
SEMANTIC AND TOPOLOGICAL REPRESENTATION
OF BUILDING INTERIORS
An Overview
B. Dom´ınguez,
´
A. L. Garc´ıa and F. R. Feito
Departamento de Inform´atica, Universidad de Ja´en, Campus Las Lagunillas s/n, Ja´en, Spain
Keywords:
Building Information Models, Geographic Information Systems, Indoor Representation.
Abstract:
Software related to urban environments has experimented a considerable growth over the last years. This trend
makes necessary the creation and management of urban models, both for cities and building indoors. There ex-
ists a huge variety of proposals dealing with the geometry, topology and semantics of building indoors. In this
paper we give an overview of a number of recent works from several research areas such as Geographic Infor-
mation Systems (GIS), Building Information Models (BIM), Building Product Models (BPM) and Computer
Aided Design (CAD) tools and propose a reference architecture which gathers the analyzed features.
1 INTRODUCTION
Building indoor information is needed for multiple
applications covering diverse areas such as GIS, BIM,
spatial databases or CAD. Each area uses different ap-
proaches to represent the information; for instance,
the most extended standard used to manage BIM
information in construction is the Industry Founda-
tion Classes (IFC) model. Even within the same re-
search area, a wide range of partial views of the same
model can be found, depending on the specific ap-
plication. A classification of models and application
areas would be useful to have a starting point before
considering the development of new approaches.
2 BIM AND GIS MODELS
In 1992, Bj¨ork (Bjork, 1992) introduces an object-
oriented model to represent semantic data of build-
ings. His work focuses on the definition of a schema
including information about spaces and their enclos-
ing entities (walls, columns, doors and windows), be-
ing a precedent of the Industry Foundation Classes
(IFC) standard.
On the other hand, in the last years GIS systems
require more and more information about indoor of
buildings. Some works have researched on this topic.
Isikdag et al. (Isikdag et al., 2008) propose use case
scenarios to implement Building Information Models
(BIM) in a geospatial environment. Van Berlo
and Laat (Van Berlo and de Laat, 2010) introduce
an implementation of the conversion from IFC to
CityGML. Cerovsek makes an exhaustive research
study about BIM technology (Cerovsek, 2010). This
work offers a number of recommendations about how
BIM models should evolve in order to make easier the
development and standardization of BIM tools.
3 2D MODELS
Franz et al. (Franz et al., 2005) analyze building mod-
els under two different points of view: cognitive sci-
ences and architecture. They summarize various ex-
isting graph-based models used in both areas, and dis-
cuss the transfer of models between them.
Lamarche and Donikian (Lamarche and Donikian,
2004) propose a method to represent the topology of
an indoor space for the simulation of crowds of hu-
mans. They compute a set of graph-represented con-
vex cells using the constrained Delaunay triangula-
tion of the floor plan. This set is then represented as
a graph with nodes for the convex cells and edges for
the neighbor convex cells (see Figure 1). This topo-
logical representation of the space allow them to iden-
tify passages, crossroads and dead ends in order to
determine bottlenecks for pedestrians.
Pl¨umer and Gr¨oger (Pluemer and Groeger, 1996)
utilize another formal representation for the aggrega-
169
Domínguez B., L. García Á. and R. Feito F..
SEMANTIC AND TOPOLOGICAL REPRESENTATION OF BUILDING INTERIORS - An Overview.
DOI: 10.5220/0003930101690174
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (GRAPP-2012), pages 169-174
ISBN: 978-989-8565-02-0
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

tion of 2D spatial objects: the nested maps, defined
as planar graphs whose cycles are structured hierar-
chically, useful to model the hierarchical structure of
closed spaces.
Hierarchical region graphs are used by Stoffel et
al. (Stoffel et al., 2007) to model the structure of spa-
tial regions and the inclusion relations among them.
The data structure includes type parameters to spec-
ify the semantics of nodes (doors, windows, etc.) and
graphs (rooms, walls, floors, etc.).
Li et al. (Li et al., 2010) represent rooms, lobbies,
inner or outer walls, doors and windows using a set
of labeled cellular units (free, occupied). A regular
decomposition of the space is then made using a grid-
graph. Algorithms from graph theory allow to solve
some problems of space analysis and agent naviga-
tion.
Zhi et al. (Zhi et al., 2003) convert architectural
floor plans into an object graph representing the struc-
ture of walls and openings, such that loops represent
closed spaces. Since rooms are obtained as minimal
loops, this work uses spatial vectors of loops to com-
pute minimal area fundamental loops.
