
CSLA: A LANGUAGE FOR IMPROVING CLOUD SLA
MANAGEMENT
Yousri Kouki and Thomas Ledoux
ASCOLA Research Team, EMN-INRIA, LINA, Ecole des Mines de Nantes, Nantes, France
Keywords:
Cloud Computing, Elasticity, Quality-of-Service (QoS), Service Level Agreement (SLA), SLA Violations.
Abstract:
Cloud computing is a paradigm for enabling remote, on-demand access to a set of configurable computing
resources as a service. The pay-per-use model enables service providers to offer their services to customers in
different Quality-of-Service (QoS) levels. Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a negotiated agreement between
a service provider and a customer where QoS parameters specify the quality level of service that the service
provider have to guarantee. However, due to the dynamic nature of the Cloud and its instability, some SLA
violations can occurred and the service providers can be charged for penalties.
In this paper, we aim at addressing the Cloud instability to better control SLA management (in particular SLA
violations) and indirectly the Cloud elasticity. We propose CSLA, a new SLA language directly integrating
some features dealing with QoS uncertainty and Cloud fluctuation. In our evaluation, we present a novel
profit model for service provider and new algorithms (for admission control and scheduling) to meet SLA
requirements (e.g. prevent SLA violations) while tackling scalability and dynamic issues.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to NIST (Hogan and al., 2011), Cloud
computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-
demand network access to a shared pool of config-
urable computing resources as services. Based on
an elasticity property, it typically involves provision-
ing of dynamically scalable and often virtualized re-
sources.
The pay-per-use model enables service providers
to offer their services to customers in different
Quality-of-Service (QoS) levels. These QoS param-
eters are used to compose some bipartisan Service
Level Agreement (SLA) between a service provider
and a service consumer. Given that Cloud architec-
tures are usually composed in several XaaS layers,
SLAs are characterized at various levels in this hier-
archy to ensure the expected QoS for different stake-
holders.
Historically, SLA has been used since the 1980s
in a variety of areas (Networking, Web Services,
etc.). Whereas SLA in utility computing systems
becomes an important research challenge, existing
SLA solutions do not tackle Cloud characteristics
such as elasticity, scalability. Initiatives such as
SLA@SOI (Wieder et al., 2011) – based on the WS-
Agreement standard (Andrieux and al., 2007) – de-
fine a consistent SLA-management framework and a
SLA model without capturing some Cloud specifici-
ties. Indeed, the Cloud paradigm is based on elastic-
ity concept and on-demand model, whereas Web Ser-
vices paradigm is focused on interoperability but not
on scalability issues. In Cloud computing, a SLA has
to be suitable for multiple layers with heterogeneous
and volatile resources in a highly dynamic environ-
ment. Moreover, performance of Cloud services may
fluctuate due to the dynamic Internet environment,
which makes the QoS inherently uncertain. To the
best of our knowledge, current SLA solutions are not
able to propose a SLA language that can cope with
the dynamic nature of clouds, the multiple QoS pa-
rameters, the broad and fluctuate network access from
many end-users.
In this paper, we aim at addressing Cloud unstabil-
ity to better control SLA management (in particular
SLA violations) and Cloud scalability. We propose
CSLA, a new SLA language to allow SLA manage-
ment strategies to be more flexible and finally Cloud
computing to be more elastic. The unstabilility is ad-
dressed by means of new features directly integrating
in our language. These scalability properties allows
CSLA to:
• cope with the error rate in SLAs so as to enable a
service provider to continue operating properly in
586
Kouki Y. and Ledoux T..
CSLA: A LANGUAGE FOR IMPROVING CLOUD SLA MANAGEMENT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003956405860591
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER-2012), pages 586-591
ISBN: 978-989-8565-05-1
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

the case of some violation;
• adapt the provider profit model to dynamic en-
vironment and QoS uncertainty. A novel profit
model, based on properties for scalability, is de-
fined;
• help a service provider to better configure Cloud
infrastructure. New configuration policies (e.g.,
scheduling, admission control, resource alloca-
tion, etc.) is proposed for configuration of Cloud
services to meet SLA requirements, while tack-
ling scalability and dynamic issues.
The rest of paper is organized as follows. Related
work are described in Section 2. Section 3 introduces
an overview of the main concepts in CSLA. Section
4 presents the benefits of CSLA. Section 5 addresses
conclusion and future work.
