
AUTOMATIC APPROACH FOR ONTOLOGY EVOLUTION
BASED ON STABILITY EVALUATION
Karim Kamoun and Sadok Ben Yahia
Faculty of Sciences of Tunis, University of Tunis El Manar, Tunis, Tunisia
Keywords: Ontology Enrichment, Ontology Evolution, Ontology Stability, Semantic Similarity Measure, Ontology
Quality Evaluation.
Abstract: The life time of ontology exploitation depends on the right way of making their evolution. So, in this paper,
we present a new approach of ontology enrichment. According to the stability describing the cohesion
between concepts, our proposal selects automatically the appropriate position for inserting new concepts to
ontology.
1 INTRODUCTION
Ontology is going to become the major factor to
represent knowledge on the Semantic Web. It is
often defined as an explicit specification of
conceptualization (Gruber, 1993), is necessary for
knowledge representation and knowledge exchange.
Usually this implies that ontology describes
concepts and relations that exist in a domain.
However, domain knowledge evolves continually in
dynamic environments, requiring regular updates of
the underlying ontologies.
The ontology evolve throw the time and can
become a huge one. So, manual trait with expert
intervention on the ontology enrichment will be
difficult. Thus, in this paper, we try to give an
automatic approach for ontology enrichment. From
evolution, ontology can become unstructured and
disorganised with low cohesion between their
concepts. In order to tackle this problem, we
consider in our approach that the stability is a strong
feature to ensure the right manner of enrichment.
The remainder of the paper is organized as
follows. Section 2 positions this paper within the
related work and motivates our proposed approach.
Section 3 introduces stability notion and however we
assess quality of enriched ontology based on its
stability. In section 4, we describe the different steps
of our automatic ontology enrichment approach.
This is followed in section 5 by an application
sample to better explain different steps. Section 6
briefly recalls our contributions and sketches
avenues for future work
.
2 RELATED WORKS
In this section, we scrutinize the related work that in
snugness to our work. This state of the art is focused
on two parts: the ontology evolution and semantic
similarity measures.
2.1 Ontology Evolution
Ontology evolution, first termed by Klein et al.
(Klein et. al., 2002), is a process which adapts the
contents of a pre-defined ontology used in practical
applications based on the environment in which the
applications are deployed. Many techniques are
proposed in literature for ontology evolution.
The authors in (Blundell and Pettifer 2004) use
conceptual graphs combined with ontology editor
tool such as “Protégé”. (Flouris et al, 2005) adapting
the principle of Belief Changes for ontology
evolution. They distinguish four operations changes:
Review and contraction for the changes associated
with the conceptualization, and update and delete for
domain changes. The methodology Boemie (Castano
et al, 2006), it uses the results of the extract
information in order to enrich and coordinate
multimedia ontologies.
Most of proposed techniques on ontology
evolution heavily rely on manual methods. Thus,
ontology evolution becomes a tedious and complex
task, especially when representing large-scaled and
in-depth domain knowledge.
452
Kamoun K. and Ben Yahia S..
AUTOMATIC APPROACH FOR ONTOLOGY EVOLUTION BASED ON STABILITY EVALUATION.
DOI: 10.5220/0003962104520455
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST-2012), pages 452-455
ISBN: 978-989-8565-08-2
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2.2 Similarity Measures
Ontology is described by structure of concepts
which the relation of subsumption (subClassOf) is
the primary relationship. This structure defines the
semantics of these concepts. The measures that
exploit this structure are called semantic measures of
concepts. Thus, Semantic measures can be used to
assess a link between two concepts of the same
ontology by exploiting their relationship.
Blanchard et al (Blanchard et al, 2008a)
classified semantic similarity measure in to three
types: measures that focus in the characteristic of
ontology’s entities, semantic relationship measures
and informational content measures.
For the first, the similarity between two concepts
is defined based on both common and
different
characteristics of those two concepts (Dice, 1945).
For the second, metric are proposed to measure
conceptual distance between two concepts of the
same ontology which is computed based on the
number of edges separating these two concepts
(Rada, 1989) or based on mscs(Ci;Cj ) which refers
to the most specific subsume (the lowest common
ancestor in the tree) of both concepts Ci and Cj) (Wu
and Palmer, 1994), or else improving measurement
accuracy by considering other semantic links in
addition to subsumption (Ganesan et al ,2003)
( Maguitman et al, 2005).
The third type, based on informational content,
distinguishes between two categories of measures.
The first one is based on textual corpus which
associate a probability P with concepts in a “is-a”
hierarchy to denote the likelihood of encountering an
instance of a concept c in a textual corpus.and others
using ontology structure (Resnik, 1999).
