
GENERATING STYLIZED DANCE MOTION FROM
LABANOTATION BY USING AN AUTONOMOUS DANCE AVATAR
Worawat Choensawat and Kozaburo Hachimura
School of Science and Engineering, Ritsumeikan University, Kyoto, Japan
Keywords:
Dance Notation, LabanEditor, 3D CG Animation, Associate Memory, Knowledge-based Systems.
Abstract:
When producing the animation of a body motion from the dance notation, the dance knowledge is a key for
accomplishing high-quality movement. This knowledge enables the dancer to know how to perform the cor-
rect movement from a movement notation score. This paper presents an approach for automatically simulating
a CG animation from Labanotation scores. We achieve this goal by the integration of a CG animation with a
dance-style interpretation module and it is called an autonomous dance avatar. In our experiment, we imple-
mented an autonomous dance avatar to perform a Japanese stylized traditional dance such as Noh-Plays. The
result shows that the autonomous dance avatar can reproduce Noh-Play correctly from Labanotation after it
has been trained with the Noh-Play knowledge.
1 INTRODUCTION
Dance community, mainly in Western countries, has
widely accepted Labanotation as a graphical notation
scheme for describing human body movement. Sim-
ilar to music score, Labanotation uses staff and sym-
bols for the purpose of recording human movements
in the fields of choreography and dance education
(Hutchinson Guest, 1977).
Labanotation does not represent the nuances of a
performance and exact movements of any particular
dancer. However, it does capture the choreographer’s
creative idea, so that any person might interpret and
perform those ideas again. Based on the aforemen-
tioned, with the same notation score, different dancers
may perform a movement differently depend on their
experience.
Labanotation is rich in symbols, and by using the
full set of symbols; almost all of our body movements
can be described. However, the resulting notation
would become extremely complicated and difficult to
comprehend. For that reason, the fundamental sym-
bols have usually been used. The question is: how
can we realize a method of describing peculiar fea-
tures and nuances of artistic, traditional dance move-
ments while suppressing the complexity in the nota-
tion score?
Hachimura and his research team have developed
a system, named LabanEditor (Kojima et al., 2002),
for editing Labanotation score and displaying the CG
character animation of its score. LabanEditor uses a
motion template for generating a CG animation from
the fundamental elements of Labanotation (as illus-
trated in Section 2). The motion template describes
the relationship between Labanotation symbols and
the rotation and translation of the corresponding joint.
However, using a single motion template, the system
cannot reproduceslightly distinct poses that are some-
times defined with the same symbol.
For a current version of LabanEditor (Choensawat
et al., 2010), the system uses the method of dynamic
templates in order to represent the nuances of dance
movements. With the dynamic template method, the
system allows users to describe a single Labanotation
score with multiple templates. However,this will load
a user task for describing every single dance motion.
Because the creation of motion templates is a dif-
ficult task for users, this burden on the users can
be lessened by having a knowledge based of dance
styles embedded in a character model. In this pa-
per, we present a dance-style interpretation module
embedded in the character model, called Autonomous
Dance Avatar. The embedded module enabled an
autonomous dance avatar to encode the pattern of
Labanotation score and select an appropriate dance
movement to the pattern from the learned knowledge.
The proposed module is built in LabanEditor.
535
Choensawat W. and Hachimura K. (2012).
