
Study on Task Decomposition in Emergency Logistics based on
System Dynamics
Jun Su
1
and Li-jun Cao
2
1
School of Management, Jinan University, Guangdong, Guangzhou, 510632, P.R.China
2
School of International Business, Jinan University, Guangdong, Zhuhai, 519070, P.R.China
Keywords: System Dynamics, Dynamic Alliance of Logistics, Task Decomposition, Emergency.
Abstract: It analyzed several key factors by system dynamics that the task decomposition in emergency logistics
impact on dynamic alliance of logistics. These factors included inter-constraints, quality of cooperation,
collaboration time, ability to adapt with each other, core capabilities of logistics. To establish diagram and
system dynamics model, it can forecast and analysis disadvantages of task decomposition in emergency
logistics. It can for the government emergency management to provide strategic adjustment decision
support. On this basis, it simulated the task decomposition of system dynamics model on dynamic alliance
of logistics by EXCEL, tested and verified this way was a feasible approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
When unexpected events occurred, government
organized the dynamic alliance of logistics quickly
for transporting emergency supplies. Their primary
job is to break down the missions into several sub-
tasks, and then look for federates of dynamic
alliance of logistics for each sub-tasks. In the
process, the government should consider which way
is the best of task decomposition.
The extent of task decomposition determines the
number of federates in logistics dynamic alliance
adapt to the emergency incident, the different
running status of logistics dynamic alliance, and the
success or failure to the emergency task ultimately.
But the extent of task decomposition influence by
many indicators, such as the mandate of the total
stipulated completion time, each sub-task stipulated
completion time, the working ability in core part of
task, and ability to adapt to each other. It should be
used to the co-ordinate system for ensuring access to
the optimal task decomposition scheme.
When unexpected event occurred, the
management system of emergency logistics is a non-
stable, non-equilibrium dynamics of the process
system. It should not be used the way as solve stable
systems to resolving such issues. The system
dynamics is to study the behavior of complex
feedback systems in the computer simulation
method, it can start from the system as a whole, find
and study of related factors within the system. It also
can focus on the dynamics of process and causality
in logistics system, and to solve complex problems
in a non-complete non-state analysis of information
(Hu et al., 2006).
Currently, it has a lot of studies in task
decomposition, particularly in large enterprises and
multi-enterprise collaboration between departments
in manufacturing. Pi (2006) studied and explored the
significance and role in task decomposition of
aerospace; Chen (1998) focused on analysis of task
decomposition in the Boeing Commercial Aircraft
Manufacturing Engineering System; Hu et al.
(2005a) proposed the optimization of the virtual
enterprise partner selection model based on the task
decomposition, and the same year, she proposed
process of building a virtual enterprise framework
based on task decomposition (Hu et al., 2005b);
Zhang et al. (2007) addressed a multi-level projects
across the enterprise network planning method based
on task decomposition, to solve multi-level program
consistency problem in cross-enterprise projects.
This article built a dynamic alliance of logistics
simulation model of task decomposition, with the
impact of the relationship between the relevant
indicators based on system dynamics theory .Finally,
it discussed the model simulation results and
applications.
301
Su J. and Cao L..
Study on Task Decomposition in Emergency Logistics based on System Dynamics.