2 RELATED WORK
A SLA is a formal contract between service con-
sumers and providers, it specifies one or more Service
Level Objectives (SLOs) to guarantee that the service
quality is delivered to satisfy pre-agreed consumers’
expectations. SLA management is important in util-
ity computing systems because it helps to improve the
customer satisfaction level and to define clear rela-
tionship between parties.
Significant level of research in SLAs languages
has been performed by the Web services commu-
nity. Several languages, such as SLAng (Lamanna
et al., 2003), WSLA (Ludwig et al., 2003) and WS-
Agreement (Andrieux and al., 2007), have been pro-
posed for establishing agreement between two par-
ties using a XML-based language. All these works
have contributed significantly to the standardisation
of SLA. However, none meets the needs for Cloud
computing environment and particularly the elasticity
concept.
In the Cloud community, there has been many pro-
posals on SLA management. The main novelty of
the European project SLA@SOI (Wieder et al., 2011)
consists of a reference architecture for multi-layer,
multi-domain SLA management. The SLA@SOI ap-
proach defines a holistic view for the management of
SLAs and implements a SLA management framework
that can be easily integrated into a service-oriented in-
frastructure. Specifically, the project aims to enable
automatic negotiation of personalised SLAs across
multiple providers.
The Foundation of Self-governing ICT Infrastruc-
tures (FoSII) research project (Emeakaroha and al.,
2010) proposes solutions for autonomic management
Figure 1: CSLA MetaModel.
of SLAs in the Cloud. One interesting aspect of this
project is the prevention of SLA violations. The self-
management interface specifies operations for sensing
future SLA violation threats based on resource usage
experiences and predefined thresholds.
The project Contrail (CONTRAIL, 2012) pro-
poses a technology to manage SLAs in Clouds fed-
erations. Reusing SLA@SOI framework as a starting
point, the focus is to provide support for the full life-
cycle of SLAs (including the Quality of Protection).
To conclude, current work in Cloud computing are
essentially focused on SLA management at differents
levels of the Cloud services stack and for different re-
source types. However, there are no proposal to deal
with the Cloud unstability or the elasticity concept.
To this end, we propose to extend current definitions
of the SLA by introducing new features such as Fuzzi-
ness on the SLA parameter and a Confidence on SLO
and SLA. In addition, we include a Penalty model in
the agreement.
3 CSLA LANGUAGE
In this section, we present an overview of the CSLA
language which has been influenced by related work
in particular WSLA and SLA@SOI.
3.1 CSLA Meta Model
A UML class diagram (see Figure 1) represents the
CSLA:ALANGUAGEFORIMPROVINGCLOUDSLAMANAGEMENT
587

Figure 2: Penalty model.
most important conceptual object types and some of
their relationships. An agreement is specified in the
form of an instance of the class CloudSLA. This in-
stance is composed of parties and obligations. A
party (typically a provider) implements some func-
tionalities, exposed as one or more services. Also, a
party might rely on services provided by other parties.
To describe this, a party can indicate the services it re-
lies on using references. Services represent the com-
mon understanding of the contracting parties of the
structure of the service, in terms of operations, ser-
vice parameters and SLA parameter that are the basis
of the SLA. Obligations section is based on guarantee
(SLO). For each guarantee, we define requirements,
confidence and penalty. A guarantee describes a sim-
ple expression or a composite expression. A simple
expression is a SLO. It is characterized by a SLAPa-
rameter, Threshold, Comparator and Fuzziness. A
composite expression is composed of other expres-
sions. The combination of guarantees is done by us-
ing the set operators defined in the class Operator.
3.2 CSLA Properties for Elasticity
Fuzziness, Confidence and Penalty are the novel prop-
erties to deal with the scalability issues.
The degree of fuzziness defines the acceptable
margin around the threshold value of a SLA param-
eter, whereas the Confidence level defines the per-
centage of compliance of SLO clauses. Furthermore,
CSLA includes Penalty model that allows the penal-
ties applied in case of SLA violation.
The SLA violation penalty model is similar to
other related works such as (Irwin et al., 2004). The
request earns a maximum value if it executes immedi-
ately and completes within its minimum run time (see
Figure 2). The value decreases linearly with queuing
delay. The value may decrease to a negative num-
ber, indicating a penalty. We model the SLA violation
penalty as linear function : P = α +βdt where β is the
penalty rate and dt is delay time.