GENERATING STYLIZED DANCE MOTION FROM LABANOTATION BY USING AN AUTONOMOUS DANCE AVATAR.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, pages 535-542
DOI: 10.5220/0003946305350542
Copyright
c
SciTePress
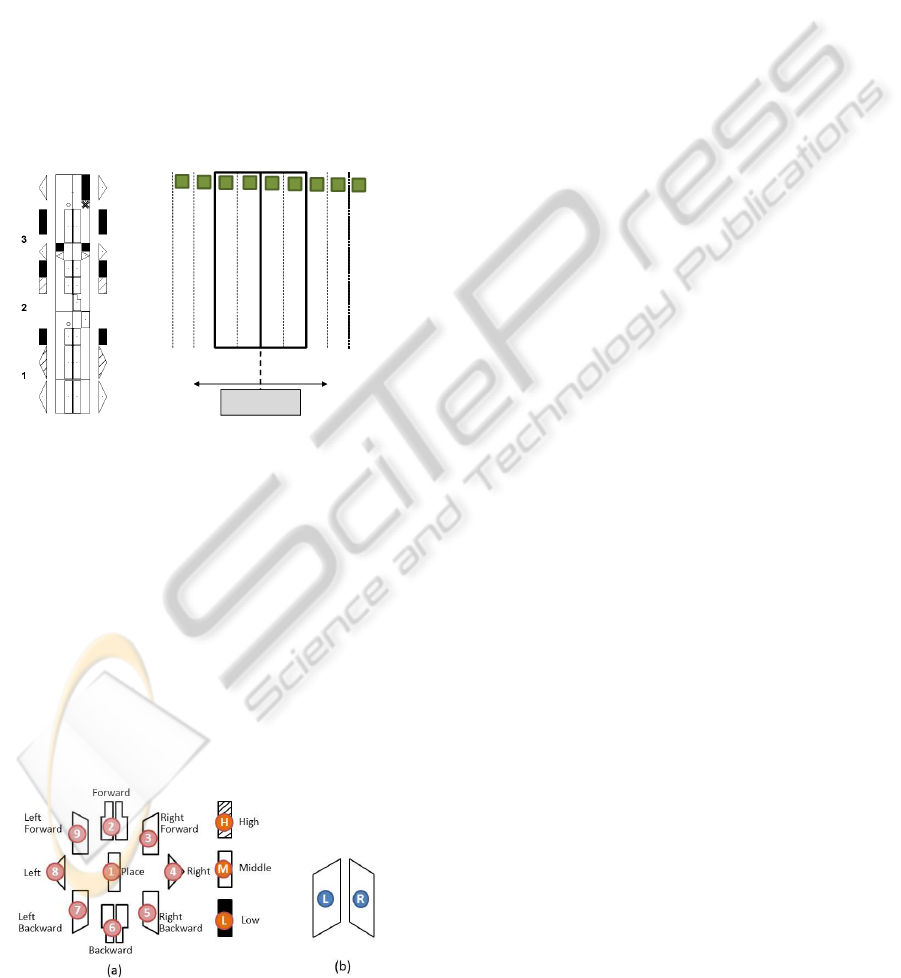
2 LABANOTATION
A Labanotation score is drawn in the form of vertical
staff where each column corresponds to a body part.
Figure 1(a) is an example of Labanotation scores cor-
responding to dance motion. Figure 1(b) shows the
basic arrangement of columns in the staff. The hor-
izontal dimension of the staff represents the parts of
the body, and the vertical dimension represents time.
The center line of the staff represents the center of the
body: Columns on the right represent the right side
of the body, and columns on the left, the left side of
the body. Symbols are placed in the columns of the
staff. The vertical length of a symbol shows the du-
ration of the movement, from its beginning to its end
(Hutchinson Guest, 1977).
^ƵƉƉŽƌƚ
^ƵƉƉŽƌƚ
ZŝŐŚƚ>ĞŐ'ĞƐƚƵƌĞ
>ĞĨƚ>ĞŐ'ĞƐƚƵƌĞ
ŽĚLJ
ŽĚLJ
>ĞĨƚƌŵ
ZŝŐŚƚƌŵ
,ĞĂĚ
>ĞĨƚ ZŝŐŚƚ
ϵĐŽůƵŵŶƐ
ϵ
ϴ
ϳ
ϲ
ϱ
ϰϯ
Ϯ
ϭ
;ĂͿ ;ďͿ
Figure 1: Labanotation scores: (a) example of Labanota-
tion scores, (b) columns of Labanotation representing body
parts.
Figure 2(a) shows direction symbols, used for de-
scribing the direction of movement of body parts. The
shape of a symbol represents the horizontal direction
of motion. Shading within a direction symbol shows
the level of a movement, i.e. vertical direction of
movement (low, middle, and high), as shown in Fig-
ure 2(a). Figure 2(b) shows the rotation signs and re-
lationship pins respectively. The motion of each body
part is expressed by a sequence of symbols placed in
Figure 2: Symbols and signs used in Labanotation: (a) di-
rection symbols, and (b) rotation signs.
the corresponding column.