DOI: 10.5220/0003963703010304
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2012), pages 301-304
ISBN: 978-989-8565-10-5
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
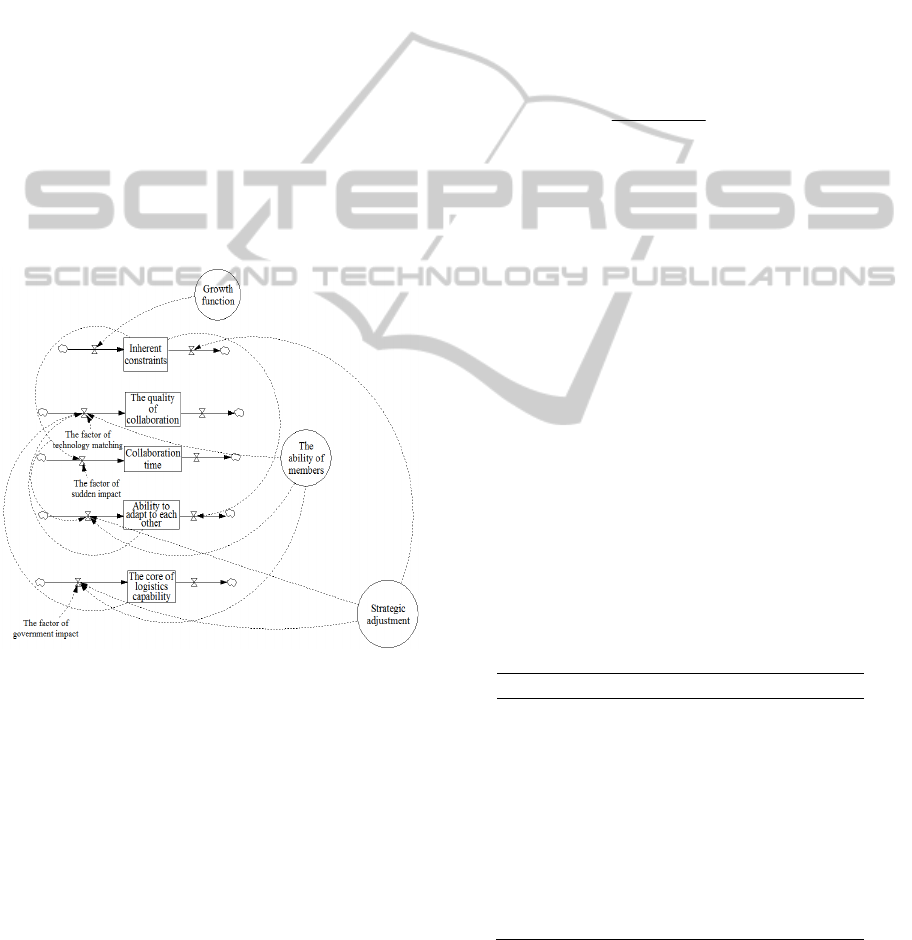
2 THE ANALYSIS OF THE
CAUSAL RELATIONSHIP IN
TASK DECOMPOSITION OF
EMERGENCY LOGISTICS
Use of system dynamics to build the flow of causal
relationship diagram, It can effectively express the
relationship of system feedback, and identify the
location of the proper task decomposition. In the
process of task decomposition of logistics dynamic
alliance, the quality of cooperation, collaboration
time and so on, can be affected by many factors,
such as logistics facilities and equipment damage,
road conditions after expected events, government
policies, as well as the impact from different quality
of the federate and so on. According to the causal
relationship between the determinants, and being
combined with other variables in the decomposition
of the project, it used VENSIM to build system flow
diagram, shown in Figure1.
Figure 1: The flow chart of causal elements in emergency
logistics task decomposition.
It is usually that the more federates the more
bindings. To be targeted strategic adjustments
timely, such as replace members of union, can
improve the collaboration efficiency and adapt of
ability, and prevent the growth trend of inherent
constraints in logistics dynamic alliance. But at the
same time, the completion time of task will be
extended, and emergency supplies cannot be
delivered on time. It can bring many dangers to the
people in disaster areas and the losses of economic.
3 CONSTRUCTION OF SYSTEM
DYNAMICS MODEL
Logistics dynamic alliance is an organization which
be needed to maintain close between logistics
enterprises. It requires federates matched hardware
and software resources. With the increasing number
of federates, the demanding of breakpoints have
become increasingly in the supply chain. It
expressed as the increasing of intrinsic constraints.
Based on this consideration, this paper
modified the Pearl curve model, the formula is
expressed as:
(1)
1
bn
K
y
ae
−
−
=
+
(1)
In here, “n” is expressed that the required total
number of enterprises in a particular task of
emergency logistics alliance, and it takes a positive
real number. The “k” is the limit of the “y”, and it
takes “50”. “a” and “b” are the model parameters,
and it takes that “a” is “1”and “b” is “1”.
In addition, it should be noted that the
followings, such as: if it has only one company in
alliance (n = 1), at this time, that means “y” is “25”,
this is the minimum constrains; but with the
increasing number of federates, the increasing “y”
was, and the “50” is assumed maximum constrains
of “y”.
It uses DYNAMO language to the identity
(Zhao, 2010). “K” is the current moment and “J” is
the last moment. “DT” said that the steps between
“K” and “J”. It makes “DT” is “1” initially, and you
can adjust it in the actual simulation process.
Conveniently, it will use the letters to replace
each variable, as shown in Table 1:
Table 1: The alphabet of variable corresponding.