3.3 Examples
We present an example of SLA between a SaaS
Figure 3: SLA example.
provider and its consumer. We describe only the obli-
gations section of SLA to demonstrate our contribu-
tion : for a maximum financial cost of 0.35 e/request
to a SaaS business intelligence service, the response
time must be less than 5 seconds with acceptable mar-
gin less than 2 seconds and the availability of the ser-
vice must be greater than 98% with acceptable mar-
gin less than 2%. SLOs guaranteed on at least 97%
of requests to the SaaS service i.e. clauses must be
met for 97% of requests to the SaaS service. If more
than 3% of requests to the SaaS service violate SLOs,
a penalty of p e/violated request is applied. Penalty
value p depends on delay time : p = α + βdt where
β=15.
In this example, we treat a composite SLO that
is composed of three simple SLOs. The first SLO is
about the financial cost, the second one is about re-
sponse time and the third one is about availability.
In summary, we present a SLA support Fault-
tolerance property via the Fuzziness, the Confidence
and the Penalty model. These parameters enable a
service provider to cope with fluctuation and QoS un-
certainty and better controled SLA violations.
4 EVALUATION
Thanks to its features Fuzziness, Confidence and
Penalty model, CSLA allows Cloud providers to pro-
pose flexible profit model and new SLA management
CLOSER2012-2ndInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
588
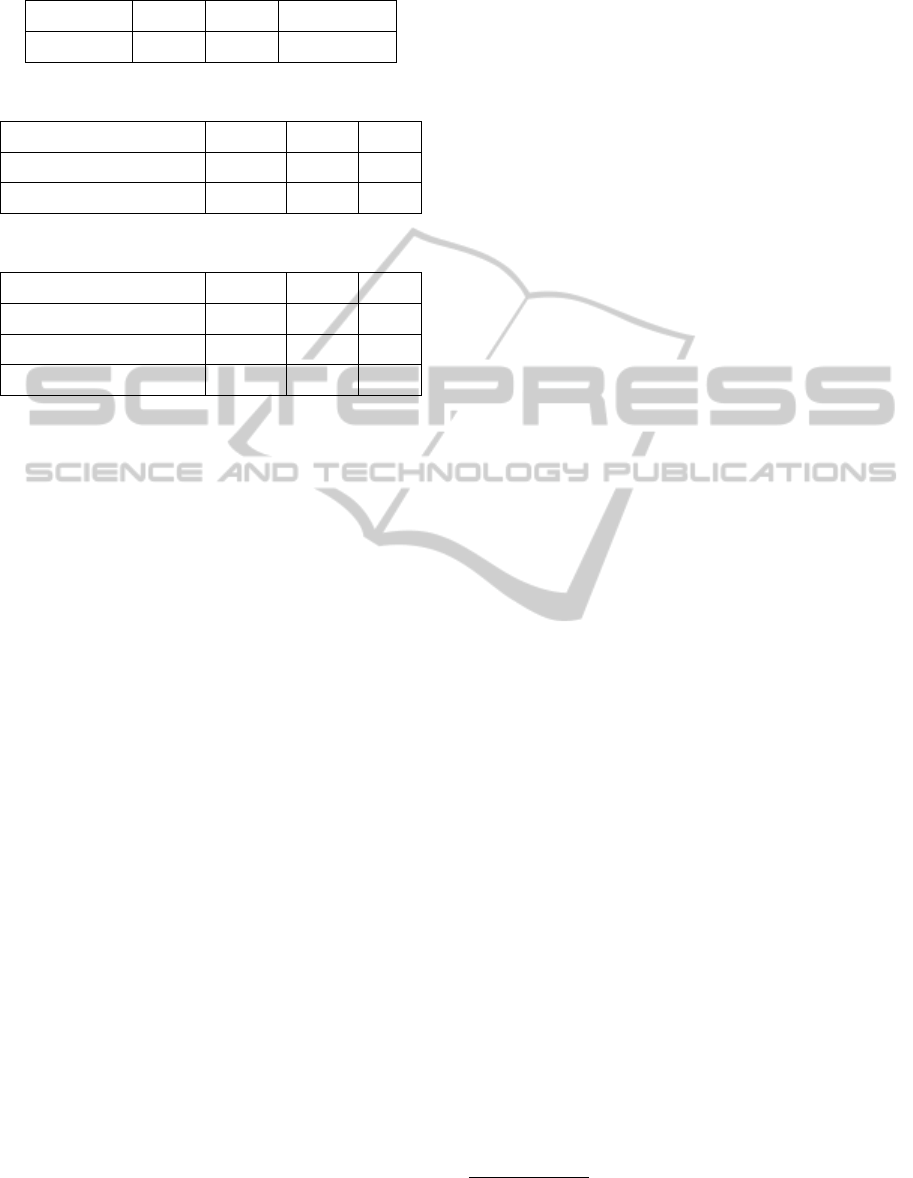
Table 1: Resources details (Windows, On-Demand).