Labanotation is rich in symbols, all type of move-
ment ranging from the simplest to the complex can be
accurately described. Its usefulness are not limited to
dancers and choreographer; the system has also been
successfully applied to every field in which there is
the need for recording human body motions e.g. ath-
letics, anthropology, and physiotherapy.
3 RELATED WORK
3.1 Utilizing Labanotation for Dance
Communities
To date, several graphics applications have been de-
veloped for preparing Labanotation scores and gener-
ating the body movement.
LabanWriter (Fox, 2000) is currently the most
widely used Labanotation editor. The system is only
for preparing Labanotation scores and recording them
in digital form. It does not provide a function for dis-
playing character animations corresponding to the no-
tation. The latest version of LabanWriter can handle
about 700 Labanotation symbols.
There have been several attempts to generate
CG animation from Labanotation. The CG anima-
tion generator transforms Labanotation scores, which
were prepared with LabanWriter, to the animation via
the commercial software LifeForms (Coyle et al.,
2002). However, LifeForms can only support the fun-
damental symbols of Labanotation.
LabanDancer (Wilke et al., 2005) is a Laban-
Writer scores to 3D animation translation tool. Like
LifeForms, LabanDancer does not have any functions
for preparing Labanotation scores and supports only
a limited number of symbols.
LabanChoreographer (Zhang et al., 2006) is intro-
duced for choreographing by retrieving the most sim-
ilar motions from a motion capture database. Labano-
tation is used as an index tool for retrieval. Character
animation is produced from motion capture data but
not from the notation.
Practically, the above application software has
some restrictions as follows. First, they lack of the
integration of both creating Labanotation scores and
producing 3D CG character animation. This is be-
cause they were separately designed and developed.
Secondly, their software mainly focused on Western
dances, and it takes no particular account of stylized
dance motions of other cultures.
We decided to implement a dance-style interpreta-
tion embedded in the character model in LabanEditor
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
536

because LabanEditor has the capability of preparing a
Labanotation score and displaying the 3D CG charac-
ter animation associated with the score.
3.2 Associative Memory
Simulating human-like learning or cognitive learning,
we focus on an associative memory as referred to
a content-addressable memory (Haykin, 1998). The
content-addressable memory is a memory organiza-
tion in which the memory is accessed by its content.
If a pattern is presented to an associative memory, it
returns whether this pattern coincides with a stored
pattern. The coincidence need not be an exact match.
An associative memory may also return a stored pat-
tern that is similar to the presented one, so that noisy
input can also be recognized.
An associative memory is used in information re-
trieval; for example, it is used for creating a memory
of related keywords to produce thesauri (or knowl-
edge bases) as introduced in (Lu et al., 2008; Chen
et al., 2003; Chen et al., 1993). These automatic
thesauri were then integrated with some existing
manually-created thesauri for assisting concept explo-
ration and query refinement. This associated mem-
ory was implemented with Hopfield networks (Ad´an-
Coello et al., 2007). However, other models such as
Boltzmann machine (Mairal et al., 2010), hypernet-
works (Zhang and Kim, 2006; Zhang, 2008) have
been applied to a search system of the word dictio-
nary and a sentence completion when missing some
words.
For the application of associative memories , we
are interested in the string matching problem. If there
is a given pattern, the problem consists in finding one
or more usually all the occurrences of a pattern in a
text. This problem has commonly occurred in many
applications involving information retrieval such as
bibliographic search and molecular biology. The con-
cept of associative memories can be used for solving
this problem. Such hypernetworks are used for learn-
ing the higher-order associations of the words from
a text corpus. As described by Zhang et al. (Zhang,
2008), the hypernetwork memory is used for gener-
ating a text dialogue for a given movie scene image.
The hypernetwork memory has the recall and recog-
nition capability. For example, a training sentence
“You need to wear it” and its source from the movie
“24”. In the recall task, the hypernetwork is given,
say, “? need to wear it” and should complete the miss-
ing word to produce ”You need to wear it”. In the
recognition task, the hypernetwork is to output “24”
as the source of the sentence.