Letters Variable
A Inherent constraints
B The quality of collaboration
C Collaboration time
D Ability to adapt to each other
E The core of logistics capability
M Strategic adjustment
N The ability of members
SF The factor of sudden impact
GF The factor of government impact
TF The factor of technology matching
With the causal relationship in Figure 1, the
alliance model is expressed as:
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
302
(1)
()
1
bn
K
pearl n
ae
−−
=
+
(2)
With the increasing number of federates, the
inherent constraints is growth. To reduce the
inherent constraints, government can make strategic
adjustments to the members of logistics dynamic
alliance. Shown as:
A.K=A.J+PEARL
(
n
)
-M
(
3
)
The growth of the quality of collaboration will be
affected by ability to adapt to each other, the core of
logistics capability, and the factor of technology
matching. Shown as:
B.K=B.J+DT*
(
D.J+E.J+N+TF
)
(4)
With the increasing of inherent constraints, the
collaboration time is increased. In addition, some
unexpected event will lead to collaboration time
changes. Shown as:
C.K=C.J+DT*
(
A.J+SF
)
(5)
Ability to adapt to each other is mainly affected
by the ability of members and the factor of
technology matching. In addition, it also can be
influenced by the government and inherent
constraints. Shown as:
D.K=D.J+DT*
(
N+TF+M-A.J
)
(6)
The core logistics capabilities can be influenced
by the decision of government. in addition, it can be
also affected by the strategic adjustment, and the
ability of members. Shown as:
E.K=E.J+DT*
(
M+N+GF
)
(7)
4 SIMULATIONS
4.1 Realization of the Simulation
It used EXCEL to achieve the model simulation.
The initial value of variable represents the initial
state of the system. According to the actual input,
these variables will be simulated by iterative
changes to future operating conditions of dynamic
alliance of logistics. The flow diagram of system
dynamics, which used in the characteristic
parameters of the reaction system, should be
depended on specific characteristics of dynamic
alliance of logistics in the simulation.
After the simulation running, firstly, it was input
the initial value of variables. Then, it can be set
parameters to simulate the actual situation according
to the special. By view of output value and table,
future running of the dynamic alliance of logistics
can be mastered. After the model data generated, the
data generated will be out of the curve form of
visual representation.
4.2 Example
It selected the representative data form one
particular Union in the task decomposition stage,
shown in Table 2, and selected the other parameters
for model to do the initial value of iteration. Here,
“n” is “10”.
Table 2: The table of initial value of each variable in
Table.
Variable A B C D E
initial value 0 20 50 10 20
The data listed in Table 2 is designed to verify
the validity of the model of artificial data. In
practice, the representative from government and
dynamic alliance of logistics enterprises provided
the data and input to the program according to the
actual. By the simulation of the data in Table 2, the
output of the model can express the relative value of
each factor trends. It verified that system dynamics
model created whether show the effectiveness of
impact of relationships between the task
decomposition and the evaluation factors or not.
And it also verified whether can achieve the best
solution by application of this model. Put the data in
Table 2 into EXCEL and get changes in each index.
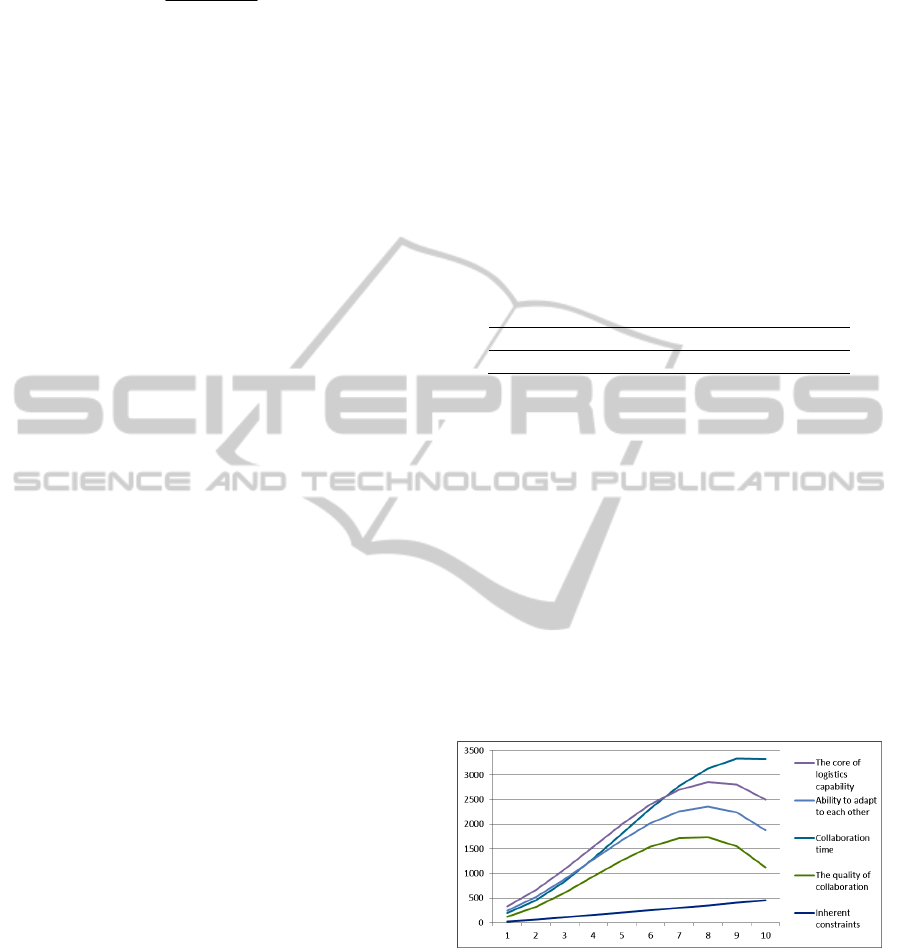
Shown as Figure 2.