Type Small Large Extra Large
Price/hour e0.12 e0.48 e0.96
Table 2: Pre-defined clauses (100% confidence).
Bronze Silver Gold
Price e/month 140 170 210
Min Response time (s) 8 5 4
Table 3: Pre-defined clauses (differents confidence).
Bronze Silver Gold
Price e/month 120 150 190
Min Response time (s) 8 5 4
SLA Confidence (%) 95 97 99
strategies. This section describes the evaluation of
those features as well as the prototype implemented
to evaluate them.
4.1 CSLA Prototype
The CSLA implementation uses Model Driven Ar-
chitecture (MDA) approach. Furthermore, we imple-
mented a modeling tool using ObeoDesigner in order
to easily define SLA graphical representations as dia-
grams with rich user interactions hiding the complex-
ity of an XML file. Obeo Designer allows to create the
graphical modeling workbenches that support CSLA
vocabulary. It supports our domain model based on
UML specific to the Cloud environment. We create
our code generators based on Acceleo.
The code generation tool is able to produce the
SLA in XML format which can then be parsed by the
Cloud provider. We only describe the obligations sec-
tion of SLA to show our contribution (see Figure 3).
4.2 Profit Model
We define a flexible profit model for Cloud providers.
Based on Fuzziness, Confidence and Penalty model,
our language handles the elasticity of Cloud, which
is traditionally not considered. The goal is to prevent
SLA violations to avoid penalties that are costly to
providers. Thanks to the Confidence property of the
SLA, some violations can be ”absorbed” and finally
these violations are not considered as real violations.
From the consumers point of view, it is not necessar-
ily a problem since the Cloud provider proposes new
prices for rental according to the Confidence level (see
Table 2 and Table 3). Prices (e/month) were fixed
arbitrary but can be calibrated with experience and
statistics.
1
Let us suppose that a SaaS provider sign an agree-
ment with its consumer. The properties defined in the
SLA are as follows: for a maximum financial cost of
150 e/month to the SaaS business intelligence ser-
vice, the request response time must be less than 5
seconds with acceptable margin less than 2 seconds.
SLOs guaranteed on at least 97% of requests to the
SaaS service. If more than 3% of requests to the SaaS
service violate SLOs, a penalty of p e/violated re-
quest is applied. Penalty value p depends on delay
time : p = α + βdt where β=15.
Let the total number of consumer queries be 100.
SaaS provider capability to cope and perform under a
violation is presented by the following examples :
• Fuzziness: let a response time of a request be
equal to 6 seconds. This request is considered like
not violated since 6 < 5 + 2.
• Confidence: let the number of processed requests
be 97 and the number of violated requests be 3.
The penalty is equal to 0 because the confidence
is 97%.
• Penalty: let the response time of a request be 8
seconds. The penalty will be equal to p(8 − 7) =
p(1).
The total profit earned by the SaaS provider for serv-
ing the total consumers requests is defined in equation
1.
pro f it =
C
∑
i=1
PrServ
i
−Cost (1)
where C is the total number of consumers, PrServ
i
the service price and Cost the total cost incurred to
the SaaS provider by serving the total consumers re-
quests.
The total cost is defined by equation 2:
Cost =
M
∑
j=1
V mCost
j
+
P
∑
k=1
PenaltyCost
k
(2)
where M is the total number of VMs hosting the SaaS
application, V mCost
j
is the cost of V M
j
, P is the to-
tal number of penalties-consumer and PenaltyCost
k
is
the cost of consumer penalties.
The VM cost depends on the price of VM and
rental duration ( see equation 3).
V mCost
j
= PrV M
j
.duration
j
(3)
PrV M is per instance-hour consumed for each
VM instance. duration
j
is the sum of instance-hour
of VM j.