As suggested above, we can adopt an associative
memory for generating a dance motion from Labano-
tation. In terms of Labanotation, a posture (or pose)
is a position of the body as represented by a combi-
nation of Labanotation symbols. Then, a pose can be
defined as a smallest unit of a Labanotation score. In
an analogous manner, a Labanotation score would be
comparable to a sentence of which words are equiva-
lent of Labanotation units and characters are Laban-
otation symbols. Lastly, the source of sentences are
comparable to a dance-style movement. The method-
ology of the dance-movement generation by using the
associative memory will be described in Section 5.
4 LABANEDITOR
LabanEditor is an interactive graphical editor for edit-
ing Labanotation scores and displaying the 3D CG
character animation associated with scores. The in-
teractive interface for preparing Labanotation score
allows users to input and edit the score by drag-and-
drop techniques. When replaying the Labanotation
score, users can observe the animation with a red hor-
izontal line cursor moving upward corresponding to
the animation progresses, as shown in Figure 3.
In the LabanEditor system, Labanotation scores
can be represented as a simple format called Labano-
tation Data (LND), which uses alphanumeric charac-
ters to represent basic symbols. The example of LND
representation is shown in Figure 4(b). The lines that
begin with “#” indicate the fundamentalparameters of
Labanotation. The movement of a body part is spec-
ified in the line followed by a command “direction”,
which corresponds to the Labanotation direction sym-
bols. Figure 4 illustrates how a Labanotation score is
convert to LND structure.
Figure 3: LabanEditor
LND describes a pose of the body at each timing
just like key-frame body postures for animation, so
GENERATING STYLIZED DANCE MOTION FROM LABANOTATION BY USING AN AUTONOMOUS DANCE
AVATAR
537

, Ğ Ă Ě Ğ ƌ
^ LJ ŵ ď Ž ůƐ
Ž Ě LJ Ɖ Ă ƌ ƚ Ɛ
ŝƌ Ğ Đ ƚ ŝŽ Ŷ > Ğ ǀ Ğ ů ^ ƚĂ ƌ ƚ Ŷ Ě
ϭ
Ϯ
ϯ
ϰ
ϱ
ϲ
η ď Ğ Ă ƚ ϰ ͬ ϰ
η ƚ Ğ ŵ Ɖ Ž ϭ Ϯ Ϭ
Ě ŝ ƌ Ğ Đ ƚ ŝŽ Ŷ ůͺ Ɛ Ƶ Ɖ Ɖ Ž ƌ ƚ Ɖ ů Ă Đ Ğ ŵ ŝĚ Ϭ ͘ Ϭ Ϭ ͘ Ϭ
Ě ŝ ƌ Ğ Đ ƚ ŝŽ Ŷ ƌ ͺ Ɛ Ƶ Ɖ Ɖ Ž ƌ ƚ Ɖ ů Ă Đ Ğ ŵ ŝĚ Ϭ ͘ Ϭ Ϭ ͘ Ϭ
Ś Ž ůĚ Đ Ğ Ŷ ƚĞ ƌ Ϭ ͘ Ϭ
Ě ŝ ƌ Ğ Đ ƚ ŝŽ Ŷ ƌ ͺ Ă ƌ ŵ ĨŽ ƌ ǁ Ă ƌ Ě ŵ ŝĚ Ϭ ͘ Ϭ Ϯ ͘ Ϭ
Ě ŝ ƌ Ğ Đ ƚ ŝŽ Ŷ ůͺ Ă ƌ ŵ ůĞ Ĩ ƚ ůŽ ǁ Ϯ ͘ Ϭ ϰ ͘ Ϭ
Ě ŝ ƌ Ğ Đ ƚ ŝŽ Ŷ ƌ ͺ Ă ƌ ŵ ĨŽ ƌ ǁ Ă ƌ Ě Ś ŝ Ő Ś Ϯ ͘ Ϭ ϰ ͘ Ϭ
;ď Ϳ
ϭ Ϯ
ϯ
ϰ
ϱ
ϲ
;Ă Ϳ
Figure 4: Relationship between Labanotation score and
LND.
that we can produce motion of a body part by sim-
ply applying interpolation between start and end key-
frame poses. A key-frame pose of a body part at a
time corresponding to an end of a symbol is defined
by a Labanotation symbol. The system converts di-
rection symbols into animation key-frames by using
a motion template for a mapping between the symbol
and its corresponding pose of the body part.