Figure 2: The changes map in each index to model.
The simulation results of the analysis of the figure:
(1) Adding a degree of inherent constraints
will bring the improving of the quality of
collaboration. However, when the alliance members
to a certain amount of time, the quality of
collaboration will deteriorate. The ability to adapt to
each other also will be bad.
(2) Internal constraints may not necessarily
bring about the extension of time collaboration. As
StudyonTaskDecompositioninEmergencyLogisticsbasedonSystemDynamics
303

members of the co-ordinated, but to a certain extent,
increasing of the number of members will cut down
the collaboration time.
By validated, it can illustrate the feasibility of this
model. This model can provide some reference value
of information to the government in the extent of the
emergency task decomposition.
4.3 Significance
Mainly reflected in two aspects:
(1) Some person from emergency
management department of government and
dynamic alliance of logistics are in charge of
discussing to achieve the initial values of variable.
Next to simulation, it can be given the optimal
extent of decomposition. Then informed of the
operational status of the future trend of alliance, it
can help the government have more in-depth grasp
of the dynamic alliance of logistics.
(2) When the emergency of task
decomposition cannot be changed, it can design a set
of strategies of different intensity adjustment
programs and put it simulate together with the
current of initial value from logistics alliance. This
has been a different result set. From these results,
select a few good according to the logistics alliance
needs and the strategic adjustment of the
corresponding intensity is the best solution. It can
provide a basis for strategic adjustment in
emergency management for government.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This text used the method of system dynamics to
construct modeling and simulation studies in task
decomposition of dynamic alliance of logistics in the
supply chain of emergency. Based on analysis of the
key elements of the task decomposition of causality
in dynamic alliance of logistics, it established a
causal flow diagram and system dynamics model.
And furthermore, it used random data to achieve the
simulation in EXCEL. As can be conclude from the
simulation results, the design of the model can
express the causal relationship between the key
factors of the task decomposition in emergency
logistics effectively. The conclusion is in line with
the operation of conventional dynamic alliance of
logistics.
REFERENCES
Bin Hu et al., 2006. Modeling and Simulation of
Corporate Lifecycle Using System Dynamics. Chinese
Journal of Management Science, 3, 142-147.
Ya-feng Pi., 2006. Study on Spaceflight Model Work
Breakdown Structure (WBS). Journal of North China
Institute of Astronautic Engineering, 16(3), 1-3.
Gang Chen, 1998. Application of Work
BreakdownStructure in Boeing. Aviation Engineerging
& Mainienance, 2, 33-35.
Xin-yue Hu et al., 2005. Partner optimal selection of
Virtual Enterprises Based on Work Breakdown
Structures. Manufacturing Automation, 27(1), 24-27.
Xin-yue Hu.et al., 2005b. Configuration Process of Virtual
Enterprises Based on Work Breakdown Structures.
Industrial Engineering Journal, 8(6), 15-20.
Hong-guo Zhang et al., 2007. Hierarchical network
planning method based on WBS for cross-enterprise
collaborative project. Computer Integrated
Manufacturing Systems, 13(3), 513-519.
Ming-guang Zhao, 2010. Analysis of the granularity of
task decomposition in enterprise alliance based on
system dynamics. Machinery Design & Manufacture,
9, 254-256.
ICEIS2012-14thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
304