For The second category, (Blanchard et al,
2008b) present new method for computing the
information content of concept by considering only
the taxonomic structure of the ontology. Otherwise,
(Blanchard et al, 2008b) proposes four hypothesis of
instance distributions which used to compute the
informational content of a concept.
The same authors (Blanchar et al, 2008b)
propose a new measure PSS “the Proportion of
Shared Specificity” which takes into account the
density of links in the graph between two concepts.
This measure is based on one of the hypothesis
described above and called Ps. This hypothesis
implies an uniform distribution among the set of
sons of each concept, the informational content of a
concept depends on the number of sibling of the
subsuming concepts.
The enrichment approach based on stability
assessment we that we are going to propose can
apply various similarity measures in particular the
PSS measure.
3 STABILITY EVALUATION
There many approaches for ontology assessment, a
survey is described in (Brank et al, 2005). We think
that the most useful approach of ontology quality
evaluation is the one based on the use of the
ontology in real world application. The user, who
interacts with ontology based system, is interested in
the response to their request queries. So, we look for
the stability of the results regarding ontology
evolution with evaluating the semantic and structural
change between initial ontology and its enrichment.
It is evaluated based on semantic relation between
concepts of ontology. Thus, when the stability is
reached, the ontology will still with the same
semantic structure. This will lead to the same
response to user queries through enrichment.
The ontology stability according to the enrichment is
considered as semantic difference between initial
ontology and enriched one. The semantic difference
can be computed relatively to similarity between
concepts which evaluate its cohesion.
The stability is
computed using the average of the similarities
between the concepts of different ontologies (O
1
as
initial ontology and O
2
is the enrichment of O
1
).
∑∑
==
−
=
n
i
n
j
O
j
O
i
O
j
O
i
n
ccsimccsim
OOStability
11
2
21
),(),(
),(
2211
(1)
where n is the cardinality or the number of concepts
contained in O
1
and O
2
is the enrichment result of
O
1
)(
21
OO ⊂
.
1
O
i
C
represents the concept
i
C
in
ontology O
1
and Sim is the semantic similarity
measure between two concepts. We choose the
information content PSS (Proportion of shared
specificity) as similarity measure (Blanchar et al,
2008b). If the function of stability tends to 0, the
ontology evolution will be considered to be perfect
and don’t affect the stability of the ontology.
4 ENRICHMENT APPROACH
We propose a new approach for adding new
concepts to ontology. It should consider the stability
and semantic relation to get the right way for
enrichment. Indeed, adding new concepts must be
with minimizing the affect on the structure and the
semantic of ontology. It is made by the following
AUTOMATICAPPROACHFORONTOLOGYEVOLUTIONBASEDONSTABILITYEVALUATION
453

procedure.
4.1 Enrichment Procedure
Our enrichment approach is based on three steps
which try to select the suitable inserting position of
new concepts to the ontology. Furthermore, we look
for the better semantic insertion and the ontology
stability.
- Step1: extract the positions in ontology to insert
new concepts. These positions are considered to be
super -classes for inserting new concepts and will
be selected with regard to semantic similarity. For
that, we chose WordNet similarity measure (called
sim
WordNet
) to get the set of candidate supper-
classes concepts (called: Ec
superClass
) for insertion.
Ec
superClass
= { C/ sim
WordNet
(C,Cnew)>
δ
}
(2)
Where Cnew is the concept to insert in the ontology
and δ is the threshold to get better similarity.
- Step2: From the selected inserting positions of
the super-class set Ec
superClass
, we select the super-
class concept which maximize ontology stability:
)),((max
sup iierClass
OOstabilityC =
(3)
Where O is the initial ontology and O
i
is one
possible enrichment ontology with selected inserting
super-class Ci (Ci∈ Ec
superClass
.)
- Step3: construction of the new ontology with
adding new concepts as subclass to the selected
super-class (C
superClass
) from the previous step.
4.2 Case Study
We take an illustrative example of a simple ontology
named koala.owl defined by Knublauch in the
reference site of Protege-OWL:
(http://protege.stanford.edu/plugins/owl/owl-library/
koala.owl). The ontology Koala.owl includes 20
concepts except the concept of the virtual root (owl:
Thing). It describes the concepts related to humans
and marsupials (subclasses of mammals). We have
removed from this ontology three concepts in order
to obtain an initial ontology koala (vi) that includes
17 concepts which we try to enrich it with 3
concepts that we have removed to finally reach our
pristine ontology koala.owl (figure 1).