For generating a animation, the system converts
LND into animation key-frames by using a motion
template file for a mapping between the symbol and
its corresponding pose of the body part. The motion
template file describes the relationship between a di-
rection symbol at the particular column and the rota-
tion and translation of the corresponding joint.
Figure 5 shows a notation and description in a mo-
tion template file, and the resulting pose. The symbol
marked “A” in Figure 5 (a) is mapped to the descrip-
tion of the part marked “A” in the motion template
file shown in Figure 5 (b), which indicates a target
pose of the right arm achieved by rotating the right
shoulder joint 90 degree counterclockwise around the
y-axis from the standard pose as shown in Figure 5
(c).
5 AUTONOMOUS DANCE
AVATAR
An autonomousdance avatar is a character model em-
bedded with an capability of dance-style interpreta-
tion. The interpretation of dance styles is the re-
call and classification process of stored Labanota-
tion scores and their associated motion templates. To
achieve that, we started with teaching a dance avatar
to have a dance-style memory, which is an associative
memory between Labanotation scores and the corre-
Figure 5: Relationship between user input symbols and a
template file; (a) user input symbol, (b) part of a template
file, and (c) target pose corresponding to the template in (b).
sponding movements. The dance-style memory is an
associative function between scores and their move-
ments as shown in Figure 6. Figure 6 is an example
of stylized traditional dances, Noh-Plays where the
leftmost column shows Labanotation scores related to
four unit movements (called Kata) and the snapshots
of the corresponding CG animation.
Figure 6: CG character animation of four Kata: (a) Hiraki,
(b) Tachi, (c) Shitai-tome, and (d) Ougi-kazashi.
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
538

The dance-style memory can be designed and
implemented with a two-layered, associative mem-
ory. The first layer involves a recall process
of known poses. For example, as shown in
Table 1, a combination of Labanotation sym-
bols associated with pose#20 comprises three sym-
bols of (l
support,place,mid), (r support,place,mid),
(r arm,forward,mid), which these symbols are related
to Labanotation symbols #1, #2, and #4 as shown in
Figure 4 (a). After that, the second layer classifies a
sequence of poses to a trained dance style; for exam-
ple, a sequence of pose#20 and #10 is classified as
motion#3.
Table 1: Dance-style interpretation with a two-layered, as-
sociative memory.
Layer Query Recall/
Recognition
1
st
Labanotation unit Pose No.
(l support,place,mid)
pose#20(r support,place,mid)
(r arm,forward,mid)
(l arm,left,low)
pose#10
(r arm,forward,high)
2
nd
Sequence of poses Movement
(#20, #10) motion#3
(#5, #7, #30) motion#8
To summarize, we divide a task of autonomous
dance avatar into two sequential subtasks as follows:
1. Decompose a Labanotation score into a number
of units, and
2. Store and retrieve dance styles in/from the two-
layered, associate memory.
The interpretation consists of storing and retriev-
ing processes as described in Algorithms 2 and 2, re-
spectively. First of all, both algorithms must start with
the decomposition of Labanotation scores into units,
and then follow by training or testing stages as shown
in Algorithms 2 and 2), respectively. Algorithm 2 de-
scribes the implementation of an associative memory
for storing Labanotation units and ,then, dance-style
patterns which a pattern can be formed as a concate-
nation of units while Algorithm 2 shows the retrieving
method of dance-style patterns.
Given an unknown Labanotation score, we can as-
sign a set of motion templates to it by applying Algo-
rithm 2. After decomposing the Labanotation score,
Algorithm 2 starts with retrieving a stored unit from
the 1
st
-layer, associative memory for all units. Lastly,
we adopt a concept of string matching for searching a
input : A set of Labanotation scores and its
corresponding motion templates
output: A storage of dance-style patterns
1 Decompose Labanotation scores into units;
2 Create a two-layered, associative memory for
storing dance-style patterns;
1
st
: storing Labanotation units
2
nd
: storing a sequence of Labanotation units
and its associated motion tempates
Algorithm 1: Developing the dance-style pat-
tern storage.
set of motion templates. A sequence of units is analo-
gous to a text. That is to find an occurrence of a set of
patterns (defined in Algorithm 2) in the text. This can
be implemented by the 2
nd
-layer, associative memory.
input : An unknown Labanotation score
output: A set of motion templates associated
with its score
1 Decompose the Labanotation score into units;
2 for each Labanotation unit do
3 Retrieve a most matching Labanotation unit
from the 1
st
-layer, associative memory;
4 end
5 Retrieve a set of motion templates from the
2
nd
-layer, associative memory;
Algorithm 2: Retrieving a dance-style pattern
from the storage.