1
The economic model for costing the rental price value
of each VM instance is out of scope of this paper.
CSLA:ALANGUAGEFORIMPROVINGCLOUDSLAMANAGEMENT
589

Figure 4: Number of SLA violations.
Figure 5: Provider profit.
The penalty cost is based on confidence property
and penalty model (see equation 4, 5 and 6).
PenaltyCost
k
=
V
∑
l=p
k
Penalty
l
(4)
where Penalty
l
is the penalty of violation l, V is
the total number of violation of consumer k and C is
the confidence of consumer k.
p
k
=
∑
V
k
− (100 −C
k
) (5)
where p
k
is the number of violations that are con-
sidered.
Penalty
l
= α + β.dt (6)
where β is the penalty rate and dt is delay time
A Cloud provider can maximize the profit by re-
ducing the resource cost, which depends on the num-
ber and type of initiated VMs. To this end, we use
scheduling algorithms such as MinAvailCapacity
designed to minimize the number of VMs by utiliz-
ing already initiated VMs. If there are more than one
initiated VM with enough available capacity to pro-
cess the query q, then the query q is assigned to the
machine with minimum available capacity.
We compare our flexible profit model, which takes
into account different confidences and supports fuzzi-
ness (see Table 3) with the previous profit model (see
Table 2). We examine algorithms with 1000 cus-
tomers. All values are summarized in Table 1, Ta-
ble 2 and Table 3. To evaluate the impact on the per-
formance of our proposed model, we vary arrival rate
from 100 to 1000 requests per second. Five differ-
ent types of request arrival rate are used. All of re-
sults present the average obtained by 10 experiment
runs. Results (see Figure 4 and Figure 5) show that,
our profit model is better when compared to the pre-
vious model. Figure 4 shows that our profit model
minimize the number of (considered) SLA violations
during variation of request arrival rate then the profit
provider increases as it can be seen from Figure 5.
4.3 SLA Management Strategies and
Configuration Policies
With CSLA, new SLA management strategies are also
possible. We propose scheduling and resource allo-
cation algorithms for SaaS provider to maximize his
profit.
SaaS provider has to manage the multiple con-
sumers’demand and obligations described in the
SLAs. In other words, it has to balance between
the cost minimization and satisfaction of the SLA re-
quirements. To achieve this goal, we propose an al-
gorithm based on Fuzziness, Confidence and Penalty
model.
A service provider can maximize the profit by re-
ducing the resource cost, which depends on the num-
ber and type of initiated VMs. We propose a new al-
gorithm designed to minimize the number of VMs by
using Fuzziness, Confidence and Penalty model. Our
algorithm is based on MinAvailCapacity and it in-
volves two main phases:
• Admission control based on confidence.
• Scheduling based on fuzziness and penalty model.
In admission control phase, the idea is to control
SLA violations so as to increase the percentage of
not considered violations. Whereas, in the schedule
phase, we schedule the new request in manner to ben-
efit from fuzziness and support the penalty model.
We examine algorithms with 1000 customers.
Values are summarized in Table 1 and Table 3. To
evaluate the impact on the performance of our pro-
posed algorithm, we vary three parameters: arrival
rate, VM capacity and penalty rate factor. All of re-
sults present the average obtained by 10 experiment
runs. In each experiment, we vary one parameter.
