 2008.
In Figure 7 the dimensions used in CFE to
classify the training levels are shown. The training
levels include the organic positions levels of the
employees, the competence or skills levels and the
levels of specialty to have the appropriate
qualification to his position profile, competences and
specialties.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper described an approach to personalize the
training of operators of power electricity generation.
Although the approach is applied in the context of
electric power generation, it can be adapted to other
cognitive training environments. The training
courses are personalized on the basis of job position
and the operator‘s training history. The personalized
training is complemented with the certification of
labor competences.
Table 1: Competence oriented master in power plant
operation specialty courses.
1 2 3 4 5
Thesis
Seminar
Thesis
Seminar
Thesis
Seminar
Project
Thesis
Seminar
Diagnosis
Evaluation
Goal
Negotiatin
Controllrs
Simulatin
Agent
Operation
Recovry
Strategs
Energy
Balance
Tactic
Projects
Performn
Measurm
Thermo
Economic
Performn
Tests
Fuel
Consumpt
Problem
Identificat
Plant
Modificati
Thermo
Fluids
Combusti
Start Up
Maintenan
Planning
Performan
Evaluation
Correctiv
Actions
Communc
Techniqs
Tests
Coordinati
Maintenan
Execution
Informatin
Managem
Preventiv
Actions
Knowlede
Managem
Tests
Planning
Maintenan
Results
Informatin
Systems
Failure
Analysis
Figure 7: The training classifying dimensions.
REFERENCES
Adelsberger, H. H. (ed), “Handbook on Information
Technologies for Education and Training”, Second
edition, 2008, Springer-Verlag Heidelberg
ADL Sharable Content Object Reference Model Version
1.2: The SCORM Overview. Advanced Distributed
Learning (2001), http://www.adlnet.org
Brusilovsky, P., Vassileva, J.: Course sequencing
techniques for large-scale web based education. Int.
Journal Cont. Engineering Education and Lifelong
Learning 13(1/2), 75–94 (2003)
Martinez, M., Foundations for Personalized Web Learning
Environments, Journal of Asychronous Learning
Networks, 4(2), 2001
Gascueña, J. M. et al., “Ontologies for student and domain
models in adaptive and collaborative Learning system”
Advances in Artificial intelligence Theory, Research
on Computing Science 16, 2005, pp. 33-42
TOWARDSPERSONALIZEDTRAININGOFELECTRICPOWERGENERATIONOPERATORS
375