5.1 Decomposition of a Labanotation
Score
A Labanotation score is a set of symbols aligned
along a time line as explained in Section 2. Given
a set of symbols, we can find a minimum number
of subsets where a subset must compose of coinci-
dent symbols. Each subset represents as a unit. Al-
gorithm 3 shows how to break down a score into a
number of units as similar to the minimum clique par-
tition problem where the problem and its solution is
described in the graph algorithms and applications as
found in (Cenek and Stewart, 2003).
Given a score, vertices can be represented by sym-
bols appearing in the score. Let l
i
, c
i
, u
i
be lowest,
center, and highest points of symbol i, respectively.
Edges e
ij
will be one if and only if
l
i
≤ c
j
≤ u
i
OR l
j
≤ c
i
≤ u
j
.
GENERATING STYLIZED DANCE MOTION FROM LABANOTATION BY USING AN AUTONOMOUS DANCE
AVATAR
539

For example, we will show a decomposition by
a simple example. Given a Labanotation score as
shown in Figure 7, we can find four cliques by ap-
plying Algorithm 3 as shown in Table 2.
1 2 3
4
5
6
7
8
9
5 7
6
1 2
3 4
8 9
;ĂͿ ;ďͿ ;ĐͿ
Figure 7: Transform a Labanotation score to an undirected
graph G(V, E): (a) a Labanotation score, (b) Labeling sym-
bols with 1 to N where N is a number of symbols in the
score, and (c) the corresponding graph V = {1, . . . , N};N =
9.
5.2 Associative Memory
The purpose to use of an associative memory is for
building a dance knowledge. The knowledge can be
constructed by using a training set of input and target.
After training, the memory is equivalent to a mapping
function between inputs and the associative outputs.
This can be accomplished by using the Bayesian sta-
tistical theory (Agrawal and Srikant, 1994; Liu et al.,
1998). We are implementing an associative mem-
ory for interpreting Labanotation scores to motions.
The interpretation from scores to motions must pass
throughout poses as an in-between data as described
in Table 1. Subsequently, our model is a two-layered,
associative memory where the first layer is for match-
ing between Labanotation symbols and a Labanota-
input : A Labanotation score
output: A set of Labanotation units
1 Draw an undirected graph G(V, E), where V is
a set of all symbols appearing in the score;
2 Determine E = {e
ij
} by using the equation
below;
e
ij
=
1 if c
i
∈ [l
j
, u
j
]
0 otherwise
3 Partition V into a minimum number of cliques;
Algorithm 3: Decomposing a Labanotation
score to a set of minimum units.
Table 2: Example of a list of Labanotation units.
Labanotation score: Figure 7(a)
No. of symbols: 9
No. of units: 9 (minimum of cliques)
Clique No. Set of symbols
q
1
{1, 2, 3, 4}
q
2
{5, 6}
q
3
{6, 7}
q
4
{8, 9}
Motion template No. Pattern
t
1
q
1
q
2
t
2
q
3
q
4
tion unit, and the second is for assigning a sequence
of Labanotation units with a motion template file.
For the first-layer, the memory is used for convert-
ing a Labanotation score to a sequence of poses. We
first store the Labanotation units referred as poses, af-
ter that the memory can recall the stored poses. For
unknown pose in the recall process, the memory will
try to search the most similar pose even if some miss-
ing symbols are occurred. The implementation is
based on the statistical theory of the joint probability
of a Labanotation symbol S and a Labanotation unit
U as shown below:
P(S, U|W
1
) = P(x
S
, x
U
|W
1
) = P(x|W
1
) (1)
where W
1
is the training parameters and x = (x
S
, x
U
)
is the training pattern consisting of a Labanotation
symbol x
S
and a Labanotation unit x
U
. The imple-
mentation can be achieved by using a Bayesian clas-
sifier (Witten et al., 2011; Hall et al., 2009).