In step 1 we try to found candidate super-class
concepts using WordNet similarity. We compute the
similarity between concept root of the set of new
concepts (in our example the concept Student) and
the other ones including initial ontology. We obtain
the results described in Table1.
By
choosing the threshold of similarity δ=0,03
Table 1: WordNet similarity measure with student
concept.
student student
female 0,027 Forest 0
Marsupials 0 Parent 0,027
Animal 0 Quokka 0
person 0,09
Male 0,027
University 0,07
Female 0,027
KoalaWithPhD 0
Degree 0,04
a. initial ontology
b. new concepts to add
Figure 1: Ontology structure of koala.owl for enrichment.
and according to Table1 we have three candidate
super-classes concepts which are “Person”,
“University” and “Degree”.
Those classes are the most similar to “student”
concept and can be accordingly chosen to add this
concept as a sub-class. From the initial ontology
Koala(vi), we generate the enriched ontology
Koala(v1), Koala(v2) and Koala(v3) which consider
respectively “Person”, “University” and “Degree” as
super-class concept for new concepts to add. As a
second step, in order to select the appropriate super-
class concept from these three candidates, we
calculate stability measure for each enriched
ontology and the initial one. So, we compute the
average of difference (equation 1) between the
Matrix similarities (table2 for initial ontology,
Table3 to table5 for different possibility of
enrichment ontology).
According to different manners of adding new
concepts, we chose the resulting ontology which
minimize the semantic different for stability (table6).
So, Koala(v1) is the best enrichment resulting
ontology which add “student” concept to “person”.
It is clearly that this choice is semantically the most
appropriate according to
Koala ontology.
WEBIST2012-8thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
454
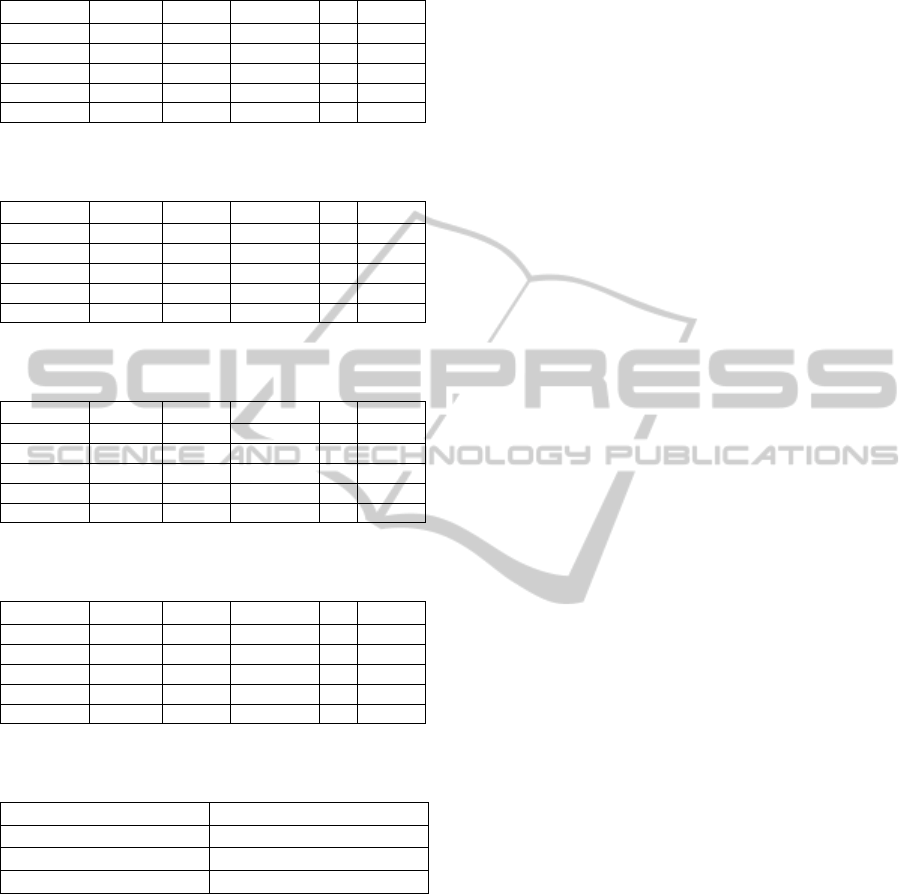
Table 2: Similarity measure of concepts pairs of ontology
Koala(vi).owl.