Hahn et al. (Hahn et al., 2006) deal with the real-
time generation of building interiors. The main char-
acteristics of the generator are: (1) the generation of
building interiors is lazy, and (2) a set of rules is fol-
lowed to ensure the correctness and realism of the re-
sults.
Merrell et al. (Merrell et al., 2010) use an ap-
proach based on bayesian networks to solve the gen-
eration of building interiors starting from high-level
requirements. An architectural program is created af-
ter training a bayesian network with real data; then the
architectural program is turned into a real floor plan
by applying optimization over the space of possible
building layouts.
4 2D MODELS WITH HEIGHT
Slingsby and Raper (Slingsby and Raper, 2007) deal
with pedestrian navigation in 3D city models. After
introducing a state of the art on 3D city modeling,
pedestrian navigation and pedestrian access within
buildings, this work proposes a model to represent
navigable spaces in cities consisting of a 2.5D rep-
resentation of building floors. In order to deal with
irregular morphology of floors, they propose the use
of four constraint elements: ramps, stairs, breaklines
and offsets.
Tutenel et al. (Tutenel et al., 2009) propose a rule-
based solver to generate indoor building scenarios au-
tomatically which works by using classes to represent
3D shapes (e.g. Sofa, Table, TV) with tags. They pro-
pose a rule layout planner, which consists of a back-
tracking mechanism executed to solve the placement
of each object. The solver computes a set of possible
locations for the current object according to the previ-
ously placed ones, assigning weights to them. Then,
it selects the most feasible location.
The arrangement of furniture is also solved by
Germer and Schwarz (Germer and Schwarz, 2009).
However, they use a different approach in which
agents are used to represent pieces of furniture. Each
agent is responsible for placing and orienting itself
properly, and finding a parent object. In order to
achieve this, each agent has three possible states: (1)
search, when it has not been processed, its parent has
been lost or the search for its position has failed; (2)
arrange, when the agent has found a possible parent;
and (3) rest, when the arrange is finally successful.
Regarding building rendering, Van Dongen (Don-
gen, 2008) proposes a technique to simulate building
interiors viewed from the street without any storage of
geometry. While buildings are modeled using single
cubes, the rendering process simulate the existence of
rooms, objects and people using a ray-tracing algo-
rithm with diffuse textures and billboard planes.
The structured floor-plan (Choi et al., 2007) con-
sists of a high-level semantic structure which accom-
plishes with nine principles about object orientation
of the model, existence of relationships among enti-
ties, managing of spatial information, levels of detail,
and automatic creation of 3D models.
5 3D MODELS
Choi and Lee (Choi and Lee, 2009; Lee, 2001) pro-
pose a graph structure called 3D Geometric Network,
constructed using the Straight Medial Axis Trans-
form. It represents the connectivity between rooms
of a building. Geometric networks also model the 3D
structure by means of adding edges between rooms
from different floors.
Van Treeck and Rank (Van Treeck and Rank,
2007) represent the topology using a radial-edge
structure (Weiler, 1988), which represents relations
among vertices, edges, co-edges, loops, faces and
bodies, and derives four different graphs: structural
components, the room faces, the relational objects
and rooms.
Borrmann and Rank (Borrmann and Rank, 2009)
propose a set of spatial operators to determine the rel-
ative position between the bounding boxes of two 3D
spatial objects among above, below, eastOf, westOf,
northOf and southOf.
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
170

Billen and Zlatanova (Billen and Zlatanova, 2003)
propose the dimensional model, a topological abstrac-
tion which analyzes complex relations between 3D
objects using four dimensional elements (0-D, 1-D,
2-D and 3-D) for each spatial object.
Boguslawski and Gold (Boguslawski and Gold,
2010) deal with the problem of representing non-
manifold CAD models using a data structure called
Dual Half-Edge (DHE), consisting basically of two
dual structures: a net of half-edges from solids and a
dual structure of connected solids.
Clemen and Gielsdorf (Clemen and Frank, 2008)
propose a systematic way to reduce the redundancy in
geometric models using a generalized representation
for models consisting of solids made up by faces con-
tained in planes, half edges and nodes, and ensuring
geometric constraints by referential integrity.