The second-layer, associate memory is used for
matching between a sequence of Labanotation units
and its corresponding motion template. Similar to the
first layer, the implementation of the second layer is
as shown below and let a sequence of units be Q and
a motion template be T.
P(Q, T|W
2
) = P(y
Q
, y
T
|W
2
) = P(y|W
2
) (2)
where W
2
is the training parameters and y = (y
Q
, y
T
)
is the training pattern consisting of a sequence of units
x
Q
and templates x
T
.
6 EXPERIMENT AND
PRELIMINARY RESULT
In experiment, we test the dance-style interpreta-
tion of Noh-Plays. For a brief description, Noh-
plays are one of the most famous and characteristic
Japanese traditional performing arts. Noh movements
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
540

Figure 8: Snapshot of the CG animation for a Labanotation score comparing between the dance avatar with Noh knowledge
and the normal avatar.
are highly stylized and unique. ‘Shimai’ is a short but
principal performance extracted from the whole Noh
play. In principle, each Shimai is composed of a num-
ber of prescribed movement units known as ‘Kata’, or
form.
For the preparation of a dance-style database, we
recorded the Noh-Plays (performed by Mr. Toyohiko
Sugiura, who is the master of Kanze Noh School) by
using three video cameras in the following angles:
front, side, and perspective views, respectively. We
have the videos of 6 Shimai with 32 unique Kata in
total. By precisely observing the videos, we described
each Kata with Labanotation and their associated mo-
tion templates. We use these Labanotation score and
their associated motion templates to built the dance
knowledge.
The aforementioned process involves with the
preparation of training data that consists of Labanota-
tion scores and the associated motion templates. We
implemented the autonomous dance avatar embed-
ded in LabanEditor and used Java classes of Bayesian
classifier (Witten et al., 2011) for developing the two-
layered, associate memory. After training a dance
avatar, it can perform a Noh play correctly where an
example is shown in Figure 8. Figure 8 shows the
snapshots of the autonomous dance avatar embedded
with a dance-style interpretation module comparing
with a normal avatar. The autonomous dance avatar
can move its body according to their stored motion
patterns while the normal avatar just moved its body
following a standard movement. Even though two
avatars put their arm besides their body, they have
different postures of their left arm. The autonomous
dance avatar has its slightly bent left arm while the
other has its left arm straight out. While their move-
ment according to Labanotation unit D (Figure 8), the
autonomous dance avatar rotating its right hand differ
from that of the normal avatar.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
Since using the fundamental description of Labano-
tation cannot describe a detail of human body move-
ment, we have to create the motion template that de-
scribes the relationship between Labanotation sym-
bols and the rotation and translation of the corre-
sponding joint. In this paper, we present an au-
tonomous dance avatar in which a dance-style inter-
pretation module embedded. The embedded mod-
ule enabled an dance avatar to encode the pattern of
Labanotation score and select an appropriate dance
movement to the pattern.
The contribution of this paper is a proposed frame-
work for developing the autonomous dance avatar
which includes the following mechanisms:
1. a mechanism based on a minimum clique partition
for finding minimum independent units,
2. a mechanism incorporated an associative memory
for storing and retrieving Labanotation units, and
searching a motion template from a sequence of
Labanotation units.
GENERATING STYLIZED DANCE MOTION FROM LABANOTATION BY USING AN AUTONOMOUS DANCE
AVATAR
541

In our experiment, we test our approach against
the stylized Japanese traditional dance, Noh-Plays.
We create the database of Noh-Plays acquired from
a recorded video of a Noh expert. The experimen-
tal results shows that the autonomous dance avatar
can remember the Noh movement pattern. Compar-
ing with a normal avatar, the autonomousdance avatar
can pose its body according to Noh style. This is an
preliminary result.
As beneficial for Noh players/learners, the au-
tonomous avatar in LabanEditor can be used for the
following goals:
• Self Studying: Noh beginners have the possibil-
ity of studying body motions on their own via the
notation and CG animation.
• Expressing Idea: They can use the system as a
presentation tool for their idea about the choreog-
raphy of the performance and display in 3D CG
animation.