Female Person
Universit
.. Degree
Female 1 0,4 0,1 0
Person 0,4 1 0,2 0
Universit
0,1 0,2 1 0,5
…
Degree 0 0 0,5 . 1
Table 3: Similarity measure of concepts pairs of ontology
Koala(v1).owl.
Female Person Universit … Degree
Female 1 0,4 0,1 0
Person 0,4 1
0,3
0
Universit 0,1
0,3
1 0,5
…
Degree 0 0 0,5 . 1
Table 4: Similarity measure of concepts pairs of ontology
Koala(v2).owl.
Female Person University … Degree
Female 1 0,4 0,1 0
Person 0,4 1
0,3
0
University 0
0,2
1
0,43
…
Degree 0 0
0,43
. 1
Table 5: Similarity measure of concepts pairs of ontology
Koala(v3).owl.
Female Person University … Degree
Female 1 0,4 0,1 0
Person 0,4 1
0,3
0
University 0,1
0,3
1
0,67
…
Degree 0 0,2
0,67
. 1
Table 6: Stability measure between initial and enriched
ontology.
Koala(vi) Stability
Koala(v1) 0,03
Koala(v2) 0,08
Koala(v3) 0,09
5 CONCLUSIONS
Managing the evolution of large ontology is a hard
task. For that we propose a new automatic
enrichment procedure. This proposal makes the best
way of inserting new concepts to ontology. It
considers semantic similarity between new concepts
and their inserting supper-class. It also allows the
structural and semantic stability through ontology
evolution. As a first step, we validate our approach
with simple case study of the Koala ontology. In
further works, we will study the efficiency of our
approach for real complete ontology.
REFERENCES
T. R. Gruber, 1993. A translation approach to portable
ontology specifications, Knowledge 5 (2), pages 199-
220.
Klein M., Fensel D., Kiryakov A., and Ognyanov D. 2002:
Ontology Versioning and Change Detection on the
Web, In Proceedings of the OntoWeb-SIG3 Workshop
at the 13th International Conference on Knowledge
Engineering and Knowledge anagement.
Blundell B. and Pettifer S. 2004: Graph isualization to Aid
Ontology Evolution in Protégé, In Proceedings of 7th
International Protégé Conference, July 2004.
Flouris G., Plexousakis D. 2005, Handling Ontology
Change: Survey and Proposal for a Future Research
Direction, Technical Report FORTH-ICS/TR-362.
Castano S., Dalakleidi K., Dasiopoulou S., Espinosa S.,
Ferrara A., Hess G.N., Karkaletsis V. Kaya A., Melzer
S., Moller R., Montanelli S., Petasis G., 2006.
Delivrable D4.1 Methodology and Architecture for
Multimedia Ontology Evolution.
E. Blanchard, M. Harzallah, P. Kuntz and H. Briand.
2008a, Sur l'évaluation de la quantité d'information
d'un concept dans une taxonomie et la proposition de
nouvelles mesures. Special issue "knowledge
modeling" journal of new information technologies
(RNIT). Cepadues (12), 127-145.
L. R. Dice, 1945 Measures of the amount of ecologic
association between species. Ecology 26(3), 297–302.
R. Rada, H. Mili, E. Bicknell, and M. Blettner, 1989
Development and application of a metric on semantic
nets. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, 19, Jan/Feb.
Z. Wu and M. Palmer, 1994. Verb semantics and lexical
selection. In proceedings. of the 32nd annual meeting
of the associations for Comp. Linguistics, 133–138.
P. H. Ganesan, Garcia-Molina and J. Widom, 2003
Exploiting hierarchical domain structure to compute
similarity. ACM Trans. on Information Systems 21(1):
64–93.
A. G. Maguitman, F. Menczer, H. Roinestad, and A.
Vespignani, 2005. Algorithmic detection of semantic
similarity. In proceedings of the 14th int. conf. on
world wide web, 107–116. ACM Press.
P. Resnik, 1999. Semantic similarity in a taxonomy : An
information-based measure and its application to
problems of ambiguity in natural language. Journal of
Artificial Intelligence Research, 11: 95–130.
E. Blanchard, M. Harzallah and P. Kuntz, 2008b. A
generic framework for comparing semantic similarities
on a subsumption hierarchy. In proceedings of 18th
European Conference on Artificial Intelligence
(ECAI), 20-24.
J Brank., M Grobelnik., D Mladenic., A Survey of
Ontology Evaluation Techniques, in Proceedings of
the Conference on Data Mining and Data Warehouses
(SiKDD 2005), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2005.
AUTOMATICAPPROACHFORONTOLOGYEVOLUTIONBASEDONSTABILITYEVALUATION
455