Van Berlo and Laat (Van Berlo and de Laat, 2010)
collaborate with the introduction of an implementa-
tion of the conversion from IFC to CityGML. In or-
der to achieve this, they introduce an extension for
CityGML called GeoBIM. Therefore, the underlying
geometric, semantical and topological models are the
same in IFC and in CityGML.
A schema with four levels of detail is proposed
by Hagedorn et al. (Hagedorn et al., 2009) to repre-
sent indoor building models. This schema has some
similarities to CityGML; however the authors include
features for indoor routing, not included in CityGML.
An example of the application of BIM for com-
puter games with indoor scenarios can be found in
(Yan et al., 2010). Yan et al. propose an architec-
ture consisting of three modules: BIM, crossover and
game. Information about the buildings is managed
by the BIM module, while the crossover module is
used to exchange information between the BIM mod-
ule and the game module.
Topological houses proposed by Paul and Bradley
(Paul and Bradley, 2003) constitute a purely mathe-
matical abstraction to define houses. This formal def-
inition allows to encode houses using two structures:
PLA (points, lines and areas) and PLAV (PLA + vol-
umes).
Finally, Xu et al. (Xu et al., 2010) propose a
model including geometric, semantic and topologi-
cal aspects of 3D City Models. To achieve this, a 3D
city model is enriched with a thematic module which
contains semantic and topological information; then
the items of the thematic module are mapped onto
the geometric model. This work also introduces a
semi-automatic integration tool for the semantic en-
richment process.
6 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
AND DISCUSSION
In the above sections a number of papers from the lit-
erature have been reviewed. In this section we will
propose a model which intends to serve as a linking
point between low-level geometry, topology and se-
mantics. Later, we will compare the reviewed works
and discuss about the applicability of the cited models
to different areas.
6.1 Our Proposal: A Three-module
Framework
Our goal is to propose an architecture to represent
building indoors accomplishing with the following re-
quirements:
1. The model should cover different views of the
same model: from low-level geometry of archi-
tectural drawings to high-level semantic informa-
tion about the structural distribution and the con-
nectivity among physical spaces (e.g. adjacency
between rooms, between a room and an exterior
area of the building, etc.).
2. All the views should be related, so that infor-
mation from different levels can be mapped effi-
ciently.
3. Other information models should be easily de-
rived from our model.
In order to achieve the described requirements, we
introduce a three-level architecture containing infor-
mation about CAD drawings and topological struc-
ture of building indoor (figure 1).
The first module represents the input data of
the framework and contains CAD architectural floor
plans. They may include information about a vari-
ety of aspects such as structure, furnishing, plumb-
ing, electricity, etc. together with meta-elements such
as measurements and annotations. Due to the huge
variety of possible models represented in CAD floor
plans, we will proposea set of constraints on the range
of input data. The second module contains the infor-
mation relevantto represent the structure of a building
interior, i.e., walls and openings, obtained as the re-
sult of semiautomatically filtering the information of
the first module. The available low-level geometry el-
ements (wall lines and opening blocks), are processed
in order to obtain high-level information (walls, wall
intersections and openings). The third module con-
tains a topology graph derived from walls and open-
ings. Its associated dual graph represents the subdi-
vision of a building into closed spaces. Finally, the
SEMANTIC AND TOPOLOGICAL REPRESENTATION OF BUILDING INTERIORS - An Overview
171

room structure gathers structural and semantic infor-
mation (topology graph) and geometric information
(wall lines).
An initial approach of our proposed model has
been tested with real CAD floor plans with promis-
ing results:
• CAD floor plans have been processed semiauto-
matically in order to get semantic and topological
features like walls, rooms (including their inner
polygons and their contour).
• Geometric information from CAD floor plans is
linked to semantic information obtained semiau-
tomatically.
• We have successfully implemented modules
which automatically export instances from our
model to CityGML and COLLADA.
Figure 1: Framework based in a three-level architecture to
represent building information models.
6.2 Comparative Analysis
Before presenting a summary of the main features of
the reviewed papers (table 1), we introduce some pre-
vious considerations related with geometry, topolog-
ical connectivity, topological adjacency and seman-
tics.
6.2.1 Geometry
The majority of the reviewed papers include geomet-
rical information as the basis of their models. How-
ever, they do not deal with geometry at the same
depth. We distinguish among the following items:
1. Works that do not mention anything regarding ge-
ometry because they only focus on semantic is-
sues. They appear in table 1 with a dash (-).
2. Works mentioning geometric elements without
giving details of the underlying representation.
They appear as implicit.