Due to the limitation of paper space, we only show
the results of variation of arrival rate from 100 to
1000 requests per second. Five different types of re-
quest arrival rate are used. Simulation results show
CLOSER2012-2ndInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
590
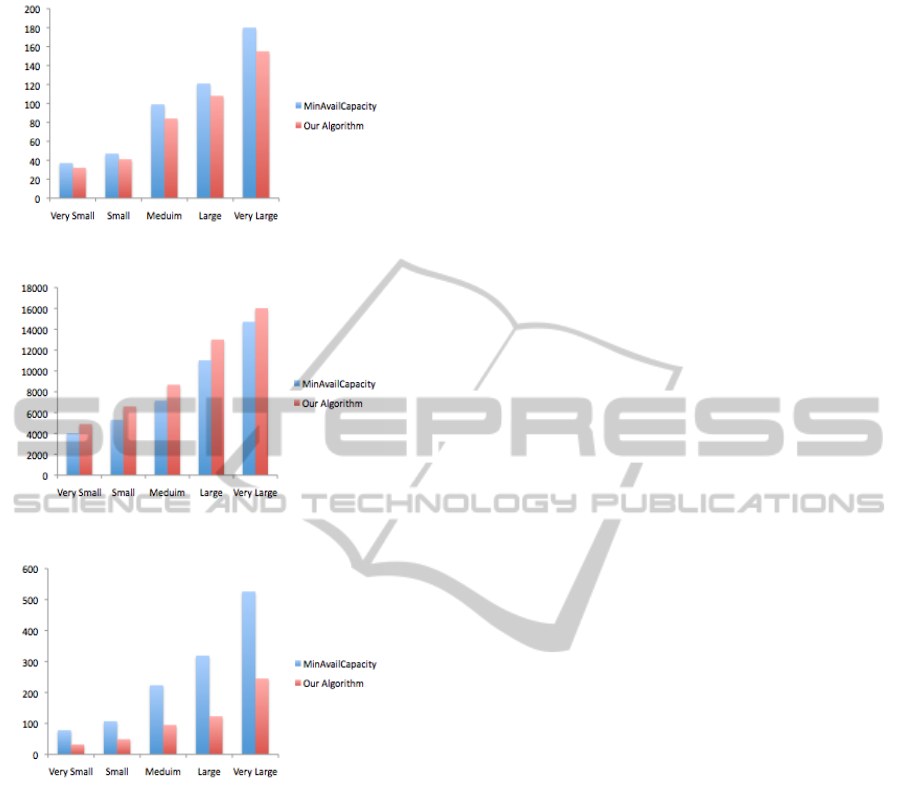
Figure 6: Number of initiated VMs.
Figure 7: Provider profit.
Figure 8: Penalty cost.
that, our algorithm – using CSLA properties – opti-
mized cost savings better when compared to standard
MinAvailCapacity. As Figure 6 shows, when the re-
quest arrival rate varies from small to very large, our
algorithm performs better to reduce the number of ini-
tiated VMs. As it can be seen from Figure 7, during
the variation of request arrival rate, the provider profit
increases because the number of VMs is reduced. Fig-
ure 8 shows that our algorithm minimize the penalty
cost during variation of request arrival rate due to con-
fidence.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Cloud computing proposes on-demand resources in a
highly dynamic and volatile environment. Therefore,
current SLA proposals should addressed inherently
the scalability and the instability issues. This paper
presents CSLA, a SLA language for improving SLA
management in Cloud computing. The instability is
addressed by means of new features directly integrat-
ing in our language. CSLA is a XML-based language
that supports several properties allowing a more con-
trolled SLA violations. Simulation results show that
the algorithm based on CSLA properties maximizes
provider profit better when compared to the previous
algorithms.
We intend to continue this work in several ways.
First, we would like to define pricing policies that
consider CSLA properties. To this end, we need more
experiments to deduce statistics for the price adjuste-
ment. Second, we continue to propose new SLA man-
agement strategies and configuration policies to max-
imise the provider profit. Finally, we intend to sup-
port negotiation phase to improve customer satisfac-
tion levels.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the MyCloud project
(ANR-10-SEGI-010).
REFERENCES
Andrieux, A. and al. (2007). Web services agreement spec-
ification (ws-agreement).
CONTRAIL (2012). http ://contrail-project.eu/.
Emeakaroha, V. C. and al. (2010). Desvi: An architecture
for detecting sla violations in cloud computing infras-
tructures. CloudComp 2010.
Hogan, M. and al. (2011). Nist cloud computing standards
roadmap, version 1.0.
Irwin, D. E., Grit, L. E., and Chase, J. S. (2004). Balancing
risk and reward in a market-based task service. 13th
IEEE International Symposium on High performance
Distributed Computing.
Lamanna, D., Skene, J., and Emmerich, W. (2003). Slang
a language for defining service level agreements.
9th IEEE Workshop on Future Trends of Distributed
Computing Systems.
Ludwig, H., Keller, A., Dan, A., King, R. P., and Franck, R.
(2003). Web service level agreement (wsla) language
specification.
Wieder, P., Butler, J., Theilmann, W., and Yahyapour, R.
(2011). Service level agreements for cloud computing.
ISBN 978-1-4614-1613-5.
CSLA:ALANGUAGEFORIMPROVINGCLOUDSLAMANAGEMENT
591