• Choreographing a Noh Play: Ability to chore-
ograph a Noh play without having to have the
knowledge of Labanotation.
In future work, the dance-style knowledge of the
autonomous dance avatar will expand to cover other
dance styles. The system of a variety of dance-style
knowledge will be implemented and evaluated in both
user and expert domains. The scope of our evaluation
will be related with the usefulness of the system, the
accuracy and quality of 3D character animation.
REFERENCES
Ad´an-Coello, J., Tobar, C., de Freitas, R., and Marin, A.
(2007). Hopfilter: an agent for filtering web pages
based on the hopfield artificial neural network model.
Data Management. Data, Data Everywhere, pages
164–167.
Agrawal, R. and Srikant, R. (1994). Fast algorithms for
mining association rules in large databases. In 20th
International Conference on Very Large Data Bases,
pages 478–499. Morgan Kaufmann, Los Altos, CA.
Cenek, E. and Stewart, L. (2003). Maximum indepen-
dent set and maximum clique algorithms for overlap
graphs. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 131(1):77–91.
Chen, H., Lally, A., Zhu, B., and Chau, M. (2003). Help-
fulmed: intelligent searching for medical information
over the internet. Journal of the American Society for
Information Science and Technology, 54(7):683–694.
Chen, H., Lynch, K., Basu, K., and Ng, T. (1993). Gener-
ating, integrating, and activating thesauri for concept-
based document retrieval. IEEE Expert, 8(2):25–34.
Choensawat, W., Takahashi, S., Nakamura, M., Choi, W.,
and Hachimura, K. (2010). Description and reproduc-
tion of stylized traditional dance body motion by us-
ing labanotation. Transactions of the Virtual Reality
Society of Japan, 15(3):379 – 388.
Coyle, M., Maranan, D., and Calvert, T. (2002). A tool for
translating dance notation to animation. In Proceed-
ings of Western Computer Graphics Symposium.
Fox, I. (2000). Documentation technology for the 21st cen-
tury. Proceedings of World Dance, pages 136–142.
Hall, M., Frank, E., Holmes, G., Pfahringer, B., Reute-
mann, P., and Witten, I. (2009). The weka data min-
ing software: an update. ACM SIGKDD Explorations
Newsletter, 11(1):10–18.
Haykin, S. (1998). Neural Networks: A Comprehensive
Foundation. Pearson Education.
Hutchinson Guest, A. (1977). Labanotation. New York:
Routledge, Chapman y Hall.
Kojima, K., Hachimura, K., and Nakamura, M. (2002). La-
baneditor: Graphical editor for dance notation. In
Robot and Human Interactive Communication, 2002.
Proceedings. 11th IEEE International Workshop on,
pages 59–64. IEEE.
Liu, B., Hsu, W., and Ma, Y. (1998). Integrating classifica-
tion and association rule mining. In Fourth Interna-
tional Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data
Mining, pages 80–86. AAAI Press.
Lu, W., Lin, R., Chan, Y., and Chen, K. (2008). Using web
resources to construct multilingual medical thesaurus
for cross-language medical information retrieval. De-
cision Support Systems, 45(3):585–595.
Mairal, J., Bach, F., and Ponce, J. (2010). Task-driven dic-
tionary learning. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intel-
ligence, IEEE Transactions on, pages 1–1.
Wilke, L., Calvert, T., Ryman, R., and Fox, I. (2005). From
dance notation to human animation: The labandancer
project. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds,
16(3-4):201–211.
Witten, I., Frank, E., and Hall, M. (2011). Data Min-
ing: Practical machine learning tools and techniques.
Morgan Kaufmann.
Zhang, B. (2008). Hypernetworks: A molecular evolu-
tionary architecture for cognitive learning and mem-
ory. Computational Intelligence Magazine, IEEE,
3(3):49–63.
Zhang, B. and Kim, J. (2006). Dna hypernetworks for infor-
mation storage and retrieval. DNA computing, pages
298–307.
Zhang, S., Li, Q., Yu, T., Shen, X., Geng, W., and Wang,
P. (2006). Implementation of a notation-based motion
choreography system. Interactive Technologies and
Sociotechnical Systems, pages 495–503.
GRAPP 2012 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
542