3. Geometric elements like vertices, edges, faces, re-
gions, discrete cells or volumes appear abbrevi-
ated respectively as V, E, F, R, DC, VO.
4. Other works use spread models like IFC,
CityGML, Geographic Markup Language (GML)
or BIM’s
6.2.2 Topology
We distinguish among connectivity and adjacency,
when applicable.
1. Two spaces in a building model are topologically
connected if there exists a door or a window be-
tween them. Thus, models with information about
openings have topological connectivity. Connec-
tivity is explicit if it appears represented in the
model, and implicit if it can be deduced by ana-
lyzing the model.
2. Two spaces in a building model are topologically
adjacent if they share at least one item (e.g. rooms
sharing one wall). Adjacency is explicit if the
model contains information about relationship be-
tween spaces, or implicit if the model does not
contains this information, but it can be deduced
analyzing the geometry.
6.3 Semantics
For each reviewed work, we specify which semantical
items it contains, according to the legend: RO, O, PA,
CR, S, T, W, L, C, CO represent respectively rooms,
openings, passages, crossroads, stories, tags, walls,
lifts, ceilings and corridors.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this work we have analyzed a number of exist-
ing approaches to the problem of the representation
of building indoor models. Initially, a set of criteria
to classify the existing models have been introduced.
According to these criteria, some works have been
classified into three main groups: (1) 2D (2) 2.5D and
(3) 3D.
Another topic covered in this paper has been the
analysis of the wide range of building models accord-
ing to geometric, semantic and topological features.
This analysis allows us to state some conclusions:
• Due to the huge variety of existing representation
models for building indoors, and the wide range of
fields of application, it is quite complex to achieve
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
172
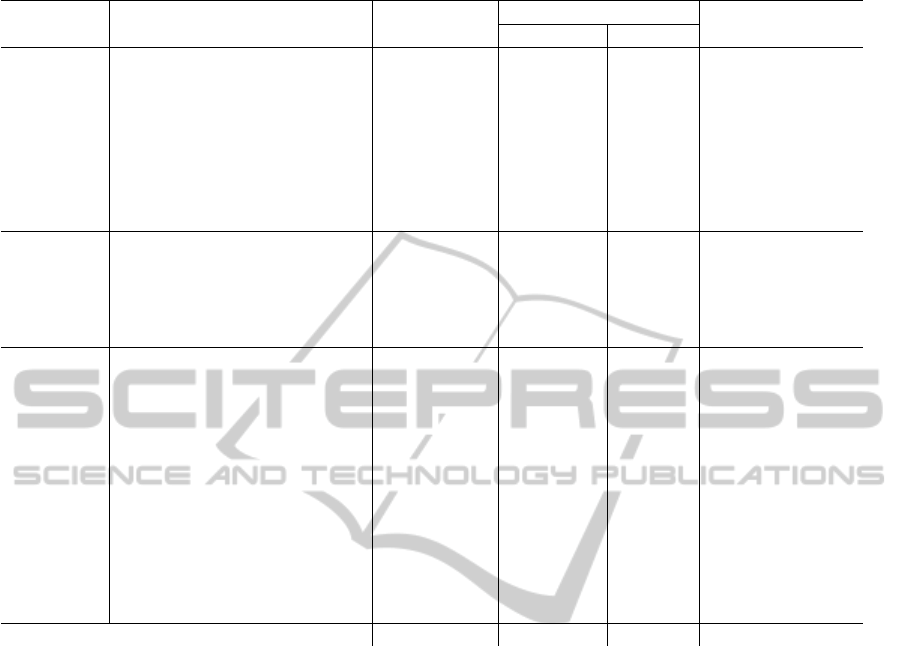
Table 1: Comparison between the overviewed works.
Group Work Geometry Topology Semantics
Connectivity Adjacency
2D models
(Franz et al., 2005) - Implicit Explicit RO, O
(Lamarche and Donikian, 2004) Implicit Explicit - PA, CR
(Pluemer and Groeger, 1996) V, E - Implicit -
(Stoffel et al., 2007) V, E, R Explicit Implicit RO, O, S
(Li et al., 2010) DC - - T
(Zhi et al., 2003) V, E, R Explicit Implicit R, O
(Hahn et al., 2006) Implicit Explicit Implicit RO, O, S
(Merrell et al., 2010) Implicit Explicit Implicit typed-RO, O
2.5D models
(Slingsby and Raper, 2007) Implicit - Implicit W, L, O
(Tutenel et al., 2009) Implicit - - RO
(Germer and Schwarz, 2009) Implicit - - RO
(Dongen, 2008) Cubes - - W, C
(Choi et al., 2007) - Explicit Implicit RO, O, S, W
3D models
(Choi and Lee, 2009) R Explicit Explicit RO, O, CO
(Clemen and Frank, 2008) V, E, F, P Explicit Explicit -
(Van Berlo and de Laat, 2010) IFC, CityGML Explicit Implicit RO, O, S, W
(Paul and Bradley, 2003) V, E, F, VO Explicit Explicit W, C
(Billen and Zlatanova, 2003) V, E, F, VO Implicit Explicit Buildings
(Hagedorn et al., 2009) GML Explicit Explicit RO, O, S, W
(Van Treeck and Rank, 2007) B-Rep Explicit Explicit RO, W
(Borrmann and Rank, 2009) VO - - Buildings
(Isikdag et al., 2008) Implicit Implicit Implicit O, S, W
(Boguslawski and Gold, 2010) V, E, F - Explicit -
(Yan et al., 2010) BIM BIM BIM BIM
(Xu et al., 2010) F, VO Explicit Explicit RO, O, S, W, C
Our proposal V, E Explicit Explicit RO, O, PA, S, W, C
Legend: V=vertices, VO=volumes, E=edges, F=faces, P = planes, R=regions
DC=Discrete cells, RO=rooms, O=openings, PA=passages, CR=crossroads
S=stories, T=tags, W=walls, C=ceilings, L=lifts, CO=corridors
unified models. Thus, we consider unavoidable a
thorough design of the problem to be solved, in-
stead of the application of general approaches.
• In most of the reviewed works, there exists a
lack of automation for getting building models,
without regard of the field (BIM, GIS, Spatial
Databases or custom models). Therefore, algo-
rithms for the extraction of semantic information
from CAD floor plans need to be developed. In
this area, we have proposed some methods to
recognize rooms semi-automatically from vector
floor plans in AutoDesk
c
DXF format, obtaining
promising initial results.
• The use of formal approaches is recommendable,
since it allows to take advantage of demonstrated
results. For example, a lot of works formulate a
problem in terms of graphs. Thus, existing algo-
rithms from graph theory can be applied without
need to demonstrate the validity of the solution.
Some of our work (in progress) tries to solve the
wall automatic recognition using graph theory.
REFERENCES
Billen, R. and Zlatanova, S. (2003). 3d spatial relationships
model: a useful concept for 3d cadastre? Computers,
Environment and Urban Systems, 27(4):411 – 425. 3D
Cadastres.
Bjork, B.-C. (1992). A conceptual model of spaces, space
boundaries and enclosing structures. Automation in
Construction, 1(3):193 – 214.
Boguslawski, P. and Gold, C. (2010). Rapid modelling of
complex building interiors. In Proceedings of the 5th
International 3D GeoInfo Conference.
Borrmann, A. and Rank, E. (2009). Specification and im-
plementation of directional operators in a 3d spatial
query language for building information models. Adv.
Eng. Inform., 23:32–44.
Cerovsek, T. (2010). A review and outlook for a [‘]building
SEMANTIC AND TOPOLOGICAL REPRESENTATION OF BUILDING INTERIORS - An Overview
173

information model’ (bim): A multi-standpoint frame-
work for technological development. Advanced Engi-
neering Informatics, In Press, Corrected Proof:–.
Choi, J. and Lee, J. (2009). 3d geo-network for agent-
based building evacuation simulation. In Lee, J. and
Zlatanova, S., editors, 3D Geo-Information Sciences,
Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography,
pages 283–299. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Choi, J. W., Kwon, D. Y., Hwang, J. E., and Lert-
lakkhanakul, J. (2007). Real-time management of spa-
tial information of design: A space-based floor plan
representation of buildings. Automation in Construc-
tion, 16(4):449–459.
Clemen, C. and Frank, G. (2008). Architectural indoor sur-
veying. an information model for 3d data capture and
adjustment. In Proceedings of the American Congress
on Surveying and Mapping.
Dongen, J. V. (2008). Interior mapping. In CGI 2008 Con-
ference Proceedings.
Franz, G., Mallot, H. A., and Wiener, J. M. (2005). Graph-
based models of space in architecture and cognitive
science - a comparative analysis. In Proceedings of the
17th International Conference on Systems Research,
Informatics and Cybernetics.
Germer, T. and Schwarz, M. (2009). Procedural arrange-
ment of furniture for real-time walkthroughs. Com-
puter Graphics Forum, 28(8):2068–2078.
Hagedorn, B., Trapp, M., Glander, T., and Dollner, J.
(2009). Towards an indoor level-of-detail model for
route visualization. In Proceedings of the 2009 Tenth
International Conference on Mobile Data Manage-
ment: Systems, Services and Middleware, MDM ’09,
pages 692–697, Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Com-
puter Society.
Hahn, E., Bose, P., and Whitehead, A. (2006). Persis-
tent realtime building interior generation. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGGRAPH symposium on
Videogames, Sandbox ’06, pages 179–186, New York,
NY, USA. ACM.
Isikdag, U., Underwood, J., and Aouad, G. (2008). An
investigation into the applicability of building infor-
mation models in geospatial environment in support
of site selection and fire response management pro-
cesses. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 22(4):504
– 519. PLM Challenges.
Lamarche, F. and Donikian, S. (2004). Crowd of virtual hu-
mans: a new approach for real time navigation in com-
plex and structured environments. Computer Graph-
ics Forum, 23:509–518.
Lee, J. (2001). 3d data model for representing topologi-
cal relations of urban features. In Proceedings of 21st
ESRI International User Conference.
Li, X., Claramunt, C., and Ray, C. (2010). A grid
graph-based model for the analysis of 2d indoor
spaces. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems,
34(6):532 – 540. GeoVisualization and the Digital
City - Special issue of the International Cartographic
Association Commission on GeoVisualization.
Merrell, P., Schkufza, E., and Koltun, V. (2010). Computer-
generated residential building layouts. ACM Transac-
tions on Graphics, 29(6):181:1–181:12.
Paul, N. and Bradley, P. E. (2003). Topological houses. In
Proceedings of the 16th International Conference of
Computer Science and Mathematics in Architecture
and Civil Engineering.
Pluemer, L. and Groeger, G. (1996). Nested maps - a for-
mal, provably correct object model for spatial aggre-
gates. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM international
workshop on Advances in geographic information sys-
tems, GIS ’96, pages 76–83, New York, NY, USA.
ACM.
Slingsby, A. and Raper, J. (2007). Navigable space in 3d
city models for pedestrians.
Stoffel, E.-P., Lorenz, B., and Ohlbach, H. (2007). Towards
a semantic spatial model for pedestrian indoor navi-
gation. In Hainaut, J.-L., Rundensteiner, E., Kirch-
berg, M., Bertolotto, M., Brochhausen, M., Chen, Y.-
P., Cherfi, S., Doerr, M., Han, H., Hartmann, S., Par-
sons, J., Poels, G., Rolland, C., Trujillo, J., Yu, E., and
Zim´anyie, E., editors, Advances in Conceptual Mod-
eling Foundations and Applications, volume 4802 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 328–337.
Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Tutenel, T., Bidarra, R., Smelik, R. M., and de Kraker, K. J.
(2009). Rule-based layout solving and its application
to procedural interior generation. In Proceedings of
the CASA workshop on 3D advanced media in gaming
and simulation (3AMIGAS).
Van Berlo, L. and de Laat, R. (2010). Integration of bim
and gis: The development of the citygml geobim ex-
tension. In Proceedings of the 5th International 3D
GeoInfo Conference.
Van Treeck, C. and Rank, E. (2007). Dimensional reduc-
tion of 3d building models using graph theory and its
application in building energy simulation. Eng. with
Comput., 23:109–122.
Weiler, K. (1988). The radial-edge structure: a topologi-
cal representation for non-manifold geometric bound-
ary modeling. Geometric Modeling for CAD Applica-
tions.
Xu, W., Zhu, Q., and Zhang, Y. (2010). Semantic modeling
approach of 3d city models and applications in visual
exploration. International Jorunal of Virtual Reality,
9(3):67–74.
Yan, W., Culp, C., and Graf, R. (2010). Integrating bim and
gaming for real-time interactive architectural visual-
ization. Automation in Construction, In Press, Cor-
rected Proof:–.
Zhi, G., Lo, S., and Fang, Z. (2003). A graph-based al-
gorithm for extracting units and loops from archi-
tectural floor plans for a building evacuation model.
Computer-Aided Design, 35(1):1–14.
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
174
